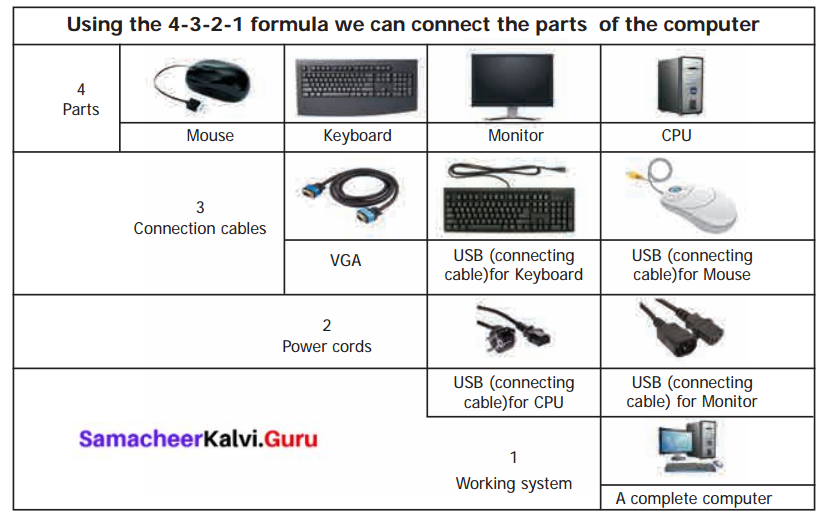
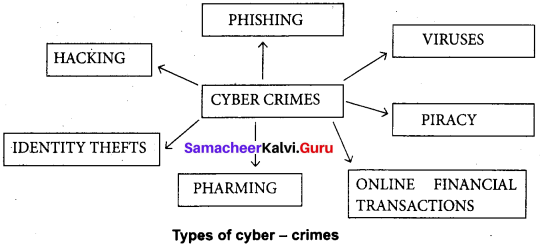
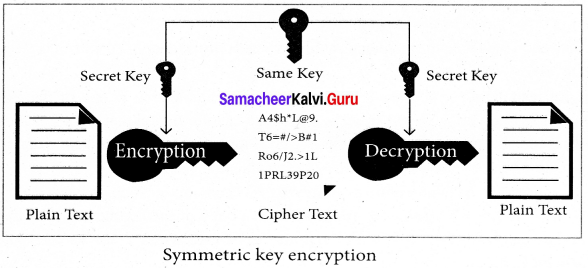
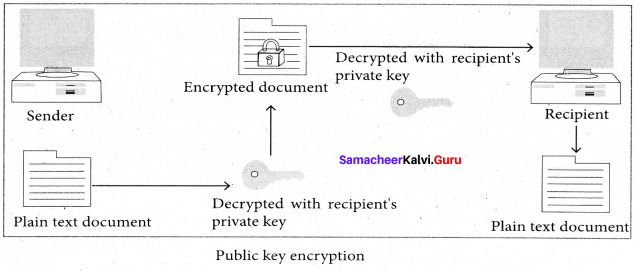
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Geography Solutions Term 3 Chapter 2 Globe
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Globe Textual Evaluation
I. Fill in the blanks:
- The line of latitude which is known as the Great Circle is __________
- The imaginary lines drawn horizontally on Earth from the West to East are called __________
- The 90° lines of latitude on the Earth are called __________
- The Prime Meridian is also called __________
- The world is divided into time zones __________ time zone
Answer:
- Equator
- Parallels of latitude
- North Pole and South Pole
- Greenwich Meridian
- 24
II. Choose the best answer :
1. The shape of the Earth is _______.
(a) Square
(b) Rectangle
(c) Geoid
(d) Circle
Answer:
(c) Geoid
![]()
Question 2.
The North Pole is ……………..
(a) 90° N Latitude
(b) 90° S latitude
(c) 90° W Longitude
(d) 90° E longitude
Answer:
(a) 90° N Latitude
Question 3.
The area found between 0° and 180° E lines of longitude is called _______.
(a) Southern Hemisphere
(b) Western Hemisphere
(c) Northern Hemisphere
(d) Eastern Hemisphere
Answer:
(d) Eastern Hemisphere
Question 4.
The 23 1/2° N line of latitude is called ……………..
(a) Tropic of Capricorn
(b) Tropic of Cancer
(c) Arctic Circle
(d) Antarctic Circle
Answer:
(b) Tropic of Cancer
![]()
Question 5.
180° line of longitude is _______.
(a) Equator
(b) International Date Line
(c) Prime Meridian
(d) North Pole
Answer:
(b) International Date Line
Question 6.
The Sun is found overhead the Greenwich Meridian at ……………..
(a) 12 midnight
(b) 12 noon
(c) 1 p.m.
(d) 11 a.m.
Answer:
(b) 12 noon
Question 7.
A day has _____.
(a) 1240 minutes
(b) 1340 minutes
(c) 1440 minutes
(d) 1140 minutes
Answer:
(c) 1440 minutes
Question 8.
Which of the following lines of longitude is considered for the Indian Standard Time?
(a) 82 1/2° E
(b) 82 1/2° W
(c) 81 1/2° WE
(d) 81 1/2° W
Answer:
(a) 82 1/2° E
Question 9.
The total number of lines of latitude are ________
(a) 171
(b) 161
(c) 181
(d) 191
Answer:
(c) 181
Question 10.
The total number of lines of longitude are ……………
(a) 370
(b) 380
(c) 360
(d) 390
Answer:
(c) 360
III. Circle the odd one

IV. Match the following.
| A | B |
| 0° line of latitude | Pole |
| 0° line of longitude | International Date Line |
| 180° line of longitude | Greenwich |
| 90° line of latitude | Equator |
Answer:
| A | B |
| 0° line of latitude | Equator |
| 0° line of longitude | Greenwich |
| 180° line of longitude | International Date Line |
| 90° line of latitude | Pole |
V. Examine the following statements :
- The Earth is spherical in shape.
- The shape of the Earth is called a geoid.
- The Earth is flat.
Look at the options given below and choose the correct answer.
(a) 1 and 3 are correct
(b) 2 and 3 are correct
(c) 1 and 2 are correct
(d) 1,2 and 3 are correct
Answer:
(c) 1 and 2 are correct
![]()
VI. Examine the following statements :
Statement I : The lines of latitude on Earth are used to find the location of a place and define the heat zones on Earth.
Statement II: The lines of longitudes on Earth are used to find the location of a place and to calculate time.
Choose the correct option :
(a) Statement I is correct; II is wrong
(b) Statement I is wrong; II is correct
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are wrong
Answer:
(c) Both the statements are correct
VII. Name the following :
- The imaginary lines drawn horizontally on Earth.
- The imaginary lines drawn vertically on Earth.
- The three dimensional model of the Earth.
- India is located in this hemisphere based on lines of longitude.
- The network of lines of latitude and longitude.
Answer:
- Latitudes
- Longitudes
- globe
- Eastern hemisphere
- Earth grid
VIII. Answer Briefly :
Question 1.
What is a geoid?
Answer:
- The Earth cannot be compared with any other geometrical shape as it has a very unique shape.
- Hence, its shape is called a geoid (earth shaped).
![]()
Question 2.
What is local time?
Answer:
- The time in a particular region or area expressed, with reference to the meridian passing through it. (or)
- When the sun is overhead on a particular line of longitude, it is 12 noon at all the places located on that line of longitude. This is called local time.
Question 3.
How many times would the sun pass overhead a line of longitude?
Answer:
The sun is overhead on a line of longitude only once a day.
Question 4.
What are lines of latitude and longitude?
Answer:
- The imaginary lines that run east and west direction on the Earth are called lines or parallels of latitude
- The imaginary lines drawn vertically connecting the North pole and the south pole are called lines or meridians of longitude.
Question 5.
Name the four hemispheres of the Earth.
Answer:
- Northern Hemisphere,
- Southern Hemisphere,
- Eastern Hemisphere and
- Western Hemisphere.
IX. Give Reasons :
Question 1.
The 0° line of longitude is called the Greenwich Meridian.
Answer:
- All nations of the world agreed to have the Greenwich Meridian as the international Standard Meridian (0°).
- This line of longitude is called the Prime Meridian and it is also known as the Greenwich Meridian because it passes through Greenwich.
Question 2.
The regions on Earth between North & South lines of latitude (66 V20) and poles (90°) is called Frigid Zone
Answer:
This region receives very slanting rays of the sun. The temperature is very low. Hence, this region is known as Frigid Zone.
Question 3.
The International Date Line runs zigzag.
Answer:
- The International Date line is not straight.
- If the line is drawn straight, two places in the same country world have different dates.
- So the International Date line is found zigzag in certain places to avoid confusion.
IX. Give reason:
Question 1.
The 0° line of longitude is called the Greenwich Meridian.
Answer:
- All nations of the world agreed to have the Greenwich Meridian as the international Standard Meridian (0°).
- This line of longitude is called the Prime Meridian and it is also known as the Greenwich Meridian because it passes through Greenwich.
Question 2.
The regions on Earth between North & South lines of latitude (66 Vi°) and poles (90°) is called Frigid Zone.
Answer:
- From the Arctic circle (66 ‘A° N) to the North Pole (90° N) and from the Antarctic circle (66 Vi0 S) to the South Pole (90° S) the sun’s rays full further inclined, through „ out the year.
- The temperature is very low.
- Hence this region is known as Frigid Zone.
![]()
Question 3.
The International Date Line runs zigzag.
Answer:
- The International Date line is not straight.
- If the line is drawn straight, two places in the same country world have different dates.
- So the International Date line is found zigzag in certain places to avoid confusion.
X. Answer in detail :
Question 1
What are the uses of globe?
Answer:
- Since the Earth is huge and we live on a very area, we are not able to see the Earth as a whole.
- But when we travel to space, we can see the Earth as a whole.
- So, in order to see the shape of the Earth as a whole and to know its unique features, a three dimensional model of the Earth was created with a specific scale in the name of globe.
Question 2.
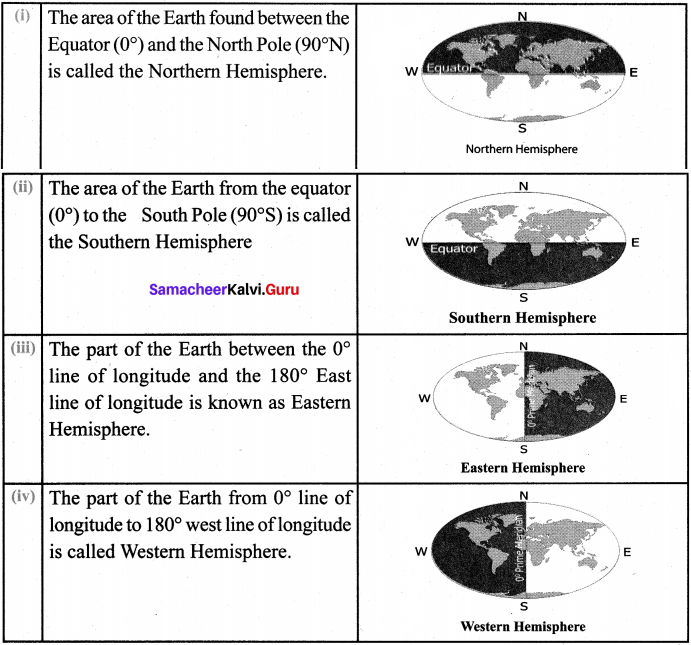
How are the hemispheres divided on the basis of lines of latitude and longitude?
Explain with diagrams.
Answer:
Question 3.
What are the significant lines of latitude? Explain the zones found between them,
Answer:
The significant lines of latitude are
(a) Equator – 0°
(b) Tropic of Cancer – 23 1/2°N
(c) Tropic of Capricorn – 23 1/2°S
(d) Antarctic Circle – 66 1/2°S
(e) Arctic Circle – 66 1/2°N
(f) North Pole – 90°N
(g) South Pole – 90°S.
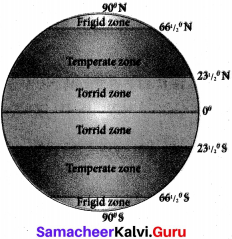
(i) Torrid zone:
The region from the Equator towards the Tropic of Cancer (231A°N) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23 1/2 40S) is called the Torrid Zone.
(ii) Temperate zone:
From the Tropic of Cancer (23!/2°N) to the Arctic Circle (661/2°N) and from the Tropic of Capricorn (23 1/2 0S) to the Antarctic Circle (661/2°S), the Sun’s rays fall slantingly. Moderate temperature prevails in this region. Hence, this region is called Temperate Zone.
(iii) Frigid zone:
From the Arctic Circle (66 1/2°N) to the North Pole (90°N) and from the Antarctic Circle (66 1/2 0S) to the South Pole (90°S), the Sun’s rays fall further inclined, throughout the year. Hence, this region is called Frigid Zone.
Question 4.
Explain; Indian Standard Time.
Answer:
- The longitudinal extend of India is from 68° 7’E to 97° 25’E
- As many as twenty nine lines of longitude pass through India.
- Having 29 standard time is not logical.
- Hence 821/2° E line of longitude is observed as the prime meridian to calculate the Indian standard Time.
XI. Activity :
Question 1.
There are five positions marked on the grid given below. Look at them carefully and fill the blanks with reference to the lines of latitude and longitude. The first one is done for you.
- The latitudinal and longitudinal reference of point A 40° N 30° W
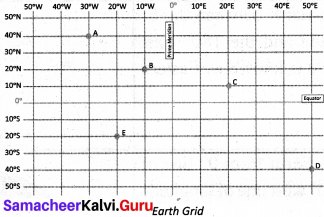
- The latitudinal and longitudinal reference of point B 2Q°N 1Q° W.
- The latitudinal and longitudinal reference of point C 10° N 20° E.
- The latitudinal and longitudinal reference of point D 40° S 50° E,
- The latitudinal and longitudinal reference of point E 20° S 20°. W.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Globe IntextActivities
Question 1.
What is the difference in time between the GMT and 1ST?
Answer:
Indian Standard Time is 5 hours and 30 minutes ahead of Greenwich Mean Time.
Eg: 7:15 a.m. GMT is 12:45 p.m. 1ST (that is GMT + 5 hrs and 30 min.
Question 2.
If it is 5 a.m. at New York City, USA. what would be the time at New Delhi, the capital of India?
Answer:
If it is 5 a.m. at New York City, USA., then the time at New Delhi would be 3:30 p.m. (India time is 10 hours and 30 minutes ahead New York, United States).
Question 3.
If it is 12 Midnight at London, what would be the time in India?
Answer:
If it is 12 Midnight at London, then the time in India would be 5:30 a.m.
![]()
Question 4.
The standard time of Sydney city in Australia is found to be at a difference of _____ hours from that of the GMT.
Answer:
10 Hours. It is according to Australian Eastern Standard Time, (GMT+10). But during Summer, it will be 11 Hours. (GMT+11).
Question 5.
Mr. Senthamizh travels by flight from Chennai to London. He boarded the aeroplane at 9a.m After 12 hours of travel, at what time (GMT) would he have reach London?
Answer:
He would reach London at 3.30 p.m. GMT.
Question 6.
Based on the longitudinal extent, in which hemisphere is our country located? Look at the globe and answer.
Answer:
Based on the longitudinal extent, our country is located in Eastern hemisphere
HOTS
Question 1.
Based on the latitudinal extent, in which hemisphere is India located?
Answer:
Based on the latitudinal extent, our country is located in Northern hemisphere
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Globe Additional Questions:
I. Fill In the blanks:
- When we travel to space, we can see the ______ as Whole
- The Earth is ______ at the poles.
- The Earth bulges at the ______
- The Earth moves around the ______
- The Earth rotates from the ______
- The Earth is inclined on its axis at an inclination of ______
- The first globe was created by the ______
- Aryabhatta wrote ______
- The first person to draw the lines of latitude and longitude was ______
- Geographia’ was written by ______
- The latitudinal extent between 1° line of latitude on Earth is ______
- The sun’s rays ______ equally on all parts of the earth.
- The lines of longitude converge at the ______
- Two opposite meridians form a ______
- Based on the longitudinal extent, India is located in the ______
- The Royal Astronomical observatory is located in ______
- The sun is overhead on a line of longitude a day ______
- The word meridian is derived from the Latin word ______
- Local time is calculated when the sun is ______
- Russia has time zones ______
Answer:
- Earth
- Flat
- Equator
- Sun
- West to East
- 23 1/2°
- Greeks
- Aryabhatta Siddhanta
- Ptolemy
- 111 km
- do not fall
- Poles
- Great-circle
- hemisphere.
- Eastern
- England
- only once
- Meridianus
- Overhead at noon
- 7
II. Choose the best answer :
Question 1.
The Earth is ____
(a) Oval shaped
(b) Flat
(c) Spherical shaped
(d) Rectangular
Answer:
(c) Spherical shaped
![]()
Question 2.
The latitude which divides the Earth into two halves
(a) Tropic of Cancer
(b) Tropic of Capricorn
(c) Arctic Circle
(d) Equator
Answer:
(d) Equator
Question 3.
Tropic of Cancer is Otherwise called as ……………..
(a) Kadagavari
(b) Nilanaduvarai
(c) Magaravarai
Answer:
(a) Kadagavari
Question 4.
The region from the Equator towards the Tropic of Cancer, is known as .
(a) Torrid Zone
(b) Temperate Zone
(c) Frigid Zone
(d) Heat Zone
Answer:
(a) Torrid Zone
Question 5.
The International Meridian Conference (1884) was held in ……………..
(a) Canada
(b) Mexico
(c) Washington DC
Answer:
(c) Washington DC
III. Circle the odd one :

IV. Match the following.
a) | Geographia | (i) | Horizontal |
b) | Aryabhatta | (ii) | Vertical |
| c) | Latitudes | (iii) | Centre |
d) | Longitudes | (iv) | Ptolemy |
e) | Equator | (v) | Astronomer |
Answer:
- iv
- v
- i
- ii
- iii
V. Examine the following statements :
a.When you move towards the East from any meridian the time increases.
b.When you move towards the West from any meridian the line decreases.
c.The earth rotates from West to East on its own axis.
Look at the options given below and ehoose the correct answer,
- a and c are correct
- b and c are correct
- a and b are correct
- a, b, c are correct
Answer:
(4) a, b, c are correct
VI. Examine the following statements :
Statement I : The 180° line of longitude has been fixed as the International Date of Line, drawn on the Pacific Ocean between Alaska and Russia through Bering Strait.
Statement II : The part of the Earth between the 0° line of longitude and the 180° East line of longitude is known as Western Hemisphere.
Choose the correct option :
(a) Statement I is correct; II is wrong
(b) Statement I is wrong; II is correct
(c) Both the statements are wrong
(d) Both the statements are correct
Answer:
(a) Statement I is correct; II is wrong
VII. Name the following :
- 0° latitude.
- 23 1/2°S latitude.
- 23 1/2°N latitude.
- 66 1/2°S latitude.
- 66 1/2°N latitude.
Answer:
- Equator
- Tropic of Capricorn
- Tropic of Cancer
- Antarctic Circle
- Arctic Circle
VIII. Answer Briefly:
Question 1.
What was mentioned by Aryabhatta in his book?
Answer:
In his ‘Aryabhatta Sidhanta’ Aryabhatta mentioned that the stars in the sky seems to move towards the West because of the Earth’s rotation on its axis.
![]()
Question 2.
Who was Ptolemy?
Answer:
- Ptolemy was a Greco – Roman mathematician, astronomer and geographer.
- He was the first person to draw the lines of latitude and longitude on a map.
Question 3.
Mention about ‘Geographia’.
Answer:
- Geographia was authored by Ptolemy.
- He gave a detailed description about the Earth’s surface to size and circumference.
- He also mentioned about many locations based on the lines of latitude and longitude
Question 4.
How many parallels are found on the Earth?
Answer:
- The lines of latitude consist of 89 parallels in the Northern Hemisphere.
- There are 89 parallels in the Southern Hemisphere.
- One at the Equal and the two poles are found as points.
- Totally there are 181 parallels found on earth.
![]()
Question 5.
What are called meridians of longitude?
Answer:
The imaginary lines drawn vertically connecting the North Pole and the South Pole are called lines or meridians of longitude.
Question 6.
What is a Prime Meridian?
Answer:
The 0° line of longitude is called the Prime Meridian.
Question 7.
What are Western Longitudes?
Answer:
The lines of longitude that are found between the Prime Meridian (0°) and 180° West line of longitude are called Western longitude.
Question 8.
What is known as Eastern Hemisphere?
Answer:
The part of the Earth between the 0° line of longtitude and the 180° East line of longtitude is known as the Eastern Hemisphere.
Question 9.
What is GMT?
Answer:
Greenwich Mean Time : GMT is the mean solar time at the Royal observatory in Greenwich, London, reckoned from midnight.
Question 10.
How many time zones are there in the USA?
Answer:
The United States is spread across six time zones. From west to east, they are Hawaii, Alaska, Pacific, Mountain, Central and Eastern.
Question 11.
How many time zones in Europe, Africa, Australia and Asia.
Answer:
- Europe – 11 time zones
- Africa – 6 times zones
- Australia – 3 time zones
- Asia – 11 time zones
Question 12.
What is the time difference between
- India and Greenwich Mean Time
- India and U.S.A
- India and Dubai
- India and Australia.
Answer:
- India is 5 hours 30 minutes ahead of Greenwich Mean Time.
- India is 10 hours and 30 minutes ahead of Washington, DC, U.S.A.
- India is 1 hour and 30 minutes a head of Dubai.
- Australia is 5 hours and 30 minutes ahead of India. (Canberra Act)
IX. Give Reasons:
Question 1.
The length of the lines of latitude decreases from the equator.
Answer:
- Since the Earth is geoid shaped, the length of the lines of latitude decreases from the Equator towards the South and North Poles.
- The 90° North and South Poles are not found as lines but as points.
![]()
Question 2.
All the places on earth do not have the same amount of temperature.
Answer:
- The Sun’s rays do not fall equally on all parts of the earth.
- They fall vertically over the equator and slanting towards the poles.
- Thus all the places on earth do not have the same amount of temperature
Question 3.
The region from the Equator towards the Tropic of Cancer (23‘/2°N) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23!4°S) is called Torrid Zone.
Answer:
- The Sun’s rays fall vertically over this region and the average temperature is very high.
- Hence this region is known as the Torrid Zone.
X. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Write a note an Latitudes.
Answer:
- The imaginary lines which are drawn horizontally on East – West direction on the Earth are called the lines or parallels of latitudes.
- The 0° line of latitude which divides the Earth into two halves is known as the Equator.
- From the equator, parallel lines are drawn towards the North and South Poles at equal intervals.
- The latitudinal extent between 1° line of latitude on Earth is 111 km.
- Since the Earth is geoid shaped, the length of the lines of latitude decreases from the equator towards the south and North poles.
- The lines of latitude that are drawn horizontally between the equator and the North Pole are called Northern latitudes.
- Those which are found between the equator and the South Pole are called Southern Latitudes.
- The area of the Earth found between the Equator (0°) and the North Pole (90°N) is called the Northern Hemisphere.
- The area of the Earth from the equator (0°) to the South Pole (90°S) is called the Southern Hemisphere.
![]()
Question 2.
Write a note on Longitudes.
Answer:
- The imaginary lines drawn vertically connecting the North Pole and the South Pole are called lines or meridians of longitude.
- These lines of longitude are seen as semi circles.
- The 09 line of longitude is called the Prime Meridian.
- There are 180 lines of longitude towards the East and West from the Prime Meridian.
- So there are totally 360 lines of longitude.
- These lines converge at the poles. The 180°W and 180°E line of longitude are the same line.
- The lines of longitude that are found between the Prime Meridian and the 180° East line of longitude are called Eastern Longitudes.
- The lines of longitude that are found between the Prime Meridian (0°) and the 180° West line of longitude are called Western Longitudes.
- The part of the Earth between the 0° line of longitude and the 180° East line of longitude is known as the Eastern Hemisphere.
- The part of the Earth from 09 line of longitude to 180° West line of longitude is called Western Hemisphere.








 Output:
Output: