You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
![]()
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Solutions Term 3 Chapter 3 Perimeter and Area Ex 3.1
Question 1.
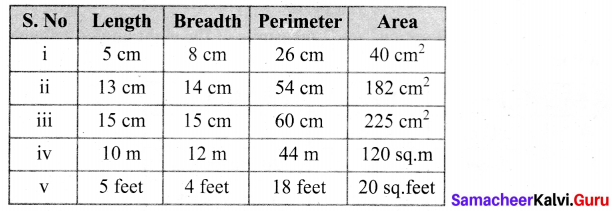
The table given below contains some measures of the rectangle. Find the unknown values.
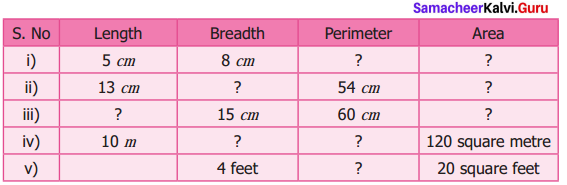
Solution:
(i) Area of the rectangle = (length × breadth) sq unit.
Perimeter of a rectangle = 2(1 + b) units.
l = 5 cm
b = 8 cm
∴ p = 2 (l + b) cm = 2 (5 + 8) cm = 2 × 13 cm
p = 26 cm
Area = (l × b) cm2 = (5 × 8) cm2
A = 40 cm2
(ii) l = 13 cm
p = 54 cm
Perimeter = 2 (l + b) units
54 = 2 (13 + b) cm
\(\frac{54}{2}\) = 13 + b
27 = 13 + b
b = 27 – 13
b = 14 cm
Area = l × b sq. unit = 13 × 14 cm2
A = 182 cm2
(iii) b = 15 cm
p = 60 cm
p = 2 (l + b) units
60 = 2 (l + 15) cm
\(\frac{60}{2}\) = l + 15
30 = l + 15
l = 30 – 15 .
l = 15 cm
Area = l × b unit2 = 15 × 15 cm2 = 225 cm2
A = 225 cm2
(iv) l = 10 m
Area = 120 sq metre
Area = l × b sq.m
120 = 10 × 6
b = \(\frac{120}{10}\)
b = 12 m
Perimeter =2 (l + b) units = 2(10 + 12) units = 2 × 22 m
A = 44 m
(v) b = 4 feet.
Area = 20 sq. feet
Area = l × b sq .feet
20 = l × 4
l = \(\frac{20}{4}\) feet
l = 5 feet
Perimeter = 2 (l + b) units.
p = 2 (5 + 4) feet = 2 × 9
p = 18 feet
Completing the unknown values in the table.
Question 2.
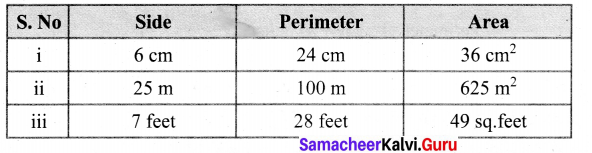
The table given below contains some measures of the square. Find the unknown values.
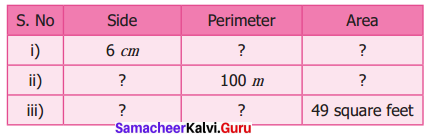
Solution:
Perimeter of a square = (4 × side) units
Area of a square = (side × side) unit2
(i) s = 6 cm
Perimeter = 4s units = 4 × 6 cm = 24 cm
P = 24 cm
Area = s × s unit2 = 6 × 6 cm2 = 36 cm2
A = 36 cm2
(ii) Perimeter = 4 × s unit
100 = (4 × s) m
\(\frac{100}{4}\) = s
s = 25 m
Area = s × s unit2= 25 × 25 m2 = 625m2
A = 625m2
(iii) Area = s × s unit2
49 = s × s square feet
s2 = 72
s = 7 feet
Perimeter = 4 × s unit = 4 × 7 feet = 28 feet
Perimeter = 28 feet
Completing the unknown values in the table
Question 3.
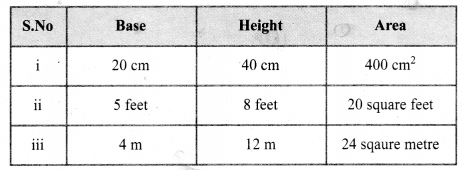
The table given below contains some measures of the triangle. Find the unknown values.
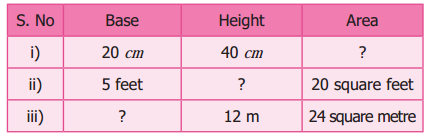
Solution:
Area of the right triangle = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × (base × height) unit2
(i) b = 20 cm
h = 40 cm
Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (b × h) cm2 = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 20 × 40 = 400 cm2
A = 400 cm2
(ii) b = 5 feet
Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × b × h unit2
= 20 = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 5 × h sq. feet
\(\frac{20 \times 2}{5}\) = h
h = 8 feet
(iii) Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × (base × height) unit2
24 = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × b × 12 m2
base = \(\frac{24 \times 2}{12}\) m = 4 m
Base = 4m
Tabulating the unknown values
![]()
Question 4.
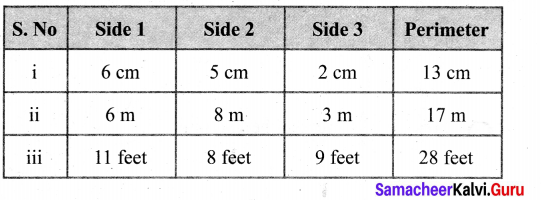
The table given below contains some measures of the triangles. Find the unknown values.
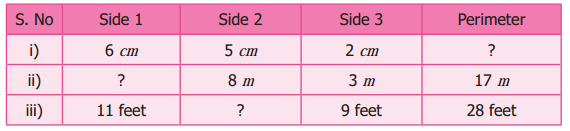
Solution:
Perimeter of a triangle = sum of three sides.
(i) Perimeter = 6 + 5 + 2 cm = 13 cm
p = 13 cm
(ii) Perimeter = (side 1 + side 2 + side 3) m
17 = (side 1 + 8 + 3) m
17 m = (side 1 + 11) m
side 1 = 17 – 11 = 6m
(iii) Perimeter = side 1 + side 2 + side 3
28 feet = 11 feet + side 2 + 9 feet
28 ft = 20 feet + side 2
28 – 20 = side 2
side = 8 feet
Tabulating the unknowns.
Question 5.
Fill in the blanks.
i) 5 cm2 = mm2
Hint: 1 cm2 = 100 mm2
ii) 26 m2 = cm2
Hint: 1 m2 = 10000
iii) 8 km2 = m2
Hint 4 1 km2– 1000000 m2
Solution:
(i) 500
(ii) 2,60,000
(iii) 80,00,000
Question 6.
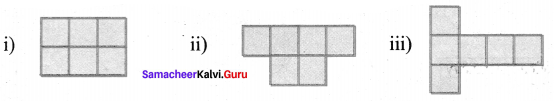
Find the perimeter and area of the following shapes.
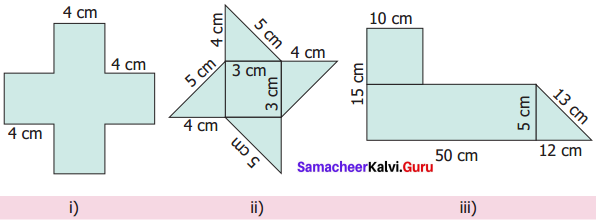
Solution:
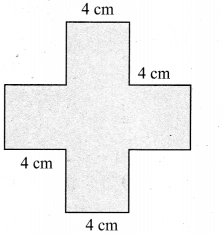
(i) Perimeter = (4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4) cm = 48 cm
Perimeter = 48 cm
Area of 5 squares of side 4 cm
Area of a square = (side × side) unit2
∴ A = 5 × (4 × 4) cm2 = 5 × 16 cm2 = 80 cm2
80 cm2
(ii) Perimeter = (4 + 5 + 4 + 5 + 4 + 5 + 4 + 5)cm = 36cm
Perimeter = 36 cm
Area of a square of side 3cm + Area of 4 right triangles
= (3 × 3) + [4 × \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 4 × 3] cm2 = (9 + 24) cm2 = 33 cm2
Area = 33 cm2
(iii) Perimeter = (50 + 12 + 13 + 40 + 10 + 10 + 10 + 5) cm = 150 cm
Perimeter = 150 cm
Area = Area of a rectangle + Area of a square + Area of a right triangle.
= (l × b) + (s × s) + ( \(\frac{1}{2}\) × b × h) cm2
= (50 × 5) + (10 × 10) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 12 × 5) cm2
= (250 + 100 + 30) cm2 = 380 cm2
Area = 380 cm2
![]()
Question 7.
Find the perimeter and area of the rectangle whose length is 6 m and breadth 4 m.
Solution:
l = 6 m, b = 4 m Perimeter of the rectangle
= 2 (l + b) units
= 2 (6 + 4) m
= 2 (10) m
= 20 m
Area of the rectangle = l × b sq units
= 4 × 6 m²
= 24 m²
Question 8.
Find the perimeter and the area of the square whose side is 8 cm.
Solution:
Perimeter of a square = (4 × side) units
Side = 8 cm
∴ Perimeter = 4 × 8 cm = 32 cm
Perimeter = 32 cm
Area of a square = (side × side) unit2 = (8 × 8) cm2 = 64 cm2
Area = 64 cm2
Question 9.
Find the perimeter and area of the right angled triangle whose sides are 6 feet, 8 feet and 10 feet.
Solution:
Perimeter of the triangle
= (a + b + c) units
= (6 + 8 + 10) feet
= 24 feet
Area of the triangle = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × b × h sq units
\(\frac{1}{2}\) × 6³× 8 feet square
= 24 sq. feet
Question 10.
Find the perimeter of
i) A scalene triangle with sides 7 m, 8 m, 10 m
ii) An isosceles triangle with equal sides 10 cm each and third side is 7 cm.
iii) An Equilateral triangle with side 6 cm.
Solution:
i) Perimeter of a scalene triangle = (7 + 8 + 10) m = 25 m
ii) The three sides of the isosceles triangle are 10 cm, 10 cm and 7 cm
∴ Perimeter = (10 + 10 + 7) cm = 27 cm
iii) An equilateral triangle with side 6 cm.
The sides of equilateral triangle are 6 cm, 6 cm and 6 cm
∴ Perimeter = (6 + 6 + 6) cm = 18 cm
![]()
Question 11.
The area of a rectangular shaped photo is 820 sq. cm. and its width is 20 cm. What is its length? Also find its perimeter.
Solution:
Given Area = 820 cm²
Width = 20 cm
Area of the rectangle
= l × b sq. units
820 = l × 20
\(\frac{820}{20}\) = l
41 = l
length l = 41 cm
Perimeter = 2(l + b) units
= 2(41 + 20) cm
= 2(61) cm
= 122 cm
Question 12.
A square park has 40 m as its perimeter. What is the length of its side? Also find its area.
Solution:
Given perimeter = 40 m
Perimeter of a square = 4 × Length of a side
40 = 4 × Length of a side
∴ Length of its side = \(\frac{40}{4}\) m = 0 m
∴ Side of the park = 10m
Area of a square = (Side × side) unit2 = (10 × 10) m2 = 100 m2
∴ Area of the Park = 100 m2
Question 13.
The scalene triangle has 40 cm as its perimeter and whose two sides are 13 cm and 15 cm, find the third side.
Solution:
Let the third side be C
perimeter = (a + b + c) units
40 = 13 + 15 + C
40 = 28 + C
C = 40 – 28
C = 12 units
C = 12 cm
Question 14.
A field is in the shape of right angled triangle whose base is 25 m and height 20 m. Find the cost of levelling the field at the rate of ₹ 45/- per sq. m.
Solution:
Area of a right angled triangle = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × (base × height) unit2
base = 25 m
height = 20 m
∴ Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × (25 × 20)
Area = 250 m2
Cost of levelling per m2 = ₹ 45.
∴ Cost of levelling 250 m2 = 250 × 45 = ₹ 11,250
Cost of levelling = ₹ 11,250
Question 15.
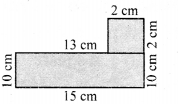
A square of side 2 cm is joined with a rectangle of length 15 cm and breadth 10 cm. Find the perimeter of the combined shape.
Solution:
Perimeter of the combined shape = Lengths of the outer boundaries
= (15 + 10 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 13 + 10) cm = 54 cm
Perimeter = 54 cm
Objective Type Questions
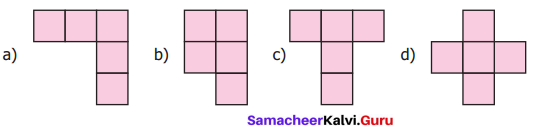
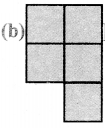
Question 16.
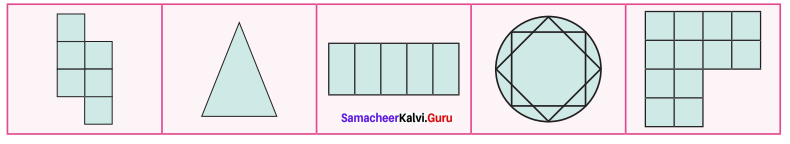
The following figures are of equal area. Which figure has the least perimeter?
Solution:
Hint:
(a) 12 units
(b) 10 units
(c) 12 units
(d) 12 units
Question 17.
If two identical rectangles of perimeter 30 cm are joined together, then the perimeter of the new shape will be
(a) equal to 60 cm
(b) less than 60 cm
(c) greater than 60 cm
(d) equal to 45 cm
Solution:
(b) less than 60 cm
Hint:
![]()
Question 18.
If every side of a rectangle is doubled, then its area becomes times.
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 6
Solution:
(c) 4
![]()
Question 19.
The side of a square is 10 cm. If its side is tripled, then by how many times will its perimeter increase?
(a) 2 times
(b) 4 times
(c) 6 times
(d) 3 times
SolutionL
(d) 3 times
30 × 4 = 120 = 3 × 40
Question 20.
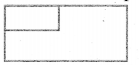
The length and breadth of a rectangular sheet of a paper are 15 cm and 12 cm respectively. A rectangular piece is cut from one of its corners. Which of the following statement is correct for the remaining sheet?
(a) Perimeter remains the same but the area changes
(b) Area remains the same but the perimeter changes
(c) There will be a change in both area and perimeter
(d) Both the area and perimeter remains the same
Solution:
(c) There will be a change in both area and perimeter
Hint: