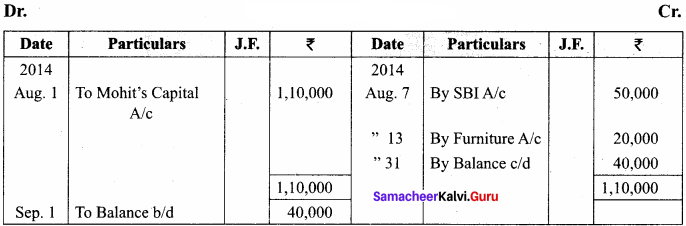
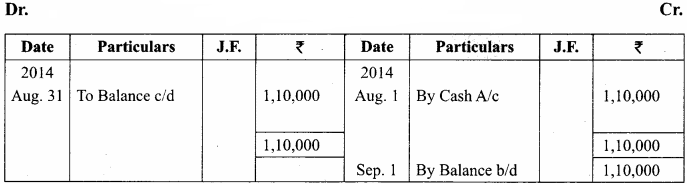
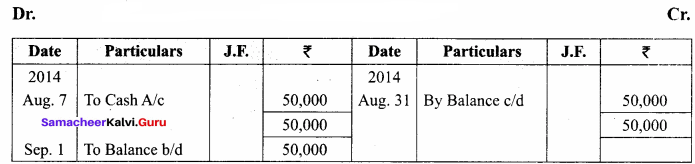
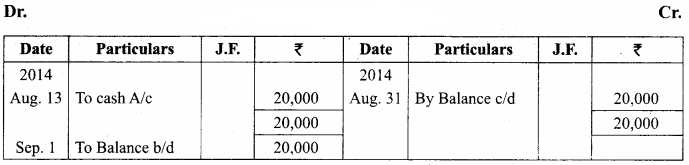
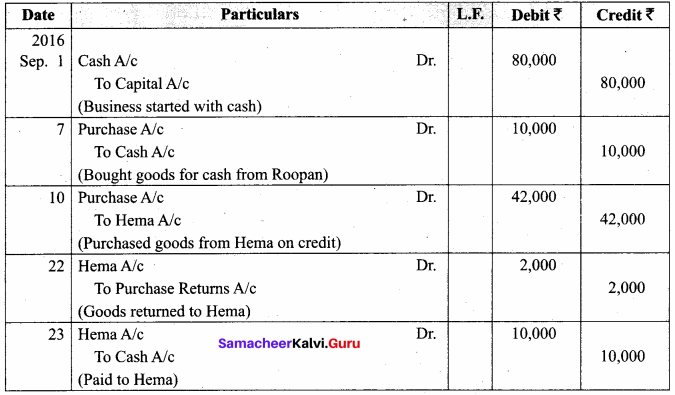
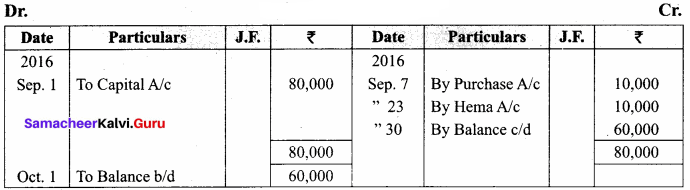
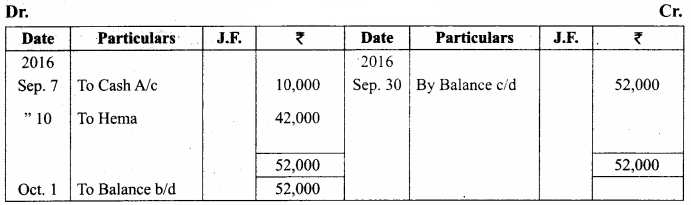
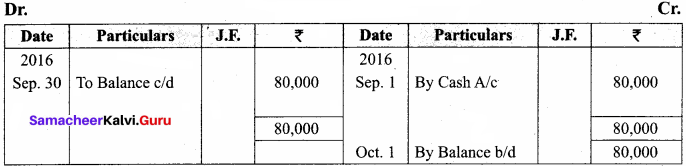
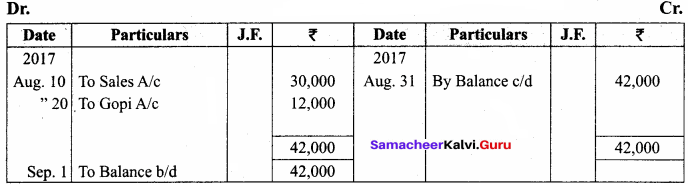
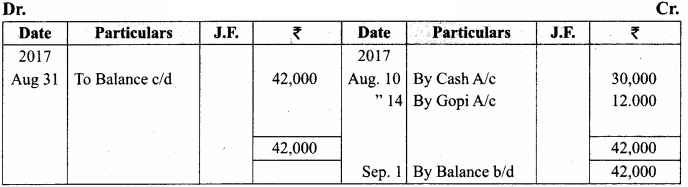
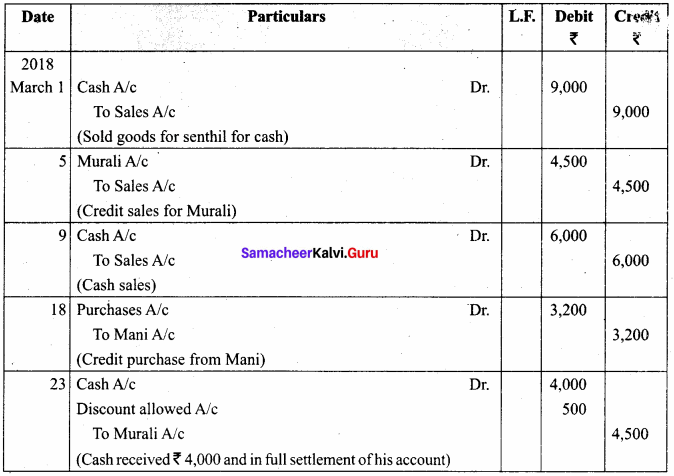
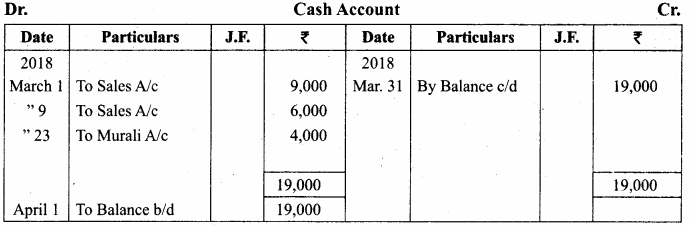
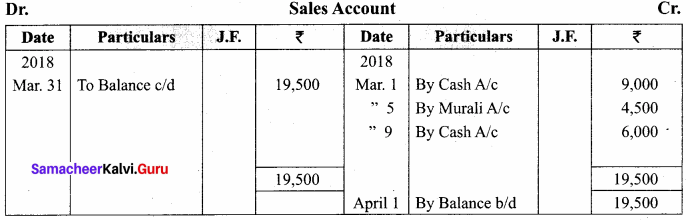
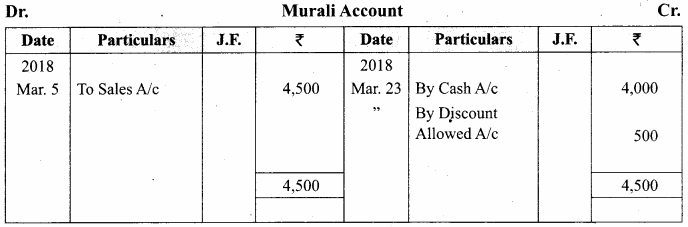
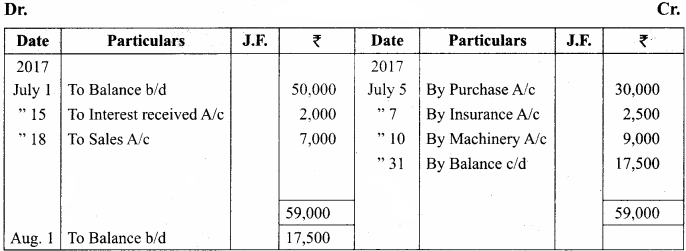
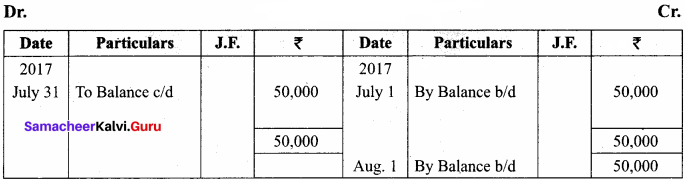
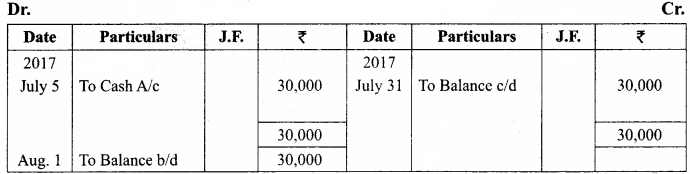
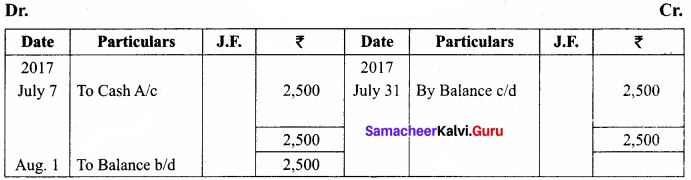
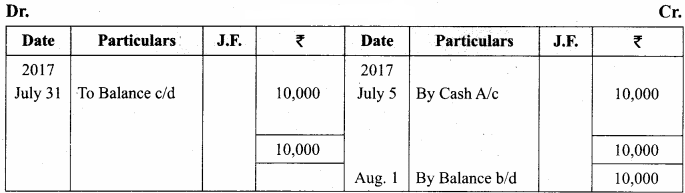
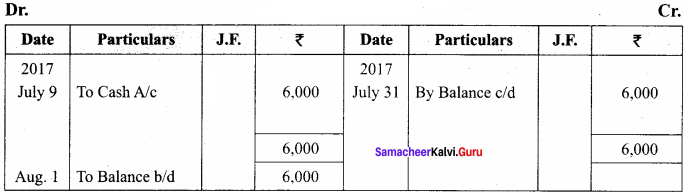
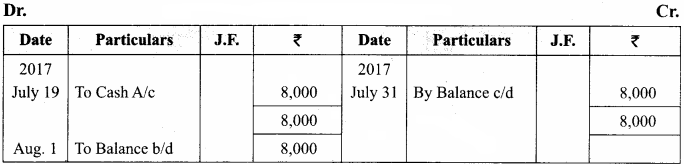
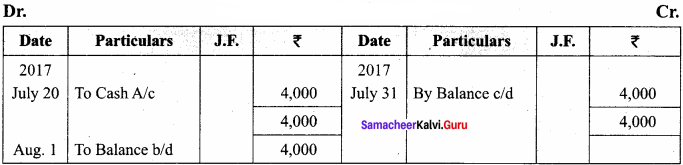
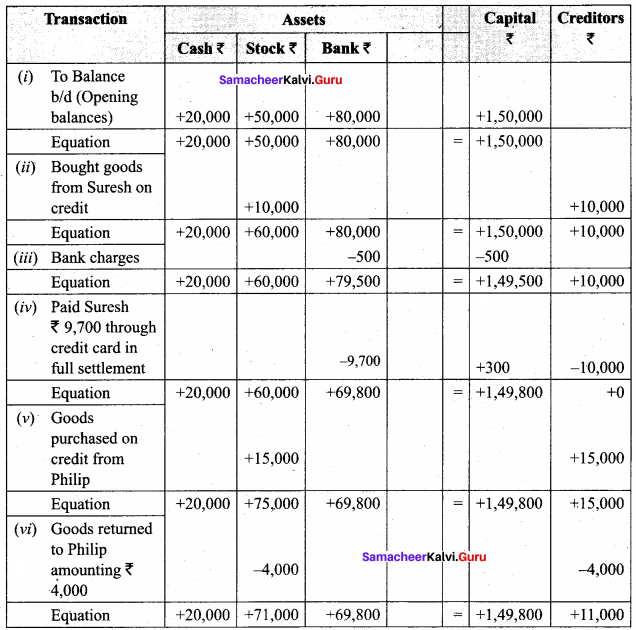
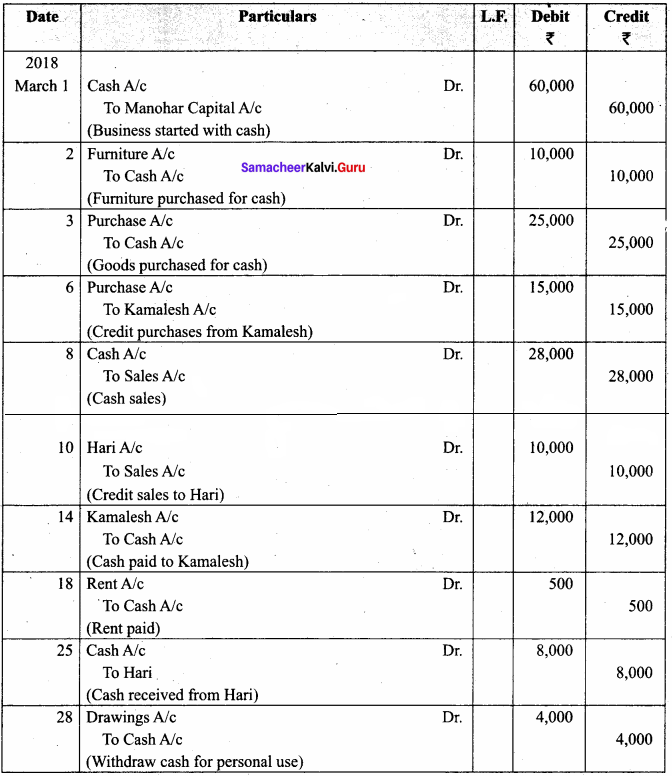
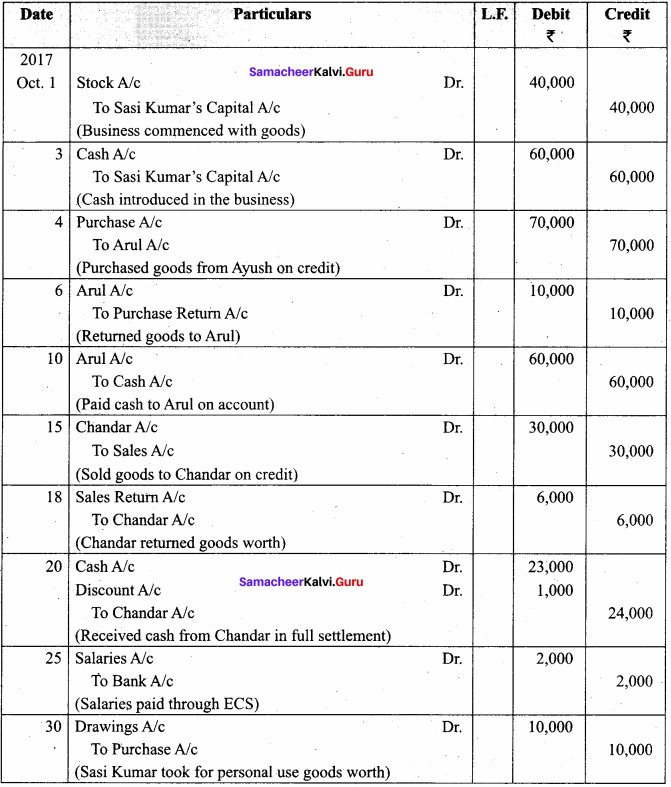
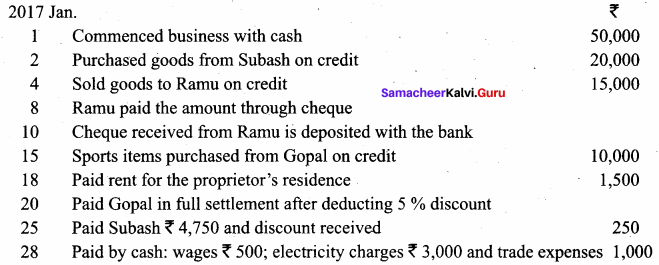
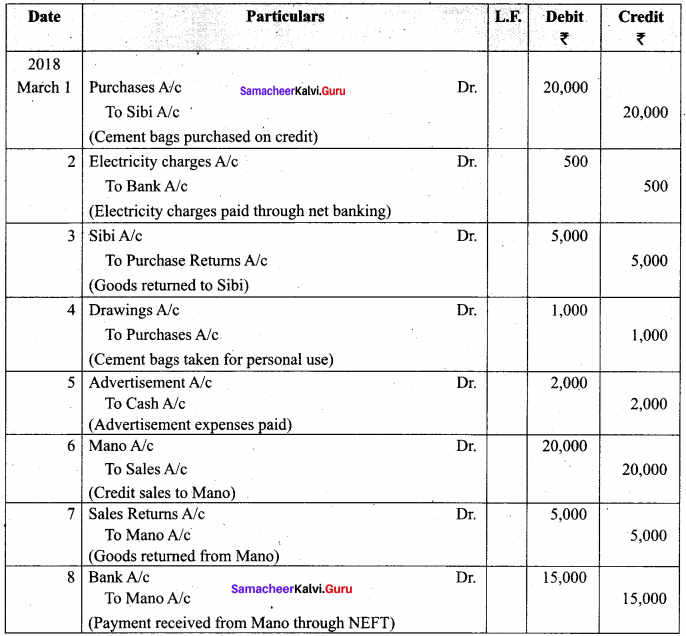
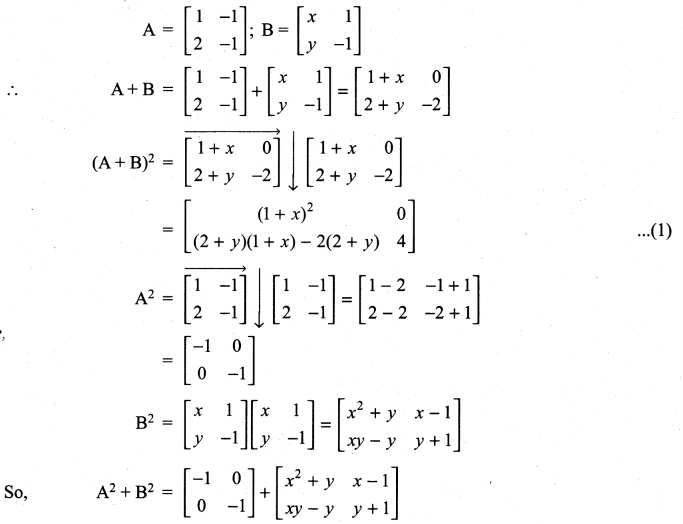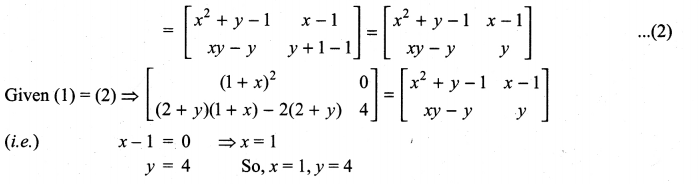You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 7 Matrices and Determinants Ex 7.1
11th Maths Exercise 7.1 Answers Question 1.
Construct an m × n matrix A = [aij], where aij is given by
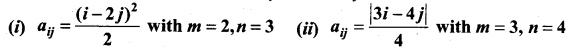
Solution:
(i) aij = \(\frac{(i-2 j)^{2}}{2}\)
Here m = 2, n = 3
So we have to construct a matrix of order 2 × 3
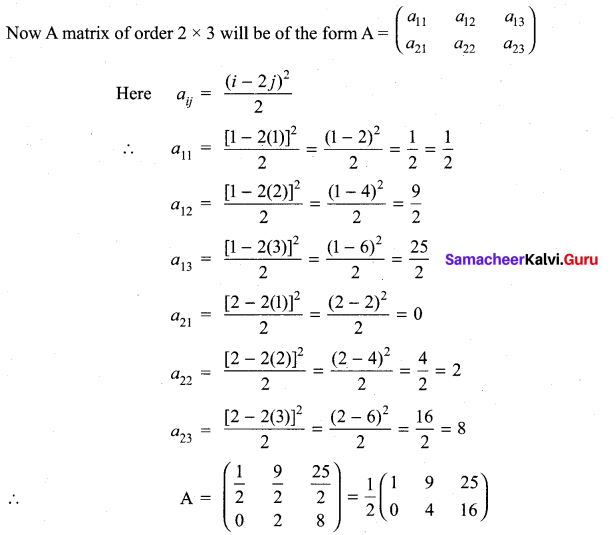
(ii) Here m = 3 and n = 4
So we have to construct a matrix order 3 × 4
The general form of a matrix of order 3 × 4 will be
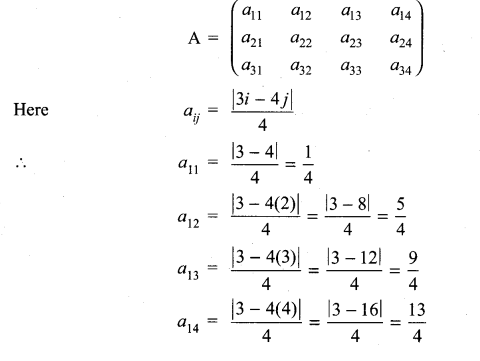
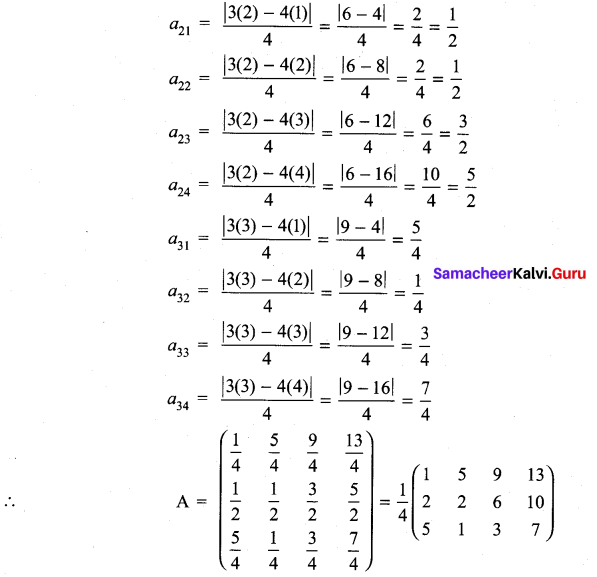
11th Maths Exercise 7.1 Question 2.
Find the values of p, q, r and s if
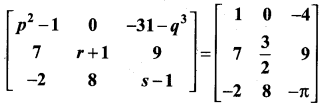
Solution:
When two matrices (of same order) are equal then their corresponding entries are equal.
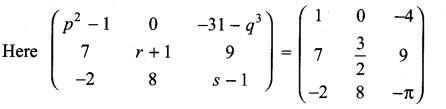
⇒ p2 – 1 = 1
⇒ p2 = 1 + 1 = 2
p = ± \(\sqrt{2}\)
-31 – q3 = -4
-q3 = -4 + 31 = 27
q3 = -27 = (-3)3
⇒ q = -3
r + 1 = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
⇒ r = \(\frac{3}{2}\) – 1 = \(\frac{3-2}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
s – 1 = π
⇒ s = – π + 1 (i.e.,) s = 1 – π
So, p = ± \(\sqrt{2}\), q = -3, r = 1/2 and s = 1 – π
11th Maths Matrices And Determinants Solutions Question 3.
Determine the value of x + y if 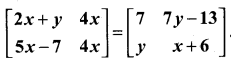
Solution:
\(\left[\begin{array}{cc}{2 x+y} & {4 x} \\ {5 x-7} & {4 x}\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{cc}{7} & {7 y-13} \\ {y} & {x+6}\end{array}\right]\)
⇒ 2x + y = 7 ………….. (1)
4x = 7y – 13 ………….. (2)
5x – 7 = y …………… (3)
4x = x + 6 ……………. (4)
from (4) 4x – x = 6
3x = 6 ⇒ x = \(\frac{6}{3}\) = 2
Substituting x = 2 in (1), we get
2(2) + y = 7 ⇒ 4 + y = 7 ⇒ y = 7 – 4 = 3
So x = 2 and y = 3
∴ x + y = 2 + 3 = 5
11th Maths 7.1 Exercise Question 4.
Determine the matrices A and B if they satisfy
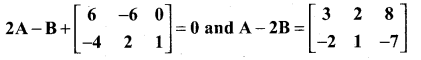
Solution:
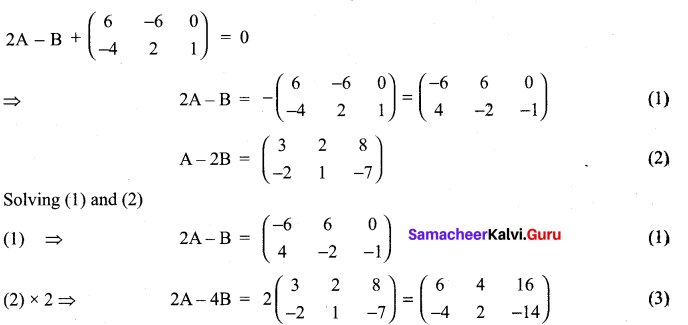

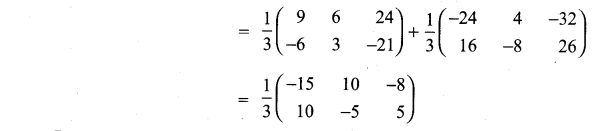
11th Maths Volume 2 Exercise 7.1 Question 5.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll}{\mathbf{1}} & {\boldsymbol{a}} \\ {\mathbf{0}} & {\mathbf{1}}\end{array}\right]\), then compute A4
Solution:
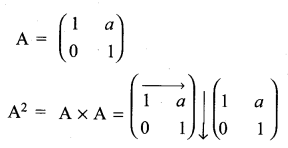
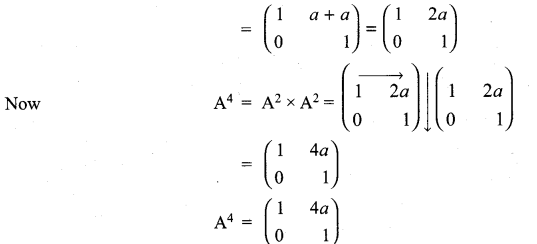
11th Maths Matrix Solutions Question 6.
Consider the matrix Aα = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}{\cos \alpha} & {-\sin \alpha} \\ {\sin \alpha} & {\cos \alpha}\end{array}\right]\)
(i) Show that AαAβ = Aα + β.
(ii) Find all possible real values of satisfying the condition Aα + ATα = 1.
Solution:
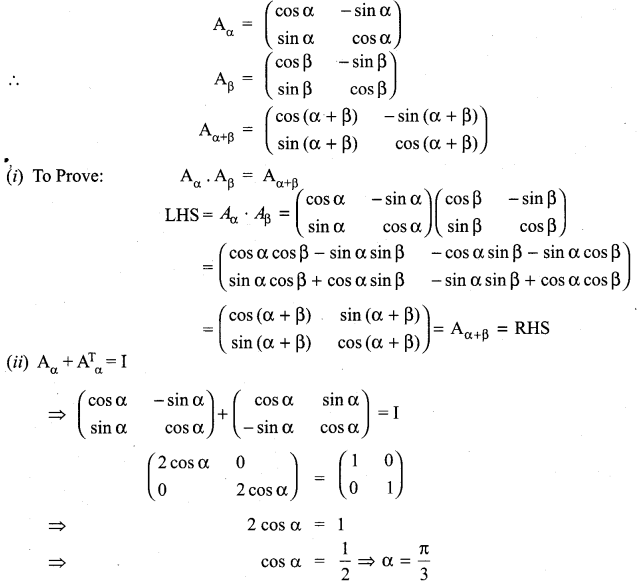
General solution is α = 2nπ + \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), n ∈ Z
11th Maths Exercise 7.1 Tamil Medium Question 7.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr}{4} & {2} \\ {-1} & {x}\end{array}\right]\) such that (A – 2I) (A – 3I) = 0, find the value of x.
Solution:
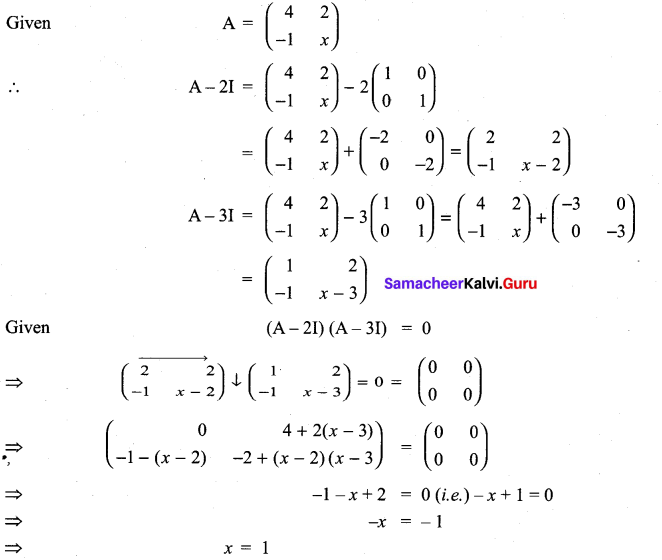
11th Maths Matrices And Determinants Pdf Question 8.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}{\mathbf{1}} & {\mathbf{0}} & {\mathbf{0}} \\ {\mathbf{0}} & {\mathbf{1}} & {\mathbf{0}} \\ {\boldsymbol{a}} & {\boldsymbol{b}} & {-\mathbf{1}}\end{array}\right]\), show that A2 is a unit matrix.
Solution:
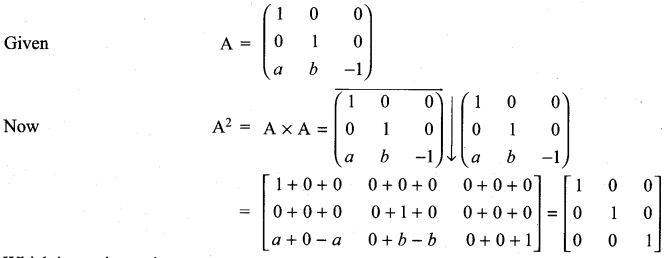
Exercise 7.1 Class 11 Maths State Board Question 9.
If A = 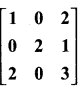 and A3 – 6A2 + 7A + KI = 0, find the value of k.
and A3 – 6A2 + 7A + KI = 0, find the value of k.
Solution:
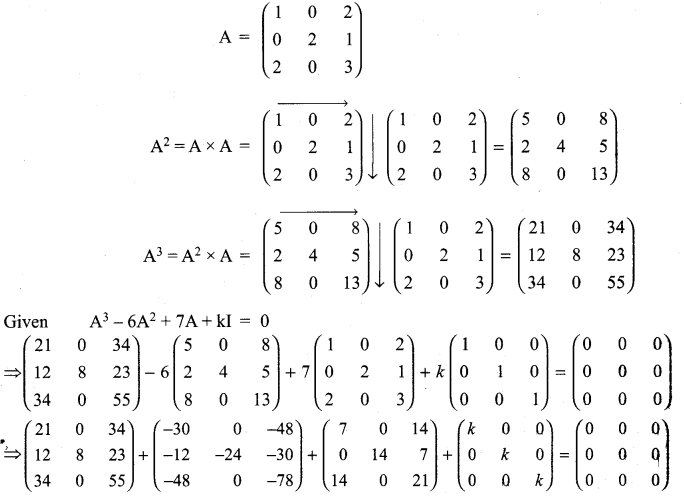
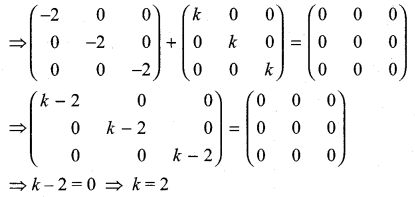
11th Maths 7.1 Question 10.
Give your own examples of matrices satisfying the following conditions in each case:
(i) A and B such that AB ≠ BA.
(ii) A and B such that AB = 0 = BA, A ≠ 0 and B ≠ 0.
(iii) A and B such that AB = 0 and BA ≠ 0.
Solution:
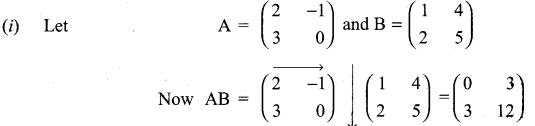
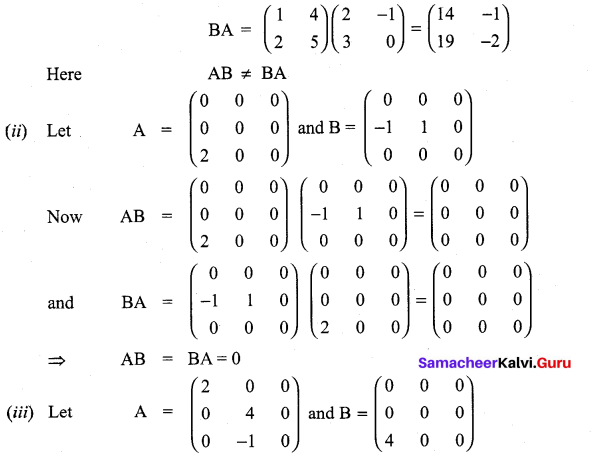
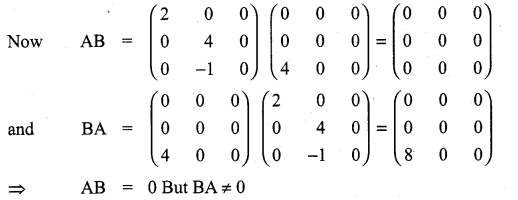
11th Maths Matrix And Determinants Question 11.
Show that f(x) f(y) = f(x + y), where f(x) = 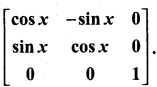
Solution:
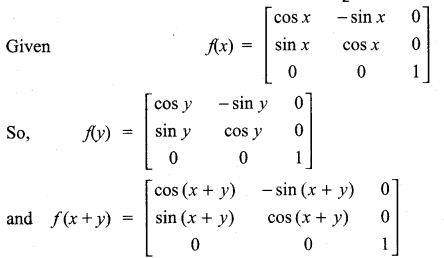
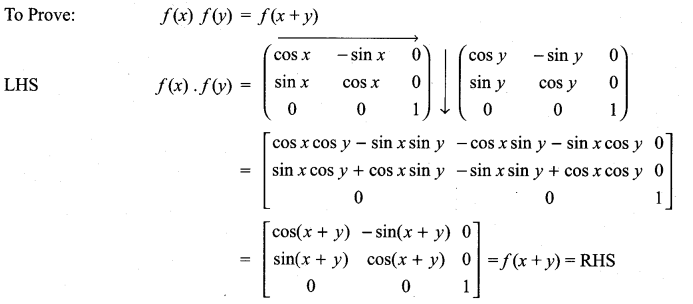
11th Maths Exercise 7.1 In Tamil Question 12.
If A is a square matrix such that A2 = A, find the value of 7A – (I + A)3.
Solution:
Given A2 = A
So 7A – (I + A)3 = 7A – (I + 3A + 3A2 + A3]
= 7A – I – 3A – 3 A2 – A3
Given A2 = A
7A – I – 3A – 3A – A3 = -I + A – A3
= -I + A – (A2 × A)
= -I + A – (A × A) = -I + A – A2
= -I + A – A = -I
So the value of 7A – (I + A)3 = -I.
Question 13.
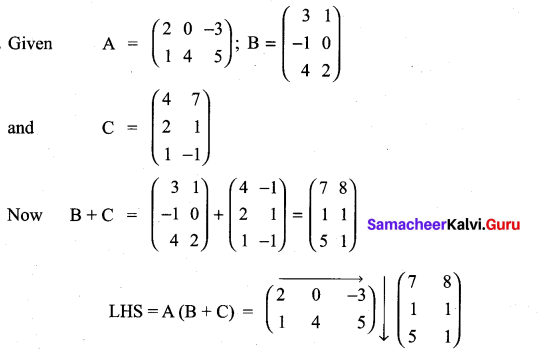
Verify the property A (B + C) = AB + AC, when the matrices A, B and C are given by
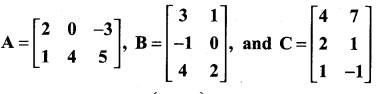
Solution:
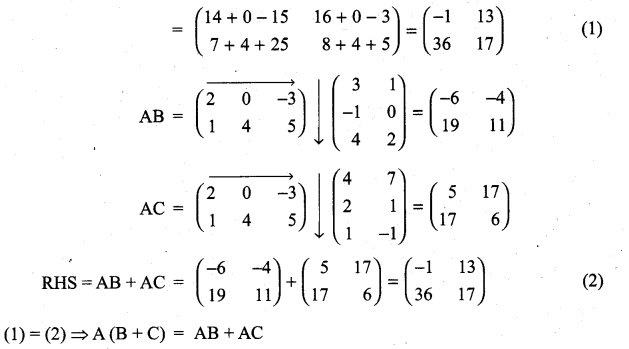
11th Maths Volume 2 Exercise 7.1 Answers Question 14.
Find the matrix A which satisfies the matrix relation 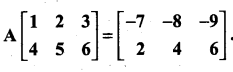
Solution:
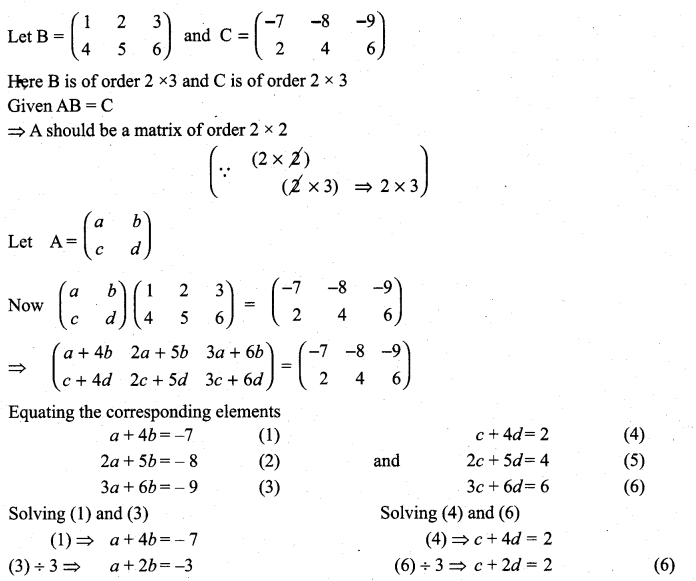

![]()
11 Maths Exercise 7.1 Question 15.
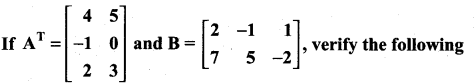
(i) (A + B)T = AT + BT = BT + AT
(ii) (A – B)T = AT – BT
(iii) (BT)T = B.
Solution:
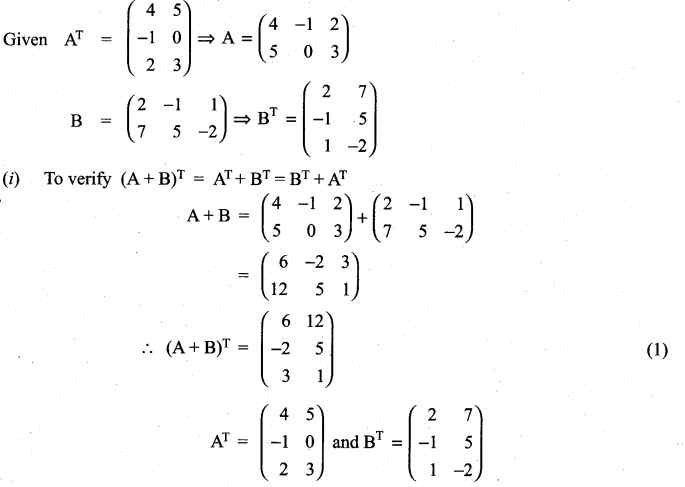
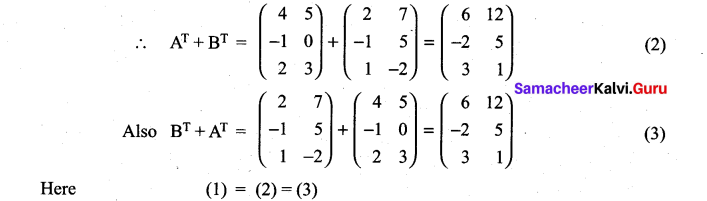
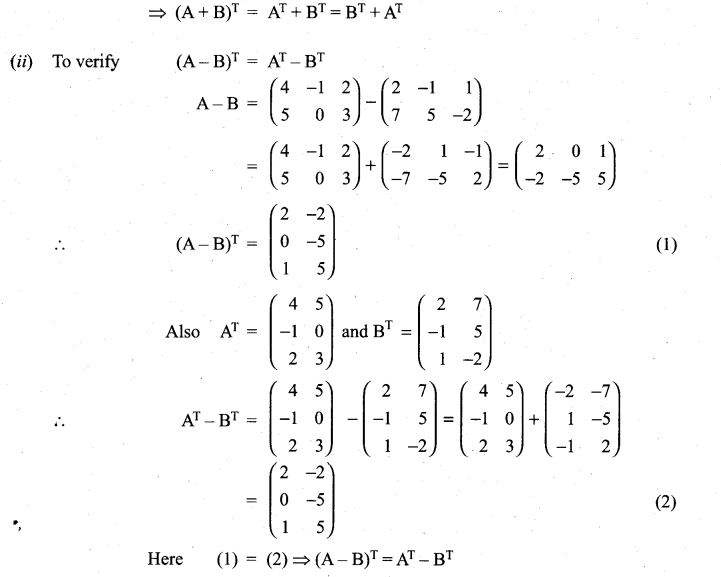
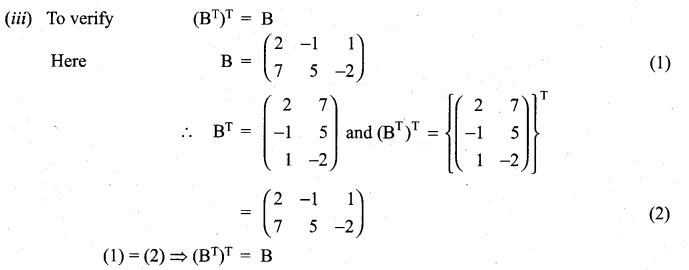
11th Maths 7th Chapter Question 16.
If A is a 3 × 4 matrix and B is a matrix such that both ATB and BAT are defined, what is the order of the matrix B?
Sol.
A is a matrix of order 3 × 4
So AT will be a matrix of order 4 × 3
AT B will be defined when B is a matrix of order 3 × n
BAT will be defirted when B is of order m × 4
from (1) and (2) we see that B should be a matrix of order 3 × 4
Question 17.
Express the following matrices as the sum of a symmetric matrix and a skew-symmetric matrix:

Solution:
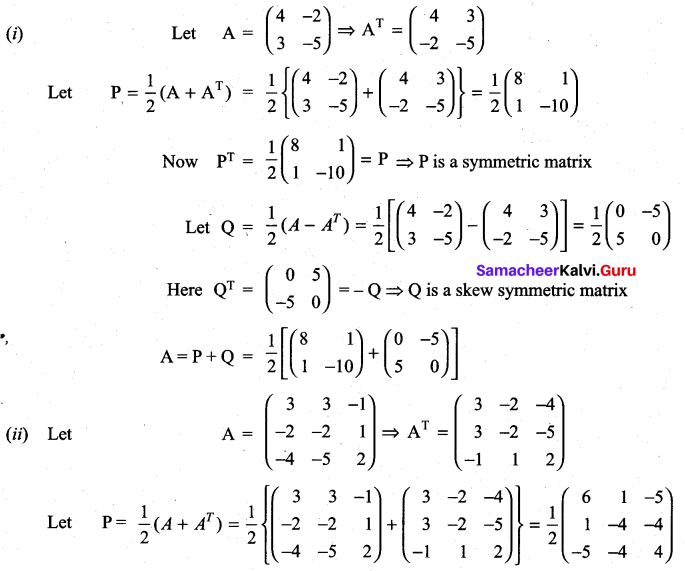
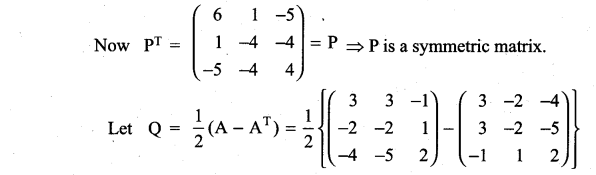
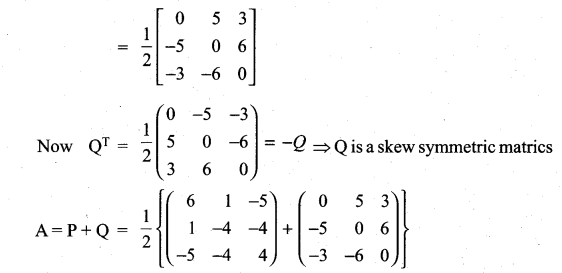
Matrices And Determinants Class 11 State Board Solutions Question 18.
Find the matrix A such that 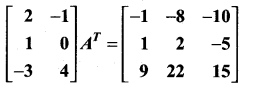
Solution:
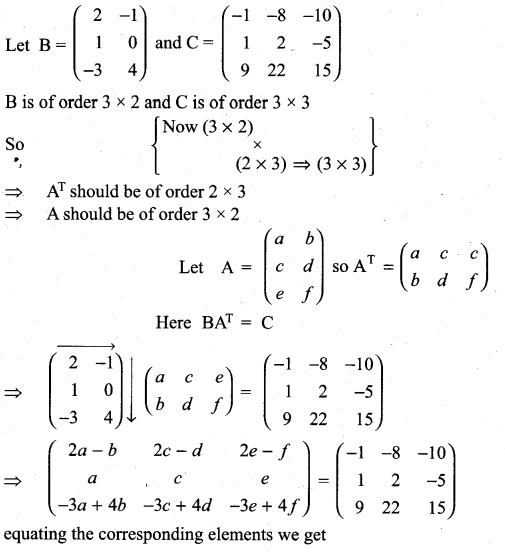
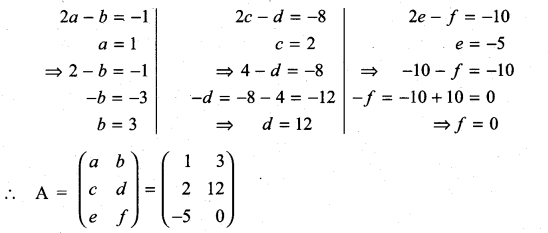
11th Maths Determinants Solutions Question 19.
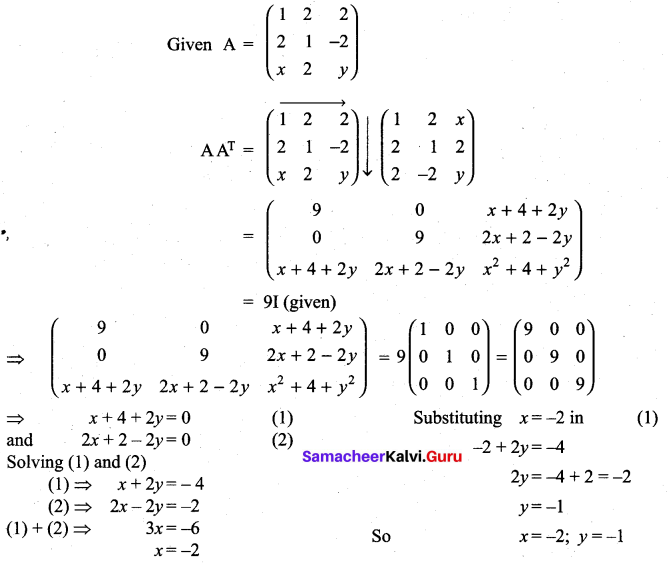
If A = 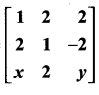 is a matrix such that AAT = 9I, find the values of x and y.
is a matrix such that AAT = 9I, find the values of x and y.
Solution:
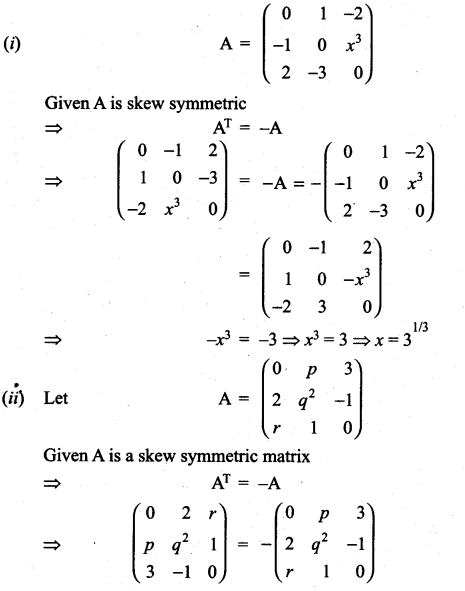
Question 20.

Solution:
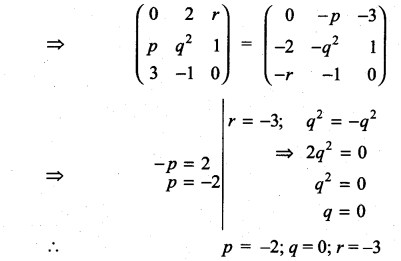
Class 11th Maths Exercise 7.1 Question 21.
Construct the matrix A = [aij]3×3, where aij = i- j. State whether A is symmetric or skew- symmetric.
Solution:
Given A is a matrix of order 3 × 3
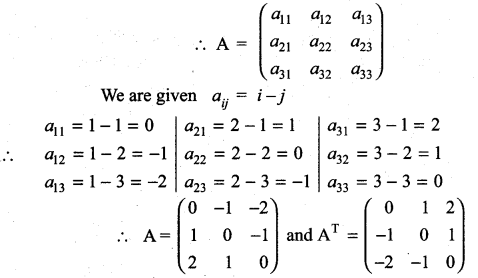
Here AT = -A
⇒ A is skew symmetric
Matrices And Determinants Class 11 Solutions Pdf Question 22.
Let A and B be two symmetric matrices. Prove that AB = BA if and only if AB is a symmetric matrix.
Solution:
Let A and B be two symmetric matrices
⇒ AT = A and BT = B …………….. (1)
Given that AB = BA (2)
To prove AB is symmetric:
Now (AB)T = BTAT = BA
(from(1)) But (AB)T = AB by ………….. (2)
⇒ AB is symmetric.
Conversely let AB be a symmetric matrix.
⇒ (AB)T = AB
i.e. BTAT = AB
i.e. BA = AB (from (1))
⇒ AB is symmetric
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Question 23.
If A and B are symmetric matrices of same order, prove that
(i) AB + BA is a symmetric matrix.
(li) AB – BA is a skew-symmetric matrix.
Solution:
Given A and B are symmetric matrices
⇒ – AT = A and BT = B
(i) To prove AB + BA is a symmetric matrix.
Proof: Now (AB + BA)T = (AB)T + (BA)T = BTAT + ATBT
= BA + AB = AB + BA
i.e. (AB + BA)T = AB + BA
⇒ (AB + BA) is a symmetric matrix.
(ii) To prove AB – BA is a skew symmetric matrix.
Proof: (AB – BA)T = (AB)T – (BA)T = BTAT – ATBT = BA – AB
i.e. (AB – BA)T = – (AB – BA)
⇒ AB – BA is a skew symmetric matrix.
11th Maths 7th Lesson Question 24.
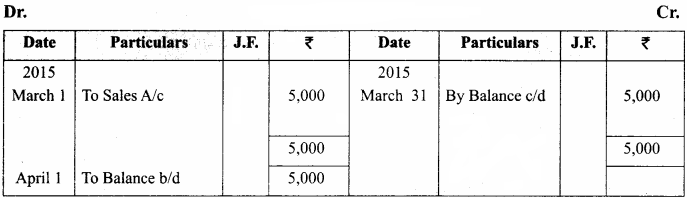
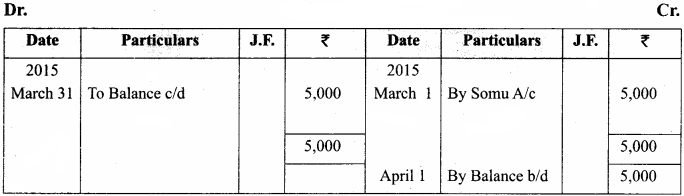
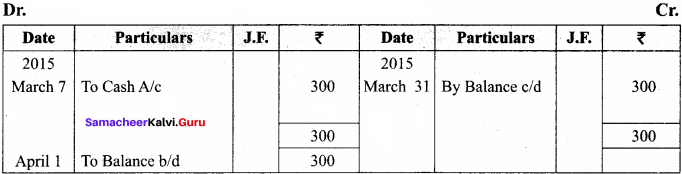
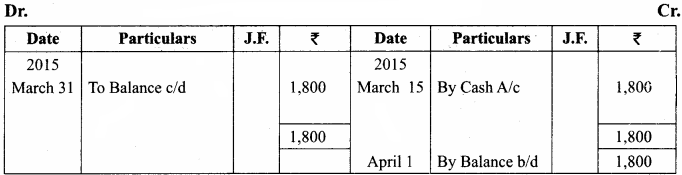
A shopkeeper in a Nuts and Spices shop makes gift packs of cashew nuts, raisins and almonds.
Pack I contains 100 gm of cashew nuts, 100 gm of raisins and 50 gm of almonds. Pack-II contains 200 gm of cashew nuts, 100 gm of raisins and 100 gm of almonds. Pack-III contains 250 gm of cashew nuts, 250 gm of raisins and 150 gm of almonds. The cost of 50 gm of cashew nuts is ₹ 50, 50 gm of raisins is ₹ 10, and 50 gm of almonds is₹ 60. What is the cost of each gift pack?
Solution:
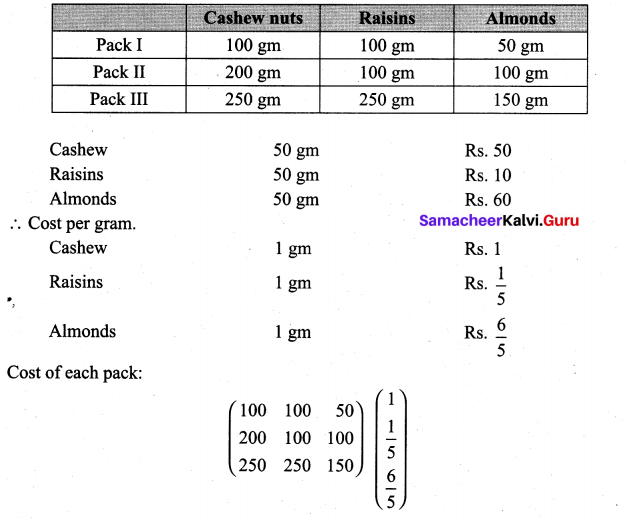

Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 7 Matrices and Determinants Ex 7.1 Additional Problems
Class 11 Maths Ex 7.1 Solutions Question 1.
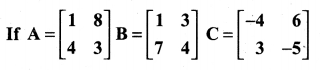
Prove that (i) AB ≠ BA
(ii) A(BC) = (AB) C
(iii) A(B + C) = AB + AC
(iv) AI = IA = A
Solution:

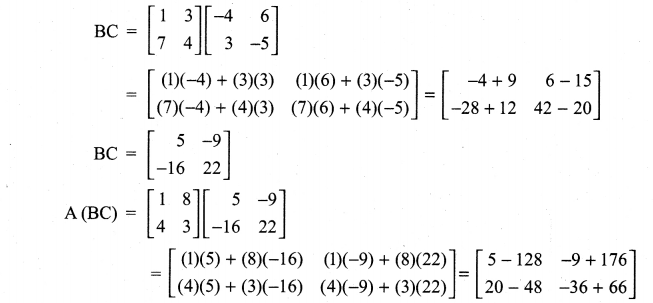
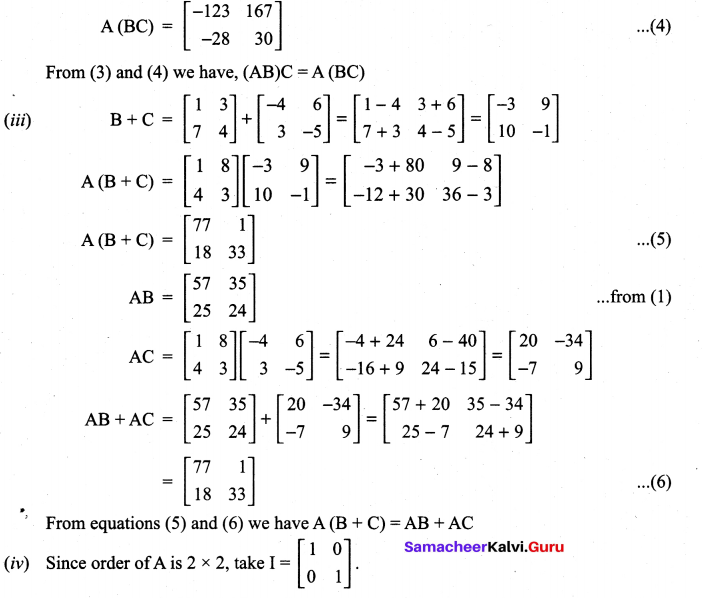
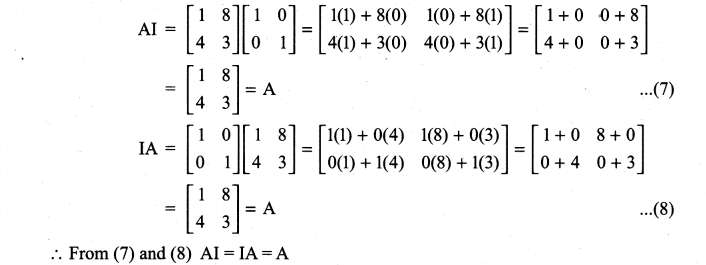
Class 11th Maths Chapter 7 Exercise 7.1 Question 2.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll}{2} & {3} \\ {4} & {5}\end{array}\right]\) find A2 – 7A – 2I.
Solution:
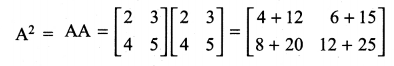
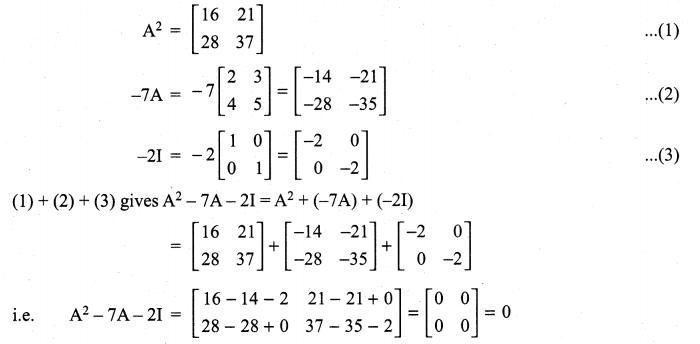
11th Maths Guide Question 3.
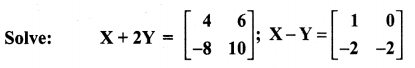
Solution:

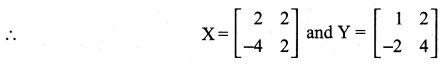
11th Maths Guide Question 4.
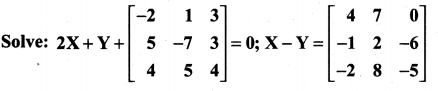
Solution:
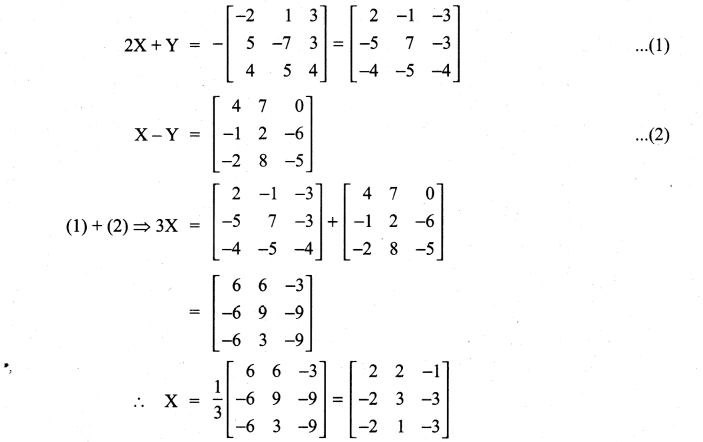
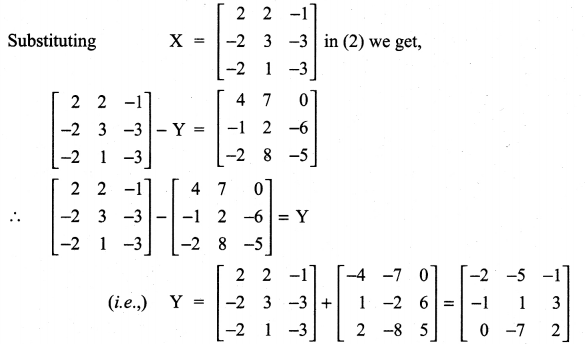
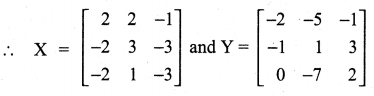
Question 5.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr}{3} & {-5} \\ {-4} & {2}\end{array}\right]\), show that A2 – 5A – 14I = 0 where I is the unit matrix of order 2.
Solution:
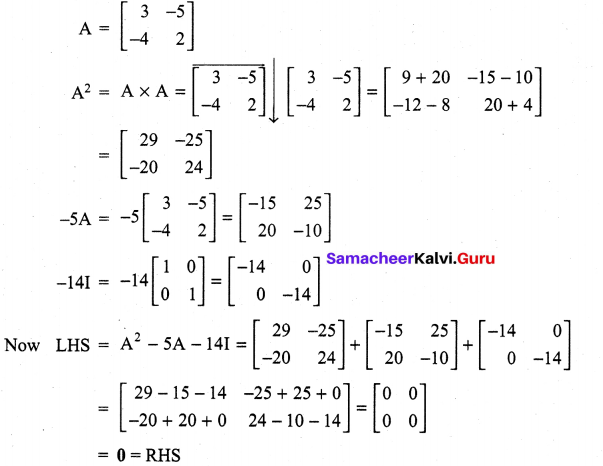
Question 6.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr}{3} & {-2} \\ {4} & {-2}\end{array}\right]\), find k so that A2 = kA – 2I
Solution:
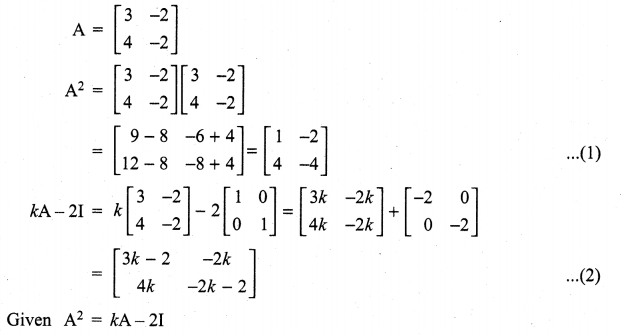
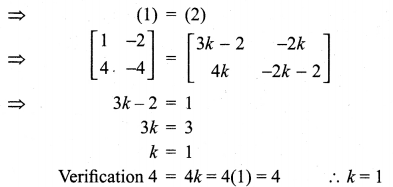
Question 7.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll}{1} & {2} & {2} \\ {2} & {1} & {2} \\ {2} & {2} & {1}\end{array}\right]\), show that A2 – 4A – 5I = 0
Solution:
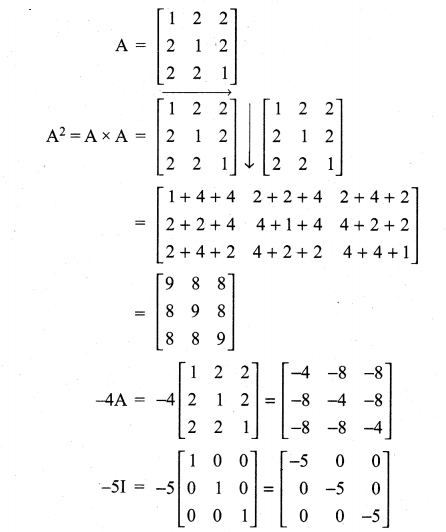
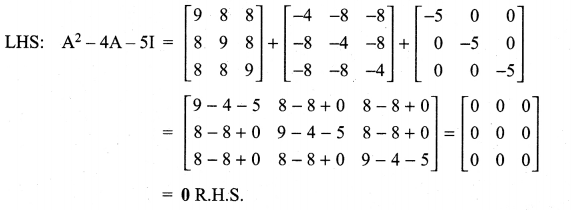
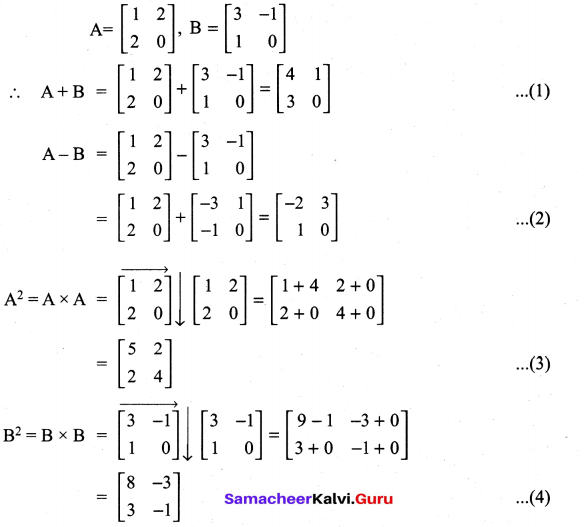
Question 8.
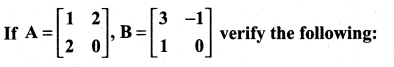
Solution:
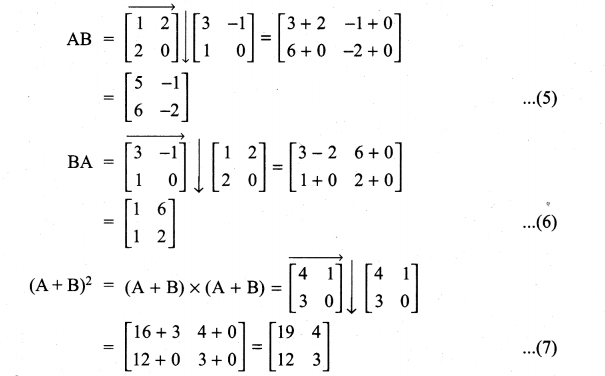
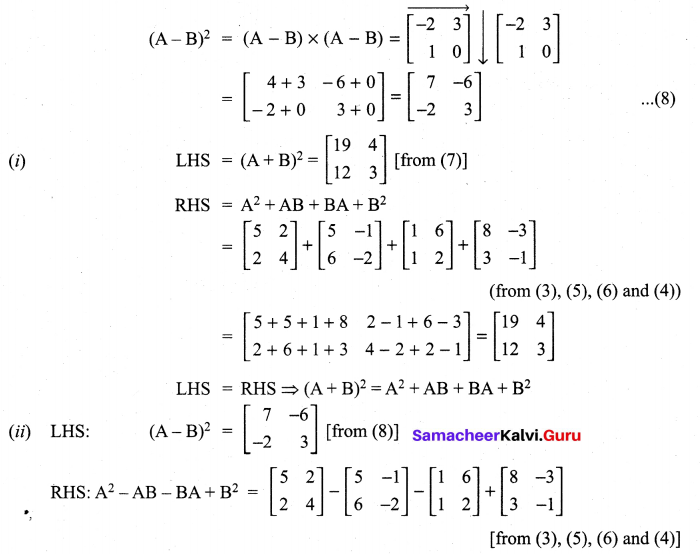
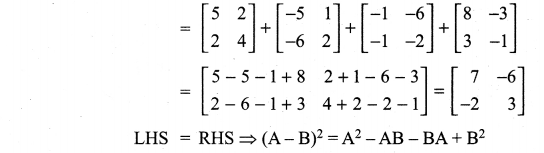
Question 9.
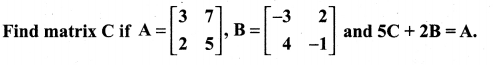
Solution:
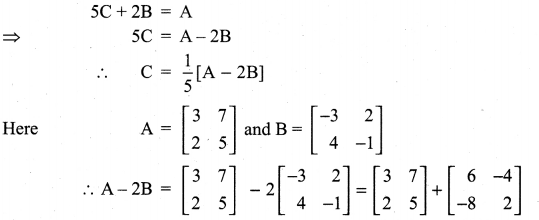
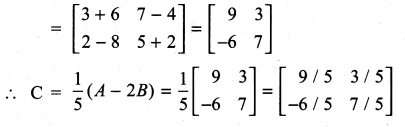
Question 10.
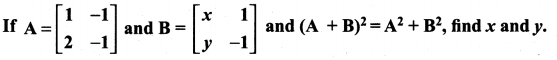
Solution: