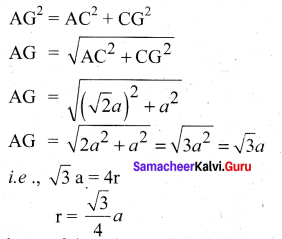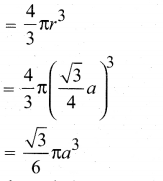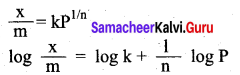Students can Download Tamil Nadu 12th Chemistry Model Question Paper 3 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 12th Chemistry Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 12th Chemistry Model Question Paper 3 English Medium
Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever: applicable
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately
- Question numbers 1 to 15 in Part I are Multiple choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer
- Question numbers 16 to 24 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are lo be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 25 to 33 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are lo be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 34 to 38 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are lo be answered in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
Part-I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [15 × 1 = 15]
Question 1.
Gibbs free energy change for the electrolysis process is expressed by
(a) ∆G° = – nFE°
(b) ∆G° = – nF
(c) ∆G° = – nE°
(d) ∆G° = nFE°
Answer:
(a) ∆G° = – nFE°
Question 2.
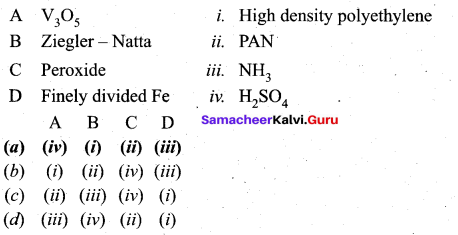
Match items in column -II with the items of column – II and assign the correct code.
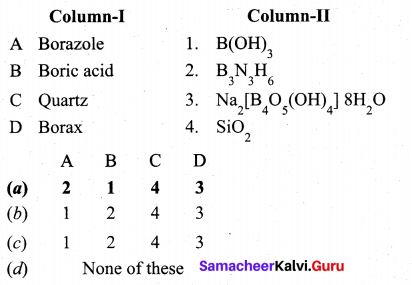
Answer:
(a)
A – 2
B – 1
C – 4
D – 3
![]()
Question 3.
Shape of ClF3 is ……………..
(a) Linear
(b) T-shape
(c) Pyrimidal
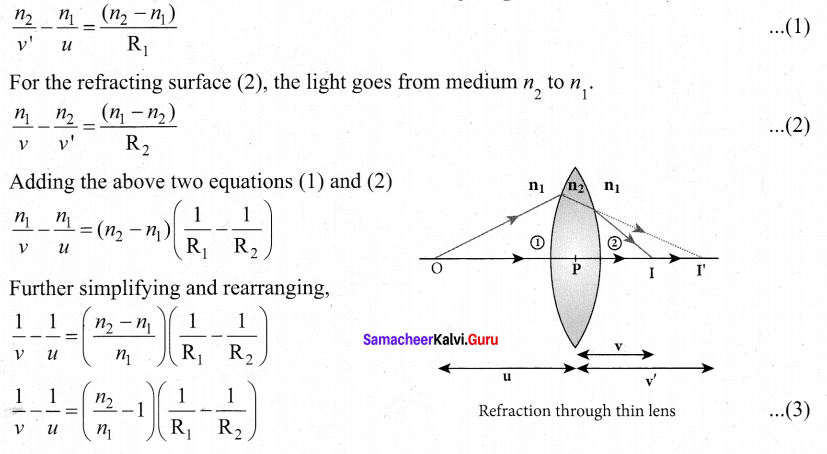
(d) Square planar
Answer:
(b) T-shape
Question 4.
The catalytic behaviour of transition metals and their compounds is ascribed mainly due to ……………..
(a) their magnetic behaviour
(b) their unfilled d orbitals
(c) their ability to adopt variable oxidation states
(d) their chemical reactivity
Answer:
(c) their ability to adopt variable oxidation states
Question 5.
Which one of the following pairs represents linkage isomers?
(a) [CU(NH3)4] [PtCl4] and [Pt(NH3)4] [CuCl4]
(b) [CO(NH3)5(NO3)]SO4 and [CO(NH3)5(ONO)]
(c) [CO(NH3)4(NCS)2]Cl and [CO(NH3)4(SCN)2]Cl
(d) both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(c) [CO(NH3)4(NCS)2]Cl and [CO(NH3)4(SCN)2]Cl’
Question 6.
Each atom in the comer of the cubic unit cell is shared by how many unit cells?
(a) 8
(b) 6
(c) 1
(d) 12
Answer:
(a) 8
![]()
Question 7.
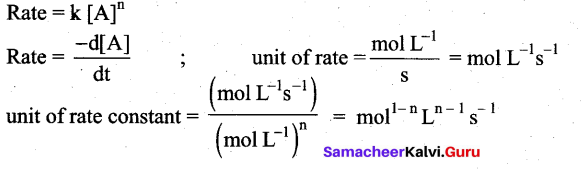
The rate constant of a reaction is 5.8 × 10-2 s-1 . The order of the reaction is ……………..
(a) First order
(b) zero order
(c) Second order
(d) Third order
Answer:
(a) First order
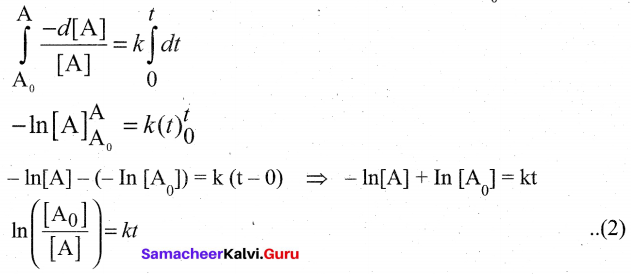
Solution:
The unit of rate constant is s”1 and it indicates that the reaction is first order.
Question 8.
The hydrogen ion concentration of a buffer solution consisting of a weak acid and its salts is given by…………………
(a) [H+] = \(\frac{\mathbf{K}_{\mathrm{a}}[\mathrm{a} \mathrm{cid}]}{[\mathrm{salt}]}\)
(b) [H+] = Ka[salt]
(c) [H+] = Ka[acid]
(d) [H+] = \(\frac{\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{a}}[\mathrm{salt}]}{[\text { acid }]}\)
According to Henderson equation
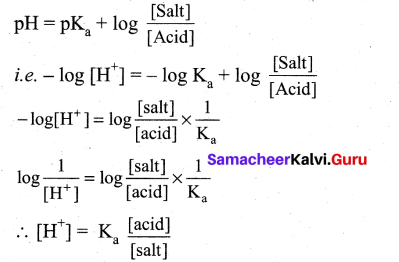
Question 9.
Kohlrausch’s law is applied to calculate ……………..
(a) molar conductance at infinite dilution of a weak electrolyte
(b) degree of dissociation of weak electrolyte
(c) solubility of a sparingly soluble salt
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 10.
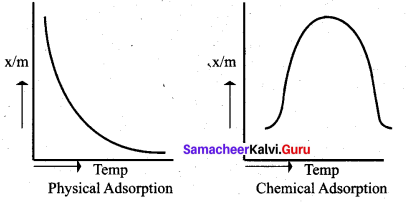
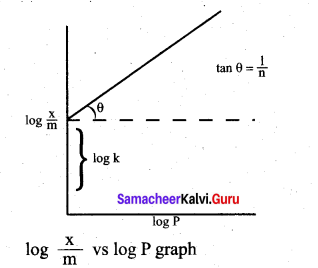
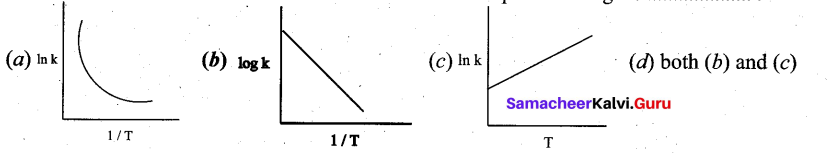
For freudlich isotherm a graph of \(\log \frac{x}{\mathrm{m}}\) is plotted against log P. The slope of the line and its y – axis intercept respectively corresponds to ………
(a) 1/n , k
(b) log 1/n ,k
(c) 1/n , log k
(d) log 1/n, log k
Answer:
(c) 1/n , log k
Solution:
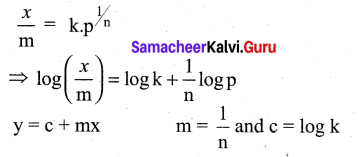
Question 11.
]The reaction of sodium methoxide with ethyl bromide follows
(a) SN1 mechanism
(b) SN2 mechanism
(c) E1 reaction
(d) E2 reaction
Answer:
(b) SN2 mechanism
Question 12.
In which of the following reactions new carbon – carbon bond is not formed?
(a) Aldol condensation
(b) Friedel craft reaction
(c) Kolbe’s reaction
(d) Wolf kishner reduction
Answer:
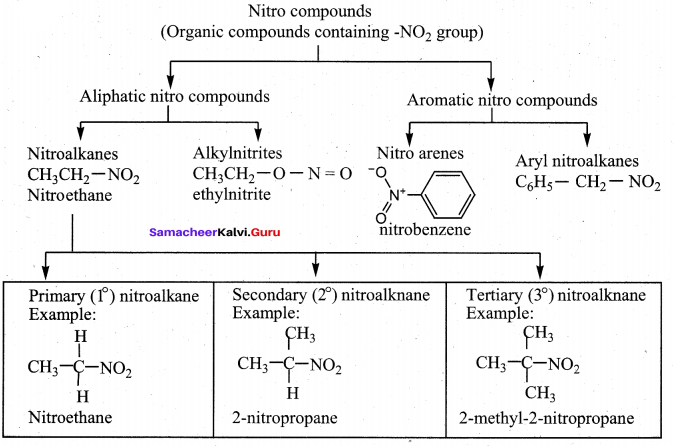
(d) Wolf kishner reduction
![]()
Question 13.
The reagent used to convert Nitromet’nane to methyl amine is
(a) Zn/NH4Cl
(b) Sn/HCl
(c) H2SO5
(d) H2S2O8
Answer:
(b) Sn/HCl
Question 14.
If one strand of the DNAhas the sequence ‘ATGCTTGA’, then the sequence of complementary
strand would be
(a) TACGAACT
(b) TCCGAACT
(c) TACGTACT
(d) TACGRAGT
Answer:
(a) TACGAACT
Question 15.
The ratio between the maximum tolerated dose of a drug and a minimum curative dose is called ……………..
(a) iso electric point
(b) therapeutic index
(c) critical point
(d) iso thermal point
Answer:
(b) therapeutic index
Part – II
Answer any six questions. Question No. 20 is compulsory. [6 × 2 = 12]
Question 16.
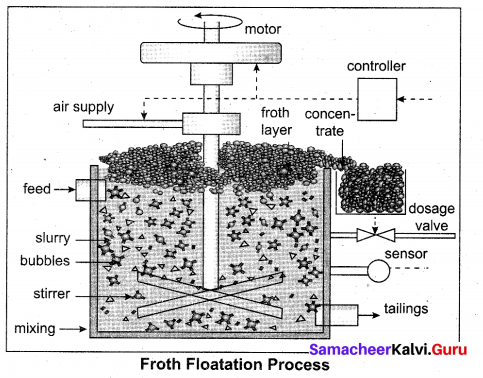
Describe the role of Sodium cyanide in froth floatation.
Answer:
- Sulphide ores are concentrated by the froth floatation process.
- Depressants are used to prevent certain type of particles from forming the froth.
- NaCN act as a depressant to separate ZnS from PbS.
Question 17.
Which is more stable? Fe3+ or Fe2+ – explain.
Fe (Z = 26) Fe → Fe2+ + 2e–
Fe → Fe3+ + 3e–
Fe2+ [Number of electrons 24]
Electronic configuration = [Ar]3d6
Fe3+ [Number of electrons 23]
Electronic configuration = [Ar]3d5
Among Fe3+ and Fe2+, Fe3+ is more stable due to half filled d-orbital. This can be explained by Aufbau principle. Half filled and completely filled d-orbitals are more stable than partially filled d-orbitals. So Fe3+ is more stable than Fe2+ .
Question 18.
Write briefly about the applications of coordination compounds in volumetric analysis.
Answer:
Hardness of water is due to the presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+ions in water. EDTA forms stable complexes with Ca2+ and Mg2+ . So the total hardness of water can be estimated by simple volumetric titration of water with EDTA.
Question 19.
Classify the following solids
(a) P4 (b) Brass
(c) Diamond
(d) NaCl
(e) Iodine
Answer:
(a) P4 – Molecular solid
(b) Brass – Metallic solid
(c) Diamond – Covalent solid
(d) NaCl – Ionic solid .
(e) Iodine – Molecular solid
![]()
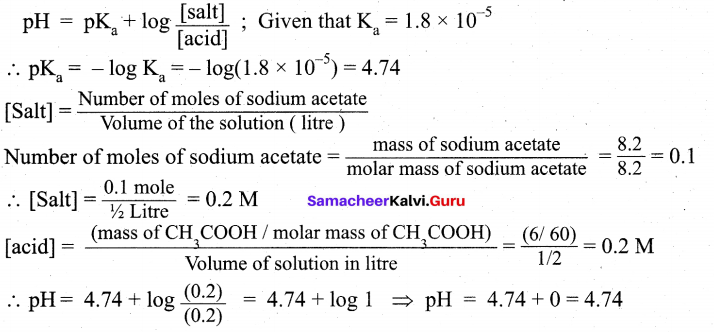
Question 20.
A lab assistant prepared a solution by adding a calculated quantity of HC1 gas 25°C to get a solution with [H3O+]= 4 × 10-5 s M. Is the solution neutral (or) acidic (or) basic.
Answer:
[H3O+] = 4 × 10-55 M
pH = -log10[H3O+]
PH = – log10 [4 × 10-5]
pH = -log10[4]-log1o[10-5]
pH = – 0.6020 – (-5) = – 0.6020 + 5
pH = 4.398
Therefore, the solution is acidic.
Question 21.
0.1M copper sulphate solution in which copper electrode is dipped at 25°C. Calculate the electrode potential of copper. [Given: E° Cu2+|Cu = 0.341
Answer:
Given that
[Cu2+] = 0.1M
E° Cu2+|Cu = 0.34
ECell = ?
Cell reaction is Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu (s)
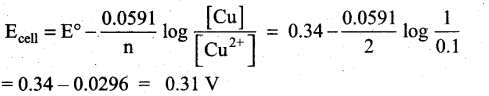
Question 22.
Can we use nucelophiles such as NH3,CH3O– for the Nucleophilic substitution of alcohols
Answer:
Increasing order of nucelophilicity,
![]()
- Higher electron density will increase the nucelophilicity.
- Negatively charged species are almost always more nucelophiles than neutral species.
- ROe has an alkyl group attached, allowing a greater amount of polarizability. This means oxygen’s lone pairs will be more readily available to reach in \(\mathrm{RO}^{\ominus}\) than in \(\mathrm{OH}^{\ominus}\) . Hence CH3O– is the better nucelophile for the nucleophilic substitution of alcohols.
- NH3 cannot act as nucelophile for the nucleophilic substitution of alcohols.
Question 23.
Aniline does not undergo Friedel – Crafts reaction. Explain.
Answer:
Aniline being a Lewis base reacts with Lewis acid AlCl3 to form a salt.
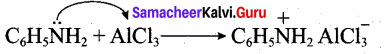
Due to the presence of a positive charge on N-atom in the salt the group – NH2 AlCl– acts as a strongly deactivating group. As a result, it reduces the electron density in the benzene ring and which inhibits the electrophilic substitution reaction. Therefore aniline does not undergo Friedel – Crafts reaction.
Question 24.
What are hormones? Give examples.
Answer:
Hormone is an organic substance that is secreted by one tissue into the blood stream and induces a physiological response in other tissues. It is an inter cellular signaling molecule. Virtually every process is a complex organism is regulated by one or more hormones. Example, insulin, epinephrine, estrogen, androgen etc.
Part – III
Answer any six questions. Question No. 32 is compulsory. [6 × 3 = 18]
Question 25.
Write a note on zeolites.
Answer:
Zeolites:
- Zeolites are three dimensional crystalline solids containing aluminium, silicon and oxygen in their regular three dimensional framework.
- They are hydrated sodium alumino silicates with general formula.
Na2O.(Al3O3).x(SiO2)y(H2O)
(x – 2 to 10; y = 2 to 6) - Zeolites have porous structure in which the monovalent sodium ions and water molecules are loosely held.
- The Si and A1 atoms are tetrahederally coordinated with each other through shared oxygen atoms.
- Zeolites structure looks like a honeycomb consisting of a network of interconnected tunnels and cages.
- Zeolite crystal act as a molecular sieve. They help to remove permanent hardness of water.
Question 26.
What is Royal water? Mention its uses.
Answer:
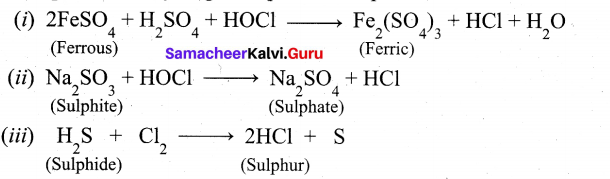
When three parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid and one part of concentrated nitric acid are mixed, aquaregia is obtained. This is also known as Royal water. This is used for dissolving gold, platinum etc.
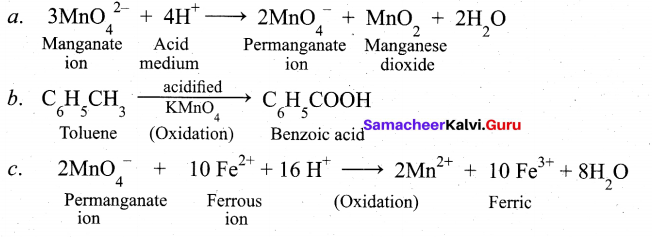
Au + 4H+ + NO3– + 4 Cl– → AUCl4– + NO + 2H2O
3Pt + 16H+ + 4NO3– + 18Cl– → 3PtCl32- + NO + 8H2O
Question 27.
Ni(CN)4]2- is diamagnetic, while [NiCl4]2- is paramagnetic , explain using crystal field theory.
Answer:
(a) [Ni(CN)4]2-
Ni = 3d8 4S2
Ni2+ = 3d8
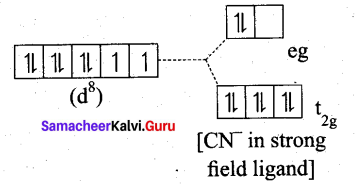
- Nature of the complex – Low spin (Spin paired)
- Ligand filled electronic configuration of central metal ion, t62g e6g
- Magnetic property : No unpaired electron (CN– is strong filled ligand), hence it is diamagnetic.
- Magnetic moment : μs = 0
(b) [NiDl4]2-
Ni = 3d8 4S2
Ni2+ = 3d8
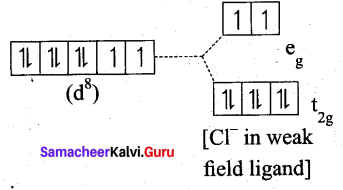
- Nature of the complex, – high spin
- Ligand filled electronic configuration of central metal ion, t62g e2g
- Magnetic property : Two unpaired electron (CF is weak field ligand). Hence it is paramagnetic
- Magnetic moment : μs= \(\sqrt{2(2+2)}\) = √8 = 2.83BM
![]()
Question 28.
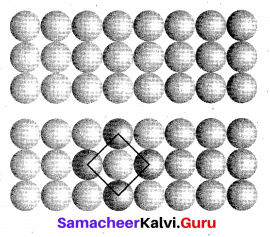
Calculate the number of atoms per unit cell of bcc type.
Answer:
- In a body centered cubic unit cell, each comer is occupied by an identical particle and in addition to that one atom occupied the body centre.
- Those atoms which occupy the comers do not touch each other, however they all touch the one that occupies the body centre.
- Hence each atom is surrounded by eight nearest neighbours and coordination number is 8. An atom present at the body centre belongs to only a particular unit cell, i.e., unshared by other unit cell.
∴ number of atoms in a bcc unit cell = \(\frac{N_{c}}{8}+\frac{N_{b}}{1}=\frac{8}{8}=\frac{1}{1}\)
= 1 + = 2.
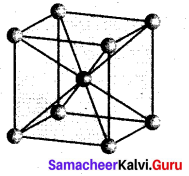
Question 29.
Identify the order for the following reactions
(i) Rusting of Iron
(ii) Radioactive disintegration of 92U238
(iii) 2A + B → products ; rate = K[A]1/2[B]2
Answer:
(i)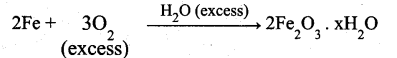
Theoritically order value may be more than one but practically one.
(ii) All radioactive disintegrations are first order reactions
(iii) 2 A + 3B → products
rate = K[A]1/2[B]2
Order = \(\frac{1}{2}+2=\frac{5}{2}=2.5\)
Question 30.
Calculate the (i) hydrolysis constant, (ii) degree of hydrolysis and (iii) pH of 0.05M sodium carbonate solut
Answer:
(i) Hydrolysis constant:
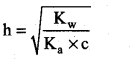
Given Kw = 1 × 10-14
c = 0.05M
pKa = 10.26
pK = -log ka
Ka = antilog of (-pKa)
Ka = antilog of (-10.26)
Ka = 5.49 × 10-11
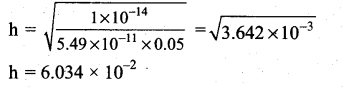
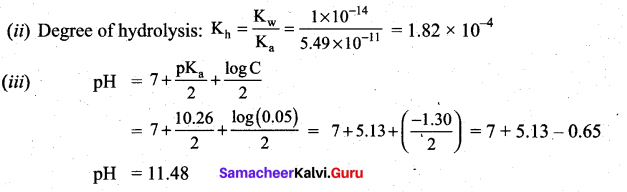
![]()
Question 31.
Write the structure of the aldehyde, carboxylic acid and ester that yield 4 – methylpent -2-en-l-ol.
Answer:
(i) Aldehyde yield 4-methylpent-2-en-l-ol is,
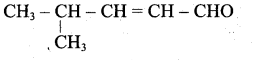
(ii) Acid yield 4-methylpent-2-en-l-ol is,
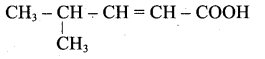
(iii) Ester yield 4-methylpent-2-en-l-ol is,
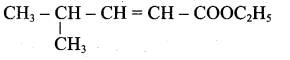
The above shown compounds udergo reduction reaction to yield 4-methylpent-2-en-l-ol.
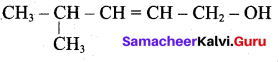
Question 32.
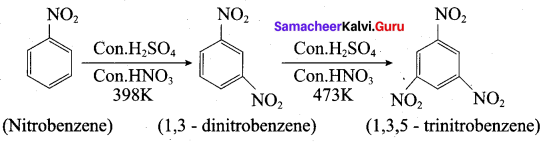
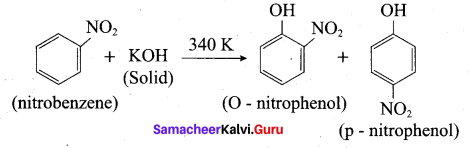
Predict the major product that would’ be obtained on nitration of the following compounds.
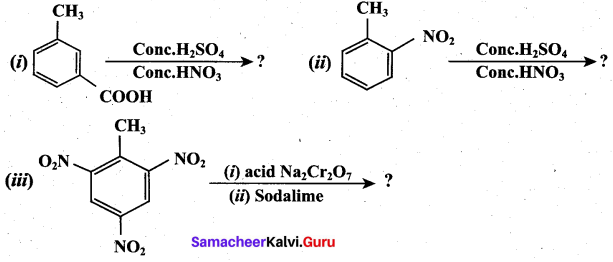
Answer:
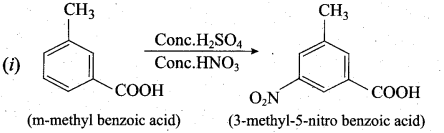
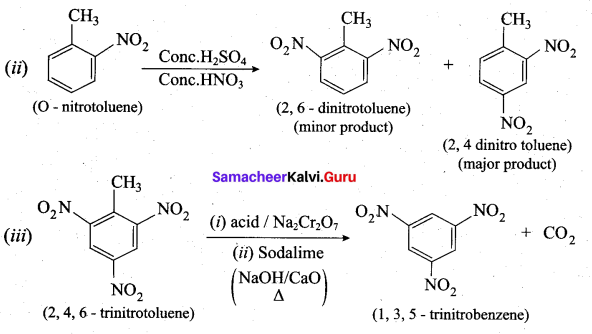
Question 33.
What are the biological functions of nucleic acids?
Answer:
- Energy carriers (ATP)
- Components of enzyme cofactors. Example : Co enzyme A, NAD+, FAD
- Chemical messengers. Example : Cyclic AMP, CAMP
![]()
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [5 × 5 = 25]
Question 34.
(a) (i) Explain the observations from the Ellingham diagram. (3)
(ii) Write a short note on anamolous properties of the first element of p-block. (2)
[OR]
(b) (i) Write the products formed in the reaction of concentrated nitric acid with zinc. (2)
(ii) d-block elements readily form complexes. Give reason. (3)
Answer:
(a) (i) 1. For most of the metal oxide formation, the slope is positive. It can be explained as follows.
Oxygen gas is consumed during the formation of metal oxides which results in the decrease in randomness. Hence, ∆S becomes negative and it makes the term, T∆S positive in the straight line equation.
2. The graph for the formation of carbon monoxide is a straight line with negative slope. In this case ∆S is positive as 2 moles of CO gas is formed by the consumption of one mole of oxygen gas. It indicates that CO is more stable at higher temperature.
3. As the temperature increases, generally ∆G value for the formation of the metal oxide become less negative and becomes zero at a particular temperature. Below this temperature, ∆G is negative and the oxide is stable and above this temperature ∆G is positive. This general trend suggests that metal oxides become less stable at higher temperature and their decomposition becomes easier.
4. There is a sudden change in the slope at a particular temperature for some metal oxides like MgO, HgO. This is due to the phase transition (melting or evaporation).
(ii) In p-block elements the first member of each group differs from the other elements of the corresponding group. The following factors are responsible for this anomalous behaviour.
- Small size of the first member.
- High ionisation enthalpy and high electronegativity.
- Absence of d-orbitals in their valance shell.
The first member of the group-13, boron is a metalloid while others are reactive metals. Moreover, boron shows diagonal relationship with silicon of group 14. The oxides of boron and silicon are similar in their acidic nature.
[OR]
(b) (i) Zinc with Cone.
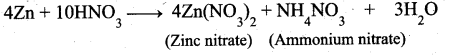
(ii) 1. Transition elements (d-block elements) have a tendency to form coordination • compounds (complexes) with a species that has an ability to donate an electron pair to
form a coordinate covalent bond.
2. Transition metal ions are small and highly charged and they have vacant low energy orbitals to accept an electron pair donated by other groups. Due to these properties, transition metals form large number of complexes.
3. Examples: [Fe(CN)6]4- , [CO(NH3)6]3+
![]()
Question 35.
(a) (i) Write the IUPAC names for the following complexes. (2)
1. Na2[Ni(EDTA)]
2. [CO(en)3]2(SO4)3
(ii) What is meant by piezo electricity? (3)
[OR]
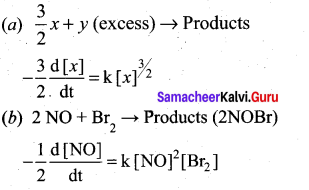
(b) (i) Consider the oxidation of nitric oxide to form NO2 (3)
2NO(g) + O2(g) 2NO2(g)
(a) Express the rate of the reaction in terms of changes in the concentration of NO, O2 and NO 2
(b) At a particular instant, when [O2]is decreasing at 0.2 mol L-1s-1 at what rate is [NO2] increasing at that instant?
(ii) Classify the following as acid (or) base using Arrhen ¡us concept (2)
1. HNO3 2. Ba(OH)2 3. H3PO4 4. CH3COOH
Answer:
(a) (1) 1. Na2[Ni(EDTA)] = Sodium Ethylenediaminetetraacetatonickelate (Il) (or)
Sodium 2,2′,2”,2”’-(ethane- I ,2-diyldinitrilo) tetraacetatonickelate(II)
2. [CO(en)3]2(SO4)3 = tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) sulphate
(ii) Piezo electricity is the appearance of an electrical potential across the sides of a crystal. When you subject it to mechanical stress. The word piezo electricity means electricity resulting from pressure and latent heat. Even the inverse is possible which is known as inverse piezo electric effect.
(b) (i)
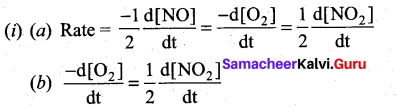
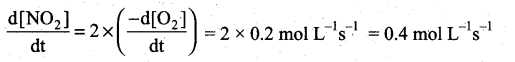
(ii) 1. HNO3 : Nitric acid, dissociates to give hydrogen ions in water. .. HNOS is acid.
2. Ba(OH)2 : Barium hydroxide, dissociates to give hydroxyl ions in water.
∴ Ba(OH)2 is base.
3. H3PO4: Orthophosphoric acid, dissociates to give hydrogen ions in water.
∴ H3PO4 is acid.
4. CH3COOH : Acetic acid, dissociates to give hydrogen ions in water.
∴ CH3COOH is acid.
Question 36.
(a) Derive an expression for Nernst equation. (5)
[OR]
(b) Describe adsorption theory of catalysis. (5)
(a) Nernst equation is the one which relates the cell potential and the concentration of the specie:
involved in an electrochemical reaction.
Let us consider an electrochemical cell for which the overall redox reaction is,
xA+yB ⇌ lC+mD
The reaction quotient Q is,
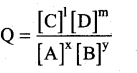
We know that,
∆G = ∆G°+RT In Q ……..(1)
∴ ∆G = -nFEcell ;∆G°=-nFE°cell
∴ equation (1) becomes
– nFEcell = nFE°cell + RT lnQ ………(2)
Substitute the Q value in equation (2)
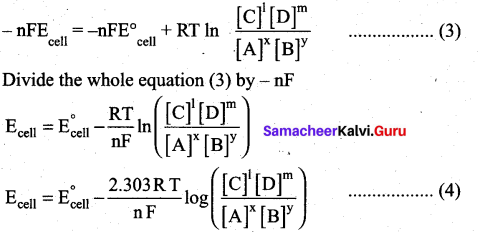
This is called the Nernst equation.
At 25°C (298 K) equation (4) becomes,
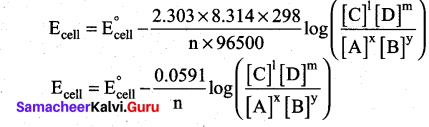
[OR]
(b) Adsorption theory:
Langmuir explained the action of catalyst in heterogeneous catalysed reactions based on adsorption. The reactant molecules are adsorbed on the catalyst surfaces, so this can also be called as contact catalysis.
According to this theory, the reactants are adsorbed on the catalyst surface to form an activated complex which subsequently decomposes and gives the product.
The various steps involved in a heterogeneous catalysed reaction are given as follows:
- Reactant molecules diffuse from bulk to the catalyst surface.
- The reactant molecules are adsorbed on the surface of the catalyst.
- The adsorbed reactant molecules are activated and form activated complex which is decomposed to form the products.
- The product molecules are desorbed.
- The product diffuse away from the surface of the catalyst.
Advantages of adsorption theory:
The adsorption theory explains the following
- Increase in the activity of a catalyst by increasing the surface area. Increase in the surface area of metals and metal oxides by reducing the particle size increases the rate of the reaction.
- The action of catalytic poison occurs when the poison blocks the active centres of the catalyst.
- A promoter or activator increases the number of active centres on the surfaces.
Question 37.
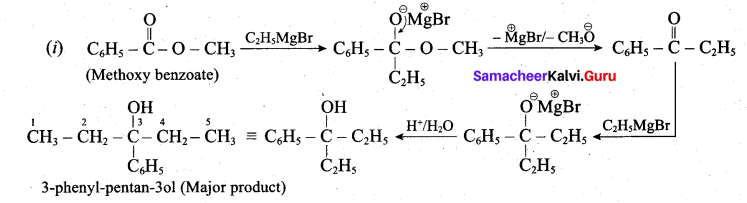
(a) (i) What is the major product obtained when two moles of ethyl magnesium bromide is treated with methyl benzoate followed by acid hydrolysis. (3)
(ii) What are essential and non-essential amino acids? Give one example of each type. (2)
[OR]
(b) How are the following conversions effected (5)
1. propanal into butanone
2. Hex-3-yne into hexan-3-one
3. phenylmethanal into benzoic acid
4. phenylmethanal into benzoin
Answer:
(a)
(ii) Essential amino acids: Amino acids which are not synthesised by the human body are called essential amino acids. Example: Valine, Leucine.
Non-essential amino acids: Amino acids which are synthesised by human body are called non-essential amino acids. Example: Glycine, Aspartic acid, etc.
[OR]
(b) 1. Propanal into butanone:
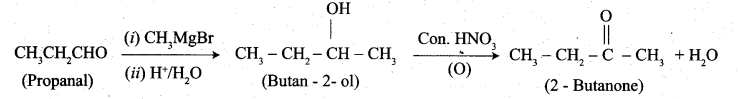
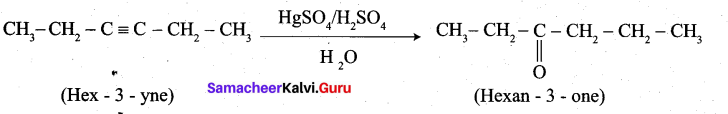
2. Hex-3-yne into hexan-3-one:
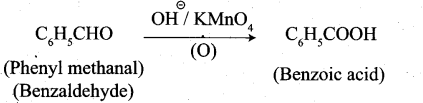
3. Phenylmeihanal into benzoic acid:
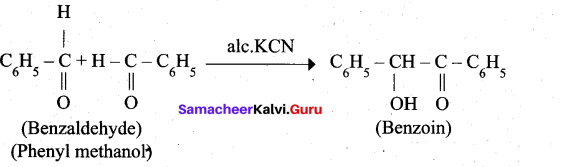
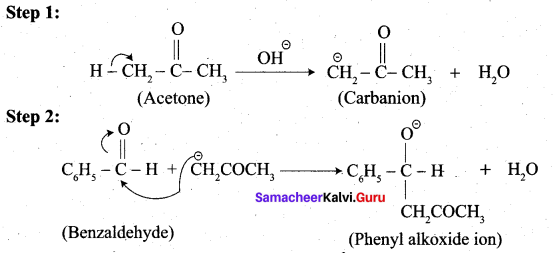
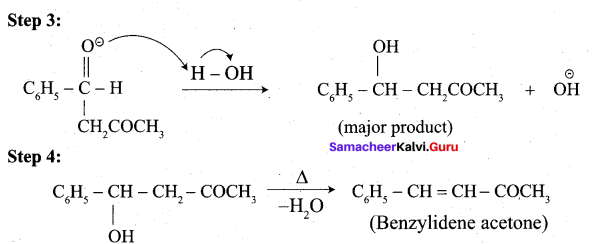
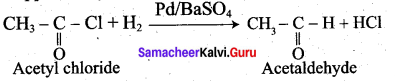
4. Phenyl methanal into benzoin:
![]()
Question 38.
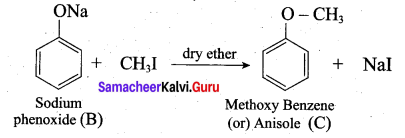
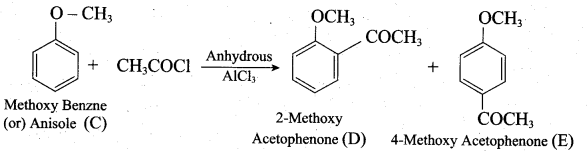
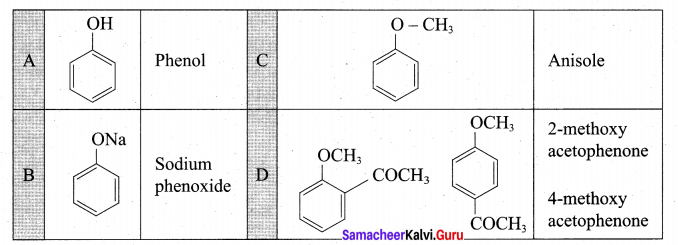
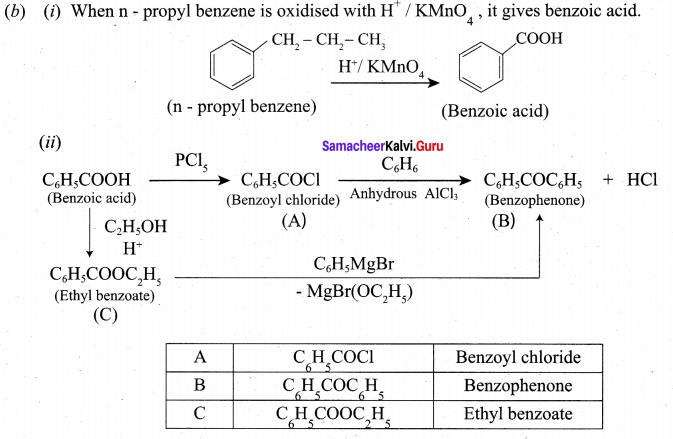
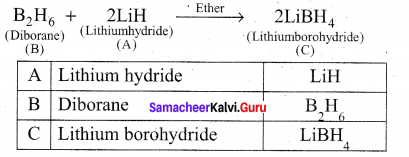
(a) Identify A to E in the following frequency. of reactions. (5)
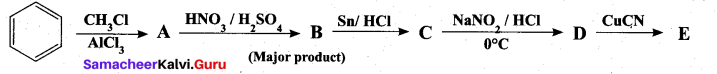
[OR]
(b) (i) What are the biological importance of proteins? (3)
(ii) Name one substance which can act as both analgesic and antipyretic. (2)
(a)
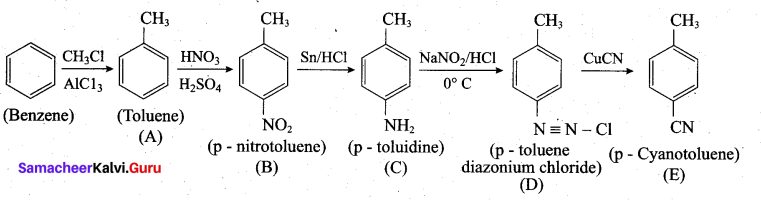
[OR]
(b) (i) Proteins are the functional units of living things play vital role in all biological processes
- All biochemical reactions occur in the living systems are catalysed by the catalytic proteins called enzymes.
- Proteins such as keratin, collagen acts as structural back bones.
- Proteins are used for transporting molecules (Haemoglobin), organelles (Kinesins) in the cell and control the movement of molecules in and out of the cells (Transporters).
- Antibodies help the body to fight various diseases.
- Proteins are used as messengers to coordinate many functions. Insulin & glucagon controls the glucose level in the blood.
- Proteins act as receptors that detect presence of certain signal molecules and activate the proper response.
- Proteins are also used to store metals such as iron (Ferritin) etc.
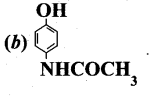
(ii) Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is a chemical substance which lowers body temperature (to normal) and also reduces body pain. Therefore it acts as both antipyretic and analgesic.




















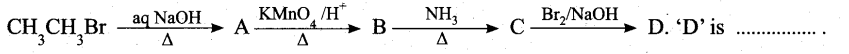
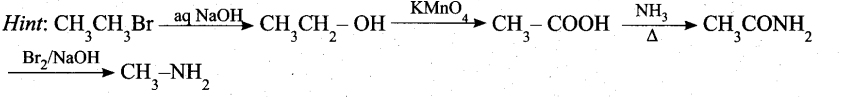
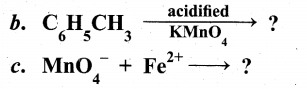
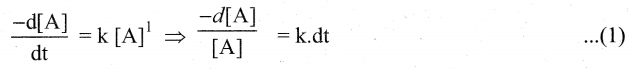
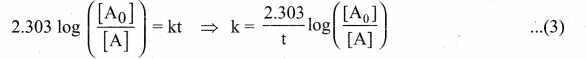
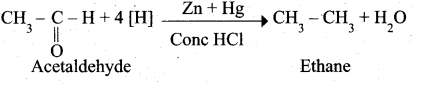



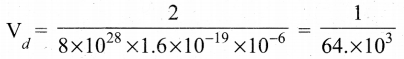
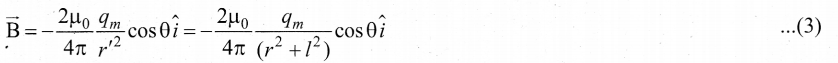

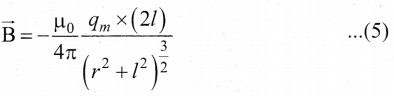
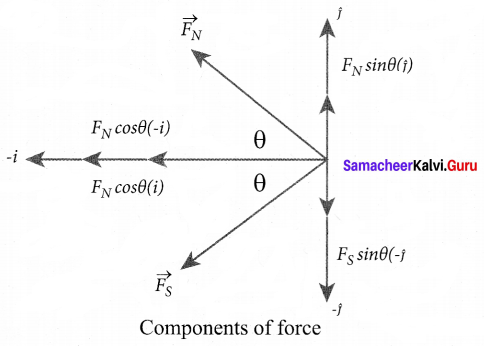
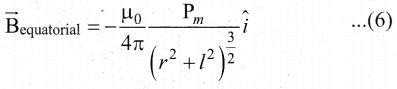
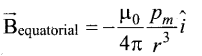

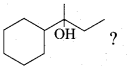
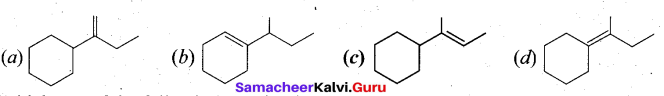
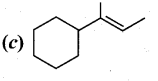

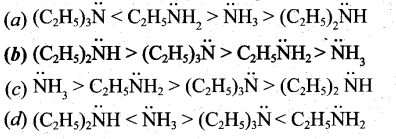
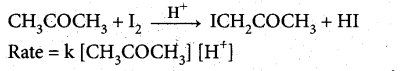
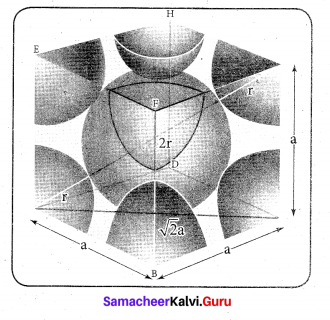
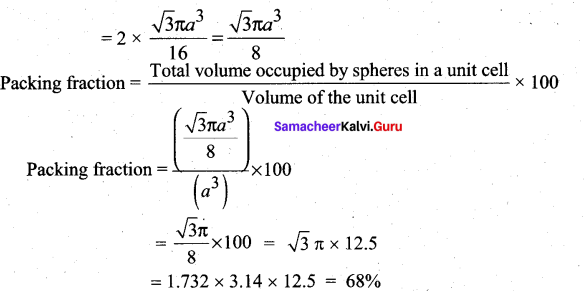
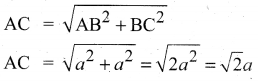 In∆ACG,
In∆ACG,