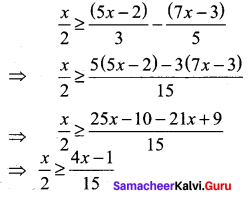
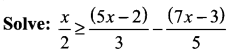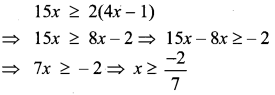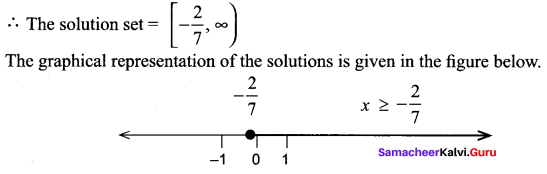Students can find the most related topics which helps them to analyse the concepts if they practice according to the chapter-wise page. It is necessary for the students to practice more Questions and Answers for Tamilnadu State Board Solutions of 11th Commerce are given in the pdf format in chapter 3 Classification of Business Activities Questions and Answers so that students can prepare in both online and offline modes. So, Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Book Solutions Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, to score good marks.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Solutions Chapter 3 Classification of Business Activities
Get the Questions and Answers, in Tamilnadu State Board 11th Commerce Solutions for Chapter 3 Classification of Business Activities. Learn the concepts of 11th Commerce Chapter-Wise by referring to the Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Chapter 3 Classification of Business Activities Questions and Answers. Hence we suggest the students to Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Book Solutions Questions and Answers pdf to enhance your knowledge.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Classification of Business Activities Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
11th Commerce Chapter 3 Book Back Answers Question 1.
The industries engaged in extraction of iron ore are known as
(a) Construction industries
(b) Manufacturing Industries
(c) Extraction industries
(d) Genetic Industries
Answer:
(c) Extraction industries
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 11th Commerce Question 2.
Auxiliaries to trade is also called as
(a) Trade
(b) Advertisement
(c) Warehousing
(d) Aids to trade
Answer:
(d) Aids to trade
Samacheer Kalvi Commerce 11th Question 3.
Production which involves several stages for manufacturing finished products is known as
(a) Analytical industry
(b) Synthetic Industry
(c) Processing industry
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Processing industry
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Solutions Question 4.
Normally high level risk is involved in
(a) Industry
(b) Commerce
(c) Trade
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) Industry
11th Commerce Answer Question 5.
Commerce is mainly concerned with
(a) Connecting producer and consumer
(b) Pricing of goods
(c) Buying and selling of goods
(d) Manufacturing of goods
Answer:
(a) Connecting producer and consumer
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Class 11 Commerce Chapter 3 Question 1.
Define Commerce.
Answer:
According to Evelyn Thomas, “Commercial operations deal with the buying and selling of goods, the exchange of commodities and the contribution of finished products”.
11th Commerce Samacheer Kalvi Question 2.
What do you mean by industry?
Answer:
Industry refers to economic activities, which are connected with conversion of resources into useful goods. The production side of business activity is referred as industry.
11th Commerce Solutions Samacheer Kalvi Question 3.
What is trade?
Answer:
The term ‘trade’ is used to denote buying and selling. It is an essential part of commerce.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Guide Question 4.
Write a short note on transportation.
Answer:
The medium which moves men and materials from one place to another is called transport. Selling all the goods produced at or near the production places is not possible. Hence, goods are to be sent to different places where they are demanded.
III. Short Answer Questions
Classification Of Business Activities Question 1.
Distinguish between Extractive industries and genetic industries.
Answer:
Extractive industries :
- These industries extract or draw out products from natural sources.
- Extractive industries supply some basic raw materials that are mostly products of geographical or natural environment.
Genetic industries:
- These industries remain engaged in breeding plants and animals for their use in further reproduction.
- The seeds, nursery companies poultry, diary, piggery, hatcheries, nursery, fisheries, apiary etc.
Classification Of Business Question 2.
What do you mean by tertiary industries?
Answer:
They do not produce goods. These industries produce utility services and sell them at a profit. They help trade, industry and commerce. This term also includes auxiliaries to trade like banking, insurance, warehouse, advertisement etc.
Classification Of Business Activity Question 3.
Write any three characteristics of commerce.
Answer:
1. Economic Activity : Commerce is an economic activity because it consists of activities which are undertaken for earning profits. A trader buys goods with the aim of selling them at a profit.
2. Exchange of Goods and Services : Commerce involves exchange and distribution of goods and services. Goods may be purchased or produced for sale. Commerce comprises both trade and aids to trade.
3. Profit Motive : The motive of commercial activities is to earn profits. Any activity which does not have the aim of profit will not be a part of commerce.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Question 4.
Narrate commerce with an example.
Answer:
Commerce refers to all those activities which are necessary for bringing goods from the place of production to the place of their consumption. Commerce includes not only trade but also services such as transport, warehousing, packaging, insurance, banking and sales promotion which are incidental or auxiliaries to trade.
IV. Long Answer Questions
Samacheer Kalvi 11 Commerce Question 1.
Explain the various kinds of industries on the basis of size.
Answer:
1. Micro Units: A unit wherein investment in plant and machinery is upto Rs. 25 lakhs in case of manufacturing and upto Rs. 10 lakhs in case of service enterprises.
2. Small Units: A manufacturing unit wherein investment in plant and machinery is more than Rs. 25 lakhs but does not exceed Rs.5 crore. In case of service enterprises these limits are Rs. 10 lakhs and Rs. 2 crore respectively.
3. Medium Units: A manufacturing unit wherein investment in plant and machinery is more than Rs.5 crore but does not exceed Rs. 10 crore. In case of service enterprises, these limits are Rs.2 crore and Rs.5 crore respectively.
4. Large Units: A manufacturing unit wherein, investment in plant and machinery exceeds Rs.10 crore. In case of a service unit investment in equipment exceeds Rs.5 crore.
Classify Business Activities Question 2.
Compare industry, commerce and trade.
Answer:
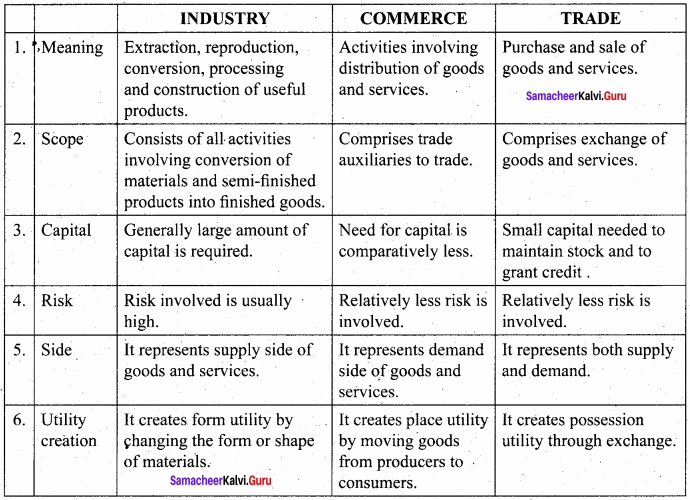
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Chapter 3 Question 3.
What are the characteristics of Commerce?
Answer:
1. Economic Activity:
Commerce is an economic activity because it consists of activities which are undertaken for earning profits. A trader buys goods with the aim of selling them at a profit.
2. Exchange of Goods and Services:
Commerce involves exchange and distribution of goods and services. Goods may be purchased or produced for sale. Commerce comprises both trade and aids to trade.
3. Profit Motive:
The motive of commercial activities is to earn profits. Any activity which does not have the aim of profit will not be a part of commerce.
4. Regularity of Transaction:
An isolated transaction does not imply commerce.
5. Creation of Utilities:
Commerce creates several types of utilities. It creates place utility by carrying goods to the place where they are needed. It makes goods available as and when demanded thereby creating time utility. By creating these utilities commerce helps to increase the volume of trade.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Book Question 4.
Write short notes on:
- Analytical industry
- Genetic industry and
- Construction industry.
Answer:
1. Analytical Industry: It analyses and separates different elements from the same materials, as in the case of oil refinery.
2. Genetic Industries: These industries remain engaged in breeding plants and animals for their use in further reproduction. The seeds, nursery companies, poultry, diary, piggeiy, hatcheries, nursery, fisheries, apiary etc are classic examples of genetic industries.
3. Construction Industries: These industries are involved in the construction of building, dams, bridges, roads, as well as tunnels and canals.
Commerce Samacheer Kalvi Question 5.
Briefly explain the auxiliaries of trade.
Answer:
Auxiliaries of trade may be classified into five categories:
1. Transportation:
Selling all the goods produced at or near the production place is not possible. Hence, goods are to be sent to different places where they are demanded.
2. Banking and Finance:
Now – a – days we cannot think of business without bank. A bank is an organization which accepts deposits of money from the public, withdrawals on demand or otherwise, and lends the same to those who need it. Necessary funds can be obtained by businessmen from a bank. Thus, banking helps business activities to overcome the v problem of finance.
3. Insurance:
Business involves various types of risks. Materials and goods held in stock or in transit are subject to the risk of loss or damage. Insurance provides protection in all such cases. On payment of a nominal premium, the amount of loss or damage and compensation for injury, if any, can be recovered from the insurance company.
4. Warehousing:
Goods are held in stock to make them available as and when required. Special arrangement must be made for storage of goods to prevent loss or damage. Warehousing helps business firms to overcome the problem of storage and facilities the availability of goods when needed.
5. Advertising:
Advertising is one of the most important methods of promoting the sale of products, particularly, consumers goods like electronic goods, automobiles, soaps, detergents etc. Advertising helps in providing information about available goods and services and inducing customers to buy particular items.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Classification of Business Activities Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question 1.
All business activities can be classified into ……………. broad categories.
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) Four
(d) Five
Answer:
(a) Two
Question 2.
Where is the mechanical appliances and technical skills used?
(a) Industry
(b) Commerce
(c) Business
(d) Trade
Answer:
(a) Industry
Question 3.
Horticulture is an example for …………….
(a) Primary industry
(b) Secondary industry
(c) Tertiary industry
(d) Local industry
Answer:
(a) Primary industry
Question 4.
……………. industry assembles different component parts to make a new product, as in the case of television, car, computer, etc.
(a) Assembling
(b) Processing
(c) Analytical
(d) Construction
Answer:
(a) Assembling
Question 5.
Professional or specialized skills and high technology are used to provide ……………. type of services.
(a) Personalised
(b) Public
(c) Distributive
(d) Quaternary
Answer:
(d) Quaternary
Question 6.
Banking, factoring, accounting and insurance come under ……………. type of service.
(a) Mechanical
(b) Financial
(c) Personal
(d) Quinary
Answer:
(b) Financial
Question 7.
Commerce represents ……………. side of goods and services.
(a) Demand
(b) Profit
(c) Supply
(d) Cost
Answer:
(a) Demand
Question 8.
Special arrangement must be made for of goods to prevent loss or damage.
(a) Transportation
(b) Pricing
(c) Storage
(d) Advertising
Answer:
(c) Storage
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is Extractive industry?
Answer:
Extractive industries extract or draw out products from natural sources. Extractive industries supply some basic raw materials that are mostly products of geographical or natural environment.
Question 2.
What is Primary industry?
Answer:
Primary industry is concerned with production of goods with the help of nature. It is a nature – oriented industry, which requires very little human effort.
Question 3.
What is Secondary industry?
Answer:
Secondary Industries are concerned with using the materials which have already been extracted at the primary stage. These industries process such materials to produce goods for final consumption or for further processing by other industrial units.
Question 4.
What is tertiary industry?
Answer:
They do not produce goods. These industries produce utility services and sell them at a profit. They help trade, industry and commerce. This term also includes auxiliaries to trade like banking, insurance, warehouse, advertisement etc.
Question 5.
What are the auxiliaries to trade?
Answer:
- Transportation
- Banking and Finance
- Insurance
- Warehousing
- Advertising
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write any three categories of Manufacturing industries.
Answer:
- Analytical Industry which analyses and separates different elements from the same materials, as in the case of oil refinery.
- Synthetic Industry which combines various ingredients into a new product, as in the case of cement.
- Processing Industry which involves successive stages for manufacturing finished products, as in the case of sugar and paper.
Share this Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for 11th Commerce Chapter 3 Classification of Business Activities Questions and Answers with your friends to help them to overcome the issues in exams. Keep visiting this site Tamilnadu State Board Solutions frequently to get the latest information on different subjects. Clarify your doubts by posting the comments and get the answers in an easy manner.