Students can Download Computer Applications Chapter 14 Open Source Concepts Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Solutions Chapter 14 Open Source Concepts
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Open Source Concepts Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – I
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
If the source code of a software is freely accessible by the public, then it is known as
(a) freeware
(b) Firmware
(c) Open source
(d) Public source
Answer:
(c) Open source
![]()
Question 2.
Which of the following is a software program that replicates the functioning of a computer network?
(a) Network software
(b) Network simulation
(c) Network testing
(d) Network calculator
Answer:
(b) Network simulation
Question 3.
Which of the following can document every incident that happened in the simulation and are used for examination?
(a) Net Exam
(b) Network hardware
(c) Trace file
(d) Net document
Answer:
(c) Trace file
![]()
Question 4.
Which is an example of network simulator?
(a) simulator
(b) TCL
(c) Ns2
(d) C++
Answer:
(c) Ns2
Question 5.
Fill in the blanks : NS2 comprises of ………………………… key languages?
(a) 13
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 4
Answer:
(c) 2
![]()
Question 6.
Choose the Correct Pair from the following to build NS2
(a) UNIX & TCL
(b) UNIX & a. C++
(c) C++ & OTcl
(d) C++ & NS2
Answer:
(c) C++ & OTcl
Question 7.
Which of the following is not a network simulation software?
(a) Ns2
(b) OPNET
(c) SSFNet
(d) C++
Answer:
(b) OPNET
![]()
Question 8.
Which of the following is a open source network monitoring software?
(a) C++
(b) OPNET
(c) OpenNMS
(d) OMNet++
Answer:
(c) OpenNMS
Question 9.
Upen NMS was released in
(a) 1999
(b) 2000
(c) 2003
(d) 2004
Answer:
(a) 1999
![]()
Question 10.
OpenNMS Group was created by ……………………….
(a) Balog
(b) Matt Brozowski
(c) David Hustace
(d) All of them
Answer:
(d) All of them
PART – II
II. Short Answer
Question 1.
Explain the History of open source software?
History of open source software:
Answer:
- In the early day of computing, programmers and developers shared software in order to learn from each other
- Eventually, it moved to the way side of commercialization of software in 1970-1980
- The Netscape communication corporation released their popular Netscape Communicator Internet Suite as free software. This made others to look into how to bring the free software ideas.
- The Open Source Initiative was founded in Feb 1998 to encourage use of the new term open- source.
![]()
Question 2.
What is meant by network simulator?
Answer:
A network simulator is a software program that replicates the functioning of a computer network. In simulators, the computer network is typically demonstrated with devices, traffic etc.
Question 3.
What is trace file?
Answer:
A significant output of simulation is the trace files. Trace files can document every incident that happened in the simulation and are used for examination.
C++ and Object-oriented Tool Command Language (OTCL) and network monitoring.
![]()
Question 4.
Write short notes on NS2?
Answer:
NS2 is the abbreviation of NETWORK SIMULATOR version 2. It was considered explicitly for exploration in network communication and event-driven open-source simulator in computer.
Question 5.
Explain NRCFOSS?
Answer:
NRCFOSS:
National Resource Centre for Free and Open Source Software an Institution of Government of India. To help in development of FOSS in India.
![]()
Question 6.
Write short note on Open NMS?
Answer:
There are two types in this Meridian and Horizon.
Meridian:
When we need stability and long term support choose Meridian which is best for Enterprises as well as businesses.
Horizon:
Horizon used where innovation occurs frequently. It is Best for IT-ecosystem, new technologies monitoring.
PART – III
III. Explain in Brief Answer
Question 1.
What are the uses of Open source Network Software?
Answer:
- Software can be used without any cost and restrictions.
- Sharing of ideas with the team.
- User friendly.
- We can add the most required features in the software.
- We can learn many ideas.
- We can make our program writing skills more efficient
- We can use any software that suits our needs.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain Free software?
Answer:
Free software a concept developed in the 1980s by an MIT computer science researcher, Richard Stallman is defined by four conditions, as outlined by the nonprofit Free Software Foundation.
Question 3.
List out the Popular open source software?
Answer:
Application software:
NS2 , OPEN NMS, Ubuntu, MySQL, PDF Creator, Open Office, 7zip GNUCASH, GIMP, BLENDER, AUDACITY, VLC, MOZILA FIREFOX, MAGENTO, ANDROID, PHP.
![]()
Question 4.
Write note on open source hardware?
Answer:
Open source hardware technology helps in spy hardware threats. In this technique we get the components of the hardware and its circuit diagram, so that we can remove suspicious spyware if found.
Question 5.
What are the main functional areas of Open NMS?
Answer:
- Service monitoring, where a number of monitor modules can govern if network-based services (ICMP, HTTP, DNS, etc.) are accessible.
- Data Gathering by using SNMP and JMX.
- Event management and notifications, which comprises of alarm reduction and a robust announcement system with accelerations and duty schedules.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain Types of Organisations related to Open Source?
Answer:
Organizations related to Open Source
- Apache Software Foundation
- The Document Foundation
- The Eclipse Foundation
- Free Software Foundation
- Linux Foundation
- Open Course Ware Consortium
- Open Source Initiative
PART – IV
IV. Explain in detail
Question 1.
Differentiate Proprietary and open source software?
Answer:
Proprietary Software:
- It refers to the software that is solely owned by the individual or the organization that developed it.
- Only the owner or publisher who holds the legal property rights of the source code can access it.
- The project is managed by a closed group of individuals or team that developed it.
- They are focused on a limited market of both skilled and unskilled end users.
- There is a very limited scope of innovation with the restrictions and all.
- Ex: Windows, MacOs, Google Earth
Open Source Software:
- It refers to the software that is developed and tested through open collaboration.
- Anyone with the academic knowledge can access, inspect, modify and redistribute the source code
- The project is managed by an open source community of developers and programmers.
- They are not aimed at unskilled users outside of the programming community.
- It provides flexibility Ex. Android, Firefox, Ubuntu
- Ex: Android, Firefox, Ubuntu
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Open Source Concepts Additional Questions and Answers
1. Choose the Best Answer
Question 1.
……………………. is usually created and updated by many programmers around the world and made finely accessible
Answer:
Open Source Software
Question 2.
Proprietary Software is owned by an …………………………
(a) Organization
(b) Individual
(c) both a and b
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) both a and b
![]()
Question 3.
……………………. helps the user and administrator easily find working status of network systems and hardware.
Answer:
Notification
Question 4.
NRCFOSS stands for …………………………
Answer:
National Resource CEnter Free and Center Free and Open Source Software
Question 5.
Pick the odd one out
(a) Apache Software Foundation
(b) The document Foundation
(c) The Eclipse Foundation
(d) The round Foundation
Answer:
(d) The round Foundation
![]()
Question 6.
BOSS stands for ………………………..
(a) Basic Output System Service
(b) Bharat Operating System Solution
(c) Basic Operating System Solutions
(d) Bug Operating System Server
Answer:
(b) Bharat Operating System Solution
Question 7.
BOSS developed by ……………………..
(a) A-DAC
(b) M-DAC
(c) D-MAC
(d) C-DAC
Answer:
(d) C-DAC
![]()
Question 8.
C-DAC is abbreviated as ………………………..
Answer:
Center for Development of Advanced Computing
Question 9.
How many Indian Languages are supported by BOSS?
(a) 15
(b) 10
(c) 5
(d) many
Answer:
(d) many
![]()
Question 10.
GPL means ……………………..
Answer:
General Public Licence
Question 11.
LGPL stands for ……………………..
Answer:
Lesser General Public License
Question 12.
The free software was developed in the year …………………….
(a) 1972
(b) 1978
(c) 1980
(d) 2003
Answer:
(c) 1980
![]()
Question 13.
Who developed Free Software?
(a) Richard Stallman
(b) Robert John
(c) both a and b
(d) DanBricklin
Answer:
(a) Richard Stallman
Question 14.
How many freedoms or conditions are defined by Richard Stallman for free software foundation?
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
Answer:
(b) 4
Question 15.
Find the statement which is wrong about Freeware?
(a) proprietary software
(b) pay to download
(c) source code cannot be changed
Answer:
(b) pay to download
![]()
Question 16.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) communication tools
(b) Bug trackers
(c) task list
(d) MIT license
Answer:
(d) MIT license
Question 17.
Which one of the following is not a open source application software?
(a) Ns2
(b) MySQL
(c) Google Earth
(d) GIMP
Answer:
(c) Google Earth
![]()
Question 18.
Identify the Proprietary software from the following.
(a) ubuntu
(b) MacOs
(c) Android
(d) Open office
Answer:
(b) MacOs
Question 19.
Pick the odd one.
(a) routers
(b) nodes
(c) access points
(d) distributors
Answer:
(d) distributors
![]()
Question 20.
Match the following
(i) objects (network) – 1. Output of simulation
(ii) State of the network – 2. links
(iii) events – 3. node placement
(iv) Trace files – 4. link failures
(a) (i)-2 (ii)-3 (iii)-4 (iv)-1
(b) (i)-1 (ii)-2 (iii)-3 (iv)-4
(c) (i)-4 (ii)-3 (iii)-1 (iv)-2
(d) (i)-4 (ii)-2 (iii)-1 (iv)-3
Answer:
(a) (i)-2 (ii)-3 (iii)-4 (iv)-1
Question 21.
……………………… is a pure event base software tool with super simulation design.
Answer:
API
![]()
Question 22.
NMS stands for
(a) National Management Server
(b) Network Management Server
(c) Node Management Server
(d) Net Managing Simulator
Answer:
(b) Network Management Server
Question 23.
FCAPS means
(a) Fault, Configuration, Accounting, Performance, Security
(b) Foreign, Country, Access, Personal, Security .
(c) Future, Chennai, Access, Performance, Server
(d) Fault, Controlled, Audit, Poor, Source
Answer:
(a) Fault, Configuration, Accounting, Performance, Security
Question 24.
Open NMS is written in
(a) Html
(b) Java
(c) C++
(d) Oracle
Answer:
(b) Java
![]()
Question 25.
……………………….. is the world’s first software for Network Monitor and Management with Open Source options.
Answer:
Open NMS
Question 26.
How many types of Open NMS are there?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(a) 2
![]()
Question 27.
(I) Horizon is the Best fo IT-ecosystem
(II) Meridian gives long term support
(III) Meridian is used for new technology monitoring
(a) I is true, II-False
(b) II, III are true
(c) I, II are true
(d) I, II, III all are true
Answer:
(c) I, II are true
Question 28.
In 1999, Open NMS was released by
(a) Steve Giles
(b) Brian Weaver
(c) Luke Rindfuss
(d) All of them
Answer:
(d) All of them
![]()
Question 29.
In Open NMS, data Gathering is by using …………………… and ………………………
Answer:
SNMP, JMX
Question 30.
Which one of the following is not a enterprise management product.
(a) Open office
(b) HP open view
(c) IBM Micro Muse
(d) IBM Tivoli
Answer:
(a) Open office
![]()
Question 31.
OTcl means …………………….
Answer:
Object-oreinted Tool Commercial Language
Question 32.
NS2 means ……………………….
Answer:
Network Simulation 2
![]()
Question 33.
SSF Net means ……………………
Answer:
Scalable Simulation Framework Net Models.
II. Short Answer
Question 1.
Give the advantages of proprietary software?
Answer:
The advantage of the proprietary software is that it gives more control, support, training, security and stability for user making the software reliable to the users.
![]()
Question 2.
Write note on BOSS?
Answer:
BOSS (Bharat Operating System Solutions) Operating System Developed in India by C-DAC (Centre for Development of Advanced Computing) Help to prompt the use of open source software in India. It Supports many India Language.
Question 3.
Mention some large enterprise management products?
Answer:
HP Open View, IBM Micro muse or IBM Tivoli.
![]()
Question 4.
What is the use of Network Software?
Answer:
To Control, Analysis the Server, System, protocol, Network, Traffic flow and reports about ups and downs of network parts.
III. Explain in Brief Answer
Question 1.
Write short note on open source software and developers?
Answer:
Open-Source Software and Developers:
OSS projects are collaboration opportunities that improve skills and build connections in the field. Domains that developers can contribute to the open source community include:
- Communication tools.
- Distributed revision control systems.
- Bug trackers and task lists.
- Testing and debugging tools.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the Demerits of Open Source Software?
Answer:
Difficult to work for beginners, Exchange of files to other software, Some time Lack of Responsibility, service and problems with hardware compatible.
Question 3.
Mention the features of Open Source Hardware?
Open Source Hardware
Answer:
- Remix
- Remake
- Remanufacture
- Redistribute
- Resell
- Study and Learn
![]()
Question 4.
List the various types of open NMS?
Answer:
There are two types in this Meridian and Horizon.
Meridian:
When we need stability and long term support choose Meridian which is best for Enterprises as well as businesses.
Horizon:
Horizon used where innovation occurs frequently. It is Best for IT-ecosystem, new technologies monitoring.
![]()
Question 5.
What is the goal of open NMS?
Answer:
The goal is for Open NMS to be an actually distributed, scalable management application platform for all features of the FCAPS (Fault, configuration, accounting, performance, security) network management model. Presently the emphasis is on Fault and Performance Management.
IV. Explain in detail
Question 1.
Differentiate Open Source Software with free software?
Answer:
Open-Source Software vs. Free Software:
Although the terms are often used interchangeably, OSS is slightly different from free software. Both deal with the ability to download and modify software without restriction or charge.
However, free software a concept developed in the 1980s by an MIT computer science researcher, Richard Stallman is defined by four conditions, as outlined by the nonprofit Free Software Foundation. These “four freedoms” emphasize the ability of users to use and enjoy software as they see fit.
In contrast, the OSS criteria, which the Open Source Initiative developed a decade later, place more emphasis on the modification of software, and the consequences of altering source code, licensing, and distribution.
Obviously, the two overlap; some would say the differences between OSS and free software are more philosophical than practical. However, neither should be confused with freeware. Freeware usually refers to proprietary software that users can download at no cost, but whose source code cannot be changed.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain Network Simulation Tool – NS2 in detail?
Answer:
Network simulation tool – NS2:
- In computer network, network simulation is a method whereby a software program , models the activities of a network by calculating the communication between the different
network objects such as(routers, nodes, switches, access points, links etc.). - A network simulator is a software program that replicates the functioning of a computer network.
- In simulators, the computer network is typically demonstrated with devices, traffic etc. and the performance are evaluated.
- Normally, users can then adapt the simulator to accomplish their precise analysis needs. The network parameters define the state of the network (node placement, existing links) and the events (data transmissions, link failures, etc.).
- A significant output of simulation is the trace files. Trace files can document every incident that happened in the simulation and are used for examination.
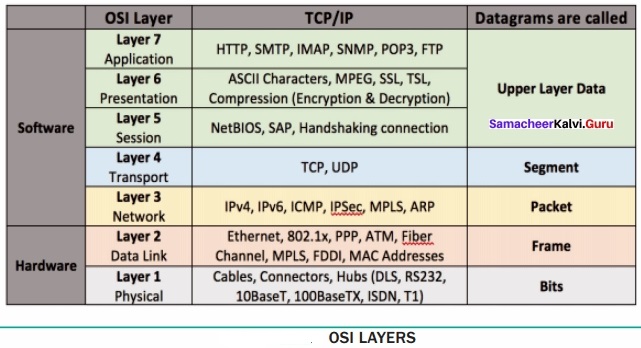
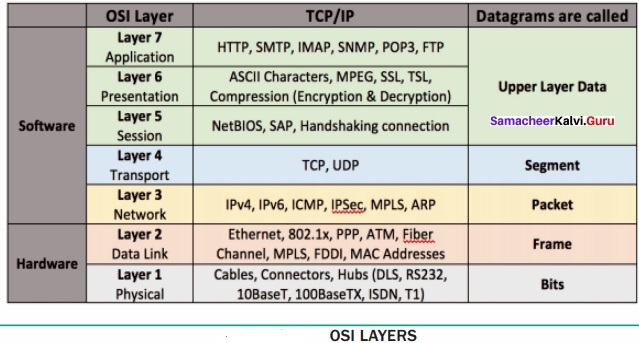
- NS2 is the abbreviation of NETWORK SIMULATOR version 2. It was considered explicitly for exploration in network communication and event-driven open-source simulator in computer.
- OTCL and C++ used to create and run NS2. NS2 works on Windows and Linux platforms, that supports wired or wireless network and also use the command line interface as a user interface, API a pure event base software tool with super simulation design, it has more models which help the user to get desired output easily.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain in Detail Open NMS?
Answer:
Open NMS
- Open NMS (Network Management System)is a free and open-source initiative grade network monitoring and management platform.
- It is established and maintained by a community of users,developers and by the Open NMS
Group, it offering services, training and support. - The goal is for Open NMS to be an actually distributed, scalable management application platform for all features of the FCAPS (Fault, configuration,accounting, performance,
security) network management model. - Presently the emphasis is on Fault and Performance Management.
It was intended to cope tens of thousands of devices from a single server as well as achieve unlimited devices using a cluster of servers. - Open NMS comprises a discovery engine to routinely configure and manage network devices without operator intervention.
- It is written in Java and is issued under the GNU (General Public License.)
- Open NMS is the Worlds first software for Network monitor and management with open source options. There are two types in this Meridian and Horizon.
- When we need stability and long term support choose Meridian which is best for Enterprises as well as businesses, for Horizon used where innovation occurs frequently. It is Best for IT-ecosystem,new
technologies monitoring.
Open Source Hardware:
- Remix
- Remake
- Remanufacture
- Redistribute
- Resell
- Study and Learn
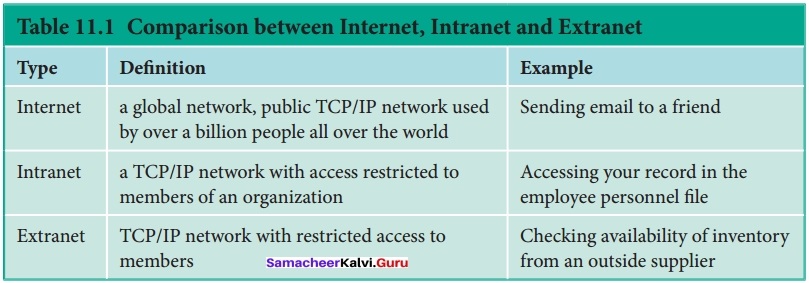
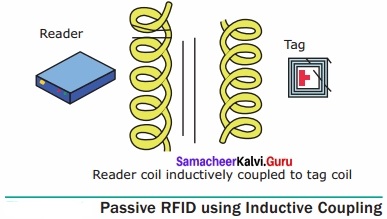
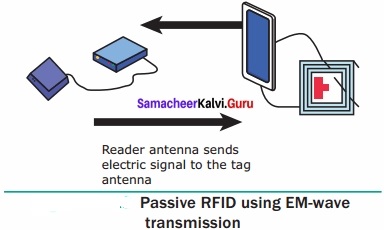
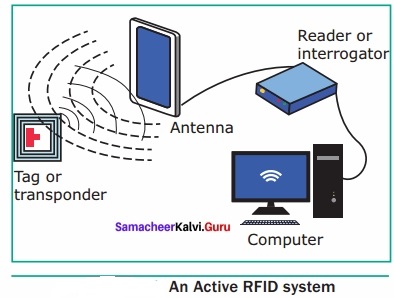


















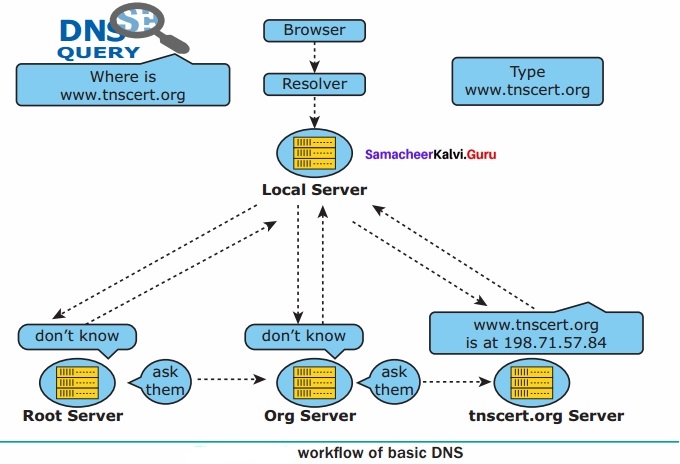
 A set of computers connected together for the purpose of sharing resources is called as computer networks. At present, Internet is the most common resource shared everywhere. Some of the shared resources are file server, web camera, speakers, printer, scanner, fax machine etc., Accessing services such as WWW (World Wide Web), Digital audio, Digital video which are shared t use applications, software, and storage servers. All are well-known the term Internet Networks of network is called Internet.
A set of computers connected together for the purpose of sharing resources is called as computer networks. At present, Internet is the most common resource shared everywhere. Some of the shared resources are file server, web camera, speakers, printer, scanner, fax machine etc., Accessing services such as WWW (World Wide Web), Digital audio, Digital video which are shared t use applications, software, and storage servers. All are well-known the term Internet Networks of network is called Internet.