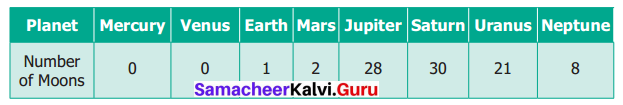
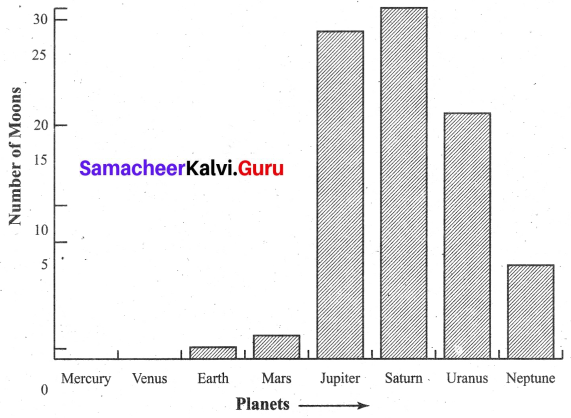
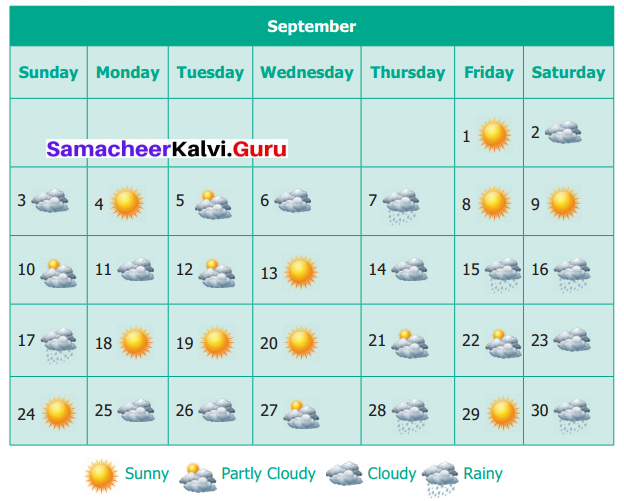
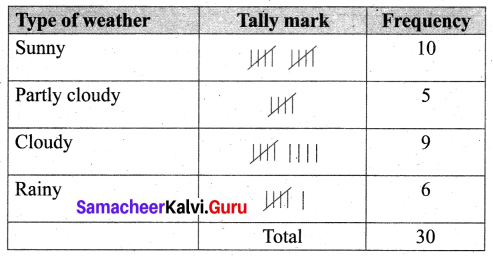
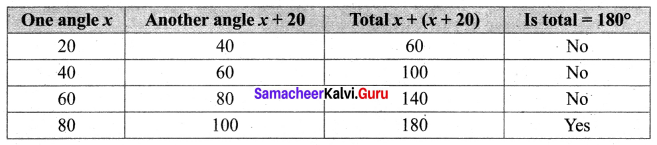
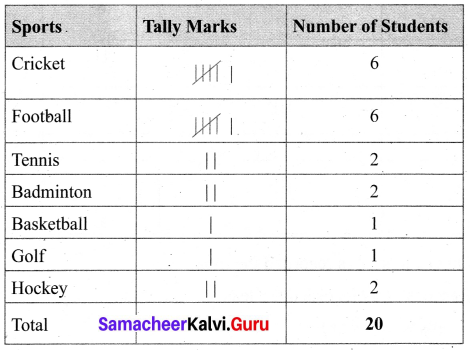
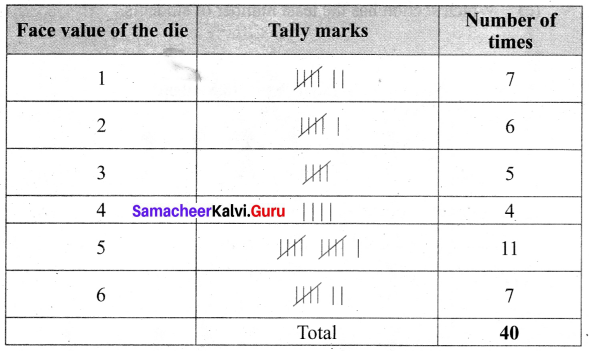
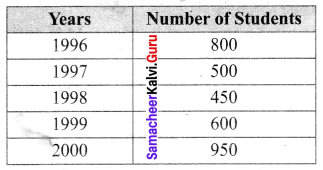
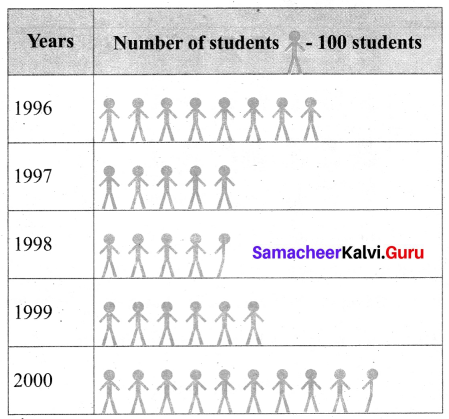
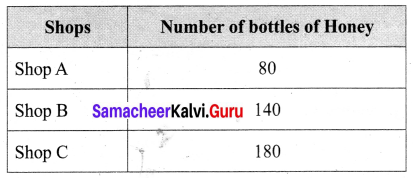
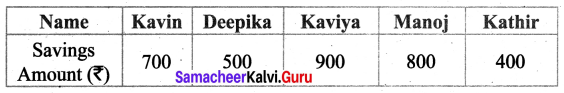
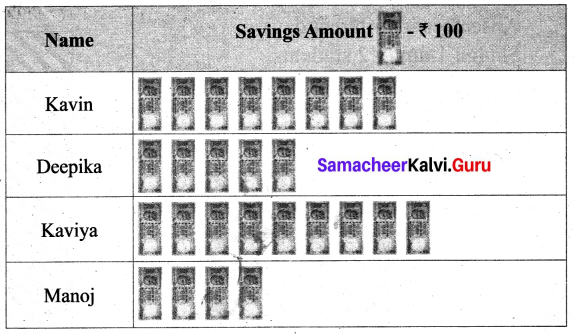
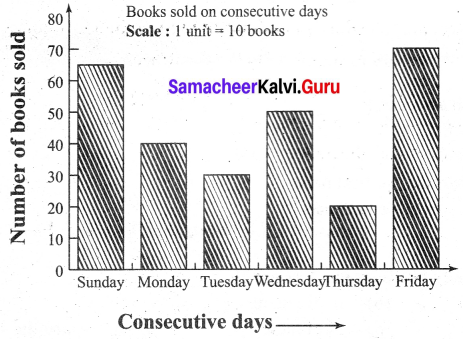
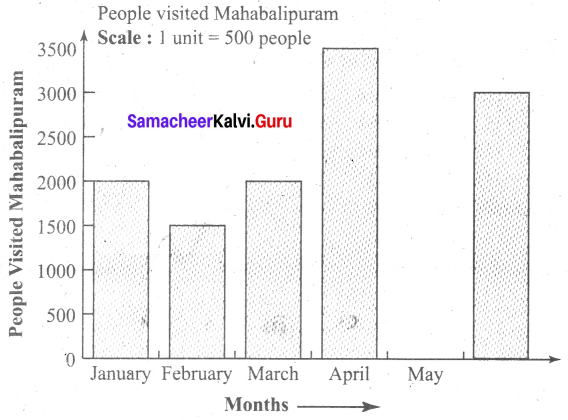
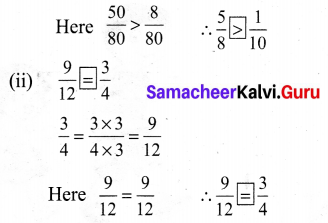
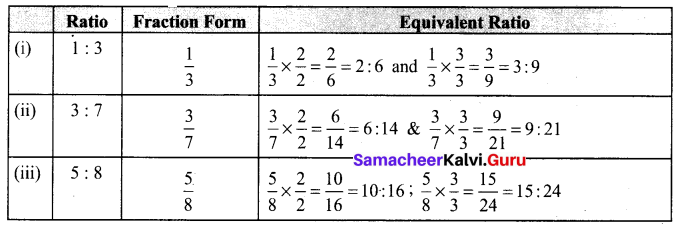
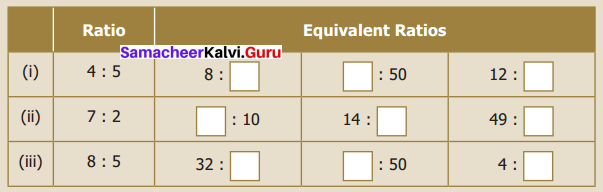
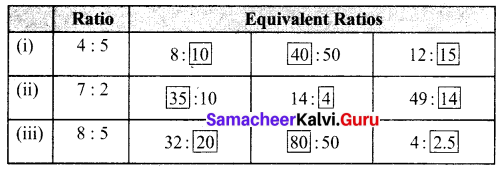
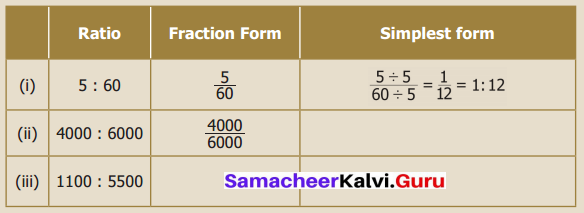
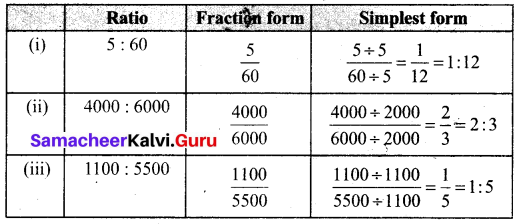
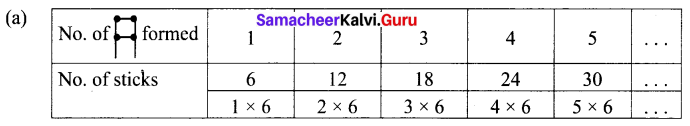
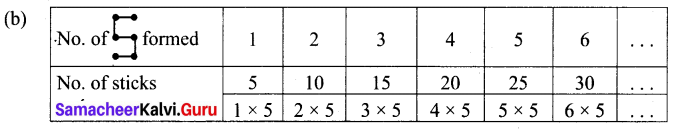
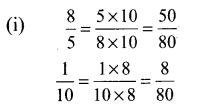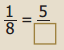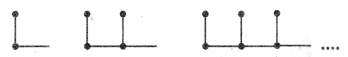You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
![]()
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Solutions Term 1 Chapter 6 Information Processing Ex 6.3
Question 1.
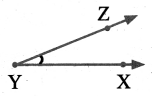
How many Triangles are there in each of the following figures?
Solution:
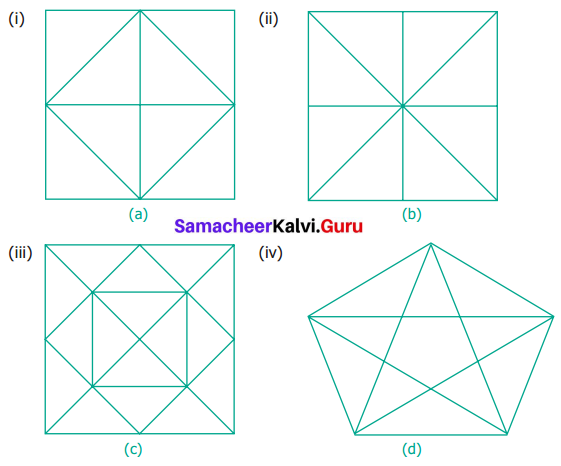
(i) The single portions A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are 8 triangles.
Taking the combination of 2 E & F, F & G & H and E & 11 are 4 triangles.
There are 8 + 4 = 12 triangles.
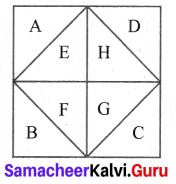
(ii) The smaller portions A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are 8 triangles.
Combining 2 at a time B & C, D & F, F & G, A & H are 4 triangles.
Taking 4 at a time
Combination of B, C, D and E; D, E, F and G; F, G, H and A; H, A, B and C are 4 triangles.
Total triangles = 8 + 4 + 4 = 16.
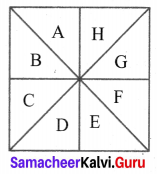
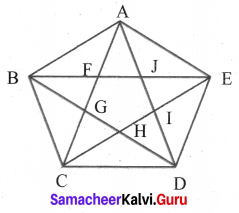
(iii) Every part A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, O and P are 16 triangles.
Combining two at a time. A & B, B & C, C & D, D & A, J & K, L & M, N & O, P & I are 8 triangles.
Taking the combination of 4, we have I, J, E & A; K, L, F and B, M, N, G and C, P, O, H and D are 4 triangles.
Taking 8 parts together we have QRS, RST, STQ, and TRQ are 4 triangles.
Total triangles = 16 + 8 + 4 + 4 = 32 triangles.
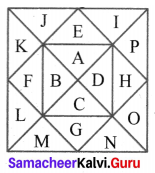
(iv)
Taking smaller triangles we have AFB, BFG, BGC, CGH, HCD, DHI, DIE, EIJ, EJAand AJF ⇒ 10 triangles.
Taking the combination of 2.
CGD, CID, DJE, DHE, EIA, EFA, AGB, AJB, BHC and BFC are 10 triangles.
Combining 3 at a time we have CED, DAE, EBA, ACB, BDC, CEF, DBJ, GDA, EBH, ACI ⇒ 10 triangles.
Other triangles are BCE, CAD, DBE, ADB and ACE are 5 triangles.
Total 10 + 10 + 10 + 5 = 35 triangles.
![]()
Question 2.
Find the number of dots in the tenth figure of the following pattern.
Solution:
(i) The number of dots given are 1, 3, 6, 10, 15,…
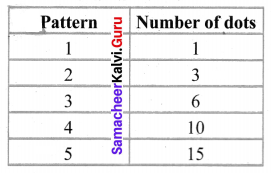
1st number = 1
2nd number = 1 + 2 = 3
3rd number = 3 + 3 = 6
4th number = 6 + 4 = 10
5th number = 10 + 5 = 15
6th number will be 15 + 6 = 21
7th number will be 21 + 7 = 28
8th number will be 28 + 8 = 36
9th number will be 36 + 9 = 45
10th number will be 45 + 10 = 55
Number of dots in the 10th figure = 55
(ii) The number of dots given are 1, 4, 9, 11, 16, 25,…
The no. of dots are in the pattern 1 × 1, 2 × 2, 3 × 3, 4 × 4, 5 × 5, …… 10 × 10
The number of dots in the 10th figure = 100.
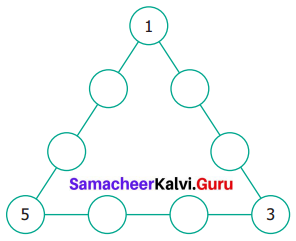
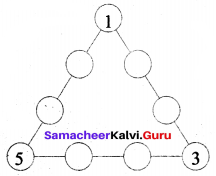
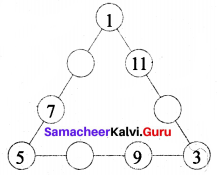
Question 3.

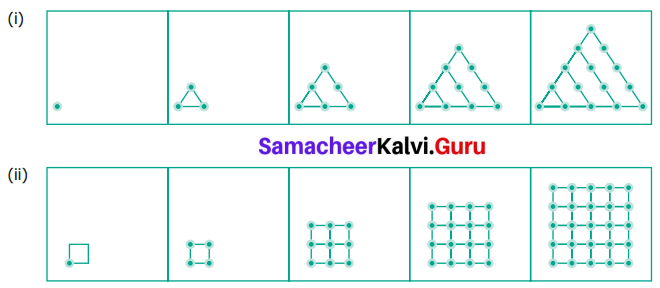
(i) Draw the next pattern.
(ii) Prepare a table for the number of dots used for each pattern.
(iii) Explain the pattern.
(iv) Find the number of dots in the 25th pattern.
Solution:
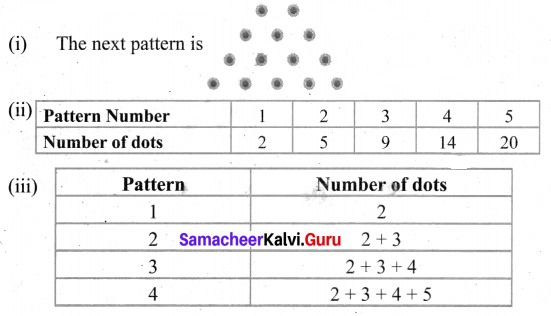
First number is 2
2nd number is 2 + 3 = 5
3rd number is 5 + 4 = 9
4th number is 9 + 5 = 14
5th number is 14 + 6 = 20
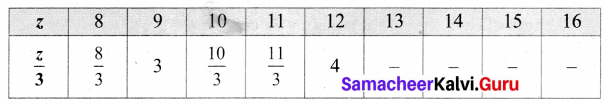
(iv) Number of dots in the 25th pattern is
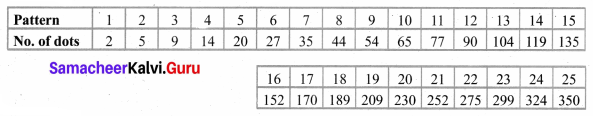
The number of dots in the 25th pattern = 350.
Question 4.
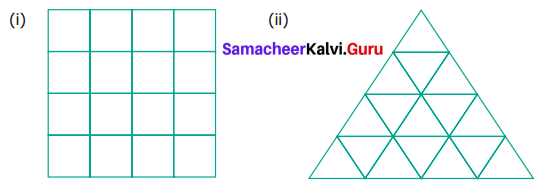
Count the number of squares in each of the following figures?
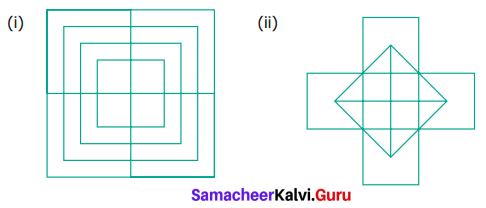
Solution:
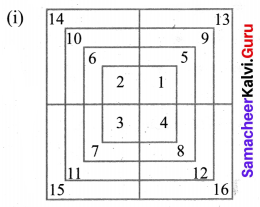
Smaller squares 4 × 4 = 16 (As numbered).
As a whole bigger = 4
Total squares = 20
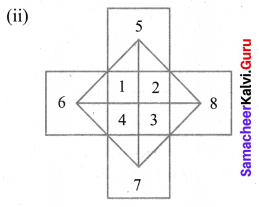
As we see in the figure in the middle 1, 2, 3, and 4 are 4 small squares.
Also, we have 9 and 10 = 2 big squares.
Outer squares 5, 6, 7, & 8 = 4.
Total = 4 + 4 + 1 + 1 = 10 squares.
![]()
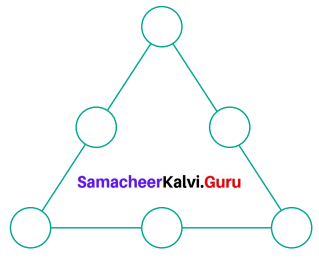
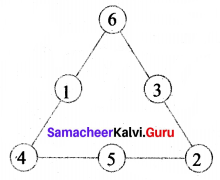
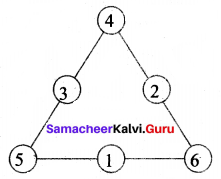
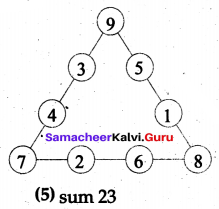
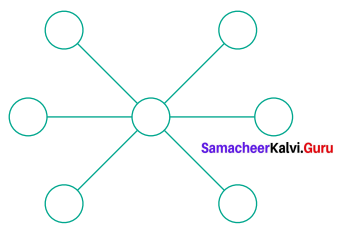
Question 5.
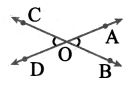
How many circles are there in the following figure?

Solution:
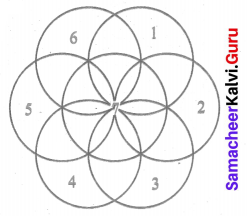
There are 7 Circles.
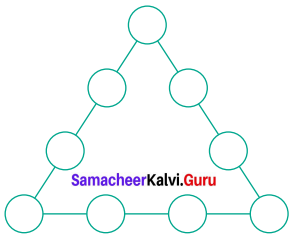
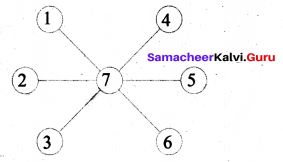
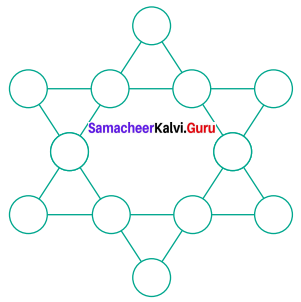
Question 6.
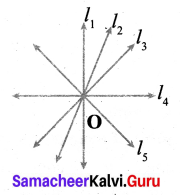
Find the minimum number of straight lines used in forming the following figures.
Solution:
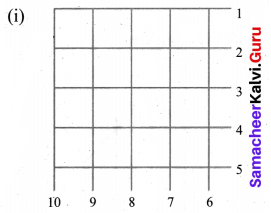
There are 5 horizontal lines and 5 vertical lines.
Total of 10 lines minimum needed.
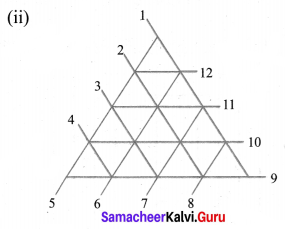
There are 12 straight lines used which is minimum.
![]()