You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science History Solutions Term 1 Chapter 4 Ancient cities of tamilagam
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Textual Evaluation 4 Ancient cities of tamilagam
I. Choose the correct answer
Ancient Cities Of Tamilagam Question 1.
Which of the following region has a city more than 6500 years old?
(a) Iraq
(b) Indus Valley
(c) Tamilagam
(d) Thondaimandalam
Answer:
(b) Indus Valley
Ancient Cities Of Tamilagam 6th Standard Question 2.
Which one of the following is a Tamil city?
(a) Iraq
(b) Harappa
(c) Mohenjo – Daro
(d) Kancheepuram
Answer:
(d) Kancheepuram
Mention The Ancient Cities Of Tamil Nadu Question 3.
Which city is not related to the Bay of Bengal?
(a) Poompuhar
(b) Thondi
(c) Korkai
(d) Kancheepuram
Answer:
(d) Kancheepuram
Ancient Cities Of Tamil Nadu Question 4.
Water management system of Tamils are known from …………………
(a) Kallanai
(b) Tanks in Kancheepuram
(c) Prakirama Pandyan Tank
(d) River Cauvery
(a) a is correct
(b) b is correct
(c) c is correct
(d) a and b are correct
Answer:
(d) a and b are correct
Question 5.
Which is not the oldest city among the following ones?
(a) Madurai
(b) Kancheepuram
(c) Poompuhar
(d) Chennai
Answer:
(d) Chennai
Question 6.
Which city is related to keezhadi excavation?
(a) Madurai
(b) Kancheepuram
(c) Poompuhar
(d) Harappa
Answer:
(a) Madurai
II. Tick the appropriate answer Match the Statement with the Reason.
Question 1.
Statement: Goods were imported and exported from the city Poompuhar.
Reason: Bay of Bengal was suitable for trading with neighbouring countries.
(a) Statement is correct, but reason is wrong.
(b) Statement and its reason are correct.
(c) Statement is wrong, but reason is correct.
(d) Both are wrong.
Answer:
(b) Statement and its reason are correct
Question 2.
(a) Thirunavukkarasar said “Kalvyil karaillatha”. This statement refers to the city Kancheepuram.
(b) Hieun Tsang said, “Kancheepuram is one among the seven – sacred places of India”.
(c) Kalidasa said, “Kancheepuram is the best city among the cities”
(a) Only a is correct
(b) Only b is correct
(c) Only c is correct
(d) All are correct
Answer:
(d) All are correct
Question 3.
Find out the correct statement
(a) Naalangadi – Night shop
(b) Allangdi – Day-time shop
(c) Ancient Roman coin factory was found at Poompuhar.
(d) Pearls were exported from Uvari near Korkai.
Answer:
(d) Pearls were exported from Uvari near Korkai
Question 4.
Find out the wrong statement.
(a) Megasthanese has mentioned Madurai in his account.
(b) Hien Tsang came to the Tamil city of Kancheepuram.
(c) Kovalan and Kannagi lived in Kancheepuram.
(d) Iraq is mentioned in Pattinapalai.
Answer:
(c) Kovalan and Kannagi lived in Kancheepuram
Question 5.
Find out the correct pair
(a) Koodal nagar – poompuhar
(b) Thoonga nagaram – harappa
(b) Thoonga Nagaram – Harappa
(d) City of Temples -Kancheepuram
Answer:
(d) City of Temples -Kancheepuram
Question 6.
Find out the wrong pair
(a) Vadamalai – Gold
(b) Western Ghats – Sandal
(c) Southern Sea – Pearls
(d) Eastern Sea – Ahil
III. Fill in the blanks :
- Kanchi Kailasanathar temple was built by_______
- _______ is known as the city of temples
- Masathuvan means _______
Answer:
- Pallava King Raja Simtia
- Kanchi
- A big trader
IV. State True or False.
- Cultural relationship with the outside world developed in Poompuhar because of its trade relationship with it.
- Women also purchased from Allangadi of Madurai without fear.
- Many rock cut temples were made during the Pallava period.
- Bodhi Dharmar belonged to Kancheepuram.
Answer:
- True
- True
- True
- True
V. Answer in one word :
Question 1.
What do you know about the term export?
Answer:
Exports are goods and services produced in one country and purchased by the citizens of another country.
Question 2.
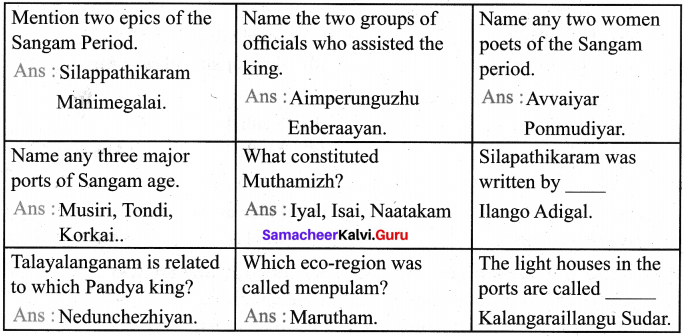
Mention the epic and the Sangam poem you read in the lesson:
Answer:
- Epic: Silappathikaram and Manimegalai
- Sangam literature: Pattinappaalai
Question 3.
Which is the oldest city in Thondai Nadu?
Answer:
Kanchi is the oldest city in Thondai Nadu.
Question 4.
Point out anyone difference between a village and a city
Answer:
The population of a city will be higher than that of a village.
Question 5.
Which civilisation is associated with the city Lothal?
Answer:
The Indus Valley Civilisation is associated with the city Lothal.
Question 6.
Name the oldest civilization of the world
Answer:
Mesopotamian civilization
VI. Answer the following :
Question 1.
Write a brief note on ancient cities of India.
Answer:
- Harappa and Mohenjodaro were prominent cities of ancient India.
- They developed along the banks of the river Indus.
- They were the symbol of urban civilization.
- They had a very good town planning, well-constructed house, well-maintained drainage system.
- They had very good civic sense.
- They developed pottery, ornaments as well as a script which is yet to be deciphered.
Question 2.
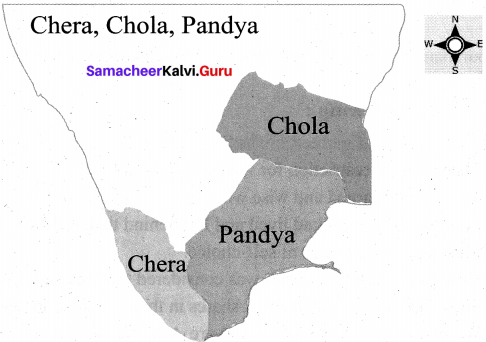
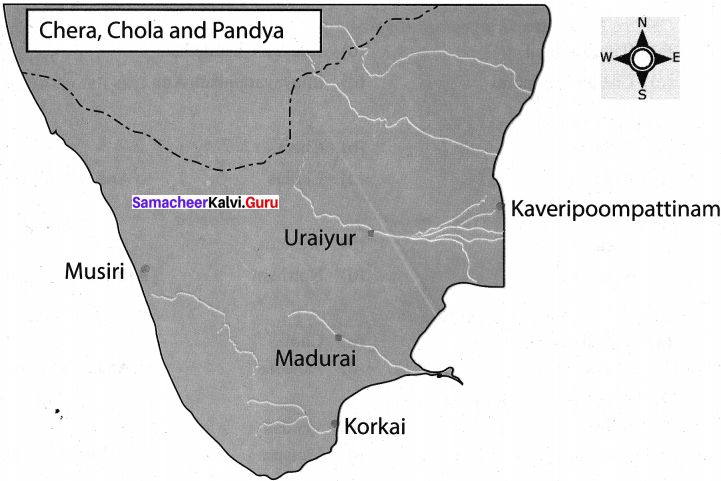
Mention the ancient cities of Tamil Nadu
Answer:
- Poompuhar
- Madurai
- Kanchi
- Korkai
- Vanchi
- Thondi
- Uraiyur
- Musiri
- Karavur
- Kaayal
- Mamallapuram
- Thanjavur
- Thagadoor
Question 3.
Discuss the sources available to know about Tamil cities.
Answer:
- Tamil literature, accounts of foreign travellers and archaeological finds provide the information about the ancient towns of Tamizhagam.
- Sangam Tamil Literature Pattinappaalai and Tamil epics Silappathikaram and Manimegalai have references about Poompuhar.
- Madurai is proudly associated with three Sangams.
- The fame of Madurai can be attested from the accounts of the Greek historian Megasthenes.
- Chanakya mentions about Madurai in his famous work Arthashastra.
- The Chinese Traveller Hieun Tsang writes about the greatness of Kanchi.
- Poet Kalidasa refers to Kanchi as the best of the towns.
Question 4.
Write about the kings who ruled Madurai?
Answer:
- The Pandyas, Cholas and Kalabras ruled Madurai.
- During the medieval times later Cholas and later Pandyas ruled Madurai.
- Then the Nayaks ruled Madurai.
Question 5.
Mention the other names of Madurai.
Answer:
- Sangam Valartha Nagaram
- Thoonga Nagaram (the city that never sleeps).
- Koodal nagar are the other names of Madurai
Question 6.
What is the difference between Naalangadi and Allangadi?
Answer:
- Naalangadi is the day market.
- Allangadi is the evening market.
Question 7.
Name the scholars who were born at Kancheepuram.
Answer:
Scholars like Dharmabalar, Jothibalar, Sumathi and Bodhi Dharmar were bom in Kanchi.
Question 8.
Which is known as the city of lakes? Why?
Answer:
There are hundreds of lakes in and around the city of Kanchi. So Kanchi is known as the city of lakes.
VII. HOTS:
Question 1.
Write a short note on Iraq.
Answer:
- Iraq has a narrow section of coast line on the northern Persian Gulf.
- There are several suggestions for the origin of the name Iraq.
- One dates back to the Sumerican city of Uruk.
- Another suggestion is that Iraq comes from the Aramaic language meaning the land along the banks of rivers.
Question 2.
Write a paragraph about the city of Poompuhar with special reference to trade.
Answer:
- Poompuhar was a port.
- Big traders and sea traders had settled down there.
- Numerous merchants from foreign countries such as Greece and Rome landed at Poompuhar.
- Brisk sea – borne trade took place in Puhar .
- Foreign traders stayed on indefinitely at Puhar.
- There are evidences of foreign settlements in the town.
Question 3.
Write about the accounts given by scholars about Kanchi.
Answer:
The Chinese traveller Hieun Tsang visited Kanchi Kadigai to pursue his further studies.
- He remarked that Kanchi can be counted as one among the seven sacred places like Budh Gaya and Sanchi.
- Poet Kalidasa says, “Kanch is the best of the towns
- Tamil poet saint Thirunavukarasar praises Kanchi as “Kalviyil Karaillatha Kanchi
Question 4.
City of Temples. Give short notes
Answer:
- Kanchi is also known as the Temple city.
- The famous Kailasanathar temple is at Kanchi.
- There are a large number of cave temples in Kanchi. So Kanchi is known as the Temple city.
Question 5.
Kancheepuram was famous for education. Prove this statement.
Answer:
- Kanchi was an educational centre.
- A place of learning is called school.
- Several schools were established in great numbers further first time in Kancheepuram.
- Jains studied in Jainapalli and Buddhists studied in Viharas.
- The greatness of Kanchi as an educational centre can be understood from the fact that the Chinese traveller Hieun Tsang visited Kanchi ‘Kadigai’ to pursue his further studies.
VIII. Student Activity :
Question 1.
Make an album about Keezhadi excavations.
Hints: Keezhadi excavations :
Answer:
- In 2013 – 2014 the Archaeological survey of India (ASI) carried out explorations in 293 sites.
- It was done along the Vaigai river Valley in Theni, Dindugal,Madurai, Sivaganga and Ramananathapuram districts.
- Keezhadi in Sivagana district was chosen for excavations.
- The artefacts in unearthed here at Pallichandhai Thidal of Keezhadi pointed to an ancient civilization.

- It might have thrived on the banks of Vaigai.
- The settlement belonged to 200 B.C
- This proves that urban civilization had existed in Tamil Nadu since the Sangam age
Question 2.
Poompuhar was famous for trading activities. Discuss.
Hints :
Answer:
- Pattinappalai, Silapathikaram and Manimegalai have refrences to the British sea – borne trade that took place in the Puhar Port.
- In Silappathikaram it is given that Kovalan’s father was a big trader and Kannagi’s father a sea – trader.
- This proves that big traders and sea traders had settled in Poompuhar.
- Numerous merchants from foreign countries such as Greece and Rome landed at Poompuhar.
- Due to busy and continuous trade, many of them stayed on indefinitely in Poompuhar.
- The traders of Poompuhar were known for their honesty and integrity.
Question 3.
Collect ctures of Pallava temple architecture
Hints : Important Lakes of Tamil Nadu :
Answer:

(i) Kailasanathar Temple at Kanchipuram built by Raja Simha.

(ii) Rathas of Mahabalipram

(iii) The shore Temple

(iv) Vaikunta perumal Temple – By Nandhi Varman II
Question 4.
Prepare a booklet describing the famous lakes of Tamil nadu
Hints:
Answer:
- Chembarambakkam Lake in Kanchipuram Dt, 40km for Chennai.
- Kaliveli Lake – Viluppuram Dt.
- Kolavai Lake – Kanchipuram Dt.
- Pulicat Lake – Coromandel Coast.
- Sholavaram Lake – Thiruvallur Dt.
- Veeranam Lake – Cuddalore Dt.
Question 5.
Make a booklet about the famous cities of Tamil Nadu.
Hints:
Answer:
- Chennai
- Coimbatore
- Thiruchirapalli
- Tiruppur
- Salem
- Erode
- Tirunelveli
- Kumbakonam Dt.
IX. Answer Grid
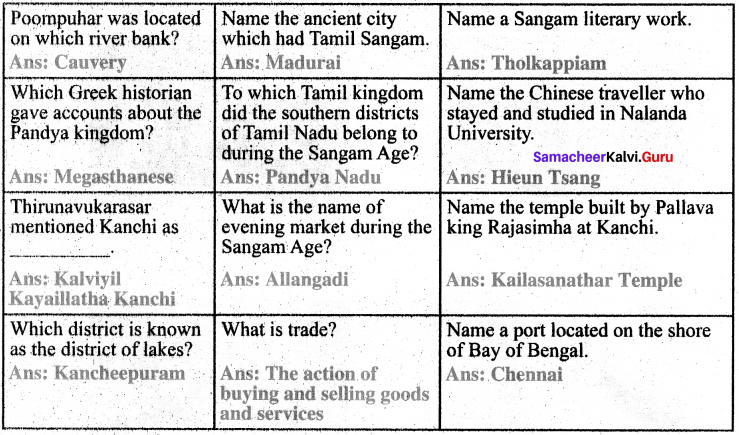
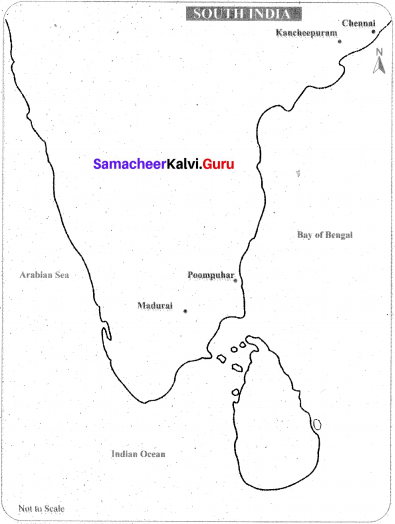
XI. Map work
Question 1.
Mark the following place in a South India map,
(a) Chennai
(b) Madurai
(c) Kancheepuram
(d) Poompuhar
(e) Arabian Sea
(f) Bay of Bengal
(g) Indian Ocean
Answer:
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science 4 Ancient cities of tamilagam Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Which is the oldest city among the following ones?
(a) Chennai
(b) Tiruppur
(c) Poompuhar
(d) Salem
Question 2.
The author of Pattinappaalai was …………….
(a) Uruttiranagannanar
(b) Seikkizhar
(c) Nakkeerar
(d) Jeyamkondar
Answer:
(a) Uruttiranagannanar
Question 3.
In Poompuhar the foreign traders began to interact with the local people because,
(a) Loading and unloading of ships took some months.
(b) Foreigners liked the local people.
(c) Foreigners wanted to learn Tamil.
(d) Foreigners wanted to stay in Poompuhar
Answer:
(a) Loading and unloading of ships took some months
Question 4.
Which of the following was an educational centre?
(a) Poompuhar
(b) Madurai
(c) Kanchi
(d) Thanjavur
Answer:
(c) Kanchi
Question 5.
We read Puhar kandam in
(a) Manimegalai
(b) Pattinappalai
(c) Arthashastra
(d) Silappathikaram
Answer:
(d) Silappathikaram
Question 6.
Thoonga Nagaram refers to
(a) Kanchi
(b) Poompuhar
(c) Madurai
(d) Korkai
Answer:
(c) Madurai
Question 7.
Pearls were found in abundance in
(a) Chozha Nadu
(b) Pandya Nadu
(c) Thondai Nadu
(d) Chera Nadu
Answer:
(b) Pandya Nadu
II. Match the statement with the Reason. Tick the appropriate answer:
Question 1.
Statement: Kanchi was an educational centre.
Reason: Hieun Tsang pursued his further studies at Kadigai.
(a) Statement and Reason are wrong.
(b) Statement correct but Reason is wrong.
(c) Both statements and Reason are correct.
(d) Statement is wrong but Reason is correct.
Answer:
(c) Both statements and Reason are correct.
Question 2.
(i) Madurai was a prominent town of Tamizhagan.
(ii) An archaeological excavation has been done in Keezhadi near Madurai.
(iii) Women purchased things from Allangadi without any fear.
(a) i) is correct
(b) ii) is correct
(c) iii) is correct
(d) i), ii) and iii) are correct
Answer:
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
Question 3.
Find out the correct statement.
(a) Tamil literature provide us information about ancient Tamizhagam.
(b) Madurai had very good maritime trade.
(c) Chandragupta’s minister was Megasthanese.
(d) In Chera nadu horses were found in abundance.
Answer:
(a) Tamil literature provide us information about ancient Tamizhagam
Question 4.
Find out the wrong statement.
(a) Poompuhar is a coastal town near the present day Mayiladuthurai.
(b) Madurai is known as city of lakes.
(c) Mohenja-Daro was a popular city of ancient civilisation.
(d) The traders of Poompuhar were known of their honesty.
Answer:
(b) Madurai is known as city of lakes.
Question 5.
Find out the wrong pair.
(a) Poompuhar – Educational centre
(b) Madurai – Koodal nagar
(c) Manimegalai – Epic
(d) Hieun Tsang – Chinese Traveller
Answer:
(a) Poompuhar – Educational centre
III. Fill in the blanks:
- The early Chola kingdom had _______ as its capital
- Kadiyalur Uruttirangannanar wrote the book _______
- Sangam Valartha Nagaram referred to _______
Answer:
- Poompuhar
- Pattinappaalai
- Madurai
IV. Sate True or False:
- Three sangams were held in Kanchi.
- Magasthanese was a historian from Rome.
- Chozha Nadu had plenty of elephants.
- Hundred of lakes were built in Poompuhar.
- Chandra Gupta wrote the book arthashastra.
Answer:
- False
- False
- False
- False
- False
V. Answer in one word :
Question 1.
Who w ere Kovalan and Kannagi?
- Kovalan and Kannagi were the well known characters of Silapathikaram.
- They lived in Poombuhar.
Question 2.
What does Pattinappaalai say about the traders of Poompuhar?
Answer:
- The traders of Poompuhar were known for their honesty and integrity.
- Pattinappaalai states that “selling any commodity at a higher price was considered bad”
Question 3.
Mention the importance of water management in Kanchi?
Answer:
- Puhar was a busy port upto 200 CE.
- It might have been either washed away by sea or destroyed by big shore waves,
- The remains of that destruction can still be seen in the present Poompuhar town.
Question 4.
What is Thoonga Nagaram?
Answer:
- Madurai is known as Thoonga Nagaram.
- Thoonga nagaram means the city that never sleeps.
VI. Answer the following:
Question 1.
Write a note on Siiappathikaram.
Answer:
- Siiappathikaram speaks about the greatness of Poompuhar.
- The lead female character of Siiappathikaram is Kannagi.
- Her father is Maanaigan. Sea traders are know by the name Maanaigan.
- The male character is Kovalan, who’s father is Maasathuvan, meaning a big trader.
- It is clear from the text that Poompuhar was a place where big traders and sea traders had settled down.
Question 2.
What do you know about the trade items of Poompuhar?
Answer:
- Horses were imported by sea.
- Pepper was procured through the land route.
- Gold that came from Vadamalai was polished and exported to the neighbouring countries.
- Sandal from western ghat, pearls from southern sea, corals from eastern sea and food items from Elam were imported.
Question 3.
Mention the importance of water management in Kanchi?
Answer:
- Water management played an important role in the agrarian society of those times.
- Hundreds of lakes were created for stroring water around the town of Kanchi.
- These lakes were well connected with canals.
- During the later period, Kanchi came to be known as the district of lakes.
- Water management skills of the ancient Tamils can be understood from the construction of Kallanai in the Chola country and the lakes and canals in Kanchi
VII. HOTS:
Question 1.
Write about the town Poompuhar.
Answer:
- Poompuhar had been built differently from other towns.
- Each social group had a separate settlement for living.
- Streets were broad and straight, dotted with well – designed houses
- It is believed that there was also a dockyard.
Question 2.
Write a short note on the economy of ancient Tamil country.
Answer:
- The main economic activities were agriculture, weaving, pearl fishery, manufacturing and construction.
- Paddy was the most important corp.
- Pepper, millets, grams and sugarcane were other commonly grown crops.
- Madurai and Uraiyur were important centres for the textile industry.
- Korkai was the centre of the pearl trade.
- There was brisk overseas trade with Rome.
- Good roads and ports also facilitated the trade.
Question 3.
What do you know about education in ancient Tamil country?
Answer:
- Education was considered important in ancient Tamilagam.
- The rulers and aristocrats of an ancient Tamilagam were always conscious of their duties to their country.
- They considered development of education as an important duty.
- Naaladiyar mentions that men gathered books in abundance and filled their house with them.
VII. HOTS :
Question 1.
Write about the town Poompuhar.
Answer:
- Poompuhar had been built differently from other towns.
- Each social group had a separate settlement for living.
- Streets were broad and straight, dotted with well-designed houses
- It is believed that there was also a dockyard.
Question 2.
Write a short note on the economy of ancient Tamil country.
Answer:
- The main economic activities were agriculture, weaving, pearl fishery, manufacturing and construction.
- Paddy was the most important corp.
- Pepper, millets, grams and sugarcane were other commonly grown crops.
- Madurai and Uraiyur were important centres for the textile industry.
- Korkai was the centre of the pearl trade.
- There was brisk overseas trade with Rome.
- Good roads and ports also facilitated the trade.
Question 3.
What do you know about education in ancient Tamil country?
Answer:
- Education was considered important in ancient Tamilagam.
- The rulers and aristocrats of an ancient Tamilagam were always conscious of their duties to their country.
- They considered development of education as an important duty.
- Naaladiyar mentions that men gathered books in abundance and filled their house with them.
- They studied science, mathematics, engineering, astronomy, logic and ethics.
- Libraries were attached to Jainapalli and Buddhist Viharas.
- The girls of Sangam Age were given a good training in literature, music and drama,
- Many women had distinguished themselves in the art of music.
- More than fifty women have been ranked among the Sangam poets