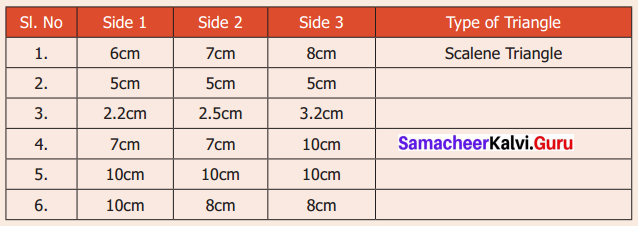
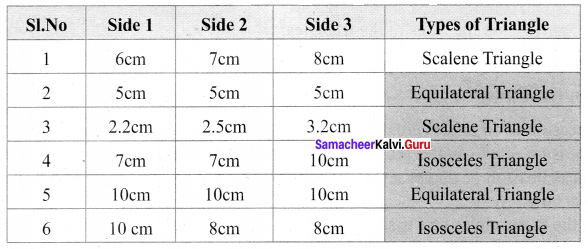
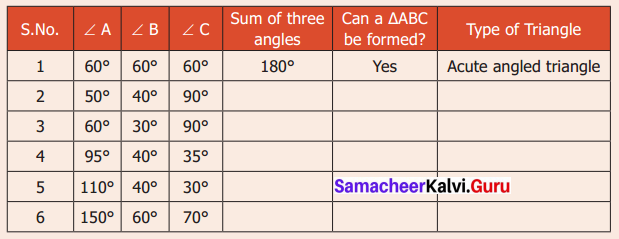
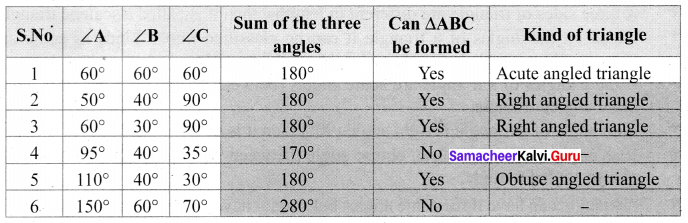
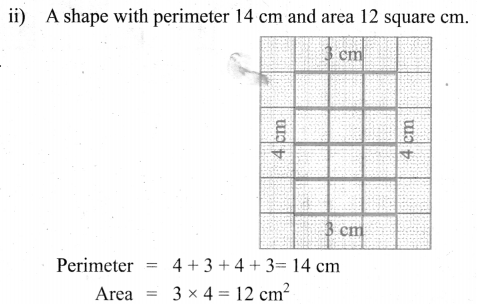
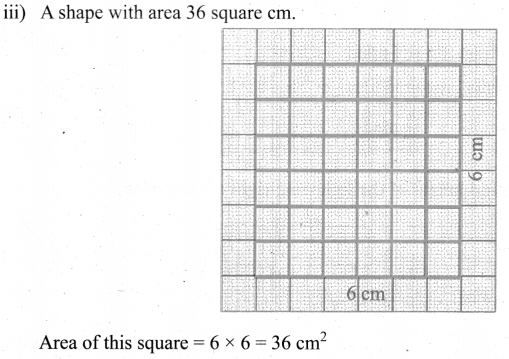
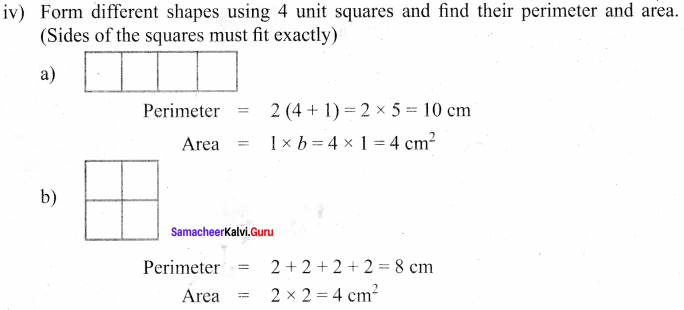
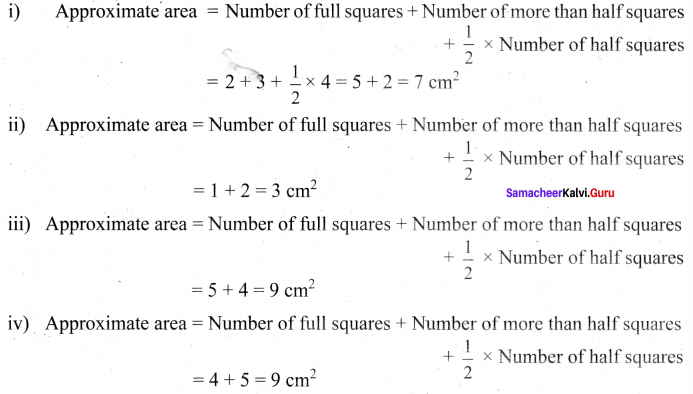
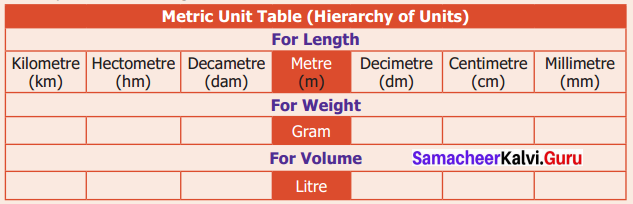
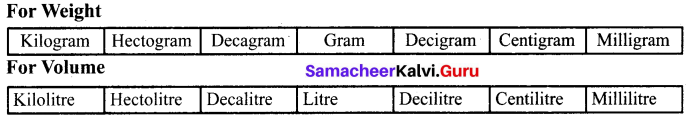
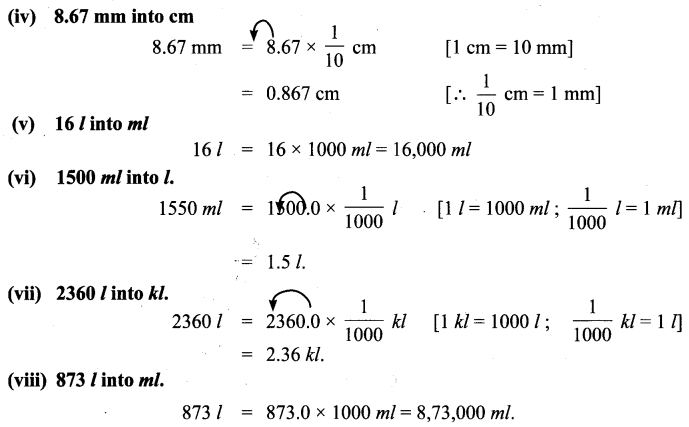
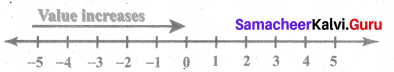
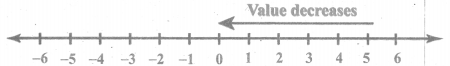
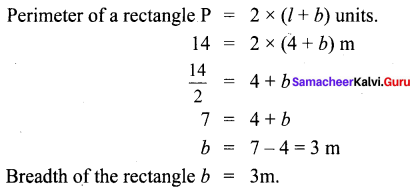You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
![]()
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Solutions Term 2 Chapter 5 Information Processing Ex 5.1
Question 1.
Convert the following numerical expressions into Tree diagrams.
(i) 8 + (6 × 2)
(ii) 9 – (2 × 3)
(iii) (3 × 5) – (4 ÷ 2)
(iv) [(2 × 4) + 2] × (8 ÷ 2)
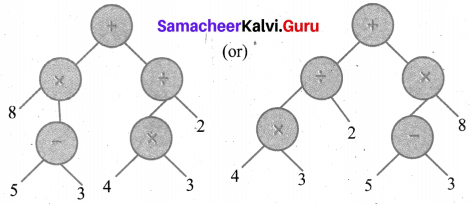
(v) [(6 + 4) × 7] ÷ [2 × (10 – 5)]
(vi) [(4 × 3) ÷ 2] + [8 × (5 – 3)]
Solution:
(i) 8 + (6 × 2)
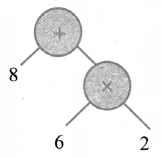
(ii) 9 – (2 × 3)
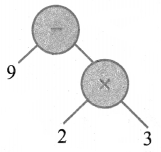
(iii) (3 × 5) – (4 ÷ 2)
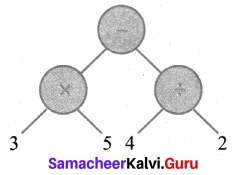
(iv) [(2 × 4) + 2] × (8 ÷ 2)
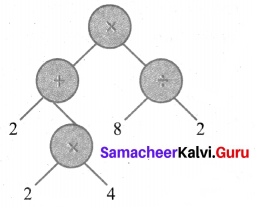
(v) [(6 + 4) × 7] ÷ [2 × (10 – 5)]
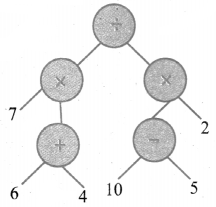
(vi) [(4 × 3) ÷ 2] + [8 × (5 – 3)]
The first expression goes to the right side branch. So that the value does not change.
![]()
Question 2.
Convert the following Tree diagrams into numerical expressions.
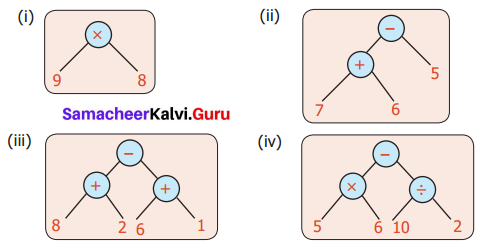
Solution:
(i) The numerical Expression is 9 × 8
(ii) The numerical expression is (7 + 6) – 5
(iii) The numerical expression is (8 + 2) – (6 + 1)
(iv) The numerical expression is (5 × 6) – (10 ÷ 2)
Question 3.
Convert the following algebraic expressions into tree diagrams.
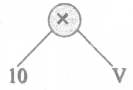
(i) 10 V
(ii) 3a – b
(iii) 5x + y
(iv) 20t × p
(v) 2(a + b)
(vi) (x × y) – (y × z)
(vii) 4x + 5y
(viii) (lm – n) ÷ (pq + r)
Solution:
(i) 10 V
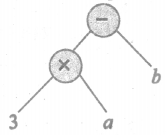
(ii) 3a – b
(iii) 5x + y
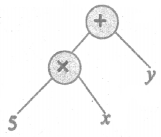
(iv) 20t × p
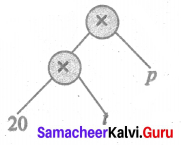
(v) 2(a + b)
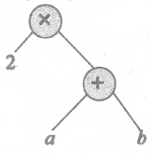
(vi) (x × y) – (y × z)
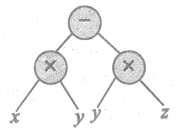
(vii) 4x + 5y
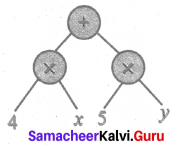
(viii) (lm – n) ÷ (pq + r)
![]()
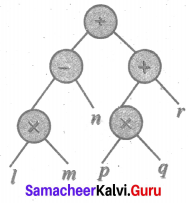
Question 4.
Convert tree diagram into Algebraic expression.
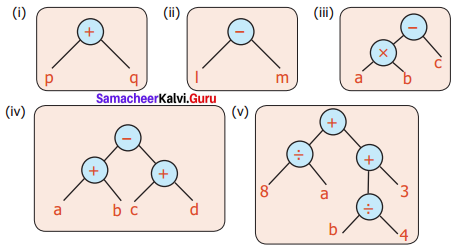
Solution:
(i) Algebraic Expression is p + q
(ii) Algebraic Expression is l – m
(iii) Algebraic Expression is (a × b) – c (or) (ab) – c
(iv) Algebraic Expression is (a + b) – (c + d)
(v) Algebraic Expression is (8 ÷ a) + [ (6 ÷ 4) + 3]