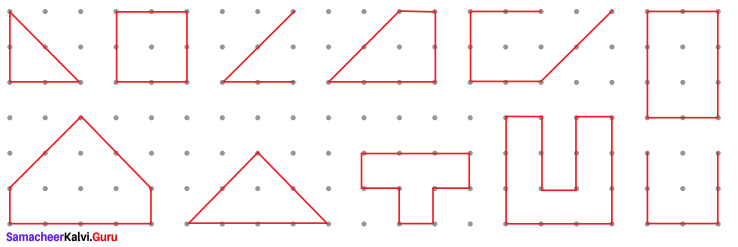
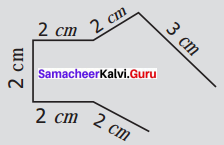
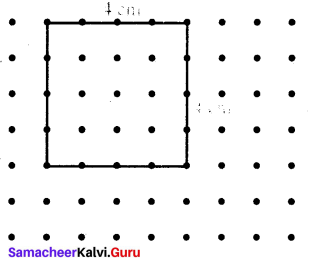
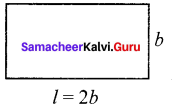
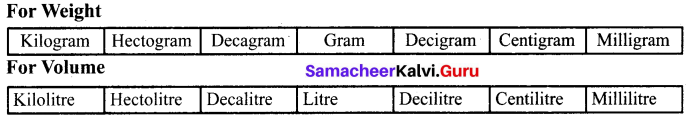
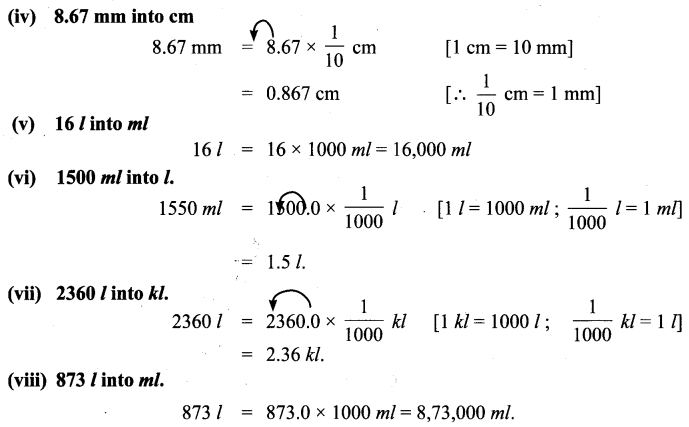
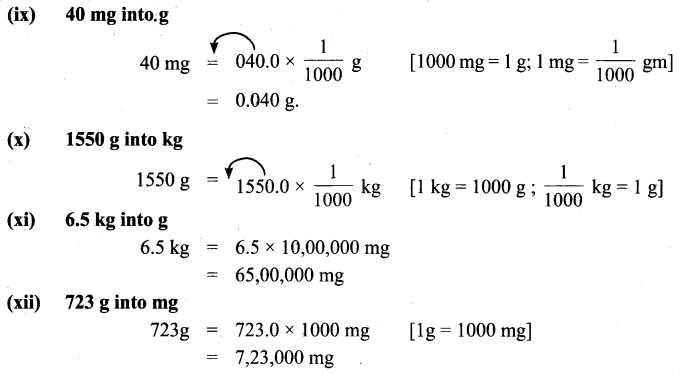
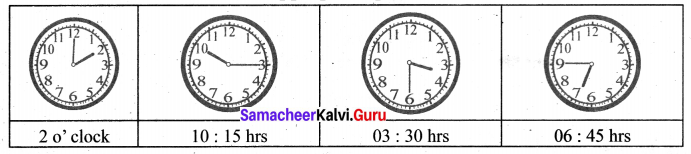
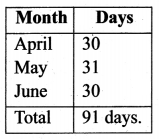
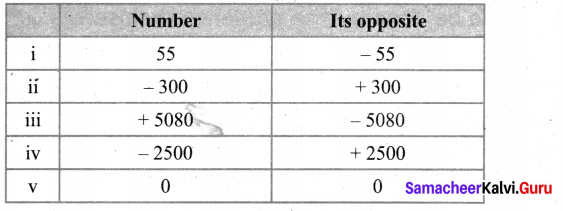
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
![]()
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Solutions Term 2 Chapter 3 Bill, Profit and Loss Intext Questions
Try These (Textbook Page No.49)
Question 1.
Arrange in ascending order
(i) C.P, M.P, Discount
(ii) M.P., S.P., Discount
Solution:
(i) Discount < C.P < M.P.
(ii) Discount < S.P < M.P
![]()
Question 2.
Which is greater S.P or M.P?
Solution:
M.P is greater than S.P