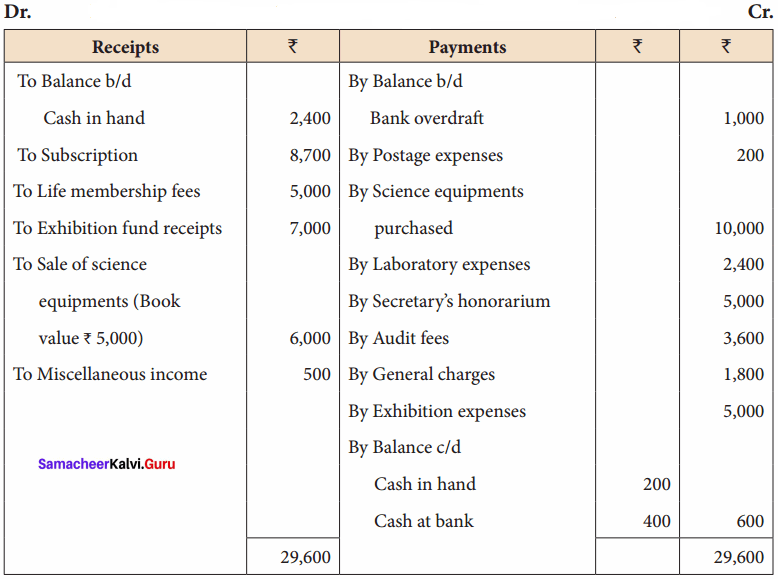
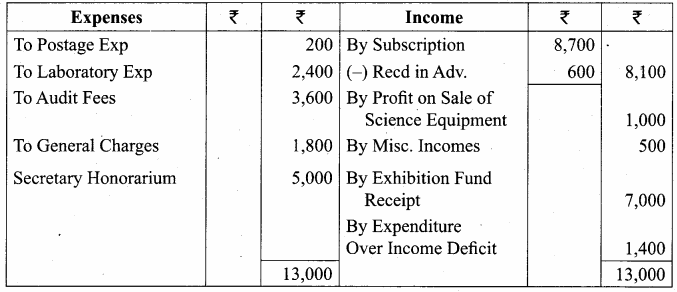
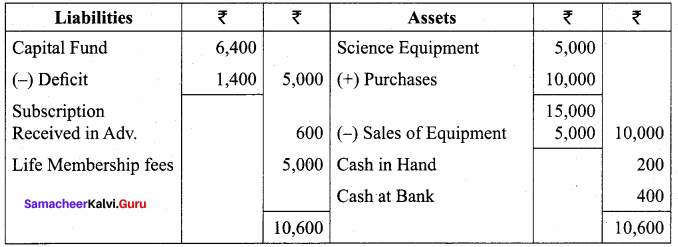
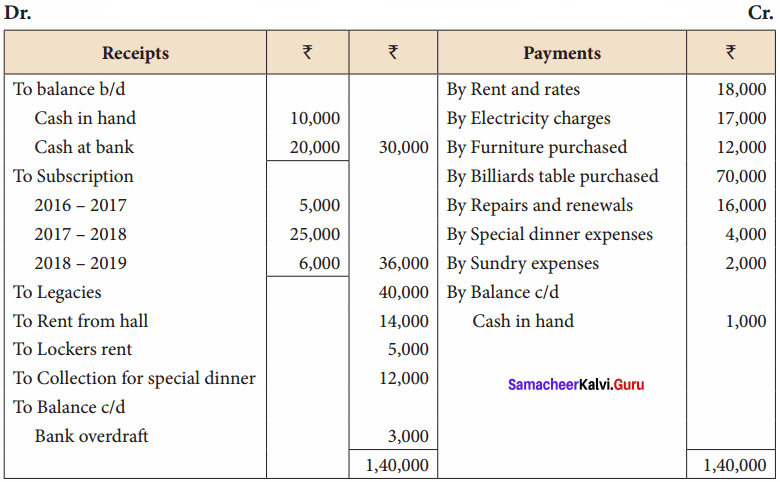
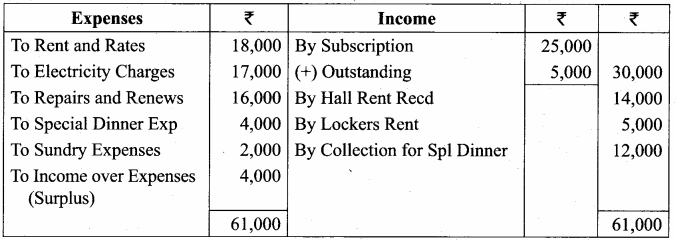
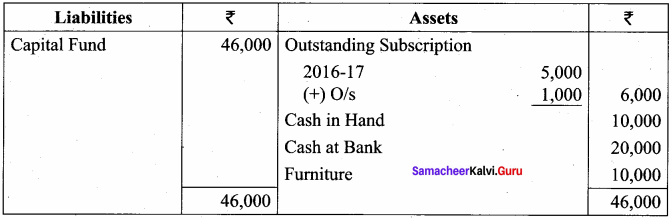
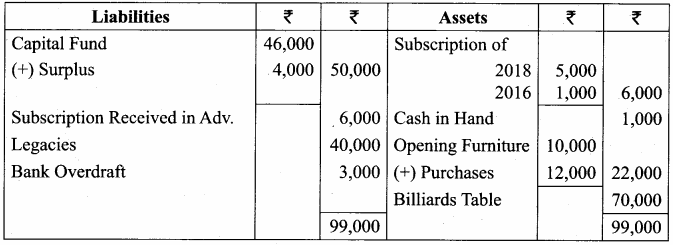
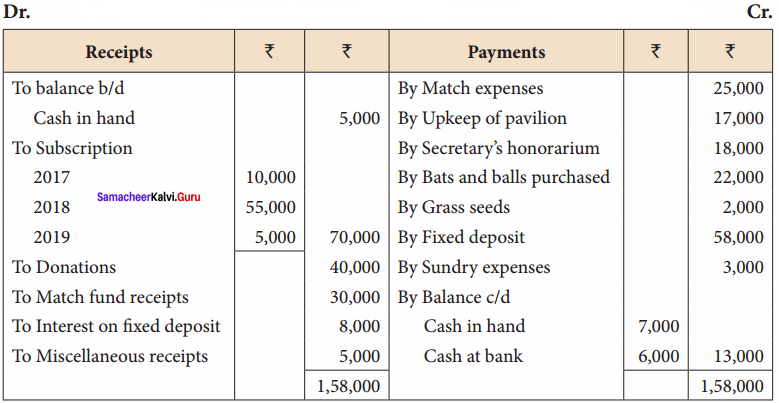
Students can Download English Lesson 2 The Red-Headed League Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes Pdf, Activity, Samacheer Kalvi 7th English Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th English Solutions Term 1 Supplementary Chapter 2 The Red-Headed League
A. Say whether the following statements are ‘True’ or ‘False’.
- Photography was Vincent Spaulding’s hobby.
- Mr. Ross did not want to hire Mr. Wilson.
- Mr. Wilson worked for Mr. Ross for six weeks.
- Mr. Jones was a lawyer.
- Spaulding dug a tunnel from the cellar of the shop to the jewellery shop.
Answer:
- False
- False
- False
- False
- False
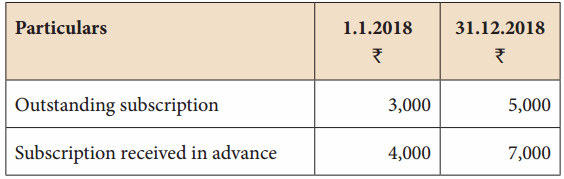
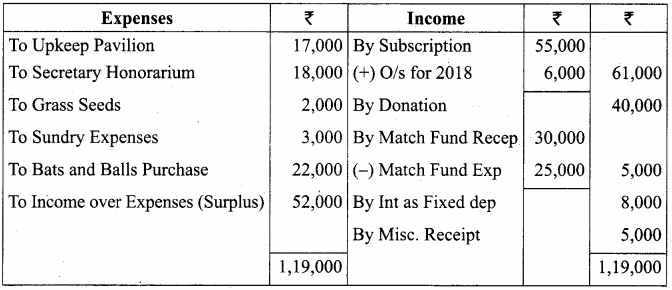
B. Complete the table based on the information from the text.
Answer:

C. Answer the following questions.
The Red-Headed League Questions And Answers Pdf Question 1.
Why did Jabez Wilson meet Mr. Holmes?
Timid Jabez Wilson was a pawnshop owner. His assistant Spaulding made him join the job of copying the Encyclopaedia from 10.00 a.m. to 2.00 a.m. After eight weeks the office is closed and dissolved. He doubted someone is playing a joke on him and so he met Mr. Holmes for a solution.
The Red-Headed League 7th Standard Question Answer Question 2.
Describe Vincent Spaulding.
Answer:
Vincent Spaulding was a clever young man. He happily worked as the assistant for Mr. Wilson in his pawn shop for half-wages. He was actually John Clay, the notorious thief.
The Red Headed League Questions And Answers Question 3.
Why did Spaulding spend a lot of time in the cellar?
Answer:
Spaulding was spending a lot of time in the cellar of the pawnshop because he was making a tunnel to get into the strong room of the bank in the next street at the back of the shop.
Red Headed League Questions And Answers Question 4.
Why was Mr. Wilson hired to copy the Encyclopaedia?
Answer:
Mr. Wilson was hired to copy the Encyclopedia to keep him away from his pawnshop from 10.00 a.m. to 2.00 p.m. every day So that when Wilson went to work, Mr. Ross and Spaulding could have time to make the tunnel from his shop to the bank.
The Red-Headed League Questions And Answers Question 5.
How did Holmes’ team catch the thieves?
Answer:
The Holme’s team was ready at the strong room in the bank on Saturday night expecting the arrival of the thieves. When Spaulding and Ross came out from underground, Holmes caught Spaulding by his arm and the others caught Ross at the other end of the tunnel.
D. Based on your reading of the text complete the pyramid arranging the sequence in the correct order,
- Holmes found the tunnel from the cellar to the bank’s strong room.
- Wilson was assigned to copy the encyclopaedia.
- Wilson asked Sherlock Holmes for help.
- Wilson got the job in The Red – Headed League.
- Spaulding and Ross were caught by the famous detective.
- One day he found the notice that ‘The Red – Headed League’ was dissolved.
- Holmes recognised Spaulding who was actually John Clay, a notorious criminal.
Answer:

Project
E. Imagine you have visited a Mystery Theme Park you have come across. Make an eye¬catching advertisement with the help of the given dues.
- a mirror maze
- scary faces
- eerie sounds
- a ghostly figure
- a pitch dark room
Answer:

Connecting To Selfs
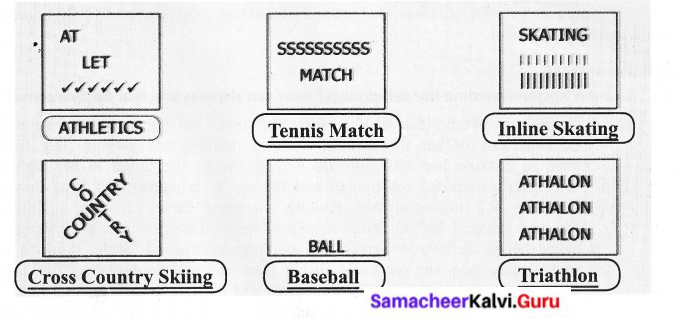
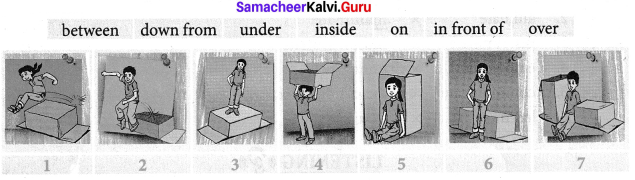
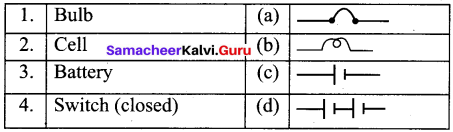
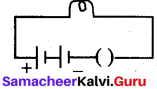
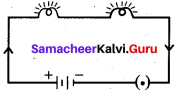
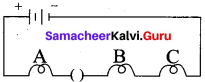
F. Observe the pictures carefully and write your answers.
Answer:

Step To Success
G. lust like the example, use the key to fill in the blanks and break the code
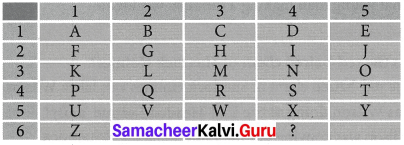
Answer:
- SECRET
- GHOST
- TRICK
- RIDDLE
- PUZZLE
The Red-Headed League Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answers
The Red-Headed League 7th Standard Question 1.
Wilson was accepted into the League by ______
(a) Dr. Watson
(b) Mr. Duncan Ross
(c) Mr. Vincent Spaulding
Answer:
(c) Mr. Vincent Spaulding
The Red Headed League 7th Standard Question 2.
I saw you hit the ______ with your walking stick
(a) ground
(b) man
(c) shop door
Answer:
(a) ground
The Red Headed League Book Back Answers Question 3.
Ross quickly gets back into the tunnel ______ wants to stop him but could not
(a) John Clay
(b) Jones
(c) Holmes
Answer:
(b) Jones
The Red-Headed League Book Back Answers Question 4.
The cellar was the shop ______ the shop
(a) behind
(b) in front of
(c) beside
Answer:
(c) beside
The Red Headed League Question Answer Question 5.
The bank does not open on ______
(a) Saturday
(b) Sunday
(c) Friday
Answer:
(b) Sunday
The Red Headed League Question And Answer Question 6.
Jabez Wilson was a timid red-haired ______
(a) doctor
(b) detective
(c) pawn broker
Answer:
(c) pawn broker
The Red Headed League Answers Question 7.
The ______ wanted Wilson away from the shop for some hours everyday.
(a) friends
(b) villains
(c) heroes
Answer:
(b) villains
The Red Headed League 7th Standard In English Question 8.
I ______ when Spaulding was happy to work for half-wages.
(a) suspected
(b) liked
(c) Holmes
Answer:
(a) suspected
II. dentify the Character / Speaker.
- “How can I get to the Strand?”
- “Yes, to the hospital”.
- “My men are waiting at the front door of the bank”.
- “You think of everything, Mr. Holmes.”
- “So Spaulding is John Clay, the notorious thief”.
- “Did you see his trousers? They were dirty”.
Answer:
- Holmes
- Dr. Watson
- Mr. Jones
- Spaulding
- Dr. Watson
- Holmes
III. Write True or False against each statement.
- Holmes and Dr. Watson move to Wilsons shop in Saxe-Coburg Square.
- Dr. Watson visits the apartment of his patient Sherlock Holmes.
- I want your help tonight. Come at nine O’clock.
- Holmes comes out from behind his box, and hits Spaulding’s arms.
- Clay saw the colour of Ross’s hair and thought of a Red-Headed League.
- “Spaulding often went down to the cellar”.
- Because making a tunnel is a clean work”.
- “Why is that young man making a tunnel?” I thought.
Answer:
- True
- False
- False
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
IV. Very Short Questions with Answers.
The Red-Headed League Worksheet Answers Question 1.
Who was the red-haired client of Sherlock Holmes?
Answer:
The red-haired client of Sherlock Holmes was Jabez Wilson.
Question 2.
What was Wilson doing at the Red-Headed League daily?
Answer:
Wilson was copying out the Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Question 3.
Where was Dr. Watson working?
Answer:
Dr. Watson was working in the hospital.
Question 4.
What did Spaulding have in his hands when he came out of the ground?
Answer:
Spaulding had a gun in his hands.
Question 5.
Why were Spaulding’s trousers dirty?
Answer:
Spaulding’s trousers were dirty because making a tunnel is dirty work.
Question 6.
What made Holmes think that the tunnel was ready?
Answer:
Holmes thought the tunnel was ready as the Red-Headed League’s office was closed.
V. Short Questions with Answers.
Question 1.
Why did Vincent show the newspaper advertisement to Mr. Wilson?
Answer:
Vincent showed the advertisement about an opening in the Red-Headed League to Mr. Wilson to make him join the job so that he would be away from his pawn shop daily for a few hours. During that time Vincent and Ross planned to dig the tunnel from the shop cellar to the bank in the next street.
Question 2.
Holmes knew London very well then why should he ask the way to Strand?
Answer:
Holmes got information from Mr. Wilson and observes the pawn shop from outside. He also wanted to know who was inside and what were they doing. So he knocks the door of the shop and asks the way to Strand for namesake and finds out the truth.
Question 3.
Spaulding was happy to work for half wages. Why?
Answer:
Spaulding didn’t seek for a job. He wanted to find entry into the pawn shop by working as an assistant to Mr. Wilson. But his aim was to make a tunnel from the shop to the bank, hence he happily agreed for half wages.
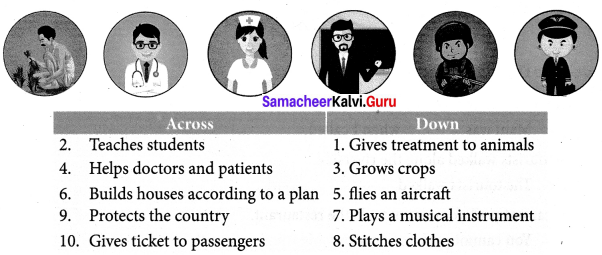
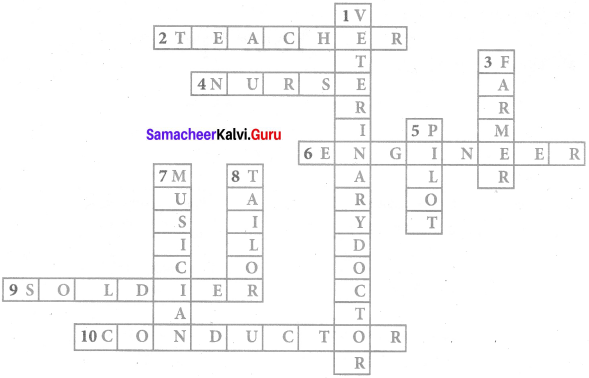
VI. Characters with job description:

VII. Paragraph Questions with Answers.
Question 1.
Why did Holmes go to look at the road behind Saxe-Coburg Square?
Answer:
Mr. Wilson’s pawn shop was at Saxe-Coburg Square. It had a cellar beneath. When Holmes hit the ground with his stick in front of the shop, he found that the cellar was at the backside of the shop where Spaulding spent most of his time. Holmes saw Spaulding’s trouser legs dirty and guessed he was digging a tunnel. He wanted to find out where the tunnel led to. So Holmes went to look at the road behind Saxe-Coburg Square that was the next street at the back of the shop and found the bank there.
Question 2.
What arrangements had Holmes made to catch the thieves in the bank? How did they catch the culprits?
Answer:
Holmes, Dr Watson, Mr. Jones and a policeman put off the lights and waited behind the crates and boxes in the strong room at the bank. At the same time policemen wereput to wait at the front door of the bank and near the pawn shop to catch the thieves. At 11.15 p.m. light came through the stone floor of the strong room in the bank. The stones moved and Spaulding arrived first with a gun, followed by Ross. Holmes came and hit Spauldings arm, made him drop his gun and caught him. Ross jumped back into the tunnel and tried to escape but the men waiting at the other end of the tunnel in the pawn shop caught him.
VIII. Read the passage and answer the questions.
1. Holmes and Watson first visit the district in which Wilson’s shop is located, where Holmes does some mysterious things: He asks directions from a clerk at the pawnshop; he taps the street out-side with his walking stick and remarks that the case is complicated by the fact that it is Saturday. Later, he asks Watson to meet him at Baker Street that evening at ten, and to come armed.
Question 1.
Where did Holmes and Watson go?
Answer:
Holmes and Watson went to the district where Wilson’s shop was located.
Question 2.
State the two mysterious things Holmes did at Wilson’s shop?
Answer:
Holmes asked directions from the pawn shop clerk and he tapped the street with his walking stick.
Question 3.
When and where did Holmes ask Dr. Watson to meet him?
Answer:
Holmes asked Dr. Watson to meet him at Baker Street on Saturday night at ten.
2. When Watson arrives, he finds two other men there: Peter Jones, an inspector from Scotland Yard, and a Mr. Merry Weather, a bank director. Holmes takes them to a branch of the City and Suburban Bank, a branch located in the same district as Wilson’s pawnshop. There they enter the vaults of the bank, where Merry Weather shows them a shipment of thirty thousand gold coins they have recently received from the Bank of France. Holmes says that they may have some time to wait, and they sit quietly in the dim vault.
Question 1.
What was the name of the inspector from Scotland Yard?
Answer:
Mr. Peter Jones.
Question 2.
Who was Mr. Merry Weather ?
Answer:
Mr. Merry Weather was a bank director.
Question 3.
Where did Holmes take Mr. Jones and Mr. Merry Weather ?
Answer:
Holmes took them to the vault of a branch of a bank located in the same district as Wilsons pawnshop.
Question 4.
Who all went to the bank?
Answer:
Holmes, Dr. Watson, Mr. Jones and Mr. Merry Weather went to the bank.
Question 5.
What did Mr. Merry Weather show them at the vault of the bank?
Answer:
At the vault of the bank Mr. Merry Weather showed them a shipment of thirty thousand gold coins that they had recently received from the Bank of France.
Question 6.
Why did Holmes and others wait at the dim vault?
Answer:
Holmes and the others were waiting at the dim vault of the bank to catch the thieves.
IX. Rearrange the Jumbled Sentences.
A.
1. Then Holmes knocks the door of the shop and meets Spaulding.
2. Holmes and Watson go to Wilson’s shop at Saxe-Coburg Square.
3. Holmes noticed the dirty trousers of Spaulding.
4. Dr. Watson visits the apartment of his friend Sherlock Holmes.
5. Holmes suspected crime and goes to look the road behind the shop.
6. Holmes hits the ground outside the shop with his walking stick.
7. Dr. Watson listens to the unusual story of the Jabez Wilson.
Answer:
4. Dr. Watson visits the apartment of his friend Sherlock Holmes.
7. Dr. Watson listens to the unusual story of the Jabez Wilson.
2. Holmes and Watson go to Wilson’s shop at Saxe-Coburg Square.
6. Holmes hits the ground outside the shop with his walking stick.
1. Then Holmes knocks the door of the shop and meets Spaulding.
3. Holmes noticed the dirty trousers of Spaulding.
5. Holmes suspected crime and goes to look the road behind the shop.
B.
1. Three men waiting at the other end of the tunnel caught Ross.
2. Suddenly through the stone floor Spaulding comes out followed by Ross.
3.”So are you John Clay! Your Red-Headed League was clever” said Holmes.
4. Watson looks at his watch it was 11.15 p.m.
5. Holmes hits Spaulding’s arms and Ross quickly gets back into the tunnel.
6. Holmes, Watson, Jones and Policeman wait in the strong room at the bank.
7. Spaulding says, “you think of everything, Mr. Holmes. You’re very clever”.
Answer:
6. Holmes, Watson, Jones and Policeman wait in the strong room at the bank.
4. Watson looks at his watch it was 11.15 p.m.
2. Suddenly through the stone floor Spaulding comes out followed by Ross.
5. Holmes hits Spaulding’s arms and Ross quickly gets back into the tunnel.
1. Three men waiting at the other end of the tunnel caught Ross.
7. Spaulding says, “you think of everything, Mr. Holmes. You’re very clever”.
3. “So are you John Clay! Your Red-Headed League was clever” said Holmes
The Red – Headed League Summary
Mr. Wilson, a red-haired pawn-shop owner, met the famous detective Mr. Sherlock Holmes to find a solution for the practical joke someone had been playing on him.
Mr. Wilson joined the Red-Headed League headed by Mr. Duncan Ross for quite a high salary of four pounds a week, on the recommendation of his assistant Vincent Spaulding who worked with him for half the wages. Wilson’s work was to copy the Encyclopaedia Britannica daily from 10.00 a.m. to 2.00 a.m. After eight weeks he is shocked to find that the office has been dissolved.
Holmes and his friend Dr. Watson visit Mr. Wilsons shop at Saxe-Coburg Square. He walks in front of the shop and taps the ground with his walking stick. He knocks the shop door and Spaulding opens. The legs of his trousers are dirty. Holmes asked Spaulding the way to Strand, pretty well knowing it. Holmes asks Dr. Watson to meet him at ten o’clock.
Holmes, Dr.Watson and Mr. Jones and a policeman await for the thief at the bank. They hide themselves behind the boxes. At 11.15 p.m. Spaulding and Ross come from underground and are caught. Spaulding is recognized to be the notorious thief John Clay.
Later Holmes explains to Dr. Watson that the Red-Headed League was just created to keep Wilson away from his shop. When he went for work daily, they had time to make the tunnel Holmes doubted Spaulding as he worked for half wages and was in the cellar most of the time. When Holmes hit the ground with his walking stick and saw Spaulding’s trousers dirty, he understood that he is making a tunnel from the pawn-shop to the Bank at the back of the shop, in the next street. As the Red-Headed League was dissolved and it was Sunday, Holmes was sure the thieves would come and he caught them red handed. A huge bank robbery was cleverly stopped.
 Answer:
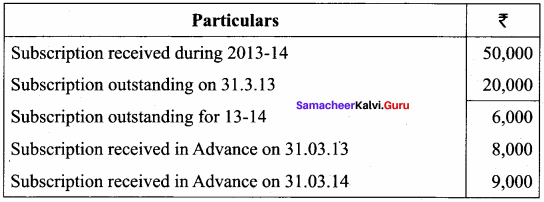
Answer:








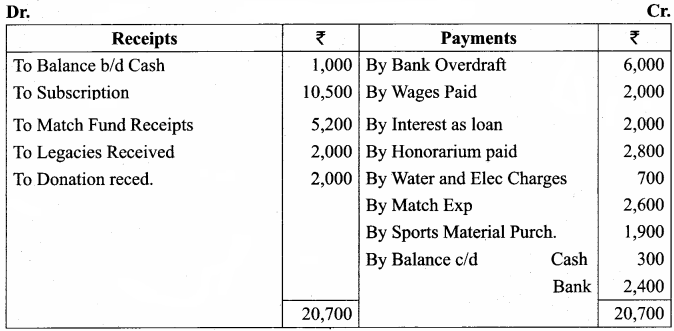
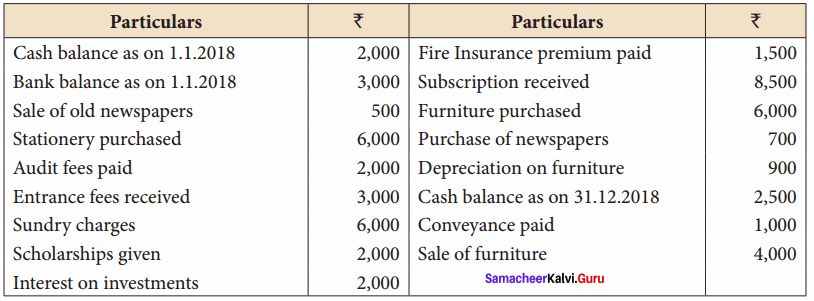
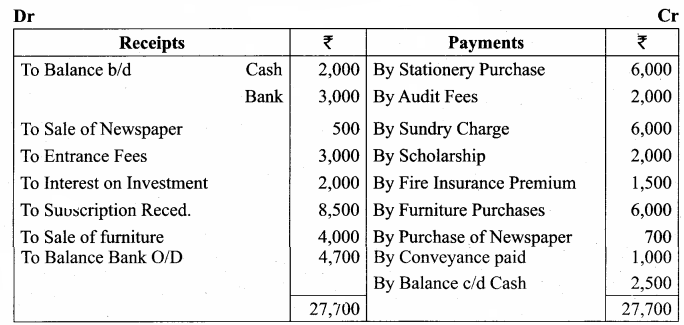
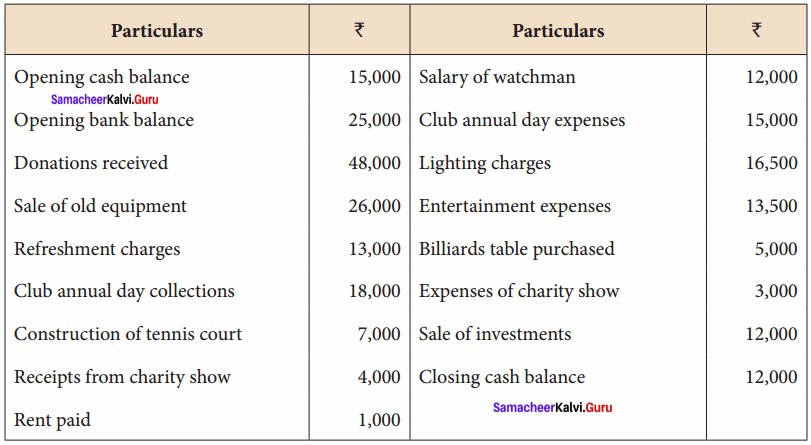
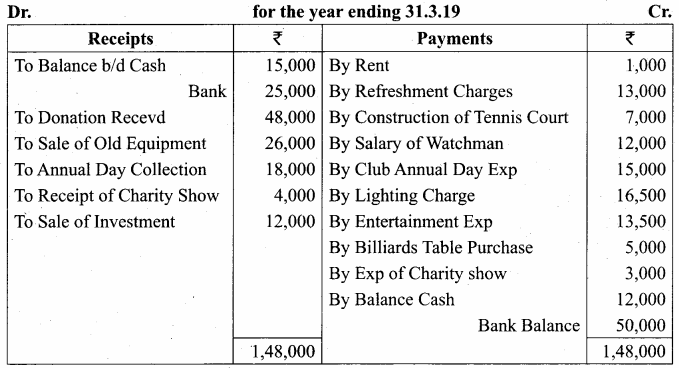
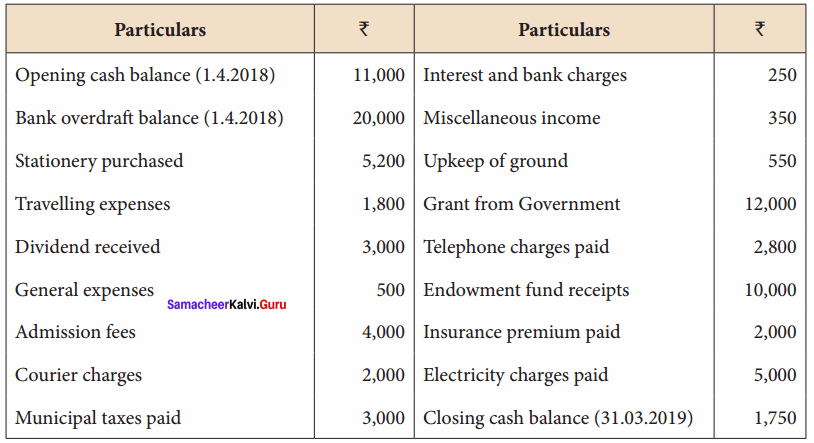
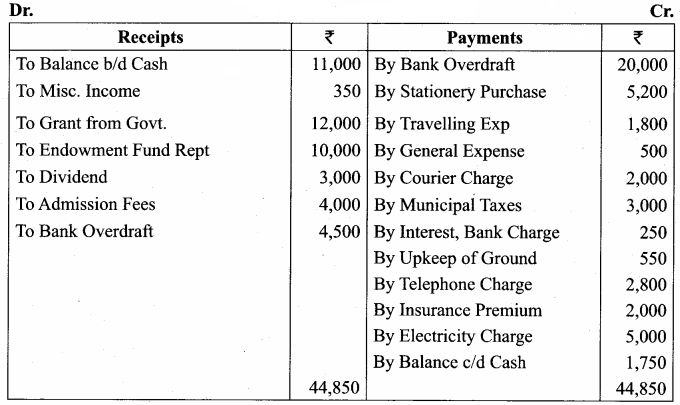
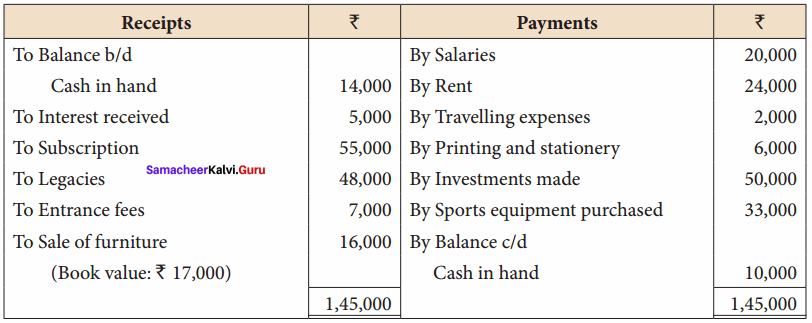
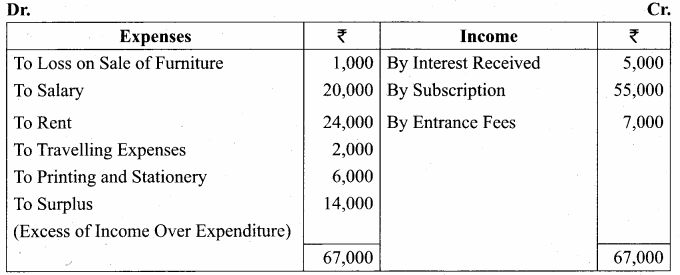
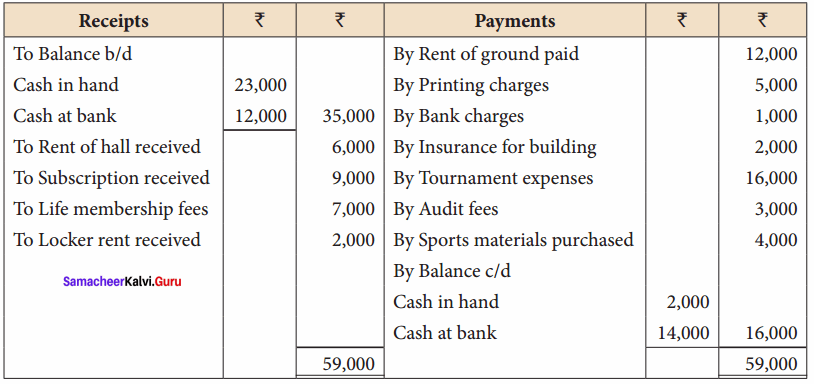
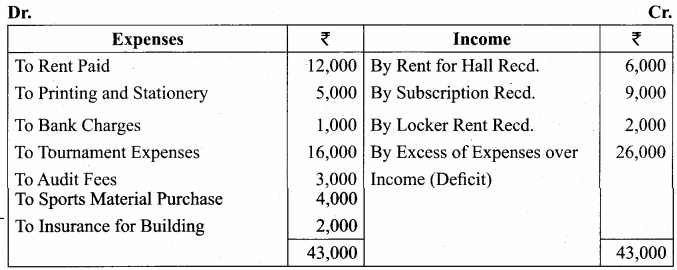
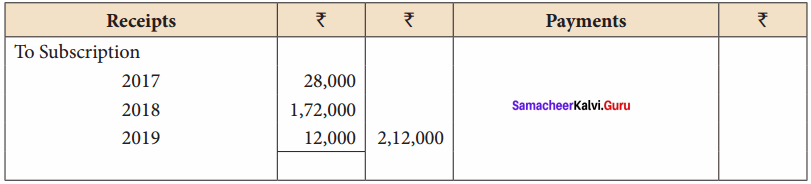

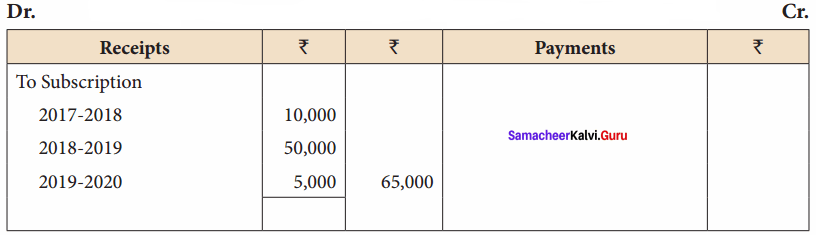
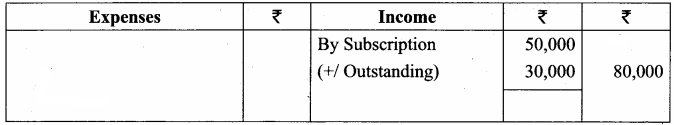
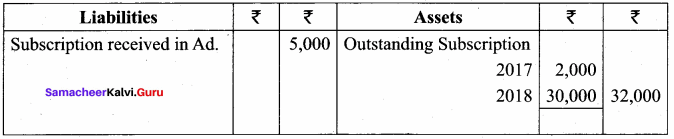
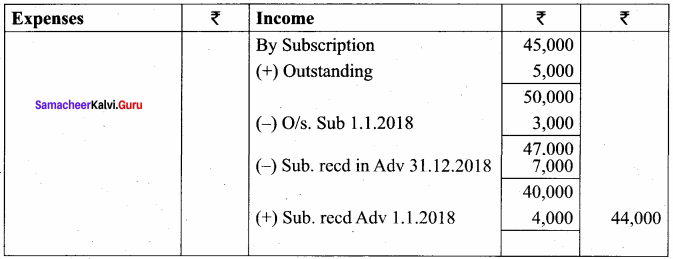
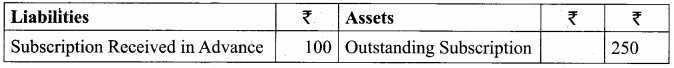
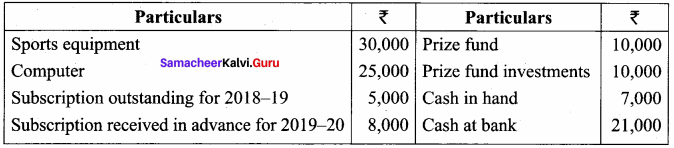
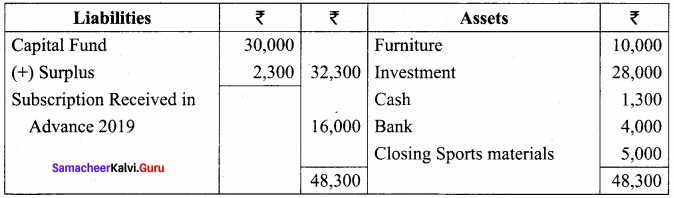
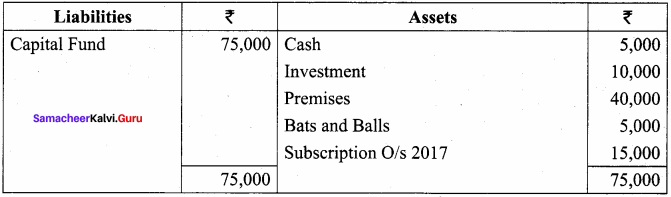
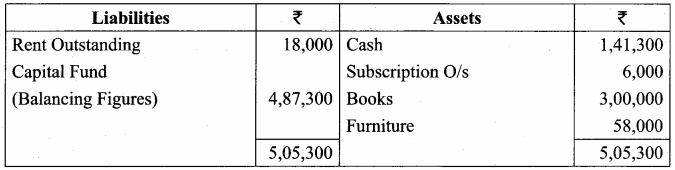
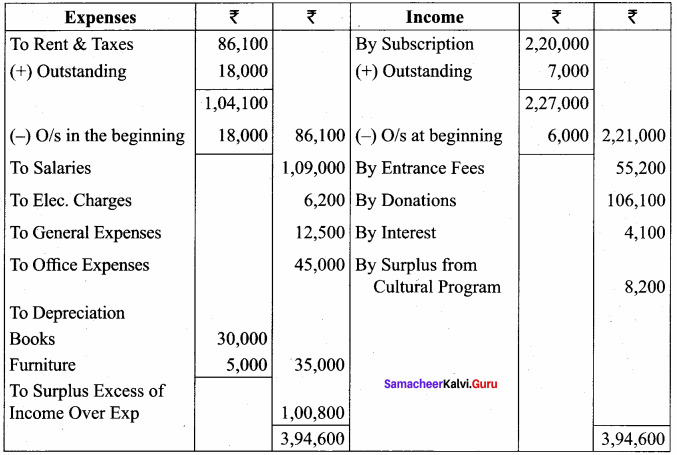
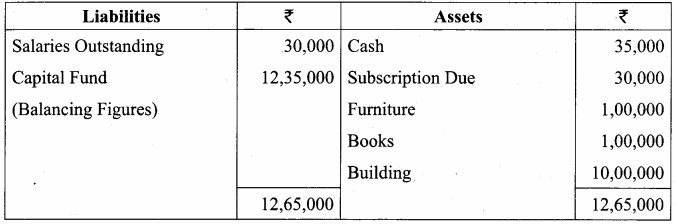
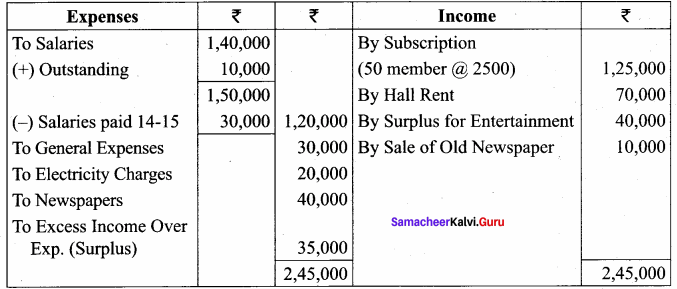
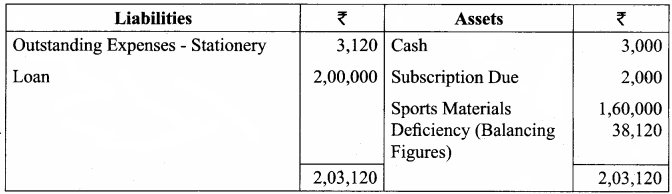
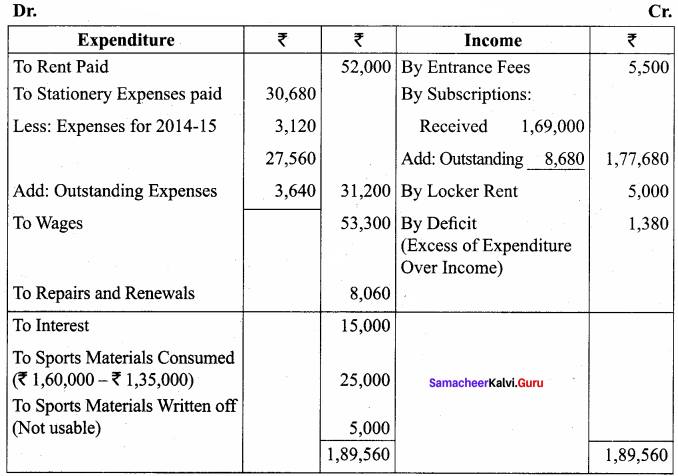
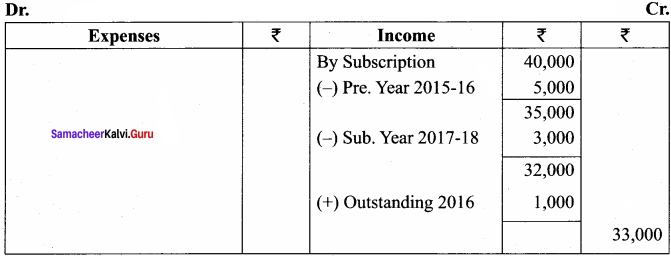 Balance Sheet as on 31.03.19
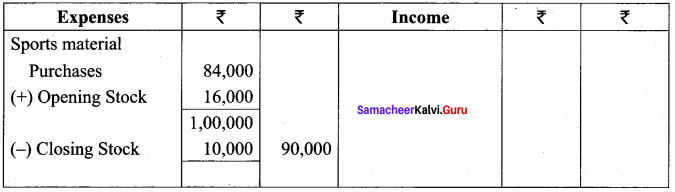
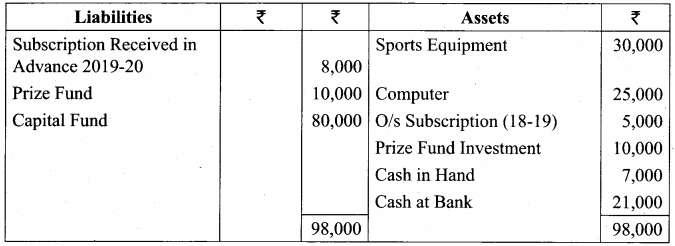
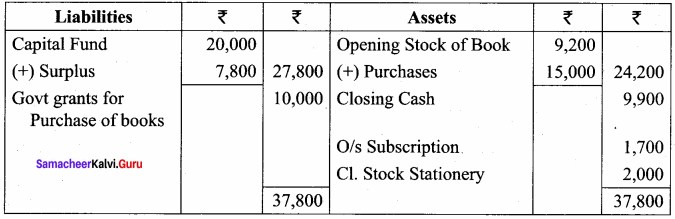
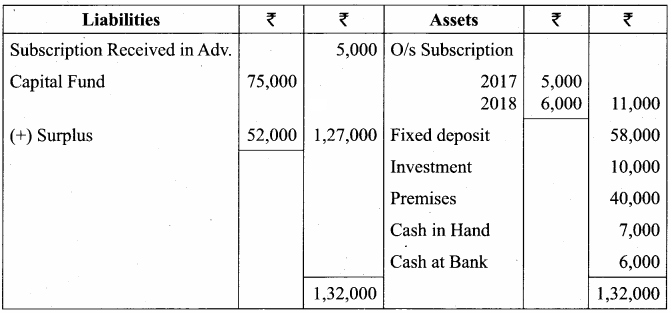
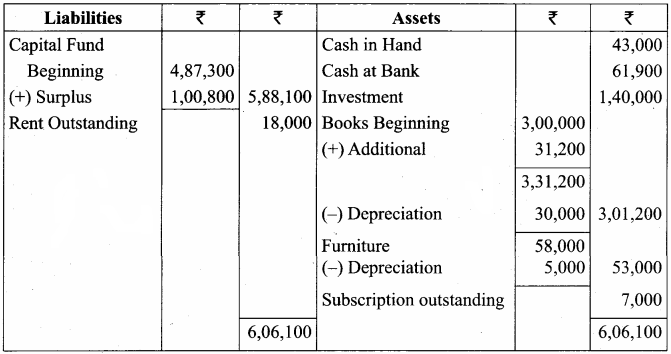
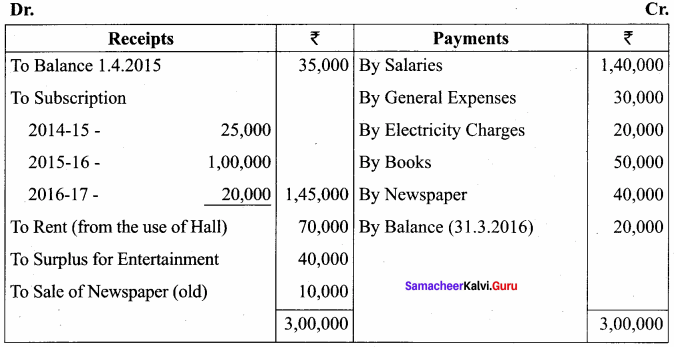
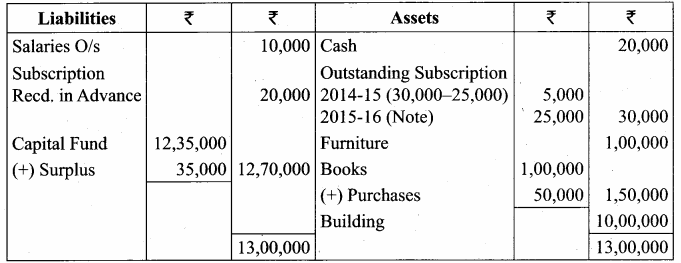
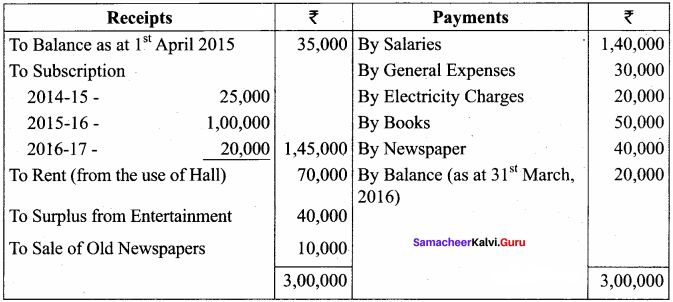
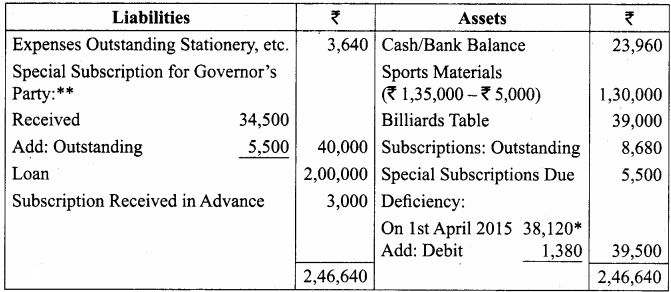
Balance Sheet as on 31.03.19