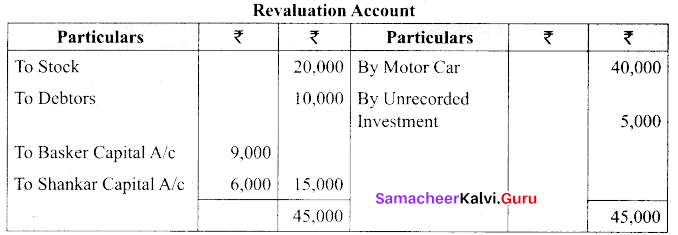
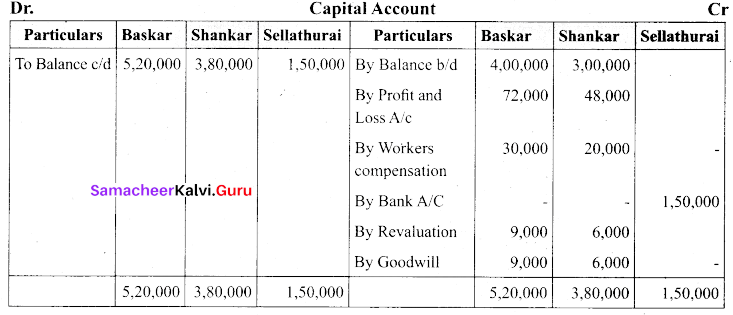
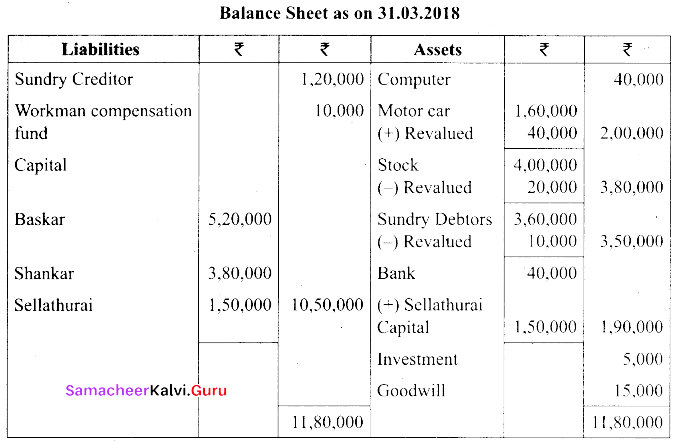
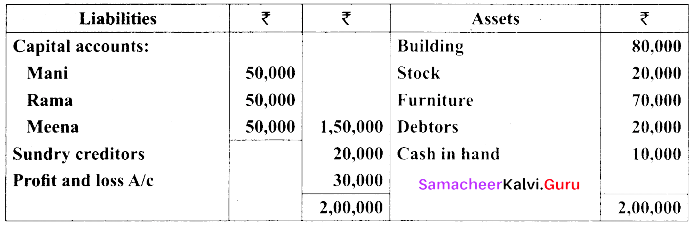
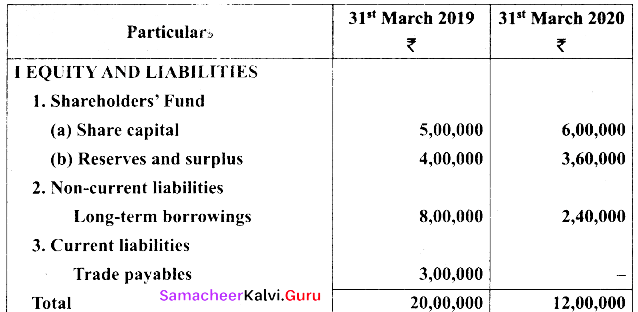
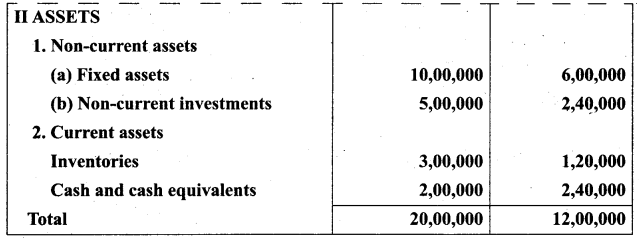
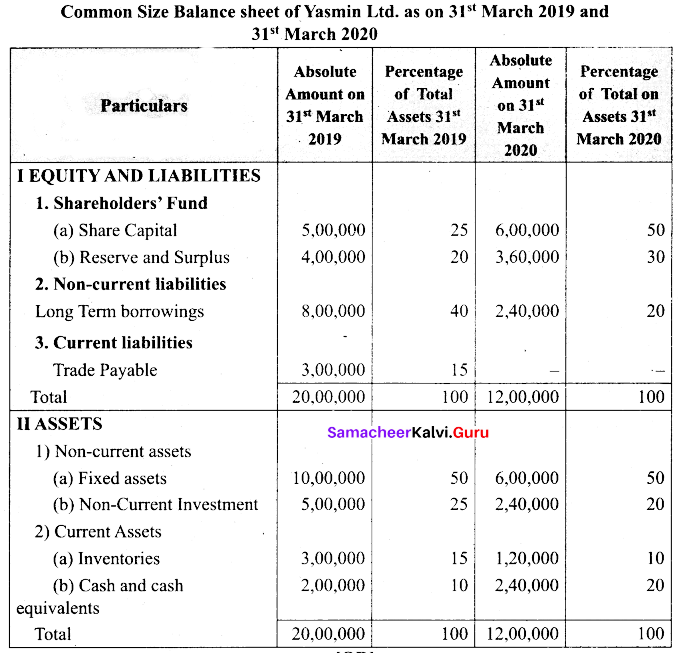
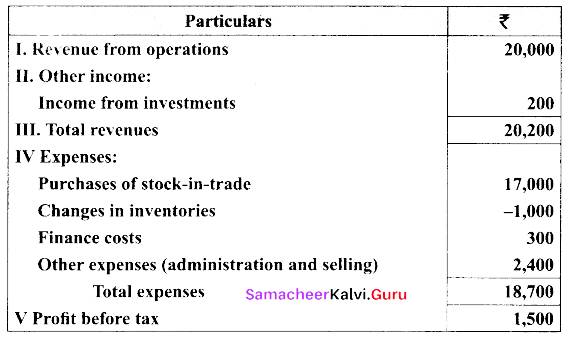
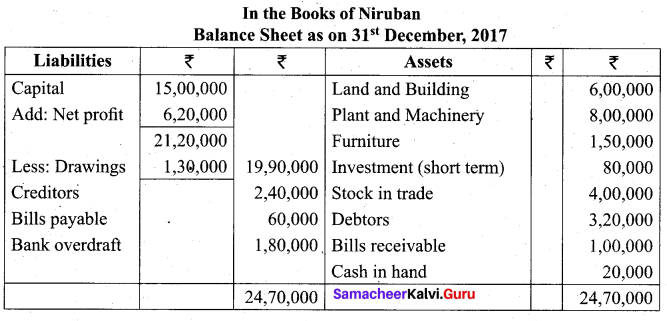
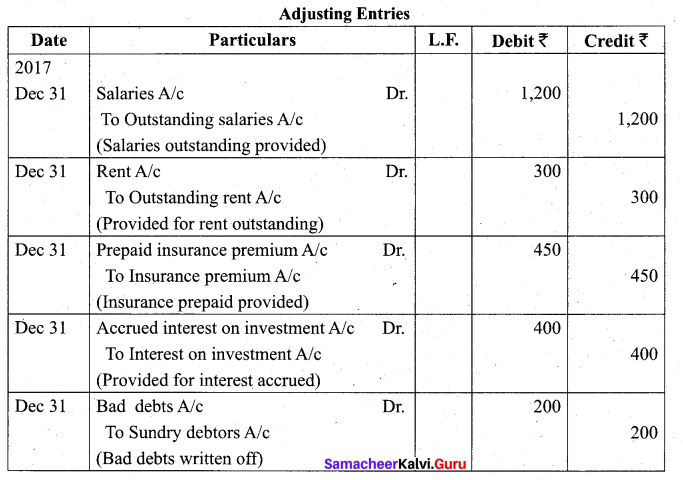
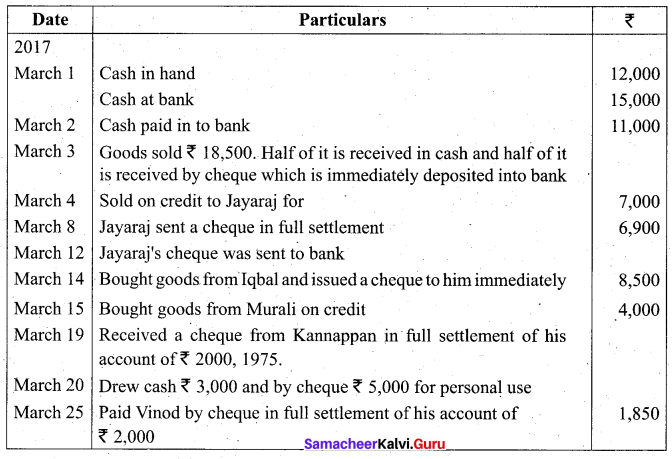
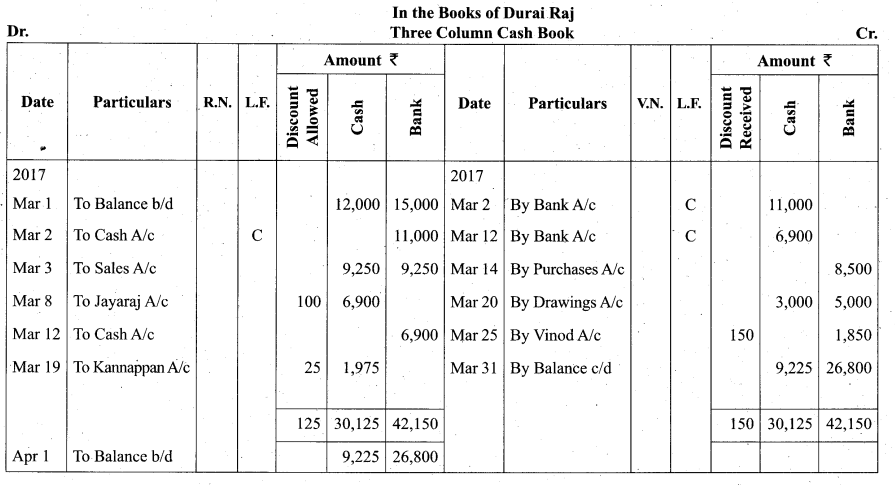
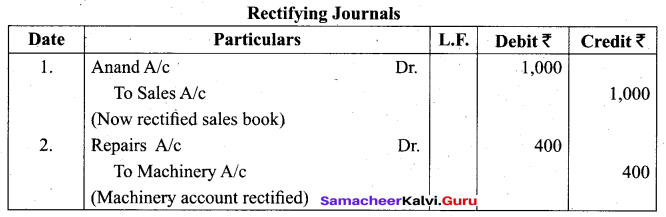
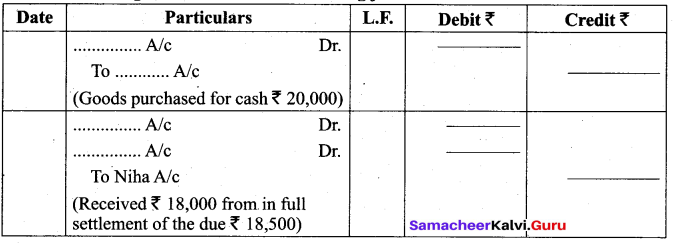
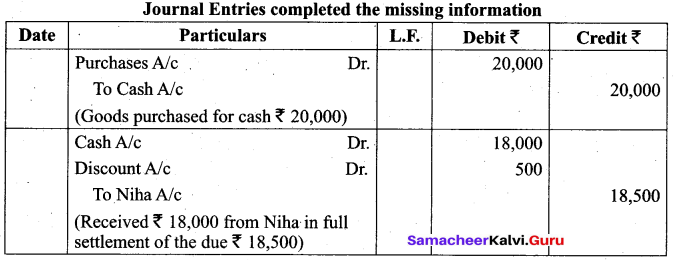
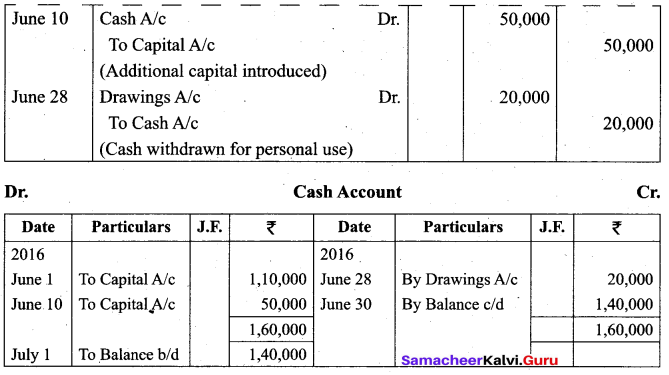
Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Biology Model Question Paper 5 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Biology Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 11th Biology Model Question Paper 5 English Medium
Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts Questions for Botany and Zoology are asked separately.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III, and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 8 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and Writing the option code and the Corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 9 to 4 in Part II are two-marks questions. This also is answered in about one or list sentences.
- Question numbers 15 to 19 in Part III are three-marks questions These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 20 and 21 in Part IV are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
Bio-Botany [Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Which of the following is a coprophilous fungi?
(a) Albugo
(b) Entomophthora
(c) Rhizopus
(d) Pilobolus
Answer:
(d) Pilobolus
![]()
Question 2.
Which one of the following statements is wrong?
(a) Cyanobacteria are also called blue-green algae
(b) Golden algae are also called desmids
(c) Eubacteria are also called false bacteria
(d) Phycomycetes are also called algal fungi
Answer:
(c) Eubacteria are also called false bacteria
Question 3.
After fertilization……………….. modifies into seed.
(a) ovary
(b) ovule
(c) carpel
(d) stigma
Answer:
(b) ovule
Question 4.
DNA bar coding was introduced by………………..
(a) Stebbins
(b) Hebert
(c) Camp & Gilly
(d) Darwin
Answer:
(b) Hebert
![]()
Question 5.
Which is the largest of the internal membranes?
(a) Golgi bodies
(b) Endoplasmic reticulum
(c) Tonoplast
(d) Nuclear membrane
Answer:
(b) Endoplasmic reticulum
Question 6.
The chlorophyll pigment found in xanthophycean algae is………………..
(a) Chlorophyll b
(b) Chlorophyll c
(c) Chlorophyll d
(d) Chlorophyll e
Answer:
(d) Chlorophyll e
Question 7.
The term Auxin was first used by ………………..
(a) Kogl.Smith
(b) Darwin
(c) F.W. Went
(d) Kurosawa
Answer:
(c) F.W. Went
Question 8.
ABA stands for ………………..
(a) Abscisic acid
(b) Ascorbic acid
(c) Acetyl Butyric Acid
(d) Acetic acid
Answer:
(a) Abscisic acid
![]()
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
What do you understand by “pinning” of phage?
Answer:
Once the contact is established between tail fibres of phase and bacterial cell, tail fibres bend to anchor the pins and base plate to the cell surface. This step is called pinning.
Question 10.
Which is responsible for pigmentation of Brown algae?
Answer:
A golden brown pigment called fucoxanthin is present and it gives shades of colour from olive green to brown to the algal members of Phaeophyceae.
Question 11.
Compare the stem nature of Corm and Rhizome.
Answer:
Corm
- Stem is succulent underground.
- Presence of erect growing tips.
Rhizome
- Stem is horizontal underground.
- Presence of lateral growing tips.
Question 12.
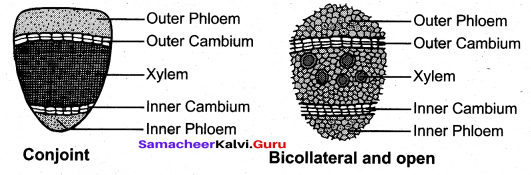
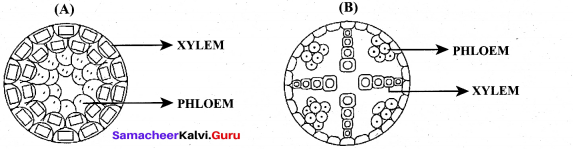
What are axial parenchyma & Ray parenchyma?
Answer:
Parenchyma arranged longitudinally along the long axis is called axial parenchyma. Ray parenchyma is arranged in radial rows.
![]()
Question 13.
State the “Law of minimum” proposed by Liebig.
Answer:
The “law of minimum” states that productivity of soil depends on amount of essential elements present in minimum quantity.
Question 14.
What is homoiomerous and heteromerous?
Answer:
In homoiomerous (algal cells evenly distributed in the thallus) and heteromerous (a distinct layer of algae and fungi present).
![]()
Part – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
Distinguish between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes.
Answer:
Prokaryotes :
- Unicellular
- Lack membrane bound nuclei
- Membrane bound organelles are absent Ex: Bacteria Membrane bound organelles are present Ex: Amoeba
Eukaryotes :
- Unicellular or multicellular
- Possess well defined nucleus
- Membrane bound organelles are present Ex: Amoeba
Question 16.
Which types of plants develop tendril? How does it helps the plant?
Answer:
In some plants Stem is very weak and hence they have some special organs for attachment to the support. So some leaves are partially or wholly modified into tendril. Tendril is a slender wiry coiled structure which helps in climbing the support.
Question 17.
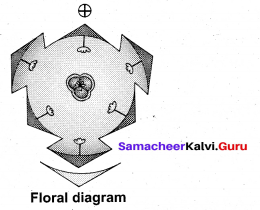
Linnaeus classification is also called sexual system of classification. Why?
Answer:
Linnaeus classification is mostly based on sexual characters like number, union, length and distribution of stamens and also on carpel characters. Hence it is called sexual system of classification.
![]()
Question 18.
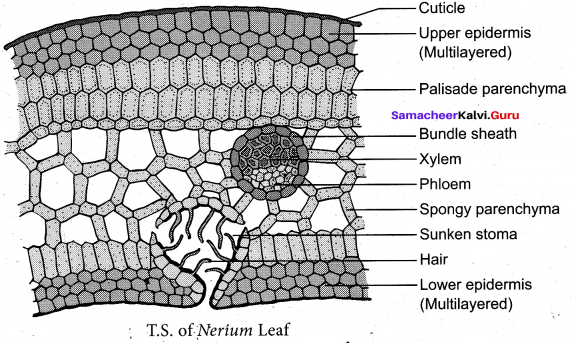
Draw a labeled diagram of T.S. of Dicot leaf.
Answer:
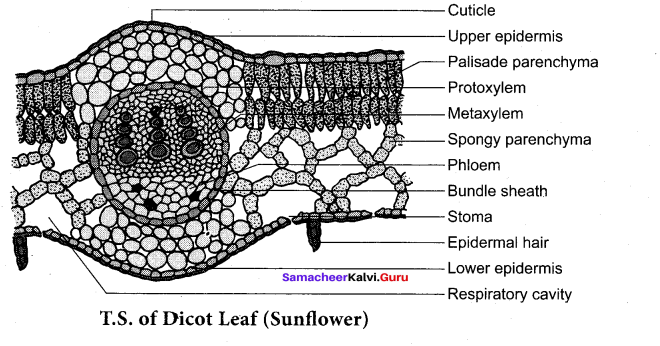
Question 19.
Why TCA cycle is called so?
Answer:
TCA cycle starts with condensation of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate in the presence of water to yield citrate or citric acid. Therefore, it is also known as CitricAcid Cycle (CAC) or Tri Carboxylic Acid (TCA) cycle.
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
Draw a flow chart depicting the classification of fruits.
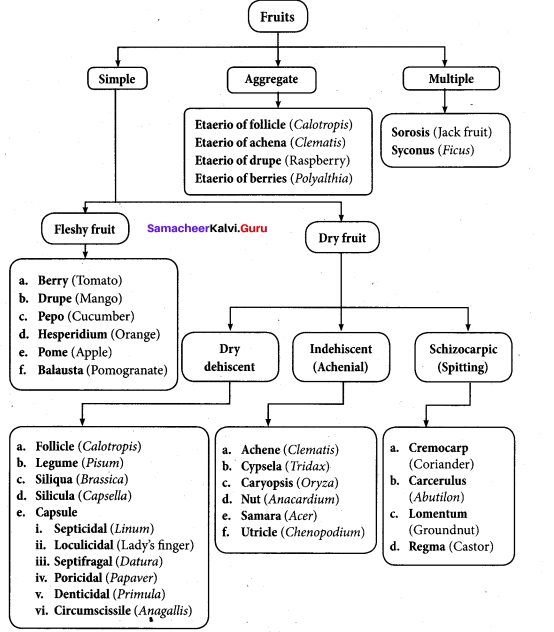
[OR]
Draw & describe the structure of Nucleus
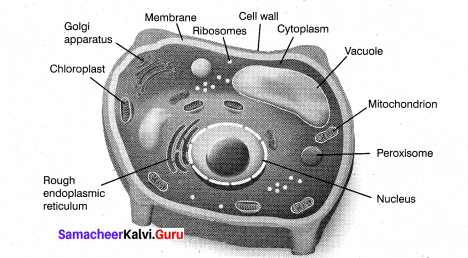
Answer:
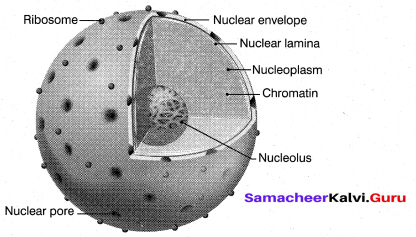
Nucleus is an important unit of cell which control all activities of the cell. Nucleus holds the hereditary information. It is the largest among all cell organelles.lt may be spherical, cuboidal, ellipsoidal or discoidal. It is surrounded by a double membrane structure called nuclear envelope,which has the inner and outer membrane.
The inner membrane is smooth without ribosomes and the outer membrane is rough by the presence of ribosomes and is continues with irregular and infrequent intervals with the endoplasmic reticulum. The membrane is perforated by pores known as nuclear pores which allows materials such as mRNA, ribosomal units, proteins and other macromolecules to pass in and out of the nucleus.
The pores enclosed by circular structures called annuli. The pore and annuli forms the pore complex. The space between two membranes is called perinuclear space. Nuclear space is filled with nucleoplasm, a gelatinous, matrix has uncondensed chromatin network and a conspicuous nucleoli. The chromatin network is the uncoiled, indistinct and remain thread like during the interphase. It has little amount of RNA and DNA bound to histone proteins in eukaryotic cells.
![]()
Question 21.
Explain Ganong’s Potometer experiment and its purpose.
Answer:
Ganongs potometer is used to measure the rate of transpiration indirectly. In this, the amount of water absorbed is measured and assumed that this amount is equal to the amount of water transpired.
Apparatus consists of a horizontal graduated tube which is bent in opposite directions at the ends. One bent end is wide and the other is narrow. A reservoir is fixed to the horizontal tube near the wider end. The reservoir has a stopcock to regulate water flow. The apparatus is filled with water from reservoir. A twig or a small plant is fixed to the wider arm through a split cock.
The other bent end of the horizontal tube is dipped into a beaker containing coloured water. An air bubble is introduced into the graduated tube at the narrow end keep this apparatus in bright sunlight and observe. As transpiration takes place, the air bubble will move towards the twig. The loss is compensated by water absorption through the xylem portion of the twig. Thus, the rate of water absorption is equal to the rate of transpiration.
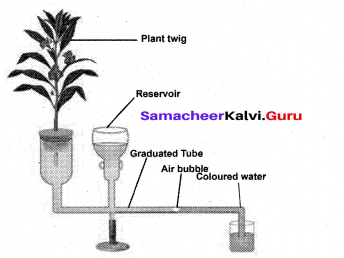
[OR]
Write in detail about functions, mode of absorption and deficiency symptoms of any five macronutrients.
Answer:
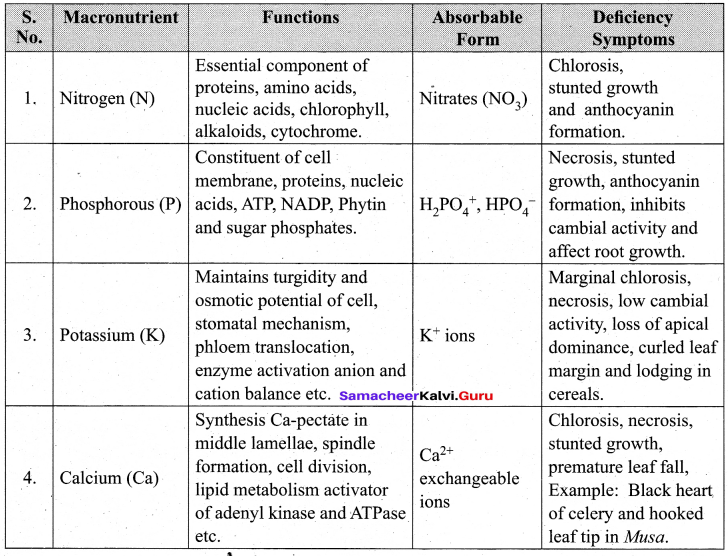
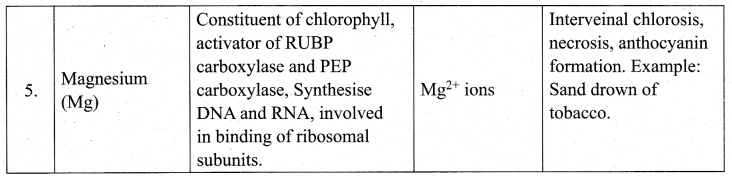
Bio-Zoology[Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – A
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Which class of protozoa is totally parasitic?
(a) Sporozoa
(b) Mastigophora
(c) Ciliate
(d) Sarcodina
Answer:
(a) Sporozoa
![]()
Question 2.
Linmulus belongs to class ………………
(a) Orychophora
(b) Insect
(c) Merostomata
(d) Crustacea
Answer:
(c) Merostomata
Question 3.
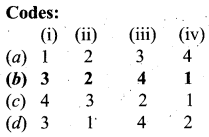
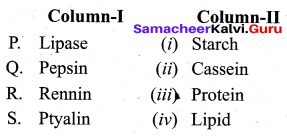
Match the List I and List II:

(a) 1 – (iv), 2 – (i), 3 – (ii), 4 – (iii)
(b) 1 – (i), 2 – (iii), 3 – (iv), 4 – (ii)
(c) 1 – (iv), 2 – (iii), 3 – (i), 4 – (ii)
(d) 1 – (i), 2 – (ii), 3 – (iv), 4 – (iii)
Answer:
(a) 1 – (iv), 2 – (i), 3 – (ii), 4 – (iii)
Question 4.
EDV stands for ……………………
(a) End digestion volume
(b) End diastolic volume
(c) End decrease volume
(d) End digestion valve
Answer:
(b) End diastolic volume
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following is an correct statement?
(a) Vascular disease – A portion of the aortic wall weakens and balloons out, forming an areurysm.
(b) Arrhythmia is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly.
(c) Coronoray heart disease – An inflammation of one or more layers of the pericardium a thin membrane that lines the heart.
(d) Heart failure – blocked or clogged arteries linut blood flow to the heart.
Answer:
(b) Arrhythmia is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly.
Question 6.
Which of the following is an incorrect statement?
(a) The excretory cells of platyhelminthes is solenocytes.
(b) Metanephridia are the tubular excretory structures in annelids and molluscs.
(c) Malphighian tubules are the excretory structures in most insects.
(d) Nematodes have rencttc cells.
Answer:
(a) The excretory cells of platyhelminthes is solenocytes.
Question 7.
What is formed by the bones of pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle and limbs?
(a) Body skeleton
(b) External skeleton
(c) Axial skeleton
(d) Appendicular skeleton
Answer:
(d) Appendicular skeleton
![]()
Question 8.
Ca+ metabolism is regulated by …………….
(a) ACTH
(b) Thyroxine
(c) Parathormone
(d) Epinephrine
Answer:
(c) Parathormone
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
Why are molecular tools used now to study taxonomy?
Answer:
Molecular tools are accurate and authentic. Hence they are used to study taxonomy.
Question 10.
What is bilateral symmetry?
Answer:
The symmetry in which the animals have to similar halves on either side of the central place in bilateral symmetry’, eg. Flatworms, annelids.
Question 11.
What are urochordates?
Answer:
The Chordates which have notochord only in the tail region of the larval stage are called urochordates. eg. Axidian.
![]()
Question 12.
Define Assimilation.
Answer:
The conversion of absorbed food materials into components of cells is called assimilation.
Question 13.
Draw the diagram of Acoelomate flatworms.
Answer:
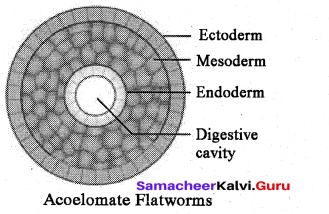
Question 14.
What is amoeboid movement?
Answer:
The movement of cells by streaming movements of the cytoplasm forming pseudo-podia is known as amoeboid movement, e.g. Macrophages.
![]()
Part – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
What are the characteristics of platyhelminthes?
Answer:
They have a dorsoventrally flattened body and hence called flatworms. These animals are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, acoelomate with organ system level of organisation. They show moderate cephalization and unidirectional movement. They are, mostly endoparasites of animals including human beings. Hooks and suckers are present in the parasitic forms and serve as organs of attachment. Their body is not segmented, but some exhibit pseudosegmentation.
Question 16.
Distinguish between true ribs and false ribs.
Answer:
True ribs : The first seven pairs of ribs are called ‘true ribs’ or vertebro-stemal ribs. Dorsally they are attached to the thoracic vertebrae and ventrally connected to the sternum with the help of hyaline cartilages.
False ribs: The 8th, 9th and 10th pairs of ribs do not articulate directly with the sternum but joined with the cartilaginous (hyaline cartilage) part of the seventh rib. These are called ‘false ribs’ or vertebro-chondral ribs.
Question 17.
Explain palmaris muscle.
Answer:
Palmaris muscle is a long narrow muscle runs from the elbow to the wrist and is important for hanging and climbing in primates. It is a muscle visible as a small tendon between the ” flexor carpi radialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris, although it is not always present. It is one of five muscles that act at the wrist joint.
Question 18.
What are the types of cultivable fish.
Answer:
Cultivable fish are of 3 types
- Indigenous or native fresh water fishes (Major carps, Catla, Labeo, Clarias).
- Salt water fishes acclimatized for fresh water (Chanos, Mullet).
- Exotic fishes are imported from other counties (Common carps).
![]()
Question 19.
Draw the diagram of metamorphosis of frog.
Answer:
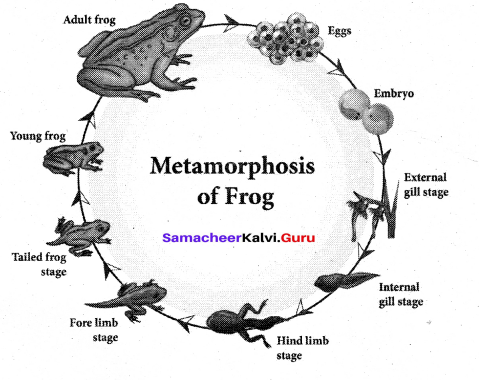
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 x 5 = 10]
Question 20.
Explain the three domains of life.
Answer:
Three domain classification was proposed by Carl Woese (1977) and his co-workers.They classified organisms based on the difference in 16S rRNA genes. The three domain system adds the taxon ‘domain’ (ugher than the kingdom. This system emphasizes the separation of Prokaryotes into two domains, Bacteria and Arachaea, and all the eukaryotes are placed into the domain Eukarya.
Archaea appears to have more in common with the Eukarya than the Bacteria. Archaea differ from bacteria in cell wall composition and differs from bacteria and eukaryotes in membrane composition and rRNA types.
1. Domain Archaea
This domain includes single celled organisms, the prokaryotes which have the ability to grow in extreme conditions like volcano vents, hot springs and polar ice caps, hence are also called extremophiles. They are capable of synthesizing their food without sunlight and oxygen by utilizing hydrogen sulphide and other chemicals from the volcanic vents. Some of the them produced methane (methanogens), few live in salty environments (Halophiles) and are thermoacidophiles which thrive in acidic environments and at high temperatures.
2. Domain Bacteria
Bacteria are prokaryotic, their cells have no definite nucleus and DNA exists as a circular chromosomes and do not have histones associated with it. They do not possess membrane bound organelles except for ribosome (70S type). Their cell wall contains peptidoglycans. Many are decomposers, some are photo-synthesizers and few cause diseases.
There are beneficial probiotic bacteria and harmful pathogenic bacteria which are diversely populated. Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic blue green algae which produce oxygen. These had played a key role in the changes of atmospheric oxygen levels from anaerobic to aerobic during the early geologic periods.
3. Domain Eukarya (Eukaryotes)
Eukaryotes are animals which have true nucleus and membrane bound organelles.DNA in the nucleus is arranged as a linear chromosome with histone proteins, ribosomes of 80S type in the cytosol and 70S type in the chloroplast and mitochondria.Animals in this domain are classified under kingdoms, namely, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia.
![]()
[OR]
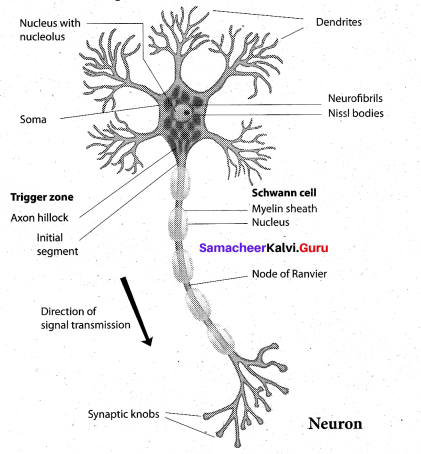
Write an essay on Neural tissue. Draw the diagram and label the parts.
Answer:
Nervous tissue exerts the greatest control over the body’s responsiveness to changing conditions. Neurons, the unit of neural system are excitable cells.The neuroglial cells which constitute the rest of the neural system protect and support the neurons. Neuroglia makes up more than one-half of the volume of neural tissue in our body.
When a neuron is suitably stimulated, an electrical disturbance is generated which swiftly travels along its plasma membrane. Arrival of the disturbance at the neuron’s endings, or output zone, triggers events that may cause stimulation or inhibition of adjacent neurons and other cells.
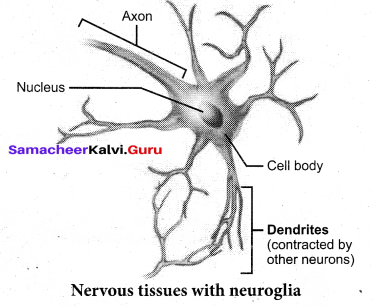
Question 21.
What are joints? Explain the types of joints.
Answer:
Joints are essential for all types of movements performed by the bony parts of the body. The joints are points of contact between bones.
Sometimes they are playing a protective role in the process. Force generated by the muscles are used to carry out the movement through joints which helps human functional activity of daily living and ambulation. The joint acts as a fulcrum of a lever.
(i) Fibrous joints or Synarthroses:
They are immovable fixed joints in which no movement between the bones is possible. Sutures of the flat skull bones are fibrous joints.
(ii) Cartilaginous joints or Amphiarthroses:
They are slightly movable joints in which the joint surfaces are separated by a cartilage and slight movement is only possible. E.g., Joints of adjacent vertebrae of the vertebral column.
(iii) Synovial joints or Diarthroses joints:
They are freely movable joints, the articulating bones are separated by a cavity which is filled with synovial fluid. Examples,
Pivot joint – between atlas and axis
Plane/gliding joint – between the carpals
Saddle joint – between the carpal and metacarpal
Ball and socket joint – between humerus and pectoral girdle
Hinge joint – knee joint
Condyloid or Angular or Ellipsoid -joint between radius and carpal.
![]()
[OR]
Tabulate the major hypothalamic hormones and their functions.
The major hypothalamic hormones and their functions:
| S.No. | Hormones | Functions |
| 1. | Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) | Stimulates the secretion of TSH |
| 2. | Gonadotropin releasing hormone(GnRH) | Stimulates the secretion of FSH |
| 3. | Corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) | Stimulates the secretion of ACTH |
| 4. | Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) | Stimulates the secretion of GH |
| 5. | Prolactin releasing hormone (PRH) | Stimulates the secretion of Prolactin |
| 6. | .Luteinizing hormone releasing hormone (LHRH) | Stimulates the secretion of LH |
| 7. | MSH releasing hormone | Stimulates the secretion of MSH |
| 8. | Growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) | Inhibits the secretion of GH |
| 9. | Prolactin inhibiting hormone (PIH) | Inhibits the secretion of Prolactin |
| 10. | MSH inhibiting hormone | Inhibits the secretion of MSH. |




























 `
`