Students can Download Maths Chapter 1 Number System Ex 1.1 Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Maths Solutions Term 1 Chapter 1 Number System Ex 1.1
7th Standard Maths Number System Exercise 1.1 Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) (-30) + ____ = 60
(ii) (-5) + ___ = -100
(iii) (-52) + (-52) = ____
(iv) ____ + (-22) = 0
(v) ____ + (-70) = 70
(vi) 20 + 80 + ___ = 0
(vii) 75 + (-25) = ____
(viii) 171 + ___ = 0
(ix) [(-3) + (-12)] + (-77) = _____ + [(12) + (-77)]
(x) (-42) + [____ + (-23)] = [____ + 15] + ____
Solution:
(i) 90
(ii) -95
(iii) -104
(iv) 22
(v) 140
(vi) -100
(vii) 50
(viii) -171
(ix) -3
(x) +15; -42; -23
7th Maths Guide Exercise 1.1 Question 2.
Say True or False.
(i) The additive inverse of (-32) is -32
(ii) (-90) + (-30) = 60
(iii) (-125) + 25 = -100
Solution:
(i) False
(ii) False
(iii) True
7th Maths Exercise 1.1 Samacheer Kalvi Question 3.
Add the following.
(i) 8 and-12 using number line.
Solution:
Starting at zero on the number line facing positive direction and move 8 steps forward reaching 8.

Then we move 12 steps
backward to represent -12 –
and reach at -4.
∴ 8 + (-12) = -4
(ii) (-3) and (-5) using number line.
Solution:
Starting at zero on the number line facing positive direction and move 3 steps backward reaching-3.
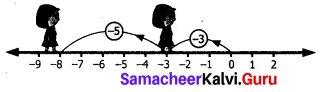
Then we move 5 steps backward to represent -5 and reach -8.
∴ (-3) + (-5) = -8
(iii) (-100) + (-10)
Solution:
(-100) + (-10) = -100 – 10 = -110
(iv) 20 + (-72)
Solution:
20 + (-72) = 20 – 72 = -52
(v) 82 + (-75)
Solution:
82 + (-75) = 82 – 75 = 7
(vi) -48 + (-15)
Solution:
-48 + (-15) = -48 – 15 = -63
(vii) -225 + (-63)
Solution:
-225 + (-63) = -225 – 63 = -288
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Maths Book Answers Question 4.
Thenmalar appeared for competitive exam which has negative scoring of 1 mark for each incorrect answers. In paper I she answered 25 question incorrectly and in paper II13 questions incorrectly. Find the total reduction of marks.
Solution:
For each incorrect question the score = -1
In paper I, score for 25 incorrect questions – 25 × (-1) = -25
In paper II, for 13 incorrect question the score = 13 × (-1) = -13
The total marks get reduced = (-25) + (-13) = -38
-38 marks will be reduced.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Maths Book Solutions Question 5.
In a quiz competition, Team A scored +30, -20, 0 and team B scored -20, 0,+30 in three successive rounds. Which team will win? Can we say that we can add integers in any order?
Solution:
Total score of team A = [(+30) + (-20)] + 0 = (+10) + 0 = 10
Total score of team B = [(-20) + 0] + (+30)
= -20 + 30 = +10
Score of team A = Score of team B.
Yes, we say that we can add integers in any order.
7th Standard Maths Exercise 1.1 Question 6.
Are (11 + 7) +10 and 11 + (7 + 10) equal? Mention the property.
Solution:
First we take (11 + 7) + 10 = 18 + 10 = 28
Now 11 + (7 + 10) = 11 + 17 = 28
In both the cases the sum is 28. ∴ (11 + 7) + 10 = 11 + (7 + 10)
This property is known as associative property of integers under addition.
7th Maths Exercise 1.1 Question 7.
Find 5 pairs of integers that added to 2.
Solution:
0 + 2 = 2
1 + 1 = 2
-1+3 = 2
-2 + 4 = 2
-3 + 5 =2 (and many more.)
Objective Type Questions
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Maths Question 8.
The temperature at 12 noon at a certain place was 18° above zero. If it decreases at the rate of 3° per hour at what time if would be 12° below zero?
(i) 12 mid night
(ii) 12 noon
(iii) 10 am
(iv) 10 pm
Solution:
(iv) 10 pm
: ’Temperature at 12 noon = 18° above zero = +18°
Rate of decrease per hour = -3°
Temperature 12° below zero = -12°
-12 is 30 units to the left of+18°
Time at which it reach -12° = \(\frac{30}{3}\) = 10 h
10 hrs after 12 noon = 10 pm
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Maths Question 9.
Identify the problem with negative numbers as its answer.
(i) -9 +(-5) + 6
(ii) 8 + (-12) – 6
(iii) -4 + 2 + 10
(iv) 10 + (-4) + 8
Solution:
(i) -9 +(-5) + 6
(i) -9 + (-5) + 6 = -14 + 6 = -8
(ii) 8 + (-12) + 6 = -4 + 6 = – 2
(iii) -4 + 2 + 10 = -2 + 10 = 8
(iv) 10 + (-4) + 8 = 6 + 8 = 14
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Maths Book Question 10.
(-10) + (+7) = ____
(i) +3
(ii) -3
(iii) -17
(iv) +17
Solution:
(ii) -3
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Standard Maths Question 11.
(-8) + 10 + (-2) = ____
(i) 2
(ii) 8
(iii) 0
(iv) 20
Solution:
(iii) 0
Maths 7th Samacheer Kalvi Question 12.
20 + (-9) + 9 = ____
(i) 20
(ii) 29
(iii) 11
(iv) 38
Solution:
(i) 20