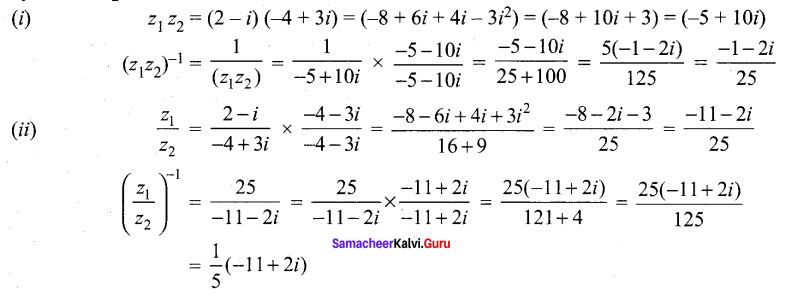
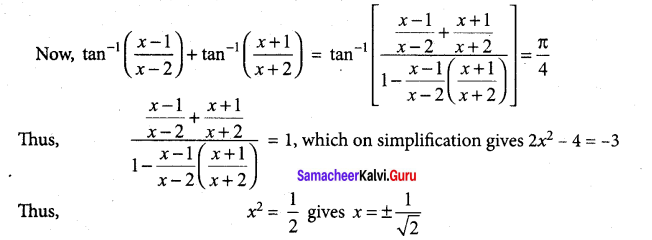
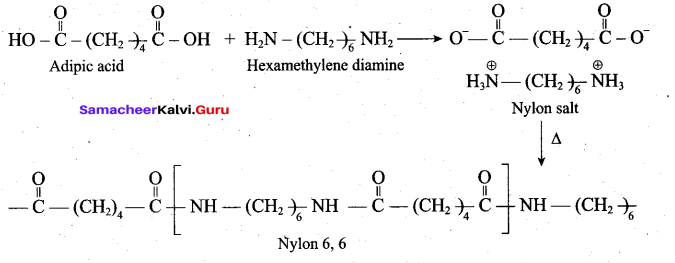
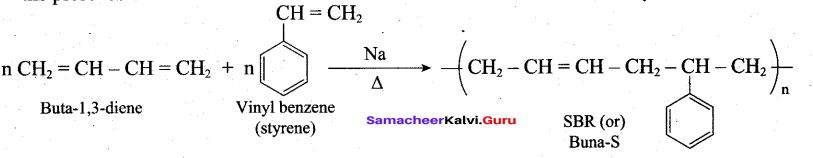
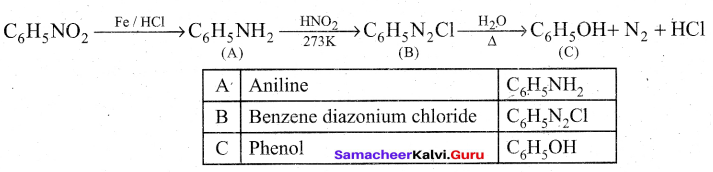
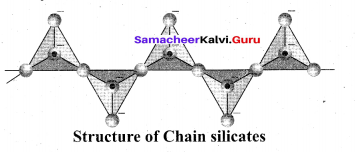
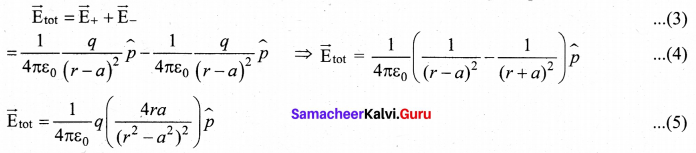
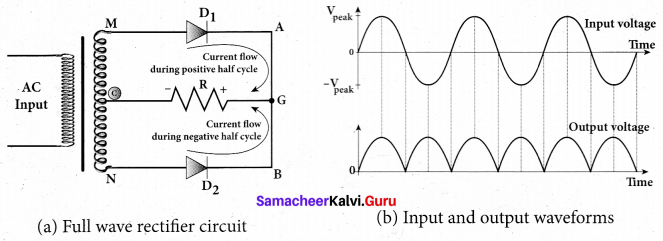
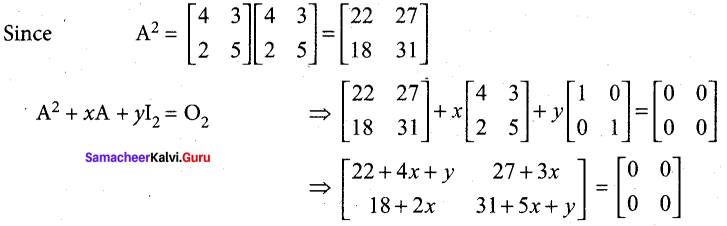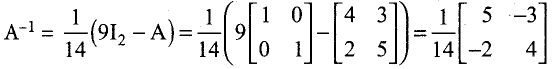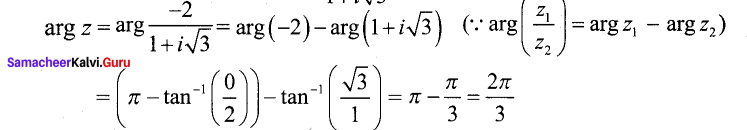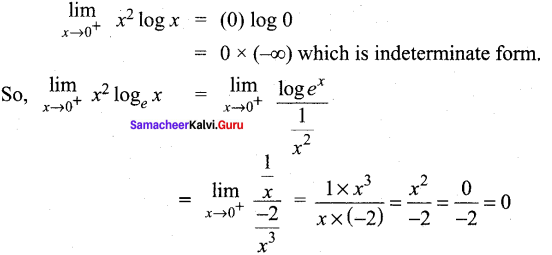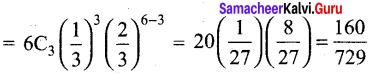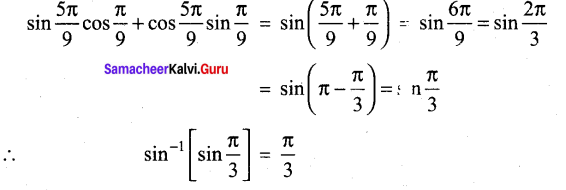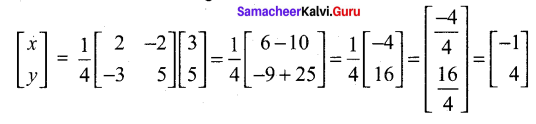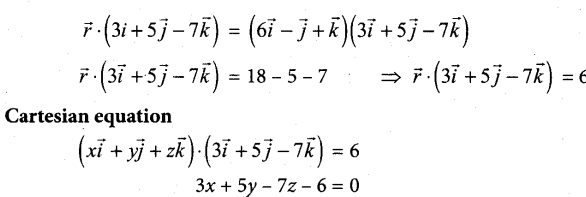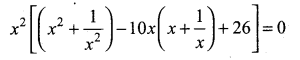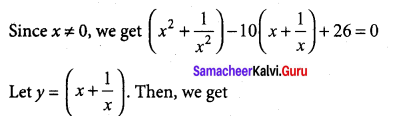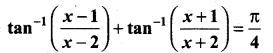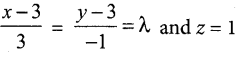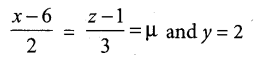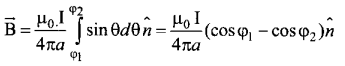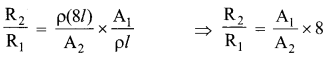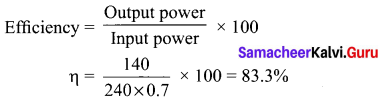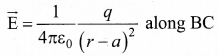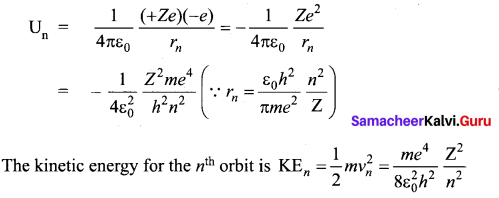Students can Download Tamil Nadu 12th Commerce Model Question Paper 1 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 12th Commerce Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
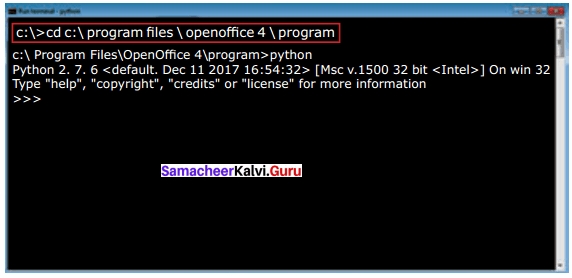
TN State Board 12th Commerce Model Question Paper 1 English Medium
Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II. III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about 50 words.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in about 150 words.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in about 250 words. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Max Marks: 90
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [15 × 1 = 15]
Question 1.
With a wider span, there will be ………… hierarchical levels.
(a) more
(b) less
(c) multiple
(d) additional
Answer:
(b) less
Question 2.
Spot market is a market when the delivery of the financial instrument and payment of cash occurs.
(a) Immediately
(b) In the future
(c) Uncertain
(d) After one mouth
Answer:
(a) Immediately
![]()
Question 3.
How many times a security can be sold in a secondary market?
(a) only one time
(b) two time
(c) three times
(d) multiple times
Answer:
(d) multiple times
Question 4.
Money market provides ……………
(a) medium term funds
(b) short term funds
(c) long term funds
(d) shares
Answer:
(b) short term funds
Question 5.
Jobbers transact in a stock exchange.
(a) For their Clients
(b) For their Own Transactions
(c) For other Brokers
(d) For other Members
Answer:
(b) For their Own Transactions
Question 6.
Registering and controlling the functioning of collective investment schemes as ………..
(a) Mutual funds
(b) Listing
(c) Rematerialisation
(d) Dematerialisation
Answer:
(d) Dematerialisation
![]()
Question 7.
Human resource management determines the …… relationship.
(a) internal, external
(b) employer, employee
(c) owner, servant
(d) principle, agent
Answer:
(b) employer, employee
Question 8.
Advertisement is a ………. source of recruitment.
(a) internal
(b) external
(c) agent
(d) outsourcing
Answer:
(b) external
Question 9.
Selection is usually considered as a,process.
(a) positive
(b) negative
(c) natural
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) negative
Question 10.
Improves skill levels of employees to ensure better job performance.
(a) Training
(b) Selection
(c) Recruitment
(d) Performance appraisal
Answer:
(d) Performance appraisal
Question 11.
Which one of the market deals in the purchase and sale of shares and debentures?
(a) stock exchange market
(b) Manufactured goods market
(c) local market
(d) family market
Answer:
(a) stock exchange market
![]()
Question 12.
In the following variables which one is not the variable of marketing mix?
(a) place variable
(b) product variable
(c) program variable
(d) price variable
Answer:
(c) program variable
Question 13.
Social marketing deals with
(a) Society
(b) Social clan
(c) Social change
(d) Social evil
Answer:
(c) Social change
Question 14.
The main objective of all business enterprises is …………….
(a) Providing service
(b) Providing better standard of life
(c) Providing necessities to the society
(d) Earn profit
Answer:
(d) Earn profit
Question 15.
As the consumer is having the rights, they are also having
(a) measures
(b) Promotion
(c) responsibilities
(d) duties
Answer:
(c) responsibilities
Question 16.
Which of the following is not a consumer right summed up by John.F.Kennedy.
(a) Right to safety
(b) Right to choose
(c) Right to consume
(d) Right to be informed
Answer:
(a) Right to safety
![]()
Question 17.
The chairman of the District Forum is
(a) District Judge
(b) High court Judge
(c) Supreme court Judge
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) District Judge
Question 18
ownership makes bold management decisions due to their strong foundation in the intimation level.
(a) Private
(b) Public
(c) Corporate
(d) MNC’s
Answer:
(a) Private
Question 19.
The property in the goods means the
(a) Possession of goods
(b) Custody of goods
(c) Ownership of goods
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(c) Ownership of goods
Question 20.
Number of parties is a bill of exchange are
(a) 2
(b) 6
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(c) 3
Part – II
Answer any seven in which question No. 30 is compulsory. [7 x 2 = 14]
Question 21.
What are the objectives of MBO?
Answer:
Management by objectives is intended primarily:
- To measure and judge performance.
- To relate individual performance to organisational goals.
- To clarify both the job to be done and the expectations of accomplishment.
- To foster the increasing competence and growth of the subordinates.
Question 22.
Write a note on OTCEI.
Answer:
The OTCEI was set up by a premier financial institution to allow the trading of securities across the electronic counters throughout the country.
![]()
Question 23.
Define Stock Exchange.
Answer:
According to Husband and Dockerary, “Stock exchanges are privately organized markets which are used to facilitate trading in securities.”
Question 24.
Give the meaning of Human Resource.
Answer:
In an organisation, the human resource are the employees who are inevitable for the survival t and success of the enterprise.
Question 25.
What is service marketing?
Answer:
Service marketing denotes the processing of selling service goods like telecommunication, banking, insurance, car rentals, healthcare, tourism, professional services, repairs etc.
Question 26.
Write short notes on: “Right to be informed.”
Answer:
Consumers should be given all the relevant facts about the product. This implies that the manufacturer and the dealer are expected to disclose all the material facts relevant and relating to the product.
Question 27.
What is GST?
Answer:
GST is the indirect tax levied on goods and services across the country. It is a comprehensive, multi-stage, destination-based tax that is levied on every value addition.
Question 28.
What is a contract of sale of goods?
Answer:
Contract of sale of goods is a contract whereby the seller transfers or agrees to transfer the property (ownership) of the goods to the buyer for a price.
![]()
Question 29.
What is the other name of business entrepreneur?
Answer:
The term entrepreneur means the person who takes steps for commencing the business. So he is otherwise called as organiser or proprietor.
Question 30.
Define Director.
Answer:
The Companies Act 2013 section 2 (34) defines a director appointed to the board of a Company is “A Person who is appointed or elected member of the Board of Directors of a company and has the responsibility of determining and implementing policies along with others in the board”.
Part – III
Answer any seven in which question No. 31 is compulsory. [7 x 3 = 21]
Question 31.
What are the process involved in MBO?
Answer:
- Defining Organisational Objectives
- Goals of Each Section
- Fixing Key Result Areas
- Setting subordinate objectives or targets
- Matching Resources with objective
- Periodical Review meetings
- Appraisal of Activities
- Reappraisal of objectives
Question 32.
Differentiate spot market from future market.
Answer:
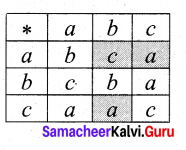
| Spot Market | Future Market |
| Spot market is otherwise called cash market. It is a market where the delivery of the financial instrument and payment of cash occurs immediately, i.e. settlement is completed immediately. | Future market is otherwise called forward market. It is a market where the delivery of asset and payment of cash takes place at a predetermined time frame in future. |
![]()
Question 33.
What are the documents required for a Demat account?
Answer:
For opening a demat account, we submit proof of identity and address along with a passport size photo and the account opening form.
- Documents for Identity: Pan card, Voters ID, Passport, Driver’s License, IT Returns, Electricity and Telephone Bills are the Identity documents.
- Documents for Address: Ration card, Passport, Voter’s ID card, Driving License, Telephone Bills, Electricity bills are the address documents.
Question 34.
Mention any three Role of Marketer.
Answer:
(1) Instigator: As an instigator, marketer keenly watches the developments taking place in the market and identifies marketing opportunities emerging in the ever changing market.
(2) Integrator: Marketer plays a role of integrator in the sense that he collects feedback or vital inputs from channel members and consumers.
(3) Implemented Marketer plays a role of implementer when he/she actually converts marketing opportunities into marketable product.
Question 35.
Discuss the objectives E-Marketing.
Answer:
The following are the objectives of E-Marketing:
- Expansion of market share
- Reduction of distribution and promotional expenses
- Achieving higher brand awareness
- Strengthening database
Question 36.
What do you understand by “Right to redressal”?
Answer:
The complaints and protests are not just to be heard: but the aggrieved party is to be granted compensation within a reasonable time period . There should be prompt settlement of complaints and claims lodged by the aggrieved customers.
Question 37.
Explain the concept of Privatisation.
Answer:
Privatisation means permitting the private sector to set up industries which were previously reserved for the public, sector. Under this policy many Public Sector Units (PSUs) were sold to private sector. The main reason for privatisation was that PSUs were running in losses due to mismanagement and political interference.
![]()
Question 38.
What are the characteristics of a bill of exchange?
Answer:
Characteristics of a Bill of Exchange:
- A bill of exchange is a document in writing.
- The document must contain an order to pay.
- The order must be unconditional.
- The instrument must be signed by the person who draws it.
- The name of the person on whom the bill is drawn must be specified in the bill itself.
Question 39.
Distinguish between Entrepreneur and Manager.
| Basis of difference | Entrepreneur | Manager |
| Motive | The very motive of an entrepreneur is to start a venture by setting of an entity. | The very motive of manager is to render service in an entity setup for execution of venture. |
| Status | Entrepreneur is owner of the entity. | Manager is a salaried employee in the entity set up for carrying on the venture. |
| Risk Bearing | Entrepreneur bears the eventual risk and uncertainty in operating the enterprise. | Manager doesn’t bear any risk in the venture, where the venture is unsuccessful he/she simply. quits the enterprise. |
Question 40.
When are alternative directors appointed?
Answer:
Alternate director is appointed by the Board of Directors, as a substitute to a director who may be absent from India, for a period which is not less than three months.
Part – IV
Answer all the following questions. [7 x 5 = 35]
Question 41
(a) Explain the various functions of management.
Answer:
- Planning:- Planning is the primary function of management. Planning is a constructive reviewing of future needs so that present actions can be adjusted in view of the established goal.
- Organising:- Organising is the process of establishing harmonious relationship among the members of an organisation and the creation of network of relationship among them.
- Staffing:- Staffing function comprises the activities of selection and placement of competent personnel.
- Directing:- Directing denotes motivating, leading, guiding and communicating with subordinates on an ongoing basis in order to accomplish pre-set goals.
- Controlling:- Controlling is performed to evaluate the performance of employees and deciding increments and promotion decisions.
- Co-ordination:- Co-ordination is the synchronization of the actions of all individuals, working in the enterprise in different capacities.
- Motivating:- The goals are achieved with the help of motivation. Motivation includes increasing the speed of performance of a work and developing a willingness on the part of workers.
Subsidiary Functions:
- Innovation:- Innovation includes developing new material, new products, new techniques in production, new package, new design of a product and cost reduction.
- Representation:- A manager has to act as representative of a company. It is the duty of every manager to have good relation with others.
- Decision-making:- Every employee of an organisation has to take a number of decisions every day. Decision-making helps in the smooth functioning of an organisation.
- Communication:- Communication is the transmission of human thoughts, views or opinions from one person to another person. Communication helps the regulation of job and co-ordinates the activities.
[OR]
(b) Compare the concept of social marketing with service marketing.
Answer:
Social marketing: Social marketing is a new marketing tool.
It is the systematic application of marketing philosophy to achieve social good.
The primary aim of social marketing is ‘social good’ such as anti-tobacco, anti-drug, anti-pollution, anti-dowry, road safety, protection of girl child.
- Service marketing: A service is any activity or benefit that one party can offer to another which is essentially intangible.
- Service marketing is a specialized branch of marketing.
- Service marketing denotes the process of selling service goods like telecommunication, banking, insurance, car rentals, healthcare, tourism and repairs.
![]()
Question 42
(a) Explain the various disadvantages of MBO.
Answer:
- MBO fails to explain the philosophy; most of the executives do not know how MBO works? what is MBO? and why is MBO necessary? and how participants can benefit by MBO.
- MBO is a time consuming process. Much time is needed by senior people for framing the MBO. Next, it leads to heavy expenditure and also requires heavy paper work.
- MBO emphasises only on short-term objectives and does not consider the long-term objectives.
- The status of subordinates is necessary for proper objectives setting. But, this is not possible in the process of MBO.
- MBO is rigid one. Objectives should be changed according to the changed circumstances, external or internal. If it is not done, the planned results cannot be obtained.
[OR]
(b) Explain the duties of consumers.
Answer:
Apart from rights, there are certain duties imposed on the consumer. The following are the duties of consumers.
- Buying Quality Products at Reasonable Price: It is the duty of a consumer to purchase a product after gaining a thorough knowledge of its price, quality and other terms and conditions.
- Ensure the Weights and Measurement before Purchase: The consumer should ensure that he/she is getting the product of exact weight and. measure.
- Reading the Label Carefully: It is the duty of the consumer to read the label of the product thoroughly.
- Beware of False and Attractive Advertisements: It is the prime duty of the consumer about the genuineness of the advertisement, before purchasing the product.
- Ensuring the Receipt of Cash Bill: It is a legitimate duty of consumers to get the cash receipt and warranty card supplied along with the bill.
Question 43.
(a) Explain the Instruments of Money Market.
Answer:
(i) Treasury Bills: Treasury bills are very popular and enjoy a higher degree of liquidity since they are issued by the Government. A Treasury bill is nothing but a promissory note issued for a specified period stated therein. The Government promises to pay the specified amount mentioned therein to the bearer of the instrument on the due date. The period does not exceed a period of one year.
(ii) Certificate of Deposits: Certificate of Deposits are short-term deposit instruments issued by banks and financial institutions to raise large sums of money. The Certificate of Deposit is transferable from one party to another. Due to their negotiable feature, they are also known as negotiable certificate of deposit.
(iii) Commercial Bills: The Commercial Bill is an instrument drawn by a seller of goods on a buyer of goods. It possesses the advantages like self-liquidating in nature, recourse to two parties, knowing exact date of transactions, transparency of transactions etc.
[OR]
(b) Explain the overall performance of State Commission.
The State Commission is to be appointed by the State Government. The person who is a judge or retired judge of high court is the president of the state commission.
Performances:
- The compensation of the value should not exceed Rs.20 lakhs and below Rs.1 crore.
- The state commission has the power to call for the records and pass orders in the district forum.
- To furnish the information which is required for the purpose of the Act to any officer.
![]()
Question 44.
(a) Explain the powers of SEBI.
Answer:
The various powers of a SEBI are explained below:
- Powers Relating to Stock Exchanges and Intermediaries: SEBI has wide powers to get the information from the stock exchange and intermediaries regarding their business transactions for inspection.
- Power to Impose Monetary Penalties: SEBI has power to impose monetary penalties on capital market intermediaries for violations.
- Power to Initiate Actions in Functions Assigned
- Power to Regulate Insider Trading: SEBI has power to regulate insider trading or can regulate the functions of merchant banker.
- Powers Under Securities Contracts Act: For the regulation of stock exchange, the Ministry of Finance issued a notification, for delegating several of its powers under the securities contract Act.
[OR]
(b) Explain the impact of LPG on Indian Economy.
Impact of Liberalization:
- Liberalization has opened up new business opportunities abroad and increased foreign direct investment.
- New market for various goods came into existence and resulted not only in urban but also in rural development.
- It became very easy to obtain loans from banks for business expansion.
Impact of Privatization:
- Privatization has a positive impact on the financial growth by decreasing the deficits and debts.
- Increase in the efficiency of government undertakings.
- Provide better goods and services to the consumers.
Impact of Globalization:
- Multinational corporations can manufacture, buy and sell goods worldwide.
- Globalization has led to a boom in consumer products market.
- The advent of foreign companies and growth in economy has led to job creation.
Question 45
(a) Describe the significance of External source of recruitment.
Answer:
External sources of recruitment include sources that lie outside the organisation. This provides a wider collection of potential employees with the necessary skillset, especially for managerial and technical positions. Existing employees can recommend suitable candidates, which may lead to a higher level of teamwork and synchronisation among employees. Hiring new employees can lead to the introduction of new blood and thus the introduction of a new set of skills and ideas. External sources of recruitment offer jobs to unskilled, semi-skilled and skilled workers.
[OR]
(b) Discuss in detail the features of a cheque.
Answer:
A cheque is a negotiable instrument drawn on a particular banker.
Features:
(i) Instrument in Writings
A cheque or a bill or a promissory note must be an instrument in writing. Though the law does not prohibit a cheque being written in pencil, bankers never accept it because of risks involved. Alternation is quite easy but detection is impossible in such cases.
(ii) Unconditional Orders
The instrument must contain an order to pay money. It is not necessary that the word ‘order’ or its equivalent must be used to make the document a cheque. It does not cease to be a cheque just because the world ‘please’ is used before the word pay. Further the order must be unconditional.
(iii) Drawn on a Specified Banker Only
The cheque is always drawn on a specified banker. A cheque vitally differs from a bill in this respect as latter can be drawn on any person including a banker. The customer of a banker can draw the cheque only on the particular branch of the bank where he has an account.
(iv) A Certain Sum of Money Only
The order must be for payment of only money. If the banker is asked to deliver securities, the document cannot be called a cheque. Further, the sum of money must be certain.
![]()
(v) Payee to be Certain
The cheque must be made payable to a certain person or to the order of a certain person . or to the bearer of the instrument. The word, person includes corporate bodies, local authorities, associations, holders of the office of an institution etc.
(vi) Signed by the Drawer
The cheque is to be signed by the drawer. Further, it should tally with specimen signature furnished to the bank at the time of opening the account
Question 46.
(a) What are the differences between on the job training and off the job training?
Answer:
| Basis for comparison | On the Job Training | Off the Job Training | |
| 1. | Meaning | The employee learns the job in the actual work environment. | The training of employees is done outside the actual work place. |
| 2. | Cost | It is cheapest to carry out. | It is costly due to the expenses like separate training room, specialist, etc. |
| 3. | Suitable for | Suitable for manufacturing related jobs. | It is suitable for managerial jobs. |
| 4. | Approach | Practical approach | Theoretical approach |
| 5. | Carried out | Provided by the experienced employee | Provided by the experts |
| 6. | Methods | Coaching, mentoring, apprenticeship, job rotation | Seminar, lectures, vestibule, field trip, e-leaming |
[OR]
(b) What are the various kinds of Debentures?
Answer:
Debenture is a document issued by the company for acknowledging the loan from the public. Debentures are classified into different categories on the basis of:
- Convertibility of the Instrument
- Security of the Instrument;
- Redemption ability; and
- Registration of Instrument.
On the basis of convertibility:
- Non-Convertible Debentures: These instruments cannot be converted into equity shares.
- Partly Convertible Debentures: A part of these instruments are converted into equity shares.
- Fully Convertible Debentures: These are fully convertible into equity shares.
- Optionally Convertible Debentures: The investor can have the option to either convert the debentures at a price decided by the issuer or agreed upon at the time of issue.
On the basis of Security:
- Secured Debentures: These instruments are secured by a charge on the fixed assets of the issuer company.
- Unsecured Debentures: These instruments are unsecured against the assets.
On the basis of Redeemability:
- Redeemable Debentures: It refers to the debentures which will be redeemed in the future.
- Irredeemable Debentures: It is a debenture, in which no specific time is specified by the companies to pay back the money.
On the basis of Registration:
- Registered Debentures: These are issued in the name of a particular person, who is registered by the company.
- Bearer Debentures: These are issued to the bearer and are negotiable instruments, and are transferred by mere delivery.
![]()
Question 41.
(a) Why the marketing is important to the society and individual firm? Explain.
Answer:
Importance of Marketing:
To the Society:
- Marketing is a connecting link between the consumer and the producer.
- Marketing helps in increasing the living standard of people.
- Marketing helps to increase the nation’s income.
- Marketing process increases employment opportunities.
- Marketing helps to maintain economic stability and rapid development in various countries.
To the Individual Firms:
- Marketing generates revenue to firms.
- Marketing gives information to the top management for taking overall decisions on production.
- Marketing and innovation are the two basic functions of all businesses.
[OR]
(b) State the qualification of directors.
Qualifications of Director: As regards to the qualification of directors, there is no direct provision in the Companies Act, 2013. In general, a director shall possess appropriate skills, experience and knowledge in the fields of finance, law, management, sales, marketing, research and other disciplines related to the business.
The following are the qualifications:
- A director must be a person of sound mind.
- A director must hold share qualification if the article of association provides such.
- A director must be an individual.
- A director should be a solvent person.
- A director should not be convicted by the Court for any offence, etc.