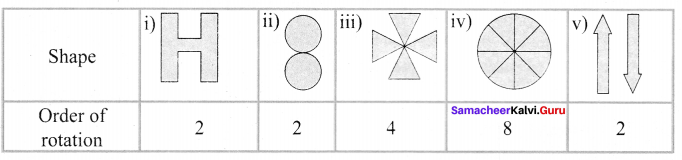
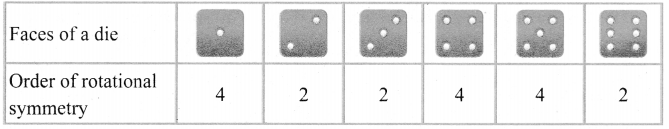
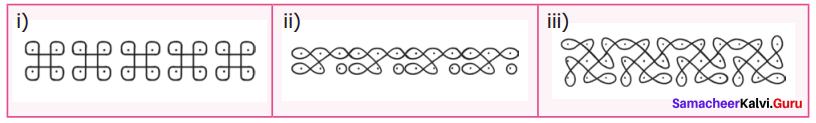
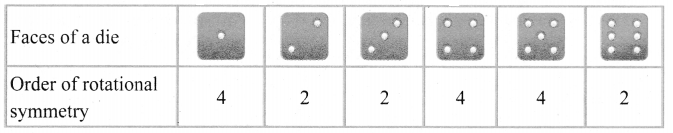
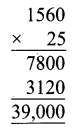You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Solutions Term 1 Chapter 3 Ratio and Proportion Ex 3.5
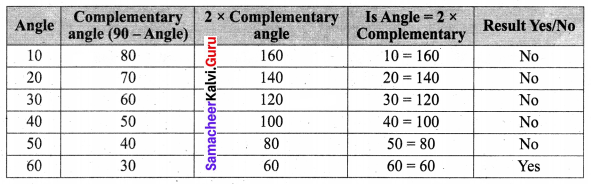
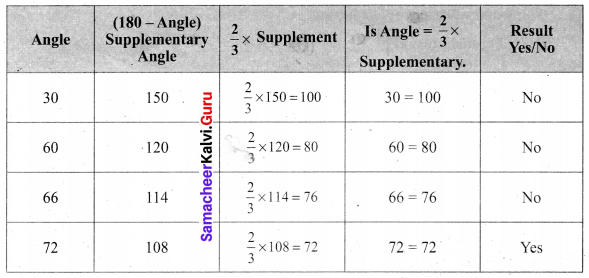
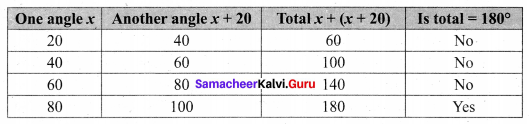
Miscellaneous Practice Problems
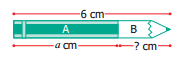
![]()
Question 1.
The maximum speed of some of the animals are given below:
the Elephant = 20 km/h, the Lion = 80 km/hr; the Cheetah = 100 km/h.
Find the following ratios of their speeds in simplified form and find which ratio is the least?
(i) the Elephant and the Lion
(ii) the Lion and the Cheetah
(iii) the Elephant and the Cheetah.
Solution:

∴ The ratio of Elephant to Cheetah is the least.
Question 2.
A particular high school has 1500 students, 50 teachers and 5 administrators. If the school grow s to 1800 students and the ratios are mentioned, then find the number of teachers and administrators.
Solution:
The ratio of Students : teachers : administrators = 1500 : 50 : 5.
The new ratio of Students : teachers : administrators = 1800 : new teachers : new administrators.
Given the ratios are maintained. i.e., they are proportional.
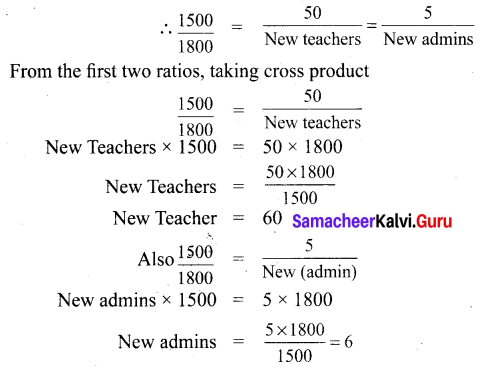
∴ For 1800 students 60 teachers and 6 administrators are needed.
![]()
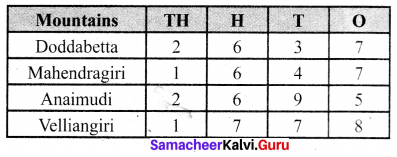
Question 3.
I have a box which has 3 green, 9 blue, 4 yellow, 8 orange coloured cubes in it.
(a) What is the ratio of orange to yellow cubes?
(b) What is the ratio of green to blue cubes?
(c) How many different ratios can be formed, when you compare each colour to any one of the other colours?
Solution:
Number of green cubes = 3
Number of blue cubes = 9
Number of yellow cubes = 4
Number of orange cubes = 8
(a) Ratio of orange to yellow cubes \(\frac{\text { Number of orange cubes }}{\text { Number of yellow cubes }}=\frac{8}{4}=\frac{2}{1}=2: 1\)
Ratio of orange to yellow cubes = 2 : 1
(b) \(\frac{\text { Number of green cubes }}{\text { Number of blue cubes }}=\frac{3}{9}=\frac{1}{3}\)
Ratio of green to blue cubes = 1 : 3
(c) The ratios can be Orange : Yellow, Orange: blue, Orange : green, Yellow : Orange, yellow : blue, yellow : green, blue : green, blue : orange, blue : yellow, green : orange, green : yellow, green : blue. Thus 12 ratios can be formed.
Question 4.
A gets double of what B gets and B gets double of what C gets. Find A : B and B : C and verify whether the result is in proportion or not.
Solution:
A : B = 2 : 1
B : C = 2 : 1
They are in proportion
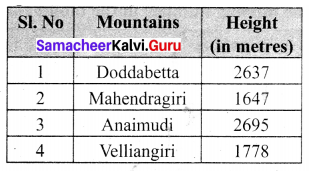
Question 5.
The ingredients required for the preparation of Ragi Kali, a healthy dish of Tamilnadu is given below.
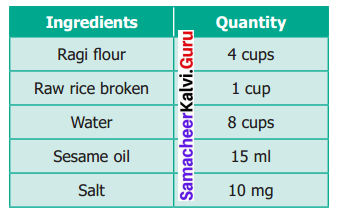
(a) If one cup of ragi flour is used then, what would be the amount of raw rice required?
(b) If 16 cups of water are used, then how much of ragi flour should be used?
(c) Which of these ingredients cannot be expressed as a ratio? Why?
Solution:
(a) Given Ragi flour: raw rice = 4 : 1
If one cup of ragi flour used then the ratio of ragi flour : raw rice = \(\frac{4}{4}: \frac{1}{4}=1: \frac{1}{4}\)
Raw rice required = \(\frac{1}{4}\) cup
(b) Ratio of water : ragi flour = 8 : 4
If 16 cups of water used then ratio of water : ragi flour = 8 × 2 : 4 × 2 = 16 : 8
8 cups of ragi flour are used.
(c) We know that the quantities of the same units can be compared. Here Ragi flour, Raw rice and water are in one unit, Sesame oil and salt are in different units, these different units cannot be compared and cannot be expressed as a ratio.
![]()
Challenging Problem (Textbook Page No. 74)
Question 6.
Antony brushes his teeth in the morning and night on all days in a week. Shabeen brushes her teeth only in the morning. What is the ratio of the number of times they brush their teeth in a week?
Solution:
Number of times = 14 : 7 = 2 : 1
Question 7.
Thirumagal’s mother wears a bracelet made of 35 red beads and 30 blue beads. Thirumagal wants to make smaller bracelets using the same two coloured beads in the same ratio. In how many different ways can she make the bracelets?
Solution:
Ratio of red beads : blue beads = 35 : 30 = 7 : 6
Also given that the bracelet made is smaller in size
∴ The possible ways are red beads : blue beads = 7 : 6 (or) 14 : 12 (or) 21 : 18 (or) 28 : 24
In 4 different way can she made.
Question 8.
Team A wins 26 matches out of 52 matches. Team B wins three-fourth of 52 matches played. Which team has a better winning record?
Solution:
Team A = \(\frac{26}{52}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Team B = \(\frac{3}{4}\) × 52 = 39
Team B has a better winning record.
Question 9.
In a school excursion, 6 teachers and 12 students from 6th standard and 9 teachers and 27 students from 7th standard, 4 teachers and 16 students from 8th standard took part. Which class has the least teacher to student ratio?
Solution:
Teacher to Student Ratio of 6th Std = 6 : 12 = 1 : 2
Teacher to Student Ratio of 7th Std = 9 : 27 = 1 : 3
Teacher to Student Ratio of 8th Std = 4 : 16 = 1 : 4
In standard 8th the ratio of teacher to student is 1 : 4 and which is the least.
![]()
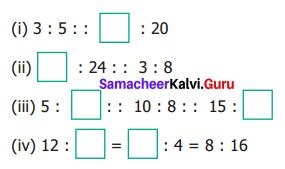
Question 10.
Fill the blanks using any set of suitable numbers 6 : …… :: ……. : 15
Solution:
6 : ……. = …….. : 15
Product of the extremes = 6 × 15 = 90
Set of suitable numbers
1 and 90, 2 and 45, 3 and 30, 5 and 18, 6 and 15
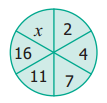
Question 11.
From your school diary, write the ratio of the number of holidays to the number of working days in the current academic year.
Solution:
Number of working days in an academic year = 220
Number of holidays = 365 – 220 = 145
\(\frac{\text { Number of holidays }}{\text { Number of working days }}=\frac{145}{220}=\frac{29}{44}\)
Number of holidays : No of working days = 29 : 44
Question 12.
If the ratio of Green, Yellow and Black balls in a bag is 4 : 3 : 5, then
(a) Which is the most likely ball that you can choose from the bag?
(b) How many balls in total are there in the bag if you have 40 black balls in it?
(c) Find the number of green and yellow balls in the bag.
Solution:
Green : Yellow : Black = 4 : 3 : 5
(i) Blackballs;
(ii) 96 balls (32 + 24 + 40);
(iii) green balls = 32
yellow balls = 24