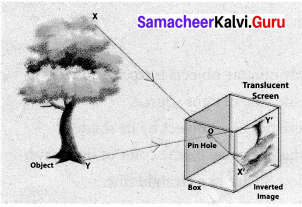
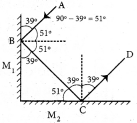
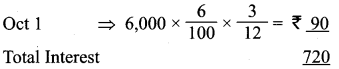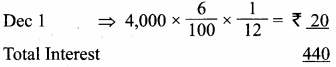Students can Download Science Chapter 2 Force and Motion Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Solutions Term 1 Chapter 2 Force and Motion
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Force and Motion Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the appropriate answer :
Force And Motion Class 7 Question 1.
A particle is moving in a circular path of radius r. The displacement after half a circle would be
(a) Zero
(b) R
(c) 2r
(d) r/2
Answer:
(c) 2r
Force And Motion Class 7 Book Back Questions And Answers Question 2.
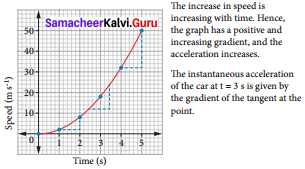
From the given v-t graph it can be inferred that the object is
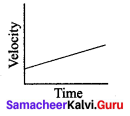
(a) in uniform motion Time
(b) at rest
(c) in non uniform motion
(d) moving with uniform acceleration
Answer:
(d) moving with uniform acceleration
Force And Motion Class 7 Questions And Answers Question 3.
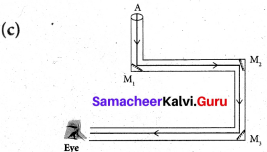
Which of the following figures represent uniform motion of a moving object correctly?
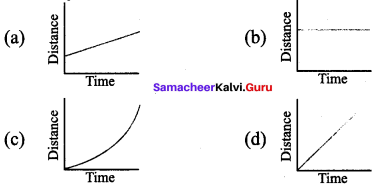
Answer:

Force And Motion 7th Standard Question 4.
Suppose a boy is enjoying a ride on a merry go round which is moving with a constant speed of 10 m/s. It implies that the boy is.
(a) at rest
(b) moving with no acceleration
(c) in accelerated motion
(d) moving with uniform velocity
Answer:
(c) in accelerated motion
7th Standard Science Force And Motion Question Answer Question 5.
What is one way you might increase the stability of an object?
(a) lower the centre of gravity
(b) raise the centre of gravity
(c) increase the height of the object
(d) shorten the base of the object
Answer:
(a) lower the centre of gravity
II. Fill in the blanks :
- The shortest distance between the two places is _______
- The rate of change of velocity is _______
- If the velocity of an object increases with respect to time, then the object is said to be in _______ acceleration.
- The slope of the speed-time graph gives _______
- In _______ equilibrium its centre of gravity remains at the same height when it is displacement
Answer:
- displacement
- acceleration
- positive
- velocity
- neutral
III. Match the following :
| 1. | Displacement | (a) | Knot |
| 2. | Light travels through vacuum | (b) | Geometric centre |
| 3. | Speed of ship | (c) | Metre |
| 4. | Centre of gravity of the geometrical shaped object | (d) | Larger base area |
| 5. | Stability | (e) | Uniform velocity |
Answer:
- c
- e
- a
- d
- b
IV. Analogy :
7th Science Force And Motion Question 1.
velocity : metre/ second :: acceleration : _______
Answer:
metre/second2
7th Standard Science Force And Motion Question 2.
length of scale : metre : : speed of aeroplane : _______
Answer:
knot
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Science Question 3.
displacement / time : velocity : : speed / time : _______
Answer:
acceleration
V. Give very short answer :
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Books Answers Question 1.
All objects having uniform speed need not have uniform velocity. Describe with the help of examples.
Answer:
An object moving in uniform circular motion is moving around the perimeter of the circle with a constant speed. While the speed of object is constant, its velocity is changing, Ex: Merry-go-round, roller coaster, planets orbiting the sun.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Books Science Question 2.
“She moves at a constant speed in a constant direction”. Rephrase the same sentence in fewer words using concepts related to motion.
Answer:
She moves in a straight line with constant velocity.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Book Question 3.
Correct your friend who says “The acceleration gives the idea of how fast the position changes”.
Answer:
There are two possible answers:
Velocity gives an idea of how fast the position changes, or Acceleration gives an idea of how fast the velocity changes.
VI. Give Short Answer :
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Question 1.
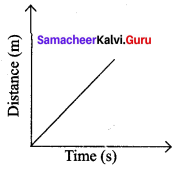
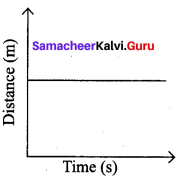
Show the shape of the distance – time graph for the motion in the following cases.
a. A bus moving with a constant speed
b. A car parked on a road side.
Answer:
(a) A bus moving with constant speed.
(b) A car parked on road side
Science Samacheer Kalvi 7th Books Question 2.
Distinguish between speed and velocity.
Answer:

Samacheer Kalvi 7th Standard Science Question 3.
What do you mean by constant acceleration?
Answer:
A body is said to have constant acceleration, if it travels is a straight line and its velocity increases or decreases by equal magnitude in equal intervals of time.
Ex: the motion of a freely falling body.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Book Answers Question 4.
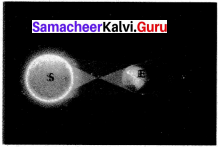
What is centre of gravity ?
Answer:
The centre of gravity of an object is the point through which the entire weight of the object appears to act.
VII. Answer in detail.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Book Back Answers Question 1.
Explain the types of stability with suitable examples.
Answer:
Stability is a measure of the body’s ability to maintain its original position.
The three types of stability are
- Stable equilibrium
- Unstable equilibrium
- Neutral equilibrium
Stable Equilibrium:
The frustum can be tilted through quite a big angle without toppling.
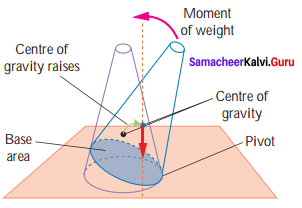
Its centre of gravity is raised when it is displaced. The vertical line through its centre of gravity still falls within its base. So it can return to its originalposition.
Unstable Equilibrium:
The frustum will topple with the slightest tilting. Its centre of gravity is lowered when it is displaced.
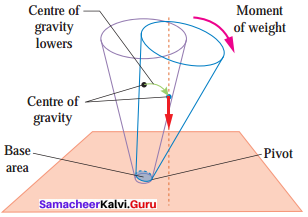
The vertical line through its centre of gravity falls outside its base.
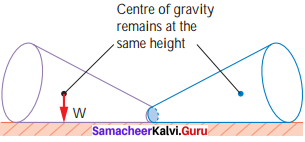
Neutral Equilibrium:
- It causes frustum to topple.
- The frustum will roll about but does not topple.
- Its centre of gravity remains at the same height when it is displaced.
- The body will stay in any position to which it has been displaced.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Standard Science Book Question 2.
Write about the experiment to find the centre of gravity of the irregularly shaped plate.
Answer:
- Make three holes in the lamina.
- Suspend the lamina from the optical pin through one of the holes
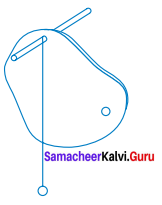
- Suspend the plumb line from the pin and mark the position of the plumb line on the lamina’
- Draw lines on the lamina representing the positions of the plumb line.
- Repeat the above steps for the holes.
- Label the intersection of the three lines as X, the position of the center of gravity of the lamina.
VIII. Numerical problems:
Samacheer Kalvi Science 7th Standard Question 1.
Geetha takes 15 minutes from her house to reach her school on a bicycle. If the bicycle lias a speed of 2 m/s, calculate the distance between her house and the school.
Answer:
Given : time taken = 15 minutes [1 min = 60 sec]
= 15 x 60 = 900 sec
Speed – 2 m/s
Distance = ?
Formula : Distance = Speed x time = 2 x 900
Distance between her house and the school = 1,800 m
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Books Question 2.
A car started from rest and travelling with velocity of 20 m /s in 10 s. What is its acceleration?
Answer:
Given :
Initial velocity of the car (u) = 0 m/s
Final velocity of the car (v) = 20 m/s
time taken = 10s
Acceleration = ?
Formula: Acceleration = \(\frac { 20 – 0 }{ 10 }\) = \(\frac { 20 }{ 10 }\)
Acceleration of the car = 2 m/s2
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Solution Question 3.
A bus can accelerate with an acceleration 1 m/s2. Find the minimum time for the bus to reach the speed of 100 km/s from 50 km/s.
Given :
Acceleration of the bus (a) = 1 m/s2
Initial velocity (u) = 50 km/s = 50 x 103 m/s
Final velocity (v) = 100 km/s = 100 x 103 m/s
time (t) = ?
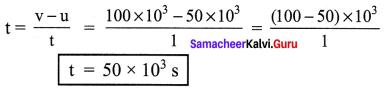
IX. Fill in the boxes:
| S.No. | First Move | Second Move | Distance (m) | Displacement |
| 1. | Move 4 meters east | Move 2 meters west | 6 | 2 m east |
| 2. | Move 4 meters north | Move 2 meters south | ||
| 3. | Move 2 meters east | Move 4 meters west | ||
| 4. | Move 5 meters east | Move 5 meters west | ||
| 5.. | Move 5 meters south | Move 2 meters north | ||
| 6. | Move 10 meters west | Move 3 meters east |
Answer:
| S.No. | First Move | Second Move | Distance (m) | Displacement |
| 1. | Move 4 meters east | Move 2 meters west | 6 m | 2 m east |
| 2. | Move 4 meters north | Move 2 meters south | 6 m | 2 m north |
| 3. | Move 2 meters east | Move 4 meters west | 6 m | 2 m west |
| 4. | Move 5 meters east | Move 5 meters west | 10 m | 0 (same place) |
| 5.. | Move 5 meters south | Move 2 meters north | 7 m | 3 m south |
| 6. | Move 10 meters west | Move 3 meters east | 13 m | 7 m west |
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Force and Motion Intext Activities
Activity
7th Samacheer Kalvi Science Question 1.
As shown in the above picture, Kavitha can reach her school in two ways. Can you tell, by choosing which path she could reach the school early.
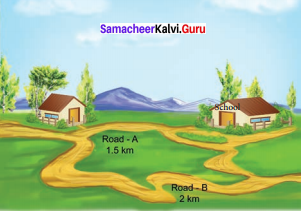
Road A
Road B
Answer:
By choosing road A kavitha could reach the school early as the distance is less compared to road B.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Answers Question 2.
Look at the nearby picture
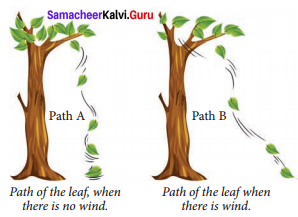
In which path the leaf will reach the ground first?
Answer:
The leaf will reach the ground first by path – A, as it reaches the ground in straight line.
Question 3.
Uma and Priya are friends studying in the same school. After school hours, they go to the nearby playground, play games and return back home. One day Uma told that she would reach the playground after visiting her grandmother’s house. The path in which they took reached the playground is shown here.
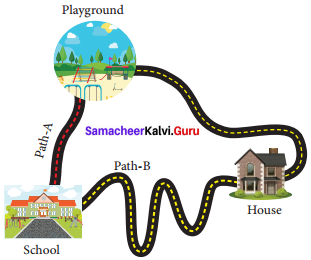
Take a twine and measure the length of the two paths (A & B). Which is the longest path among the two?
Answer:
Path A is the longest among the two. as it is not a straight line.
Question 4.
The path in which a rabbit ran is shown in figure. Find the distance and displacement of it in the two figures. Let us consider that each square is in an unit of one square meter. The rabbit starts from point A and reaches the point B.
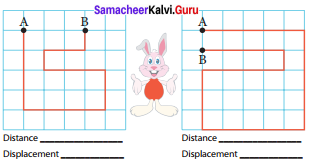
When will the distance and displacement be equal. Explain. But the starting and finishing points should be different. _______
Answer:
Distance : 17
Distance: 24
Displacement: 3
Displacement: 1
When the rabbit moves in a straight line from A to B, the distance and displacement will be equal.
Question 5.
Here we can consider the starting point as A and while the object moves from A to B the displacement is considered to be positive and from B to A it is negative.
Answer the following questions:
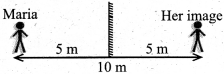
Subha goes to the nearby playground from her home.
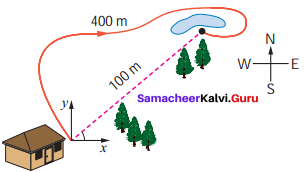
Question 1.
What is the distance she travelled?
Answer:
400 m
Question 2.
What is her displacement?
Answer:
100 m
Question 3.
The distance travelled by an object is 15 km and its displacement is 15 km. What do you infer from this?
Answer:
The object moves in a straight line in one direction without turning back.
Question 4.
The distance of a person is 30 km and his displacement is 0 km. What do you infer from this?
Answer:
The distance of a person = 30 km Displacement = 0 km.
Question 5.
The person returns to the same position where he has started.
Answer:
(i.e.) The initial and the final position is same.
Question 6.
Answer the following questions:
(i) Calculate the velocity of a car travelling with a uniform velocity covering 100 m distance in 4 seconds.
Answer:
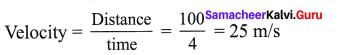
(ii) Usain Bolt covers 100 m distance in 9.58 seconds. Calculate his speed. Who will be the winner if Usain Bolt comepetes with a Cheetah running at a speed of 30 m/s

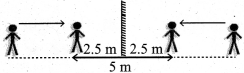
(iii) You are walking along east covering a distance of 4 m, then 2 m towards south, then 4 m towards west and at last 2 m towards north. You cover the total distance in 21 seconds, what is your average speed and average velocity?
Total distance covered = 12 m
Total time taken =21 seconds
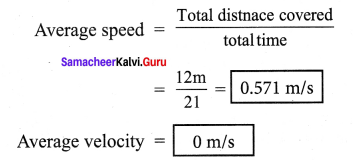
\(\frac { 12m }{ 21 }\) = 0.571 m/s
Average velocity = 0 m/s
Average velocity is zero because the starting point and the finishing point is same
∴Displacement is zero so, average velocity is also

Question 7.
(a) Change in speed
(b) Change in direction
(c) Change in both speed and direction
| The distance travelled by train | Initial velocity (u) m/s | Final velocity (v) m/s | Change in velocity (v – u) m/s | Time taken (t) s | Acceleration = change in velocity / time a = (v – u) /1 m/s2 |
| A-B | 0 | 6 | 6 | 10 | 0.6 |
| B-C | |||||
| C-D | |||||
| D-E | |||||
| E-F |
The velocity at different times of a train departing direction is given in the figure. Analyse this and complete the table .
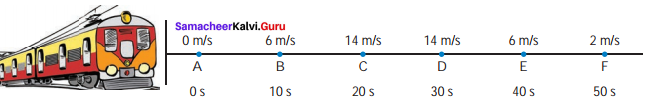
Answer:
| The distance travelled by train | Initial velocity (u) m/s | Final velocity (v) m/s | Change in velocity (v – u) m/s | Time taken (t) s | Acceleration = change in velocity / time a = (v – u) /t m/s2 |
| A-B | 0 | 6 | 6 | 10 | 0.6 |
| B-C | 6 | 14 | 14-6 = 8 | 10 | 0.8 |
| C-D | 14 | 14 | 14-14 = 0 | 10 | 0 |
| D-E | 14 | 6 | 6- 14 =-8 | 10 | -0.8 |
| E-F | 6 | 2 | 2 – 6 = -4 | 10 | -0.4 |
Analysis:
When the train covers the distance A to B and B to C, it is accelerated motion.
When it covers the distance C-D, there is no acceleration (i.e) uniform velocity.
When it covers the distance D to E and E to F it has negative acceleration or deceleration or retardation, (i.e.) Its velocity decreases with respect to time.
Question 8.
My name is cheetah. I can run at a great speed. Do you know what my speed is? 25 m/s to 30 m/s. My speed changes from 0 to 20 m/s in 2 second. See how good my acceleration is !
From the above information, can you calculate the acceleration of the cheetah?
Answer:
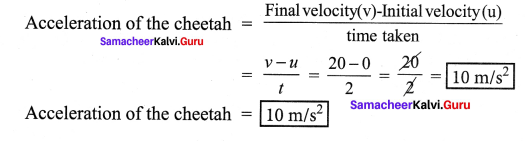
Question 9.
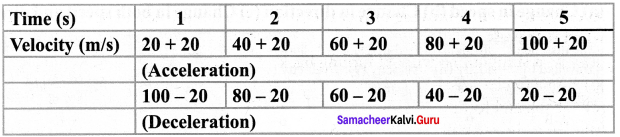
When the velocity of the object is increasing by 20 m/s the acceleration is 20 m/s2
When the velocity of the object is decreasing by 20 m/s the deceleration is 20 m/s2.
Answer:
When the velocity of the object is decreasing by 20m/s the deceleration is 20 m/s2.

The velocity of the object is decreasing by 20m/s in one second.
Question 10.
Imagine and write a story on your own for the given graph?
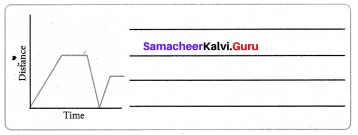
Answer:
Raghul and his father starting from home to the school by car. At the school gate, he stopped the car to drop Raghul. After 2 minutes he went back to home to pick up his mother. Then they both started to go to their work. On the way, they are waiting for the signal.
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Force and Motion Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
Distance travelled by a body in a given time
(a) is always positive
(b) can be zero or positive
(c) is always negative
(d) either (a) or (c)
Answer:
(b) can be zero or positive
Question 2.
Which of the following is correct
(a) magnitude of displacement may be greater than distance.
(b) Distance is always greater than or equal to the magnitude of displacement.
(c) Distance is always greater than the magnitude of displacement.
(d) Both are scalar quantities.
Answer:
(b) Distance is always greater than or equal to the magnitude of displacement
Question 3.
Average speed of a moving object is equal to the magnitude of its average velocity when it travels.
(a) in a straight line without turning back
(b) in a circle
(c) back and forth
(d) in a zig-zag path
Answer:
(a) in a straight line without turning back
Question 4.
A car is moving along a straight road with uniform velocity which is the correct representation
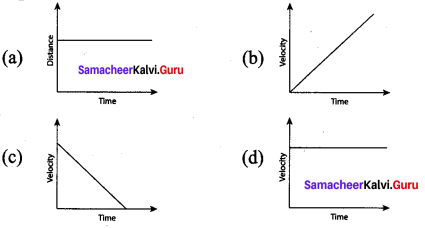
Answer:
Question 5.
The slope of a velocity-time graph gives
(a) velocity
(b) distance
(c) displacement
(d) acceleration
Answer:
(d) acceleration
Question 6.
Velocity-time graph of an object is given below the object has
(a) uniform velocity
(b) uniform retardation
(c) uniform speed
(d) variable retardation
Answer:
(b) uniform retardation
Question 7.
Which one of the following graphs is showing an object is stationary?
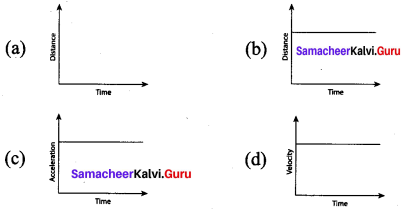
Answer:
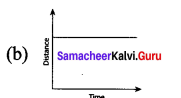
Question 8.
If the velocity of a body does not a changes , then its acceleration is ________
(a) Infinity
(b) unity
(c) Zero
(d) between zero and unity
Answer:
(c) Zero
II. Fill in the Blanks.
- The SI unit of displacement is _______
- The SI unit of speed is _______
- _______ is the length of actual path covered by a body.
- _______ is the distance trtavelled by a body per unit time
- Distance is a _______quantity.
- The displacement is zero when the initial and final positions are _______
- Speed is always positive or zero but never be _______
- When the velocity of a body increases with time, its acceleration is _______
- The acceleration of a body moving with uniform velocity is _______
- A car increases its speed from 20 km/h to 50km/h in 10 seconds. Its acceleration is _______
Answer:
- metre (m)
- m/s
- Distance
- speed
- scalar
- same
- negative
- positive
- zero
- 0.83 m/s2
III. Match the following :
| Column I | Column II | ||
| a. | Uniform motion. | (i) | Body having uniform acceleration |
| b. | Non-uniform motion. | (ii) | Body at rest. |
| c. | The velocity-time graph is a circle. | (iii) | Unequal distance covered in equal interval of time. |
| d. | Straight line parallel to time axis in position-time graph. | (iv) | Equal distances covered in equal intervals of time. |
| e. | Straight line inclined to 45° with time axis is velocity-time graph. | (v) | Not possible. |
Answer:
- iv
- iii
- v
- i
- ii
Very short Answers:
Question 1.
Give one example where the displacement is zero but the distance travelled is not zero.
Answer:
When an object travels is a circular path (ie. the initial and positions are same).
Question 2.
Is displacement a scalar quantity?
Answer:
No, displacement is a vector quantity as it depends on direction.
Question 3.
Give some examples for vector quantity.
Answer:
Displacement, velocity, force.
Question 4.
Give some examples for scalar quantity.
Answer:
Mass, distance, speed, temperature.
Question 5.
Give one example for uniform acceleration.
Answer:
The motion of a freely falling object.
Question 6.
Give one example for non-uniform acceleration.
Answer:
The motion of a car on a crowded road.
Question 7.
Give an example for retardation or declaration.
Answer:
When a person applies brake on a moving car, its velocity decreases with time.
Question 8.
What are three types of stability of an object?
Answer:
- Stable equilibrium
- Unstable equilibrium
- Neutral equilibrium
Question 9.
Mention any two conditions for stability of a body?
Answer:
- Increase the area of its base.
- Lower its centre of gravity.
V. Give Short Answer.
Question 1.
A body moves is a circle of radius ‘2R’ what is the distance covered and displacement of the body after 2 complete rounds?
Answer:
Distance covered after 2 complete rounds
= 2 x circumference of a circle
Distance =2 × 2 π(2R) = 4π(2R)
After 2 complete rounds, the body comes back to its initial position,
so, displacement = 0
Question 2.
What are the uses of graphical study of motion?
Answer:
- By simply looking at the graph, one can tell whether motion is uniform or not.
- It is useful for comparing the motions of two moving bodies.
Question 3.
Draw distance-time graphs for the following
- a stationary body
- a body moving with variable velocity
Answer:
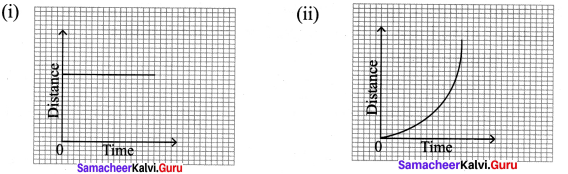
Question 4.
Draw centre of gravity of the following regular shaped objects.

Answer:
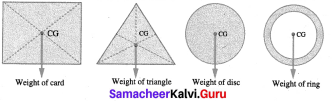
Question 5.
Mention the real life applications of centre of gravity.
Answer:
- Luggage compartment of a tour bus is located at the bottom and not on the roof.
- Racing cars are built low and broad for stability.
- Table lamps and fans are designed with large heavy bases to make them stable
Question 6.
Explain the concept which is used in the continuous movement of Thanjavur doll?
Answer:
The centre of gravity and the total weight of the doll is concentrated at its bottom most point, generating a dance-like continuous movement with slow oscillations.
Question 7.
Write note on the following :
- Nautical mile
- knot.
Answer:
- Nautical mile is the unit for measuring the distance in the field of aviation and sea transportation. One nautical mile is 1.852 km.
- The unit for measuring the speed of aeroplanes and ships is knot. One knot is the speed taken to travel one nautical mile in hour.
Question 8.
Saranya jogs from one end A to the other end B of a straight road of length 320m in 2min 40 seconds. Then she turns back and jogs 100m to point C in 1 min. what is her average velocity in jogging.
Answer:
Total displacement = 320m
From A to C displacement = 320 -100 = 220m
Time taken = 3 min 40 sec
= 180+40=220

Question 9.
A train starting from a railway station and moving with uniform acceleration attains a speed of 40 km/h in 10 minutes. Find its acceleration?
Answer:
Initial velocity (u) = Okm/h
Final velocity (v) = 40 km/h
Time (t) = 10 min = \(\frac { 10 }{ 60h }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 6h }\)
Acceleration (a) = \(\frac { v – u }{ t }\)
\(\frac { 40 – 0 }{ 1 }\) = 40 × 6
= 240 km/h
Question 10.
Define speed Mention its formula and unit.
Answer:
Speed is the rate of change of distance .
Formula : Speed = distance /time
Unit is meter/second (m/s)
Question 11.
Define velocity Mention its formula and unit.
Answer:
Velocity is the rate of change in displacement.
Formula : Velocity (v) = displacement / time
SI unit of velocity is meter / second (m/s).
Question 12.
What is uniform velocity? Give one example.
Answer:
A body has uniform velocity, if it covers equal displacement in the same direction in equal intervals of time. Eg. light travels through vacuum.
Question 13.
What is non-uniform velocity? Give example.
Answer:
If either speed or direction changes, then the velocity is non uniform. Eg. a train starting and moving out of the station.
Question 14.
Define acceleration. Mention its formula and unit.
Answer:
Acceleration is the rate of change in velocity.
Formula : Acceleration = change in velocity / time SI unit of acceleration is m/s2
Question 15.
Define the following:
- positive acceleration
- negative acceleration.
Answer:
(i) Positive acceleration:
If the velocity of an object increases with respect to time, then the object is said to be in positive acceleration or just acceleration.
(ii) Negative acceleration or deceleration or retardation:
If the velocity of an object decreases with respect to time, then the object is said to be in negative acceleration or deceleration or retardation.
VI. Long Answer
Question 1.
Write the differences between distance and displacement
Answer:
| Distance | Displacement | |
| 1. | The total length of a path taken by an object to reach one place from the other is called distance. | The shortest distance from the initial to the final position of an object. |
| 2. | Distance between two gives points may be same or different paths chosen. | Displacement between two given points is always same |
| 3. | It is a scalar quantity | It is a vector quantity |
| 4. | Distance covered is always positive or zero. | Displacement covered may be positive, negative or zero |
Question 2.
Draw velocity-time graph for the following data:
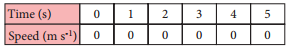
Answer:
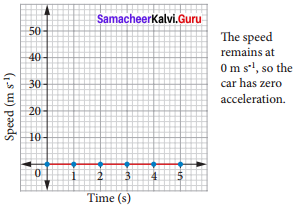
Question 3.
Bus travelling at uniform speed of m/s
![]()
Answer:
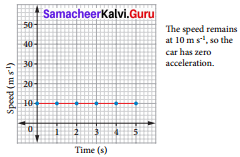
Question 4.
Bus travelling at uniform acceleration
![]()
Answer:
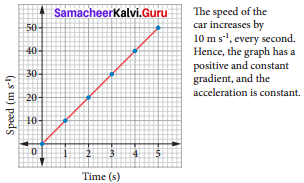
Question 5.
Bus travelling at uniform deceleration
![]()
Answer:
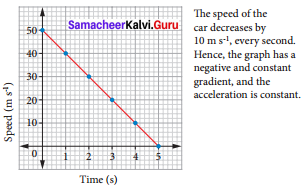
Question 6.
Bus travelling with increasing acceleration (non – uniform acceleration)
![]()
Answer: