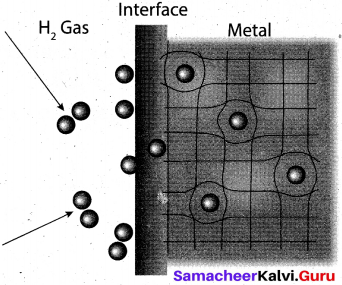
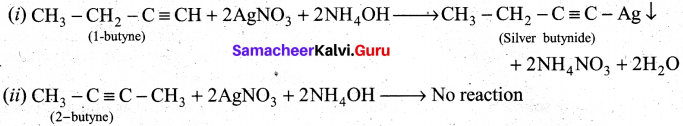
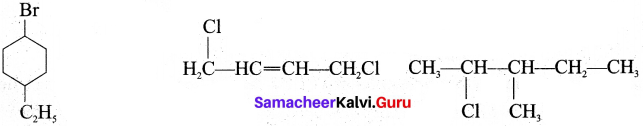
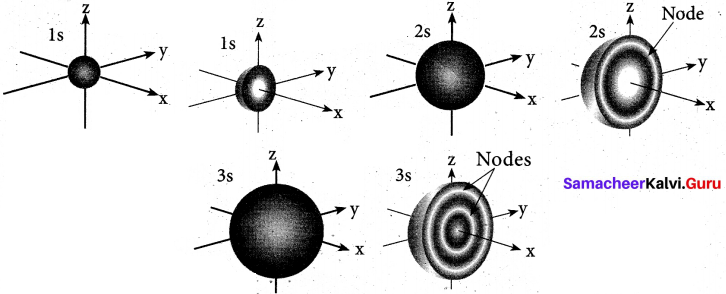
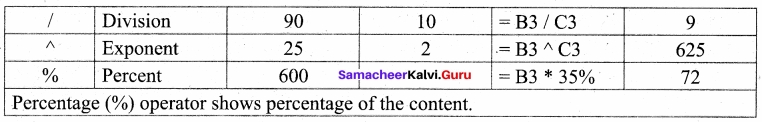
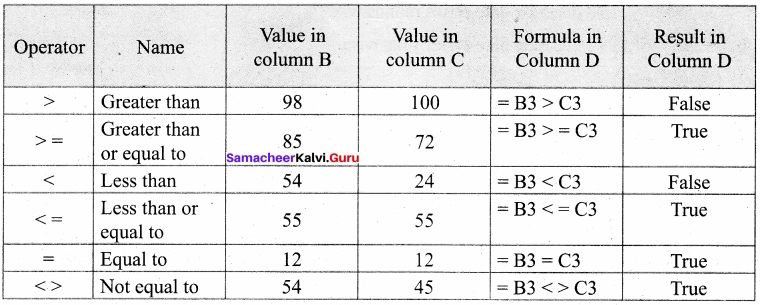
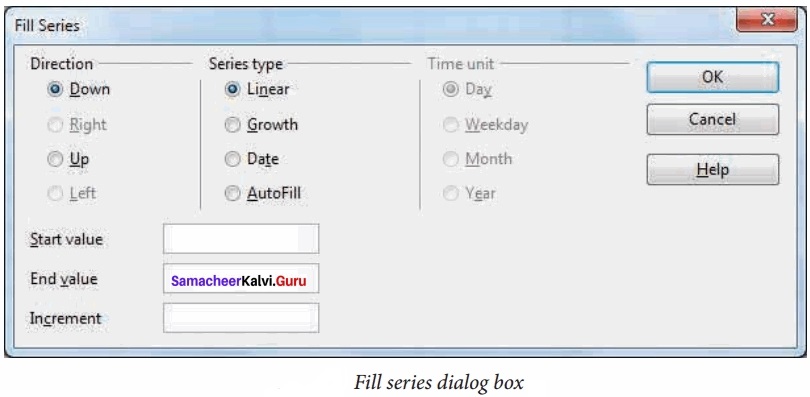
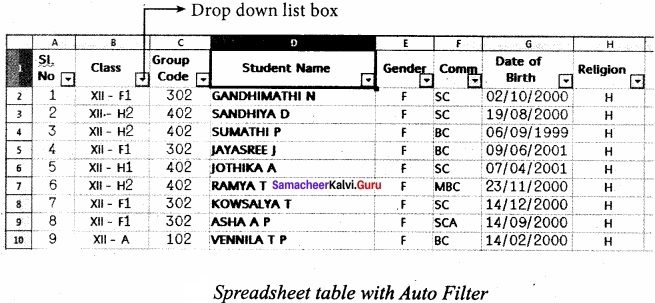
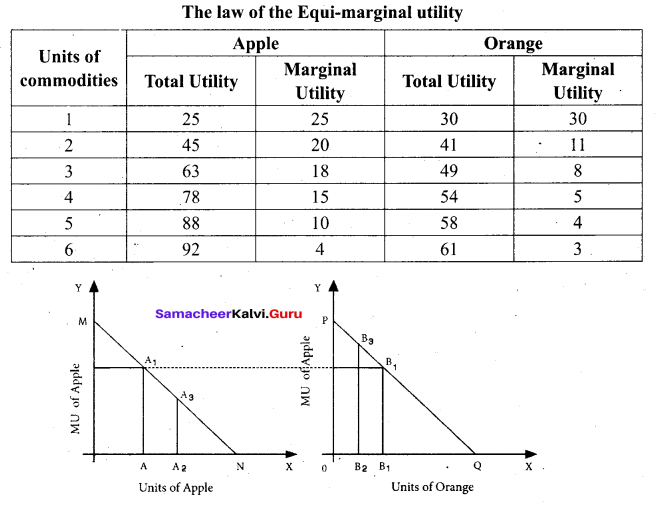
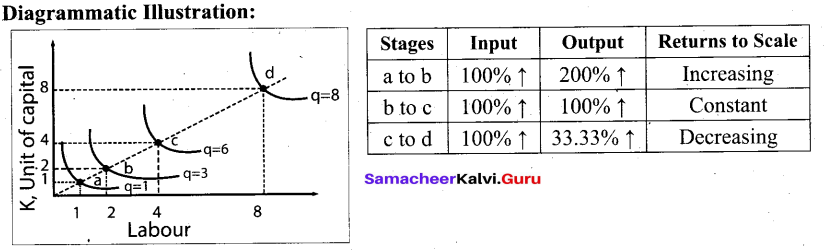
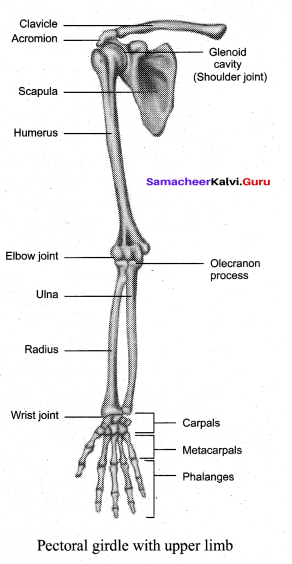
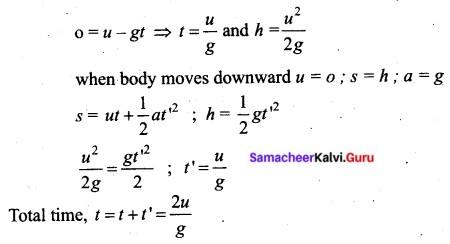
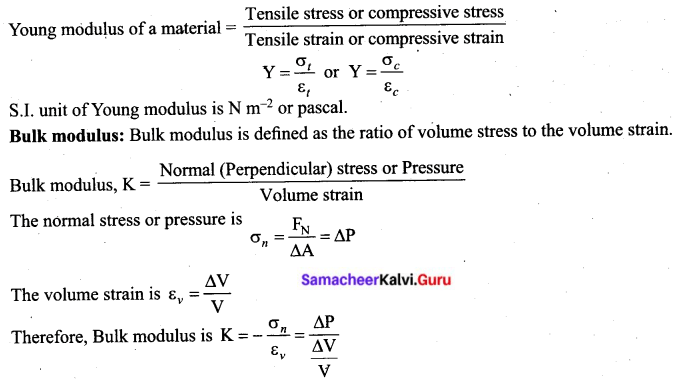
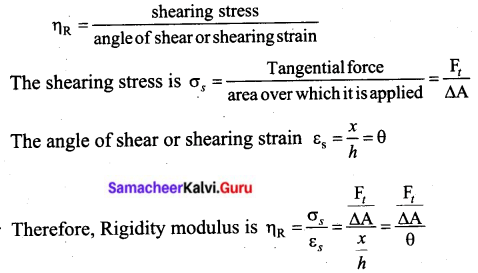
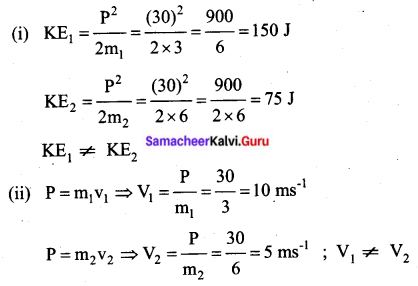
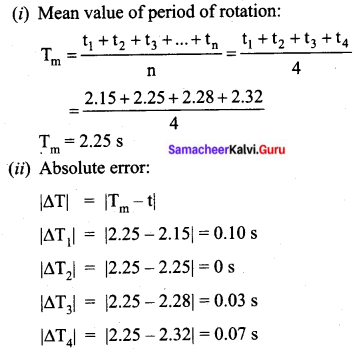
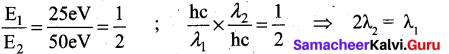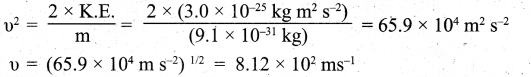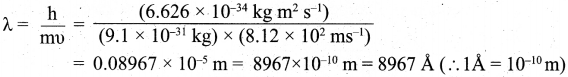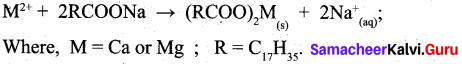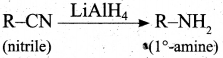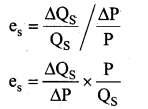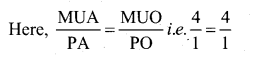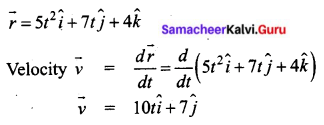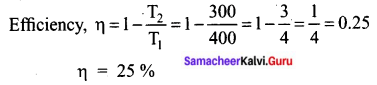Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Chemistry Previous Year Question Paper June 2019 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Chemistry Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 11th Chemistry Previous Year Question Paper June 2019 English Medium
![]()
Time: 2½ Hours
Total Score: 90 Marks
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I. II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 15 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 16 to 24 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 25 to 33 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 34 to 38 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Part-I
Answer all the Questions. [15 x 1 = 15]
Choose the most appropriate answers from the given alternatives and write the option code and corresponding answer.
Question 1.
The oxidation number of Carbon in CH2F2 is …………………………. .
(a) + 4
(b) – 4
(c) 0
(d) + 2
Answer:
(c) 0
Question 2.
The energy of an electron in the third orbit of hydrogen atom is – E. The energy of an electron in the first orbit will be.
(a) – 3E
(b) \(-\frac{E}{3}\)
(c) \(-\frac{E}{9}\)
(d) – 9E
Answer:
(d) – 9E
![]()
Question 3.
The effective nuclear charge experienced by d1 electron in the given electronic configuration, (Is)2 (2s, 2p)8 (3s, 3p)8 (3d)1 (4s)2 is ……………………. .
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 2.1
(d) 6.9
Answer:
(b) 3
Question 4.
The type of H-bonding present in orthonitro phenol and p-nitro phenol are respectively.
(a) Inter molecular H-bonding and intra molecular H-bonding
(b) Intra molecular H-bonding and inter molecular H-bonding
(c) Intra molecular H-bonding and no H-bonding
(d) Intra molecular H-bonding and intra molecular H-bonding
Answer:
(b) Intra molecular H-bonding and inter molecular H-bonding
![]()
Question 5.
When CaC2 is heated in atmospheric nitrogen in an electric furnace, the compound formed is
(a) Ca(CN)2
(b) CaNCN
(c) CaC2N2
(d) CaNC2
Answer:
Question 6.
When an ideal gas undergoes unrestrained expansion, on cooling occurs because the molecules …………………………. .
(a) are above the inversion temperature
(b) exert on attractive force on each other
(c) do work equal to the loss in kinetic energy
(d) collide with loss of energy
Answer:
(b) exert on attractive force on each other
![]()
Question 7.
Among the following statements, which on is/are correct?
(i) During cyclic process the amount of heat absorbed by the surrounding is equal to work done on the surrounding.
(ii) Refractive index is an example for intensive property.
(iii) If the enthalpy change of a process is positive then the process is spontaneous.
(iv) The entropy of an isolated system increases during spontaneous process.
(a) (i), (ii), (iii)
(b) (i), (iv)
(c) (ii), (iv)
(d) (ii) only
Answer:
(d) (ii) only
Question 8.
If Kb and Kf for reversible reaction are 0.8 x 10 5 and 1.6 x 10^ respectively, the value of equilibrium constant is.
(a) 20
(b) 0.2 x 10-1
(c) 0.05
(d) 0.2
Answer:
(a) 20
![]()
Question 9.
Assertion: Mixture of carbon tetrachloride and chloroform show positive deviation from Raoult’s law.
Reason: In the mixture, the inter molecular force of attraction between chloroform and carbon tetrachloride is weaker than those between molecules of carbon tetrachloride and chloroform molecules.
(a) Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is not the correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Both assertion and reason are false.
(d) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 10.
Shape and hybridisation of IF5 are
(a) Trigonal bipyramidal, sp3d2
(b) Trigonal bipyramidal, sp3d
(c) Square pyramidal, sp3d2
(d) Octahedral, sp3d2
Answer:
(c) Square pyramidal, sp3d2
![]()
Question 11.
Which of the following is optically active?
(a) 3-chloro pentane
(b) 2-chloro propane
(c) meso-tartaric acid
(d) glucose
Answer:
(d) glucose
Question 12.
Which of the following species is not electrophile in nature? ‘
(a) Cl+
(b) BH3
(c) H3O+
(d) +NO2
Answer:
(c) H3O+
![]()
Question 13.
group is ortho para directing and deactivating group.
(a) amino
(b) methyl
(c) halogen
(d) aldehyde
Answer:
(c) halogen
Question 14.
The raw material for Rasching process is
(a) chloro benzene
(b) phenol
(c) benzene
(d) anisole
Answer:
(c) benzene
Question 15.
cause kidney damage.
(a) Cadmium, Mercury
(b) Lead, Cadmium
(c) Freon, Fluoride
(d) Copper, Cadmium
Answer:
(a) Cadmium, Mercury
![]()
Part-II
Answer any six from the following questions. Question No. 24 is compulsory. [6 x 2 = 12]
Question 16.
What is syngas? How it is prepared?
Answer:
The mixture of CO and H2 gases are called syngas.
Preparation: C + H2O → CO + H2
Question 17.
Write any two similarities between beryllium and aluminum.
(i) Beryllium and aluminium have same electronegativity values.
(ii) BeCl2 and A1C13 forms dimeric structure. Both are soluble in organic solvents and are strong Lewis acids.
Question 18.
What is inversion temperature?
Answer:
The temperature below which a gas obey Joule-Thomson effect is called inversion temperature
\(\text { (T) } . \quad \mathrm{Ti}=\frac{2 \mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{Rb}}\)
Question 19.
What is the effect of added inert gas on the reaction of equilibrium?
Answer:
When an inert gas (i.e., a gas which does not react with any 6ther species involved in equilibrium) is added to an equilibrium system at constant volume, the total number of moles of gases present in the container increases, that is, the total pressure of gases increases, the partial pressure of the reactants and the products are unchanged. Hence at constant volume, addition of inert gas has no effect on equilibrium.
![]()
Question 20.
Linear form of carbon dioxide molecule has two polar bonds. Yet the molecule has zero dipole moment. Why?
Answer:
- The linear form of carbon dioxide has zero dipole moment, even though it has two polar bonds.
- In C02, there are two polar bonds [C = O], which have dipole moments that are equal in magnitude but have opposite direction.
- Hence the net dipole moment of the CO2 is μ = μ1 + μ2 = μ1 + (- μ1) = 0
- In this case, \(\mu=\vec{\mu}_{1}+\vec{\mu}_{2}=\vec{\mu}_{1}+\left(-\vec{\mu}_{1}\right)=0\)
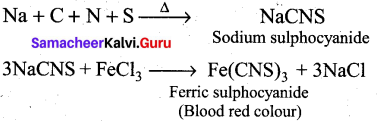
Question 21.
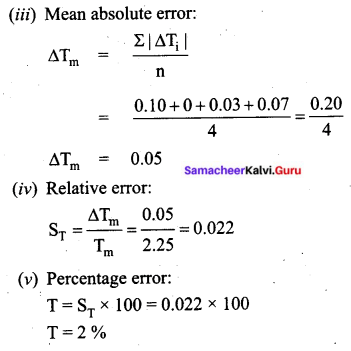
How do you detect the presence of nitrogen and sulphur together in an organic compound?
Answer:
If both N and S are present, a blood-red colour is obtained due to the following reactions
![]()
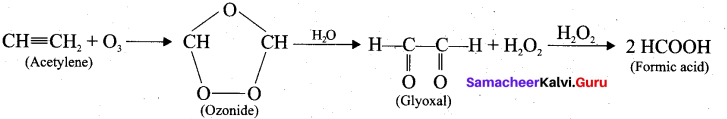
Question 22.
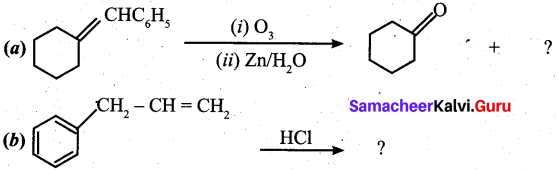
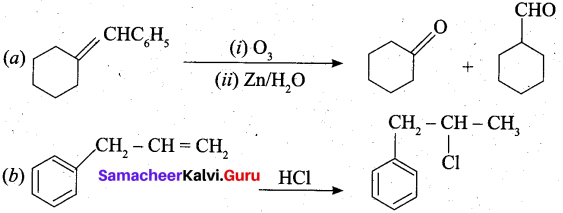
What happens when acetylene undergoes ozonolysis?
Answer:
When acetylene undergoes ozonolysis,
Question 23.
What is Green chemistry?
Answer:
- Green chemistry is a chemical philosophy encouraging the design of products and processes that reduces or eliminates the use and generation of hazardous substances.
- Efforts to control environmental pollution resulted in development of science for the synthesis of chemicals favourable to environment.
- Green chemistry means science of environmentally favourable chemical synthesis.
![]()
Question 24.
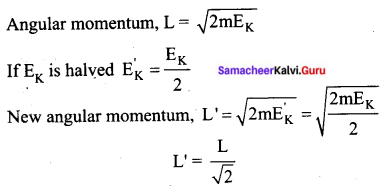
Calculate the orbital angular momentum for d and f orbital.
Answer:
Orbital angular momentum = √1(1 (1+1) h/2π.
For d orbital = √(2 x 3) h/2π = √6 h/2π
For f orbital = √(3(3 + 1)) h/2π = √12 h/2π
Part-III
Answer any six froita the following questions. Q. No. 33 is compulsory. [6 x 3 = 18]
Question 25.
What do you understand by the term mole?
Answer:
The mole is defined as the amount of a substance which contains 6.023 x 1023 particles such as atoms, molecules or ions. It is represented by the symbol “n”.
Question 26.
Ionisation potential of nitrogen is greater than that of oxygen. Explain by giving appropriate reason.
Answer:
N (Z = 7) Is2 2s2 2px1 2py1 2pz1. It has exactly half filled electronic configuration and it is more stable. Due to stability, ionization energy of nitrogen is high.
![]()
O (Z = 8) Is2 2s2 2px1 2py1 2pz1 It has incomplete electronic configuration and it requires less ionization energy. I.E1 N > I.E1 O
Question 27.
Among the alkali metal halides, which is covalent? Explain with reason.
Answer:
All alkali metal halides are ionic crystals. However lithium halides shows covalent character, as it is the smallest cation that exerts high polarising power on the halides.
Question 28.
Derive ideal gas equation.
Answer:
The gaseous state is described completely using the following four variables T, P, V and n. Each gas law relates one variable of a gaseous sample to another while the other two variables are held constant.
Therefore, combining all equations into a single equation will enable to account for the change in any or all of the variables.
- Boyle’s law: V α \(\frac{1}{P}\)
- Charles’law: V α T
- Avogadro’s law: V α n
![]()
We can combine these equations into the following general equation that describes the physical behaviour of all gases.
\(\mathrm{V} \propto \frac{\mathrm{nT}}{\mathrm{P}}\)
\(\mathrm{V}=\frac{\mathrm{nRT}}{\mathrm{P}}\), where R = Proportionately constant.
The above equation can be rearranged to give PV = nRT – Ideal gas equation. Where, R is also known as Universal gas constant.
Question 29.
Define molar heat capacity. Give its unit.
Answer:
Molar heat capacity is defined as “the amount of heat absorbed by one mole of a substance in raising the temperature by 1 Kelvin”. It is denoted as Cm.
Unit of Molar heat capacity: SI unit of Cm is JK-1 mol-1.
![]()
Question 30.
What is vapour pressure of a liquid? What is relative lowering of vapour pressure?
- The pressure of the vapour in equilibrium with its liquid is called vapour pressure of the liquid at the given temperature.
- The relative lowering of vapour pressure is defined as the ratio of lowering of vapour pressure to vapour pressure of pure solvent.
- Relative lowering of vapour pressure = \(\frac{p_{\text {solvent }}-p_{\text {solution }}}{p_{\text {solvent }}}^{\circ}\)
Question 31.
Explain a suitable method for purifying and separating liquids present in a mixture having very close boiling point.
Answer:
Fractional distillation: This method is used to purify and separate liquids present in the mixture having their boiling-point close to each other. The process of separation of the components in liquid mixture at their respective boiling points in the form of vapours and the subsequent condensation of those vapours is called fractional distillation. This method is applied in distillation of petroleum, coal tar and crude oil.
![]()
Question 32.
What is polymerisation? Explain the two types of polymerisation reaction of acetylene.
ANswer:
A polymer is a large molecule formed by the combination of large number of small molecules (monomers). This process is known as polymerisation.
Acetylene undergoes two types of polymerisation reactions, they are:
- Linear polymerisation
- Cyclic polymerisation
(i) Linear polymerisation: Acetylene forms linear polymer, when passed into a solution of cuprous chloride and ammonium chloride.
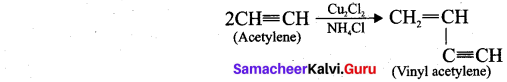
(ii) Cyclic polymerisation: Acetylene undergoes cyclic polymerisation on passing through red hot iron tube. Three molecules of acetylene polymerises to form benzene.
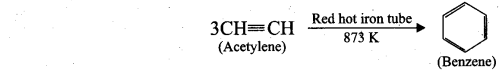
![]()
Question 33.
The bond length between all the four carbon atoms is same in 1,3 – butadine. Explain with reason.
Answer:
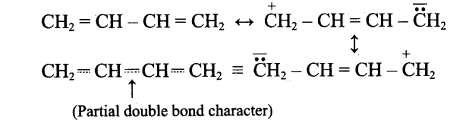
1,3-butadiene is a conjugated molecule with four overlapping p-orbital on adjacent atoms. And π-electrons are delocalised over four atoms. This shortens the bond length of central C – C bond. Thus, the bond length between all the four C-atoms are same in 1,3-butadiene.
Part – IV
Answer all the following questions. [5 x 5 = 25]
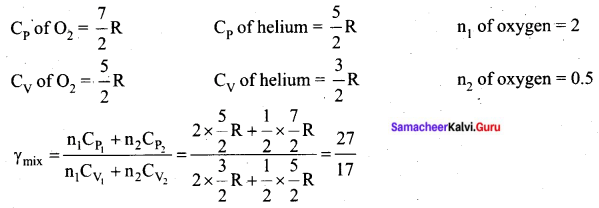
Question 34.
(a) (i) What are auto redox reactions? Give example.
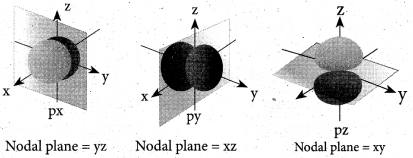
(ii) Define orbital. What are the n and 1 values of 3px and 4dx2-y2 electron?
[OR]
(b) (i) Why hydrogen peroxide is stored in plastic containers, not in glass container?
(ii) Give the general electronic configuration of lanthanides and actinides.
Answer:
(a) (i) Auto redox reactions: It is a redox reaction in which a substance act as both the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent. (Reaction occur in the same substance)
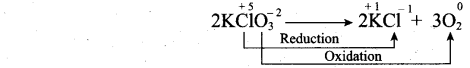
(ii) 1. Orbital is a three dimensional space which the probability of finding the electron is maximum.
2. For 3px electron – n value =3, l value =1
3. For 4dx2-y2 electron n value = 4, l value = 2
![]()
[OR]
(b) (i) The aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide is spontaneously disproportionate to give oxygen. The reaction is slow but it is explosive when it is catalyzed by metal or alkali dissolved from glass. For this reason, its solution are stored in plastic bottles.
\(\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2(\mathrm{aq})} \rightarrow \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{i})}+1 / 2 \mathrm{O}_{2(\mathrm{g})}\)
(ii) 1. The electronic configuration of lanthanides is 4f1-14 5d0-1 6s2.
2. The electronic configuration of actinides is 5f1-14 6d0-1 7s2.
Question 35.
(a) (i) Why blue colour appears during the dissolution of alkali metals in liquid ammonia?
(ii) What is Boyle’s temperature? What happens to real gases above and below the Boyle’s temperature?
[OR]
(b) (i) Derive the relation between KP and Kc for general homogeneous gaseous reaction.
(ii) How do you measure heat changes of a constant pressure?
Answer:
(a) (i) M + (x + y)NH3 → [M(NH3)x]+ + [e(NH3)y]–
The blue colour of the solution is due to the ammoniated electron which absorbs energy in the visible region of light and thus imparts blue colour to the solution. The solutions are paramagnetic and on standing slowly liberate hydrogen resulting in the formation of amide. In concentrated solution, the blue colour changes to bronze colour and become diamagnetic.
![]()
(ii)
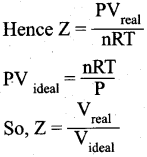
- Over a range of low pressures, the real gases can behave ideally at a particular temperature called as Boyle temperature or Boyle point.
- The Boyle point varies with the nature of the gas.
- Above the Boyle point, the compression point Z > 1 for real gases i.e. real gases show positive deviation.
- Below the Boyle point, the real gases first show a-decrease for Z, reaches a minimum and then increase with increase in pressure. So, it is clear that at low pressure and at high temperature, the real gases behave as ideal gases.
[OR]
(b) (i) Consider a generaL reaction in which all reactants and products arc ideal gases.
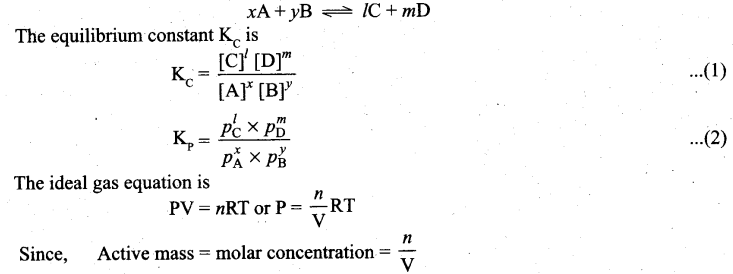
![]()
P = Active mass x RT
Based on the above expression, the partial pressure of the reactants and products can be expressed as.
\(\begin{array}{ll}
p_{A}^{x}=[\mathrm{A}]^{x} \cdot[\mathrm{RT}]^{x} & p_{\mathrm{B}}^{y}=[\mathrm{B}]^{y} \cdot[\mathrm{RT}]^{y} \\
p_{\mathrm{C}}^{\prime}=[\mathrm{C}]^{\prime} \cdot[\mathrm{RT}]^{\prime} & p_{\mathrm{D}}^{m}=[\mathrm{D}]^{m} \cdot[\mathrm{RT}]^{m}
\end{array}\)
On substitution in equation (2),
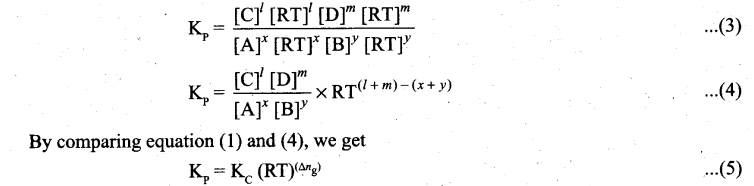
where Δng is the difference between the sum of number of moles of products and the sum of number of moles of reactants in the gas phase.
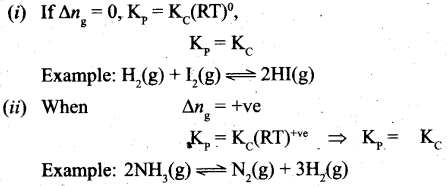
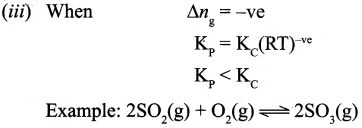
![]()
(ii) 1. Measurement of heat change at constant pressure can be done in a coffee cup calorimeter.
2. We know that ΔH = qp (at constant P) and therefore, heat absorbed or evolved, qp at constant pressure is also called the heat of reaction or enthalpy of reaction, ΔHr.
3. In an exothermic reaction, heat is evolved, and system loses heat to the surroundings. Therefore, qp will be negative and Reaction AH. will also be negative. Mixture
4. Similarly in an endothermic reaction, heat is absorbed, qp is positive and ΔHr will also be positive.
Question 36.
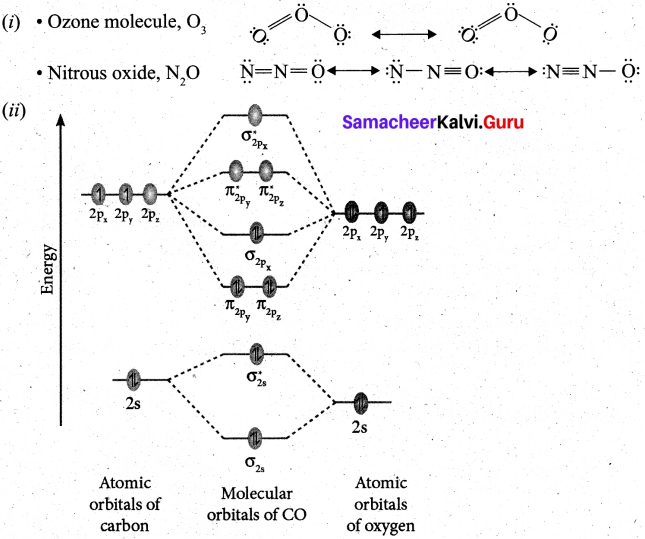
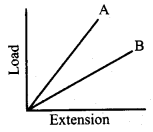
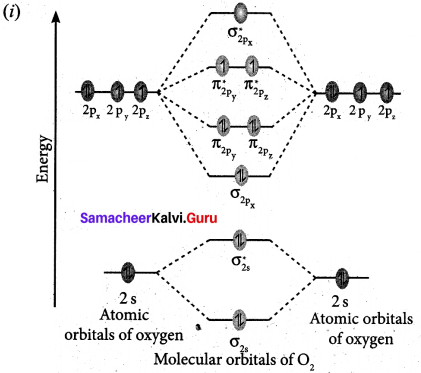
(a) (i) Draw the M.O. diagram of oxygen molecule. Calculate its bond order and magnetic character.
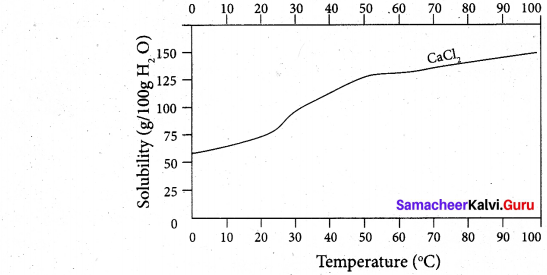
(ii) Draw and explain the graph obtained by plotting solubility versus temperature for calcium chloride.
[OR]
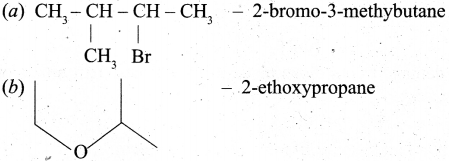
(b) (i) Write the IUPAC names of the following compunds:
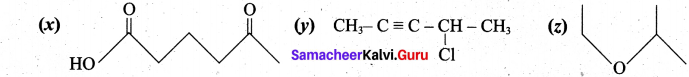
(ii) Calculate the formal charge on carbon and oxygen for the following structure
![]()
(a)
![]()
1. Electronic configuration of O atom is Is2 2s2 2p4
2. Electronic configuration of O2 molecule is
![]()
3. Bond order \(\frac{N_{b}-N_{a}}{2}=\frac{10-6}{2}=2\)
4. Molecule has two unpaired electrons, hence it is paramagnetic.
(ii) Even though the dissolution Of calcium chloride is exothermic, the solubility increases moderately with increase in temperature. Here, the entropy factor also plays a significant role in deciding the position of the equilibrium.
[OR]
![]()
(b) (i) (x) 5-oxohexanoic acid (y) 4-chloropent-2-yne (z) 2-ethoxypropane
(ii)
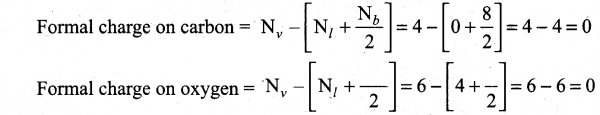
Question 37.
(a) (i) Explain about the inductive effect.
(ii) What do you mean by confirmation? Explain about staggered conformation in ethane.
[OR]
(b) (i) Among the following compounds, o-dichloro benzene and p-dichloro benzene, which has higher melting point? Explain with reason.
(ii) Write notes on the adverse effect caused by ozone depletion.
Answer:
(a) (i) Inductive effect:
1. It is defined as the change in the polarization of a covalent bond due to the presence of adjacent bonded atoms or groups in the molecule. It is denoted as I-effect.
2. Atoms or groups which lose electron towards a carbon atom are said to have a +1 effect.
Example, CH3 —, (CH3)2 CH —, (CH3)2 C— etc.
3. Atoms or groups which draw electrons away from a carbon atom are said to have a -I effect.
Example, —NO2. -I, Br, -OH, C6H5 etc.
4. For example, consider ethane and ethyl chloride. The C—C bond in ethane is non¬polar while the C-C bond in ethyl chloride is polar. We know that chlorine is more electronegative than carbon and hence it attracts the shared pair of electrons between C—Cl in ethyl chloride towards itself.

![]()
This develops a slight negative charge on chlorine and a slight positive charge on carbon to which chlorine is attached. To compensate it, the C1 draws the shared pair of electron between itself and C2. This polarization effect is called inductive effect.
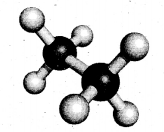
(ii) The rotation about C—C single bond axis yielding several arrangements of a hydrocarbon called conformers.
Staggered conformation: In this conformation, the hydrogens of both the carbon atoms are far apart from each other. The repulsion between the atoms is minimum and it is the most stable conformer.
[OR]
(b) (i) The melting point of p-dichloro benzene is higher than the melting point of the corresponding ortho and meta isomers. The higher melting which leads to more close packing of its moleules in the crystal lattice and consequently strong intermolecular attractive forces which requires more energy for melting.
p-dichlorobenzene > o-dichlorobenzene > m-dichlorobenZene
![]()
(ii) 1. The formation and destruction of ozone is a regular natural process, which never disturbs the equilibrium level of ozone in the stratosphere. Any change in the equilibrium level of ozone in the atmosphere will adversely affect the life in biosphere in the following ways.
2. Depletion of ozone layer will allow more UV rays to reach the earth surface and would cause skin cancer and also decreases the immunity level in human beings.
3. UV radiations affects plant proteins which lead to harmful mutation in plant cells.
4. UV radiations affect the growth of phytoplankton and as a result ocean food chain is disturbed and it even damages the fish productivity.
Question 38.
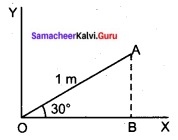
(a) (i) Calculate the uncertainty in the position of an electron, if the uncertainty in its velocity is 5.7 x 105 ms-1.
(ii) What is the mass of glucose (C6 H12 O6) in it one litre solution which is isotonic with 6 gl-1 of urea (NH2 CONH2)?
[OR]
![]()
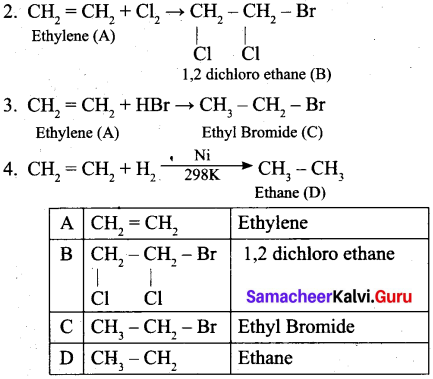
(b) (i) An organic compound (A) of molecular formula C2H6O, on heating with conc.H2SO4 gives compound (B). (B) on treating with cold dilute alkaline KMnO4 gives compound (C). Identify (A), (B) and (C) and explain the reactions.
(ii) A simple aromatic hydrocarbon (A) reacts with chlorine to give compound (B). Compound (B) reacts with ammonia to give compound (C) which undergoes carbylamine reaction. Identify (A), (B) and (C) arid explain the reactions.
(a) (i) Uncertainty in velocity = Δv = 5.7 x 105 ms-1.
Mass of an electron = m = 9.1 x 10-31 kg.
Uncertainty in position = Δx = ?
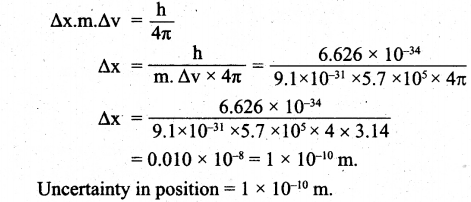
(ii) Osmotic pressure of urea solution (π1) = CRT
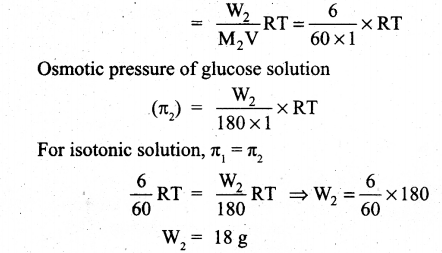
![]()
(b)
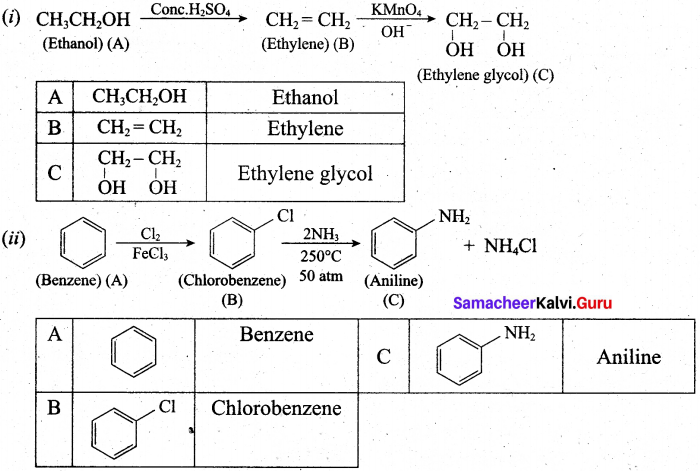
![]()