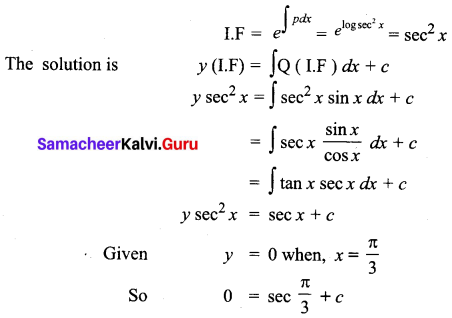
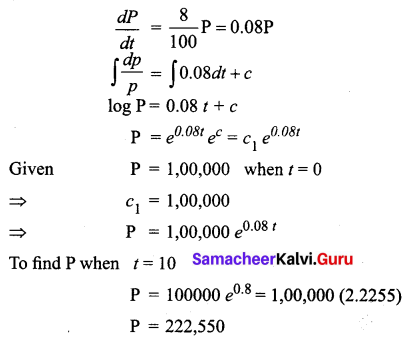
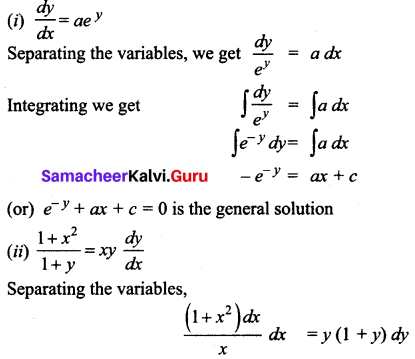
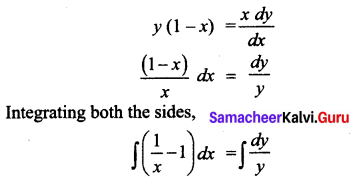
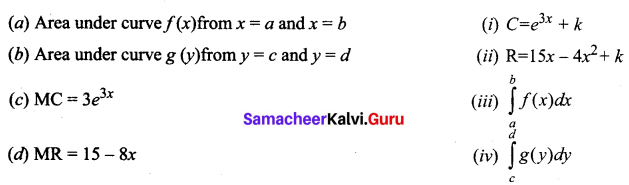
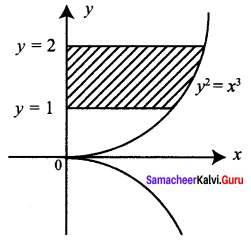
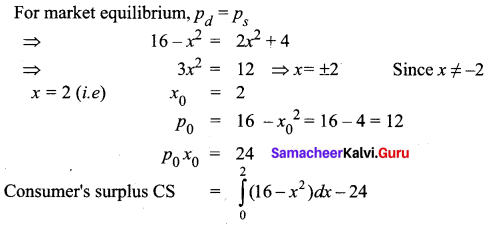
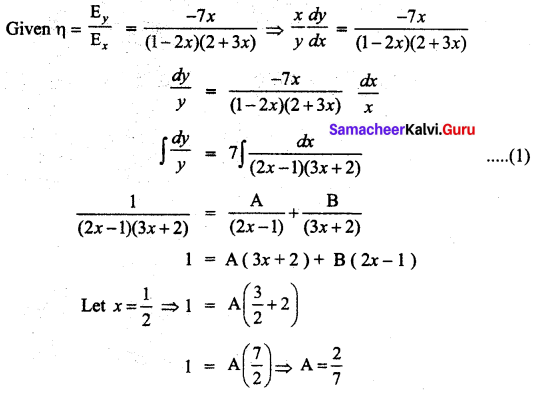
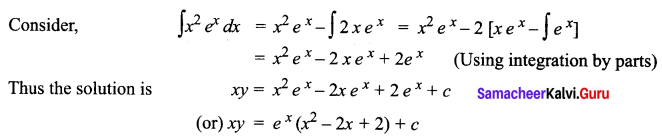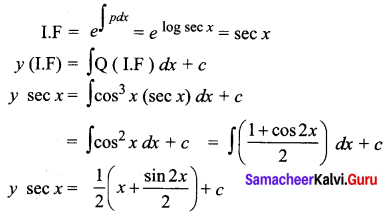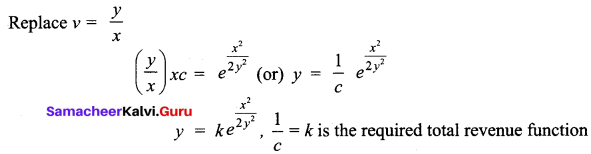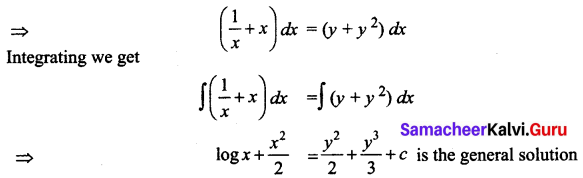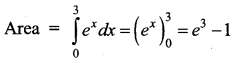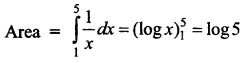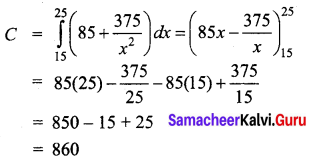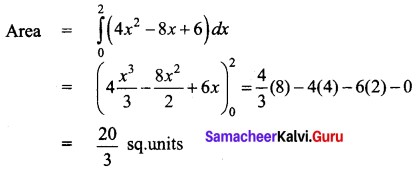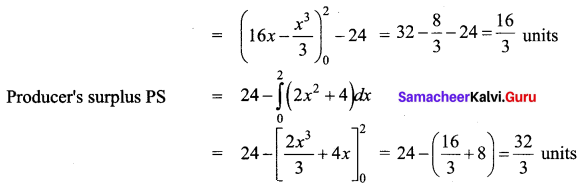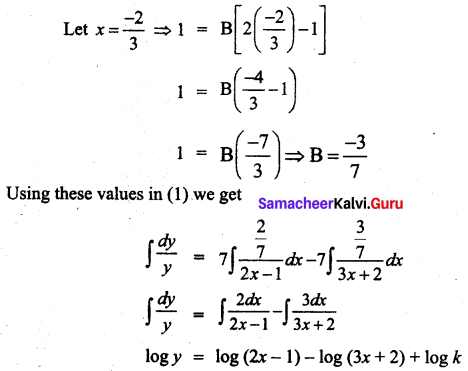Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Commerce Model Question Paper 3 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th commerce Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 11th Commerce Model Question Paper 3 English Medium
Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- questions of Part I, II. III and IV are to be attempted separately
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are objective type questions of one -mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer
- Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Parr III are three-marks questions, These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-marks questions. These are to be answered) in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) Hours
Maximum Marks: 90
Part – I
Choose the correct answer. Answer all the questions: [20 × 1 = 20]
Question 1.
Coca-cola company is an example of ………….
(a) MNC
(b) Govt Company
(c) Joint Venture
(d) Public company
Answer:
(a) MNC
Question 2.
A Government company purchases shares in the name of ………….
(a) Prime minister
(b) President
(c) Chief Justice of India
(d) State Chief Minister
Answer:
(b) President
Question 3.
The terms used in insurance are ………….
(i)) Nomination
(ii) Fixed Deposit
(iii) Indent
(iv) Surrender value
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Answer:
(b) (i) and (iv)
![]()
Question 4.
The partnership deed is also called ………….
(a) Articles of Association
(b) Articles of partnership
(c) Partnership Act
(d) Partnership
Answer:
(b) Articles of partnership
Question 5.
A warehouse holds goods as a center ………….
(a) marketing
(b) storing
(c) distribution
(d) selling
Answer:
(c) distribution
Question 6.
Match List – I with List – II and select the correct answer using the codes given below:
List – I
(i) Chain stores
(ii) Market traders
(iii) Speciality stores
(iv) Auctioneers
List – II
1. Internal trader
2. Mercantile agent
3. Fixed shop large retailers
4. ixed shop small retailers
Codes:
(a) (i) 1, (ii) 2, (iii) 3, (iv) 4
(b) (i) 4, (ii) 3, (iii) 2, (iv) 1
(c) (i) 3, (ii) 1, (iii) 4, (iv) 2
(d) (i) 4, (ii) 2, (iii) 3, (iv) 1
Answer:
(c) (i) 3, (ii) 1, (iii) 4, (iv) 2
![]()
Question 7.
Which of the following is not a land transport?
(a) Bullock cart
(b) Tramways
(c) Air transport
(d) Railway transport
Answer:
(c) Air transport
Question 8.
The main benefits of logistics is ………….
(a) productivity
(b) cost minimisation
(c) profitability
(d) storage
Answer:
(b) cost minimisation
Question 9.
…………. In Joint Hindu family business, how one gets the membership?
(a) By agreement
(b) By birth
(c) By investing capital
(d) By Managing
Answer:
(c) By investing capital
Question 10.
Co-operative fails because of ………….
(a) Unlimited Membership
(b) Cash trading
(c) Mismanagement
(d) Loss-making
Answer:
(c) Mismanagement
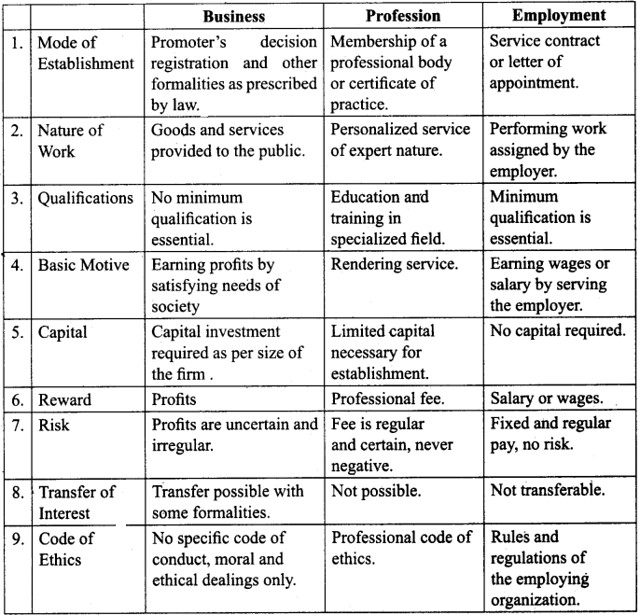
![]()
Question 11.
Occupation of an engineer is ………….
(a) Employment
(b) Business
(c) Profession
(d) Sole proprietor
Answer:
(b) Business
Question 12.
Hindrance of risk is removed by ………….
(a) Transport
(b) Insurance
(c) Warehouse
(d) Advertisement
Answer:
(b) Insurance
Question 13.
Which of the following is not an electronic banking function?
(a) NEFT
(b) RTGS
(c) ECS
(d) Safety lockers
Answer:
(d) Safety lockers
Question 14.
…………. is an acknowledgement of receipt of goods issued by dock authorities to the owner of the goods.
(a) Dock receipt
(b) Dock warrant
(c) Warehouse warrant
(d) Delivery order
Answer:
(a) Dock receipt
![]()
Question 15.
Investment limit of micro enterprise under manufacturing sector does not exceed lakhs.
(a) 10
(b) 20
(c) 25
(d) 50
Answer:
(c) 25
Question 16.
The main aim of home trade is ………….
(a) To raise the standard of living
(b) To provide the essential goods and services economically
(c) To raise the national income
(d) To obtains all type of goods
Answer:
(b) To provide the essential goods and services economically
Question 17.
Day market is called as ………….
(a) Angadi
(b) Market
(c) Nalangadi
(d) Allangadi
Answer:
(c) Nalangadi
![]()
Question 18.
In which form, the owner, establisher and manager is only one?
(a) Joint enterprise
(b) Govt company
(c) Co-operative society
(d) Sole proprietor
Answer:
(d) Sole proprietor
Question 19.
Re-export trade is otherwise called as trade.
(a) Entrepot
(b) Export
(c) Import
(d) Foreign
Answer:
(a) Entrepot
Question 20.
The Head quarters of WTO is located at ………….
(a) New york
(b) London
(c) Geneva
(d) Brazil
Answer:
(c) Geneva
Part-II
Answer any seven questions in which Question No. 30 is compulsory. [7 x 2 = 14]
Question 21.
What is meant by Allangadi?
Answer:
The night market was called as Allangadi according to Saint Poet Ilango in Silapathigaram, Madurai-Kanchi.
Question 22.
An organization which is formed voluntarily for the public service ‘One man – One vote’ principle is followed in this organization. What is that organization? Write a short note about this.
Answer:
It is a co-operative organisation. Co-operative organisation is formed for the service of the members. It can be voluntarily organised by the public. In this organisation, man is given importance than money.
![]()
Question 23.
Who is called Karta?
Answer:
All the affairs of a Joint Hindu Family are controlled and managed by one person who is known as‘Karta or Manager’.
Question 24.
Write a note on ECS.
Answer:
Electronic Clearing Service (ECS) was launched by the RBI in 1995. It is an electronic method of fund transfer from a bank to another bank.
Question 25.
What do you mean by industry?
Answer:
Industry refers to economic activities, which are connected with conversion of resources into useful goods. The production side of business activity is referred as industry.
Question 26.
Who is a sleeping partner?
Answer:
A sleeping partner is the one who contributes capital and shares in the profits or losses of the firm but does not take part in the management of the business.
Question 27.
Write the meaning of the term ‘bank’.
Answer:
In simple words, bank is an institution, which deals in money and credit. The Bank, normally refers to Commercial Bank.
Question 28.
What is a crop insurance?
Answer:
This policy is to provide financial support to farmers in case of a crop failure due to drought or flood. It generally covers all risks of loss or damages relating to production of rice, wheat, millets, oil seeds and pulses, etc.
![]()
Question 29.
What do you mean by Articles of Association?
Answer:
Articles of Association is a secondary document which contains the purpose, duties and responsibilities of the members. It has to be filed with the registrar of companies at the time of forming the company. It contains the details of the internal management of the company.
Question 30.
What is Mutual funds?
Answer:
An individual investor, who wants to invest in equities and bond with a balance of risk and return generally can invest in mutual funds. Nowadays people invest in stock markets through a mutual fund.
Part-III
Answer any seven questions in which Question No. 40 is compulsory. [7 x 3 = 21]
Question 31.
What is meant by Government company?
Answer:
A “Government company” is defined under Section 2(45) of the Companies Act, 2013 as “any company in which not less than 51% of the paid-up share capital is held by the Central Government, or by any State Government or Governments, or partly by the Central Government and partly by one or more State Governments, and includes a company which is a subsidiary company of such a Government company”.
![]()
Question 32.
Explain any three features of public corporation.
Answer:
A public corporation is a form of public enterprise, which is created by a special Act of Parliament or State Legislature.
Features:
- Special Statute:
It is created by a special Act of the Parliament or the State Legislature. The Act defines its objectives, functions and relations to the ministry. - Separate Legal Entity:
A public corporation is a separate legal entity with perpetual succession and common seal. - Capital Provided by the Government:
The capital of a public corporation is provided by the government or by agencies of the government.
Question 33.
Who can demand performance?
Answer:
- Promisee – Only a promisee can demand performance and not a stranger demand performance of the contract.
- Legal Representative – Legal representative can demand Exception performance. Contrary intention appears from the contract. Contract is of a personal nature.
- Third party – Exception to “stranger to a contract”.
Question 34.
What is Bill of lading?
Answer:
Bill of Lading, refers to a document signed by ship owner or to his agent mentioning that goods specified have been received and it would be delivered to the importer or his agent at the port of destination if good condition subject to terms and conditions mentioned therein.
![]()
Question 35.
Write short notes on:
(a) Industry
(b) Employment
Answer:
(a) Industry:
It includes all those business activities which are connected with raising, production or processing of consumer goods. Example – bread, butter and shoes.
(b) Employment:
It refers to the occupation in which people work for others and get remuneration in the form of wages or salaries. Example – manager, clerk, bank official.
Question 36.
What are the different modes of discharge by implied consent?
Answer:
Different modes of discharge by implied consent are:
(a) Novation
(b) Alteration
(c) Recession
(d) Remission
(e) Accord and Satisfaction
(f) Waiver
(g) Merger
Question 37.
State two disadvantages of franchising.
Answer:
(1) Franchising fees:
The initial franchising fee and the subsequent renewal fee can be very high in case of successful businesses. From the franchisee’s point of view, this may be a deterrent.
(2) Fixed royalty payment:
The franchisee has to make payment of royalty to the franchiser on a regular basis. This considerably reduces the income of the franchisee.
![]()
Question 38.
Who is a del-credere agent?
Answer:
The agent who guarantees to the principal the collection of cash from credit sales is called ‘del-credere agent’. If they do not pay the agent would bear the loss himself. He is given an additional commission known as del-credere commission bearing the risk.
Question 39.
Point out any three objectives of WTO.
Answer:
- Improving the standard of living of people in member countries.
- Making optimum utilization of world’s resources for sustainable development of member countries.
- Promoting an integrated more viable and durable trading system in the sphere of international business.
Question 40.
What are the contents of indent?
Answer:
Contents of an Indent:
(a) Quantity of goods sent
(b) Design of goods
(c) Price
(d) Nature of packing shipment
(e) Mode of shipment
(f) Period of delivery
(g) Mode of payment
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [7 x 5 = 35]
Question 41(a).
Dissolution of firm means dissolution of partnership. In this, the business comes to an end. Dissolution of partnership means the termination of the original partnership agreement. Explain the circumstances of dissolving the partnership through court.
Answer:
Dissolution of partnership means that the business comes to an end. It may be dissolution of firm, or dissolution of partnership.
Dissolution of firm is taken in two ways:
- Without order of the court
- With the order of the court
Dissolution with the older of the court: The court may order dissolution of a firm at a suit of a partner in any of the following circumstances:
(a) When a partner becomes insane.
(b) Permanent incapacity of any partner.
(c) Misconduct of any partner.
(d) Breach of agreement which makes the business impracticable.
(e) Transfer of interest to third person.
(f) Continued loss.
(g) When the court finds that it is just and equitable to dissolve the firm.
![]()
[OR]
Question 41 (b).
Explain any five general utility functions of commercial banks.
Answer:
Secondary functions of commercial banks can be classified into agency services and general utility services.
General Utility Functions:
- Issue of demand drafts and bankers’ cheques:
Demand drafts and Bankers’ cheques are issued to public and customers. Instead of sending money they can attach these instruments. - Accepting bill of exchange:
Banks accept bills on behalf of customers and make payments to the foreign exporter. - Safety Lockers:
Valuable documents and jewels etc can be kept in a vault provided by a bank for a rent. - Letter of credit:
This document is given by bank on behalf of importing customer to exporter, guaranteeing payment for the imports. - Travellers’ cheques:
Customers need not carry cash during travel in India or abroad. The denomination and words are printed in the cheque.
Question 42(a).
What are the hindrances of business? Explain any five hindrances.
Answer:
There are so many hindrances of business. They are as follows:
- Hindrance of Person:
The manufacturers and consumers do not know each other. It is called as hindrance of a person. It is removed by the trade or trader. The trader is connecting the producer and the consumer. - Hindrance of Place:
The manufacturing place is different from the place of consumption. This difficulty is known as hindrance of place. It is removed by the transport. - Hindrance of Time:
Goods are produced in one season but may be demanded throughout the year. Some goods are produced throughout the year, but may be used in certain season. It is known as hindrance of time. It is removed by the warehouse. - Hindrance of risk:
Fire, theft, floods, etc., may bring huge loss to the business. It is known as hindrance of risk. It is overcome by the insurance companies. - Hindrance of knowledge:
The difficulty of not knowing the place and availability of goods is known as hindrance of knowledge. It is removed by advertising and communication.
[OR]
Question 42 (b).
Every business enterprise has certain objectives which regulate and generate its activities. The objectives may be classified into five types. Explain the objectives of business.
Answer:
(1) Economic Objectives:
Economic objectives of business refer to the objective of earning profit and also other objectives that are necessary to be pursued to achieve the profit objective, which includes creation of customers, regular innovations and best possible use of available resources.
(2) Social Objectives:
Social objectives are those objectives of business, which are desired to be achieved for the benefit of the society. Since business operates in a society by utilizing its scarce resources, the society expects something in return for its welfare.
(3) Organizational Objectives:
The organizational objectives denote those objectives an organization intends to accomplish during the course of its existence in the economy like expansion and modernization, supply of quality goods to consumers and customers’ satisfaction, etc.
(4) Human Objectives:
Human objectives refer to the objectives aimed at the well-being as well as fulfillment of expectations of employees as also of people who are disabled, handicapped and deprived of proper education and training. The human objectives of business may thus include economic well-being of the employees, social and psychological satisfaction of employees and development of human resources.
![]()
(5) National Objectives:
Being an important part of the country, every business must have the objective of fulfilling national goals and aspirations.
Question 43(a).
Write the procedure for registration of a partnership firm.
Answer:
Procedure for registration of a partnership firm:
A statement should be prepared stating the following particulars:
- Name of the firm
- The principal place of business
- Name of other places where the firm carried on business
- Names and addresses of all the partners
- The date on which each partner joined the firm
- The duration of the firm
This statement signed by all the partners should be produced to the Registrar of Firms along with the necessary registration fee of Rs. 3. Any change in the above particulars must be communicated to the Registrar within 14 days of such alteration.
[OR]
Question 43 (b).
Write short notes on:
- Analytical Industry
- Genetic Industry
- Construction Industry
Answer:
- Analytical Industry:
It analyses and separates different elements from the same materials, as in the case of oil refinery. - Genetic Industries:
These industries remain engaged in breeding plants and animals for their use in further reproduction. The seeds, nursery companies, poultry, diary, piggery, hatcheries, nursery, fisheries, apiary and etc., are classic examples of genetic industries. - Construction Industries:
These industries are involved in the construction of building, dams, bridges, roads, as well as tunnels and canals.
Question 44 (a).
Explain any five essentials of a valid contract.
Answer:
- Offer and Acceptance:
There must be two parties to an agreement namely one party making the offer and the other party accepting it. - Legal Relationship:
The parties must have the intention to create legal relationship between them. An agreement of Social or domestic nature is not at all a contract. - Lawful Consideration (quid pro quo):
As per Contract Act under Sec. 2(d) Consideration means something in return. A contract without consideration becomes invalid. - Lawful Object (Section 23):
The object of agreement should be lawful and legal. It must not be immoral, illegal or opposed to public policy.’ - Free Consent (Section 13 and 14):
Consent of the parties must be free and genuine. Consent means agreeing upon same thing in the same sense at the same time i.e. there should be consensus – ad – idem. Consent is said to be free when it is not caused by coercion, undue influence, fraud, misrepresentation or mistake.
[OR]
Question 44 (b).
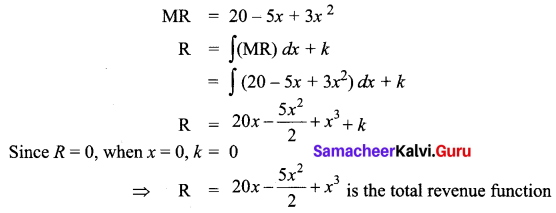
Tax is classified into direct and indirect tax. Tax is a revenue to the government. It is used for the welfare of the country. Distinguish between direct and indirect taxes.
Answer:
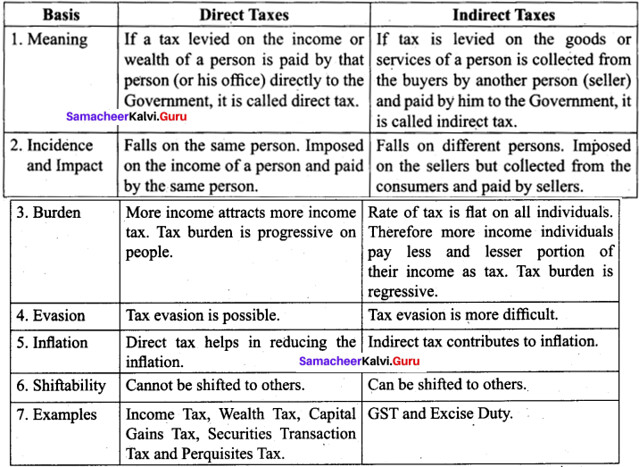
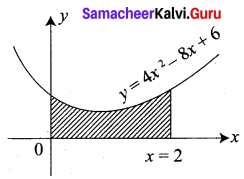
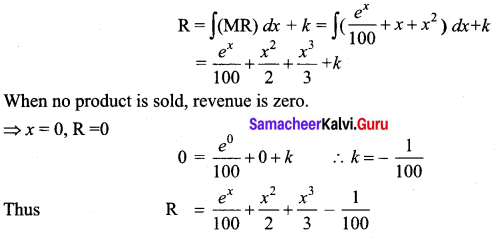
Question 45 (a).
Explain the advantages of warehousing.
Answer: