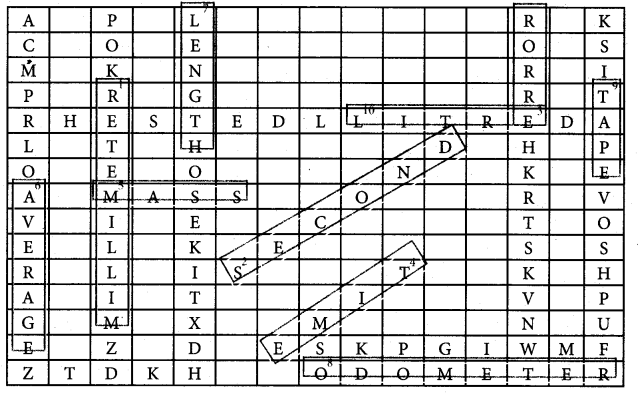
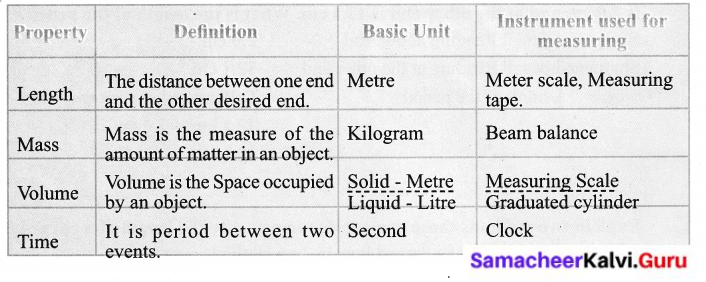
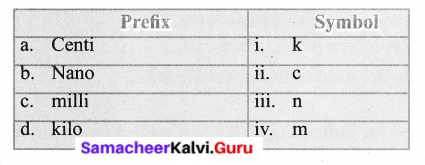
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Civics Solutions Term 3 Chapter 3 Road Safety
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Road Safety Textual Evaluation
I. Answer the following :
Question 1.
Prepare the slogans for road safety.
Answer:
Slogans on Road Safety
- Alert today – Alive tomorrow.
- Leave sooner, drive slower, live longer.
- Speed thrills but kills.
- Be alert! Accidents hurt.
- Drive carefully, to live joyfully.
- A little care makes accidents rare.
- Fast-drive could be your last drive.
- Driving faster can cause disaster
- Chance takers are accident makers.
![]()
Question 2.
Identify the following signs.
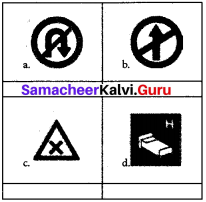
Answer:
a. No U Turn
b. No Entry
c. Cross Road
d. Hospital
Question 3.
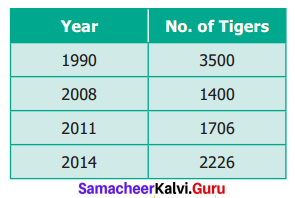
Discuss about the statistics of 2017 accidents data.
Answer:
- Nearly three persons died every ten minutes in road accidents across India last year.
- The Report, prepared by the Transport Research Wing of the Ministry of Road Transport and highways, discovered that a total of 4,64,910 road accident were reported by States and Union territories in the calender year of 2017, claiming 1,47,913 lives and causing injuries to 4,70,975 persons.
- The subject of road safety is an important one. Victims of hit and run cases would now be compensated for up to Rs one million in case of road accident fatalities.
- Among vehicle categories involved in road accidents, two-wheelers accounted for the highest share (33.9%) in total accidents and fatalities (29.8%) in 2017.
- However there has been a decline in the total number of road accidents as compared with the year 2016. In percentage terms the number of accidents in 2017 was lower by 3.3 percent and injuries 4.8 percent over that of the previous year.
Question 4.
Debate : Is Wearing helmet necessary?
Answer:
- It is important for motor cyclists to understand the risks of riding without a helmet.
- Riders who do not wear helmets are at risk of suffering traumatic brain injury if they are in an accident.
- Without protection, the head is vulnerable to a traumatic impact in an accident even when travelling at low speeds.
- Wearing helmet is absolutely necessary for riders and pillion riders.
Question 5.
Draw posters related to road safety.
Answer:

Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Road Safety Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Mandatory road signs are_________generally in shape.
(a) Circular
(b) Oval
(c) Square
(d) Hexagonal
Answer:
(a) Circular
![]()
Question 2.
The pedestrian crossing was instituted in Britain in_________
(a) 1930
(b) 1932
(e) 1934
(d) 1936
Answer:
(c) 1934
Question 3.
Children above_________ years of age should occupy the back seat.
(a) 8
(b) 12
(c) 10
(d) 14
Answer:
(b) 12
Question 4.
The Zebra crossing with black and white stripes was developed after
(a) Cold war
(b) Civil war
(c) First World war
(d) Second World war
Answer:
(d) Second World war
Question 5.
Red rings or circles give_________ instructions
(a) Positive
(b) Negative
(c) Caution
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Negative
II. Fill in the blanks:
- Cautionary road signs are generally in_________ shape.
- Informatory road signs are generally in_________ shape.
- We should wait until_________ a signal appears before proceeding.
- Amber means_________
- Traffic signs are there to_________traffic.
- Answer:
- Triangular
- Rectangular
- Caution
- green
- Regulate
III. Answer the following questions :
Question 1.
Explain the three types of traffic signs.
Answer:
- Mandatory road signs are the ones that give order regarding do’s and don’ts and are to be followed strictly. They are generally circular in shape.
- Cautionary road signs are the ones that was in the road rules regarding the road situation ahead. These signs are generally in triangular shape.
- Informatory road signs are the ones that give information regarding directions, destination etc. Informatory signs are generally rectangular in shape.
![]()
Question 2.
What do the three colours Red, Amber and Green signify?
Answer:
- Red means stop – wait behind the stop line.
- Amber means CAUTION.
- Green means Go-Proceed ahead ensuing that the way is clear.
Question 3.
Mention about the languages of the road.
Answer:
- Road signs, markings, traffic signals and other traffic devices are there to guide the road users and hence the languages of the road.
- Traffic signals are there to regulate traffic, warn about hazards and to guide the road user.
Question 4.
How should children use the pavements?
Answer:
Children should be taught to use the pavements. When walking on the road,
- Walk on any side of the road if there are food paths.
- On roads without food path walk on your extreme right side facing the oncoming traffic.
- Use Zebra crossing, foot over bridge and subways to cross the roads.
- Children below 8 years of age should cross the road with the help of elders.
![]()
Question 5.
What should not be done by children while crossing the road?
Answer:
- Do not cross the road hastily by running.
- Do not cross the road in front of or in between parked vehicles.
- Do not try to cross the road from blind comers, turnings where you are not visible to the vehicle drivers.
- Do not jump over the railings to cross the road.