You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.8
9th Maths Exercise 3.8 Question 1.
Factorise each of the following polynomials using synthetic division:
(i) x3 – 3x2 – 10x + 24
(ii) 2x3 – 3x2 – 3x + 2
(iii) -7x + 3 + 4x3
(iv) x3 + x2 – 14x – 24
(v) x3 – 7x + 6
(vi) x3 – 10x2 – x + 10
Solution:
(i) x3 – 3x2 – 10x + 24
Let p(x) = x3 – 3x2 – 10x + 24
Sum of all the co-efficients = 1 – 3 – 10 + 24 = 25 – 13 = 12 ≠ 0
Hence (x – 1) is not a factor.
Sum of co-efficient of even powers with constant = -3 + 24 = 21
Sum of co-efficients of odd powers = 1 – 10 = – 9
21 ≠ -9
Hence (x + 1) is not a factor.
p (2) = 23 – 3 (22) – 10 × 2 + 24 = 8 – 12 – 20 + 24
= 32 – 32 = 0 ∴ (x – 2) is a factor.
Now we use synthetic division to find other factor
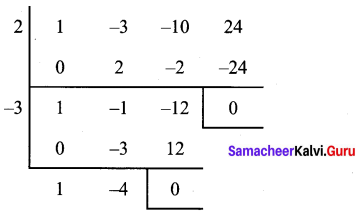
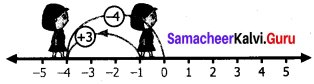
Thqs (x – 2) (x + 3) (x – 4) are the factors.
∴ x3 – 3x2 – 10x + 24 = (x – 2) (x + 3) (x – 4)
(ii) 2x2 – 3x2 – 3x + 2
Let p (x) = 2x3 – 3x2 – 3x + 2
Sum of all the co-efficients are
2 – 3 – 3 + 2 = 4 – 6 = -2 ≠ 0
∴ (x – 1) is not a factor
Sum of co-efficients of even powers of x with constant = -3 + 2 = – 1
Sum of co-efficients of odd powers of x = 2- 3= -1
(-1) = (-1)
∴ (x + 1) is a factor
Let us find the other factors using synthetic division
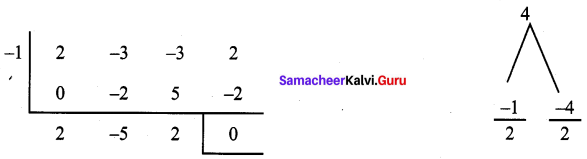
Quotient is 2x2 – 5x + 2 = 2x – 4x – x + 2 = 2x (x – 2) – 1 (x – 2)
= (x – 2) (2x – 1)
∴ 2x3 – 3x2 – 3x + 2 = (x + 1) (x – 2) (2x – 1)
(iii) -7x + 3 + 4x3
Let p(x) = 4x3 + 0x2 – 7x + 3
Sum of the co-efficients are = 4 + 0 – 7 + 3
= 7 – 7 = 0
∴ (x- 1) is a factor
Sum of co-efficients of even powers of x with constant = 0 + 3 = 3
Sum of co-efficients of odd powers of x with constant = 4 – 7 = -3
-3 ≠ -3
∴ (x + 1) is not a factor
Using synthetic division, let us find the other factors.
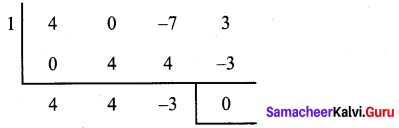
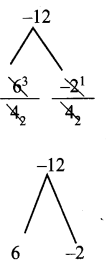
Quotient is 4x2 + 4x – 3
= 4x2 + 6x – 2x – 3
= 2x (2x + 3) – 1 (2x + 3)
= (2x + 3) (2x – 1)
∴ The factors are (x – 1), (2x + 3) and (2x – 1)
∴ -7x + 3 + 4x3 = (x + 1) (2x + 3) (2x – 1)
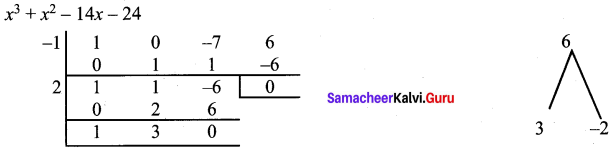
(iv) x3 + x2 – 14x – 24
Let p (x) = x3 + x2 – 14x – 24
Sum of the co-efficients are = 1 + 1 – 14 – 24 = -36 ≠ 0
∴ (x – 1) is not a factor
Sum of co-efficients of even powers of x with constant = 1 – 24 = -23
Sum of co-efficients of odd powers of x = 1 – 14 = -3
-23 ≠ -13
∴ (x + 1) is also not a factor
p(2) = 23 + 22 – 14 (2) – 24 = 8 + 4 – 28 – 24
= 12 – 52 ≠ 0, (x – 2) is a not a factor
p (-2) = (-2)3 + (-2)2 – 14 (-2) – 24
= -8 + 4 + 28 – 24 = 32 – 32 = 0
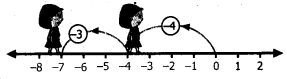
∴ (x + 2) is a factor
To find the other factors let us use synthetic division.
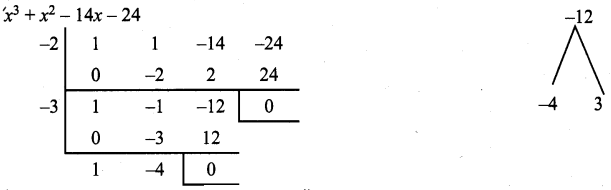
∴ The factors are (x + 2), (x + 3), (x + 4)
∴ x3 + x2 – 14x – 24 = (x + 2) (x + 3) (x – 4)
(v) x3 – 7x + 6
Let p (x) = x3 + 0x2 – 7x + 6
Sum of the co-efficients are = 1 + 0 – 7 + 6 = 7 – 7 = 0
∴(x- 1) is a factor
Sum of co-efficients of even powers of x with constant = 0 + 6 = 6
Sum of coefficient of odd powers of x = 1 – 7 = -7
6 ≠ -7
∴ (x + 1) is not a factor
To find the other factors, let us use synthetic division.
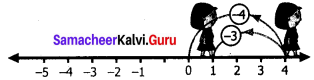
∴ The factors are (x – 1), (x – 2), (x + 3)
∴ x3 + 0x2 – 7x + 6 = (x – 1) (x – 2) (x + 3)
(vi) x3 – 10x2 – x + 10
Let p (x) = x3 – 10x2 – x + 10
Sum of the co-efficients = 1 – 0 – 1 + 10
= 11 – 11 = 0
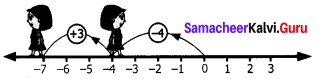
∴ (x – 1) is a factor
Sum of co-efficients of even powers of x with constant = -10 + 10 = 0
Sum of co-efficients of odd powers of = 1 – 1 = 0
∴(x + 1) is a factor
Synthetic division
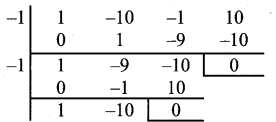
∴ x3 + 10x2 – x + 10 = (x – 1) (x + 1) (x – 10)