Students can Download Tamil Nadu 12th Computer Science Model Question Paper 4 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 12th Computer Science Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 12th Computer Science Model Question Paper 4 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 15 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer - Question numbers 16 to 24 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 25 to 33 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 34 to 38 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
PART – I
Choose the correct answer. Answer all the questions [15 x 1 = 15]
Question 1.
If the function is not a recursive one, then is used.
(a) abc
(b) gcd
(c) let
(d) let rec
Answer:
(c) let
Question 2.
The process of providing only the essentials and hiding the details is called
(a) modularity
(b) structure
(c) tuple
(d) abstraction
Answer:
(d) abstraction
![]()
Question 3.
All members in a python class are by default.
(a) private
(b) public
(c) protected
(d) local
Answer:
(b) public
Question 4.
………… is a simple sorting algorithm.
(a) binary
(b) bubble
(c) selection
(d) insertion
Answer:
(b) bubble
Question 5.
………… is an example for octal integers.
(a) 102
(b) 08
(c) 0432
(d) 0 × 43
Answer:
(c) 0432
Question 6.
Which of the following operator is used for concatenation?
(a) +
(b) &
(c) *
(d) =
Answer:
(c) *
Question 7.
…………… function returns the sum of values in a list.
(a) sum
(b) total
(c) tot
(d) ε
Answer:
(a) sum
Question 8.
GIS stands for…………
(a) Geographic Information System
(b) Grap Individual System
(c) Graph Information System
(d) Global Information System
Answer:
(a) Geographic Information System
Question 9.
The default sorting order is…………..
(a) top
(b) bottom
(c) ascending
(d) descending
Answer:
(c) ascending
Question 10.
getopt mode is given by………..
(a) ;
(b) =
(c) #
(d) :
Answer:
(d) :
Question 11.
Which operators are used to fitter records based on more than one condition?
(a) AND
(b) NOT
(c) OR
(d) a & c
Answer:
(d) a & c
Question 12.
Which key is used to run the module?
(a) F6
(b) F4
(c) F3
(d) F5
Answer:
(d) F5
![]()
Question 13.
……… is used to add the elements in the list.
(a) add
(b) insert
(c) append
(d) update
Answer:
(c) append
Question 14.
The clause used to sort data in a database ..
(a) sort by
(b) order by
(c) group by
(d) select
Answer:
(b) order by
Question 15.
Which of the following method is used as destructor?
(a) _init_( )
(b) _dest-( )
(c) _rem_( )
(d) _del_( )
Answer:
(d) _del_( )
PART – II
Answer any six questions. Question No. 21 is compulsory. [6 x 2 = 12]
Question 16.
What are the two types of parameter passing?
Answer:
- Parameter without type
- Parameter with type
Question 17.
What is mapping?
Answer:
The process of binding a variable name with an object is called mapping. = (equal to sign) is used in programming languages to map the variable and object.
Question 18.
Write note on delimiters.
Answer:
Python uses the symbols and symbol combinations as delimiters in expressions, lists, dictionaries and strings. Following are the delimiters.
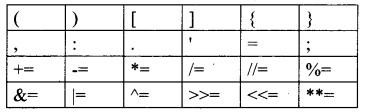
Question 19.
Write note on range () in loop.
Answer:
Usually in Python, for loop uses the range() function in the sequence to specify the initial, final and increment values. range() generates a list of values starting from start till stop-1.
Question 20.
What are the two methods of passing arguments in variable length arguments?
Answer:
In Variable Length arguments we can pass the arguments using two methods.
- Non keyword variable arguments
- Keyword variable arguments
Question 21.
Write program to remove duplicates from a list.
Answer:
Method 1:
mylist = [2, 4, 6, 8, 8, 4, 10]
myset = set(mylist)
print(myset)
Output:
{2, 4, 6, 8, 10}
Method II:
def remove(duplicate):
final_list=[]
for num in duplicate:
if num not in final list:
finallist.append(num)
return final_list
duplicate = [2, 4, 10, 20, 5, 2, 20, 4]
print(remove(duplicate))
Output:
[2, 4, 10, 20, 5]
![]()
Question 22.
List some examples of RDBMS.
Answer:
SQL server, Oracle, mysql, MariaDB, SQLite.
Question 23.
Write note on drop table command.
Answer:
Drop table command is used to remove a table from the database.
DROP TABLE Student;
Question 24.
Write note on scripting language.
Answer:
A scripting language is a programming language designed for integrating and communicating with other programming languages. Some of the most widely used scripting languages are JavaScript, VBScript, PHP, Perl, Python, Ruby, ASP and Tel.
PART – III
Answer any six questions. Question No. 29 is compulsory. [6 x 3 = 18]
Question 25.
Give the syntax for getopt module.
Answer:
The syntax for this method
<opts>, <args>= getopt.getopt( argv, options, [long_options])
Here is the detail of the parameters –

Question 26.
Differentiate Concrete data type and abstract data type.
| Concrete data type | Abstract data type |
| A concrete data type is a data type whose representation is known | Abstract data type the representation of a data type is unknown |
| Concrete data types or structures (CDT’s) are direct implementations of a relatively simple concept. | Abstract Data Types (ADT’s) offer a high level view (and use) of a concept independent of its implementation. |
Question 27.
Write note on Asymptotic notation.
Answer:
Asymptotic Notations:
Asymptotic Notations are languages that uses meaningful statements about time and space complexity.
1. Big O: Big O is often used to describe the worst-case of an algorithm.
2. Big Ω: Big Omega is the reverse Big O, if Big O is used to describe the upper bound (worst – case) of a asymptotic function, Big Omega is used to describe the lower bound (best-case).
3. Big Θ: When an algorithm has a complexity with lower bound = upper bound, say that an algorithm has a complexity O (n log n) and Ω (n log n), it’s actually has the complexity Θ (n log n), which means the running time of that algorithm always falls in n log n in the best-case and worst-case.
Question 28.
What are string literals? Explain.
Answer:
String Literals
In Python a string literal is a sequence of characters surrounded by quotes. Python supports single, double and triple quotes for a string. A character literal is a single character surrounded by single or double quotes. The value with triple-quote ”’ ”’ is used to give multi-line string literal.
strings = “This is Python”
char = “C”
multiline_str = ‘”This is a multiline string with more than one line code.”‘
Question 29.
Write a program to display Fibonacci Series 0 1 1 2 3 5………….. (upto n terms)
Answer:
nterms = int(input(“How many terms?”))
n1 = 0
n2 = 1
count = 2
# check if the number of terms is valid
if nterms <= 0:
print(“please enter a positive integer”)
elif nterms ==1:
print(“Fibonacci sequence :”)
print (n1)
else:
print(“Fibonacci sequence : “)
print (n1, “, “, n2, end = “,”)
while count < nterms:
nth = n1 + n2
print(nth, end = ‘,’)
n1 = n2
n2 = nth
count + = 1
Output:
How many terms? 10
Fibonacci sequence:
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34
![]()
Question 30.
Write the different types of function?
Answer:
- User-defined Functions
- Built-in Functions
- Lambda Functions
- Recursion Functions
Question 31.
Write a note on pow( ) function.
Answer:
pow ()
Description: Returns the computation of ab i.e. (a**b ) a raised to the power of b.
Syntax : pow (a, b)
Example:
a = 5
b = 2
c = 3.0
print (pow (a,b))
print (pow (a,c))
print (pow (a+b, 3))
Output:
25
125.0
343
Question 32.
Write a note on Return Statement.
Answer:
- The return statement causes your function to exit and returns a value to its caller. The point of functions in general is to take inputs and return something.
- The return statement is used when a function is ready to return a value to its caller. So, only . one return statement is executed at run time even though the function contains multiple return statements.
- Any number of ‘return’ statements are allowed in a function definition but only one of them is executed at run time.
Question 33.
Explain Intersection with example.
Answer:
Intersection (symbol: ∩) A ∩ B
Defines a relation consisting of a set of all tuple that are in both in A and B. However, A and B must be union-compatible.
Example:
| Table A ∩ B | |
| Studno | Name |
| csl | Kannan |
| cs3 | Lenin |
PART – IV
Answer all the questions. [5 × 5 = 25]
Question 34 (a).
Explain various types of variable scope.
Answer:
There are 4 types of Variable Scope, let’s discuss them one by one:
Local Scope:
Local scope refers to variables defined in current function. Always, a function will first look up for a variable name in its local scope. Only if it does not find it there, the outer scopes are checked.
Look at this example
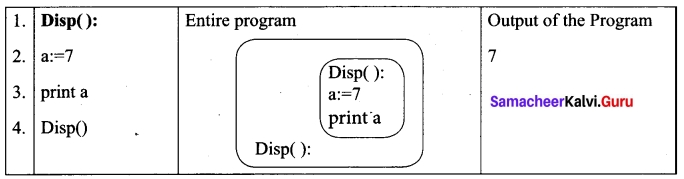
On execution of the above code the variable a displays the value 7, because it is defined and available in the local scope.
Global Scope:
A variable which is declared outside of all the functions in a program is known as global variable. This means, global variable can be accessed inside or outside of all the functions in a program.
Consider the following example
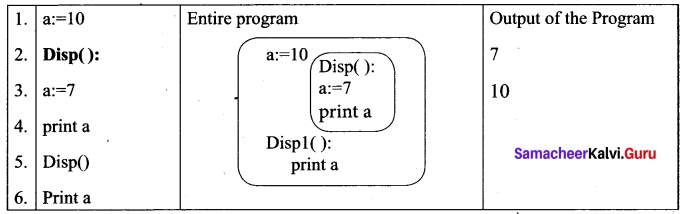
On execution of the above code the variable a which is defined inside the function displays the value 7 for the function call Disp() and then it displays 10, because a is defined in global scope.
Enclosed Scope:
All programming languages permit functions to be nested. A function (method) with in another function is called nested function. A variable which is declared inside a function which contains another function definition with in it, the inner function can also access the variable of the outer function. This scope is called enclosed scope.
When a compiler or interpreter search for a variable in a program, it first search Local, and then search Enclosing scopes.
Consider the following example.
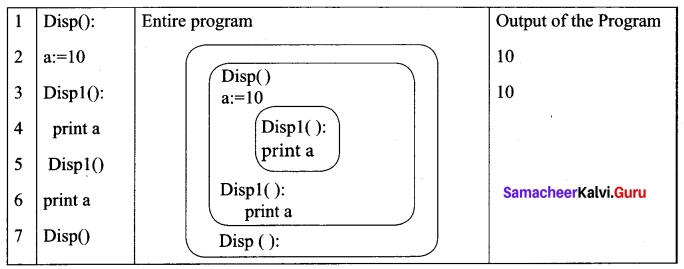
In the above example Disp 1 () is defined with in Disp (). The variable ‘a’ defined in Disp () can be even used by Disp 1 () because it is also a member of Disp ().
Built-in Scope:
Finally, we discuss about the widest scope. The built-in scope has all the names that are pre-loaded into the program scope when we start the compiler or interpreter. Any variable or module which is defined in the library functions of a programming language has Built-in or module scope. They are loaded as soon as the library files are imported to the program.
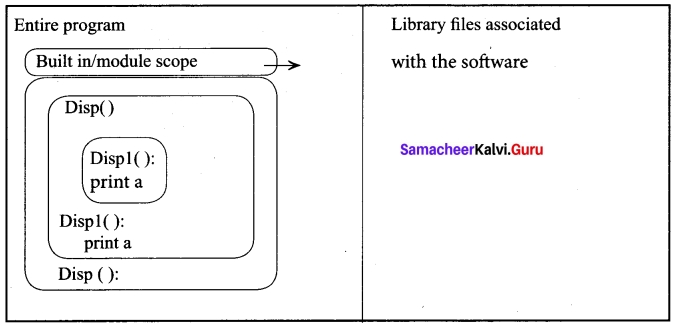
Normally only Functions or modules come along with the software, as packages. Therefore they will come under Built in scope.
![]()
[OR]
(b) Explain pure functions with example.
Answer:
Pure functions are functions which will give exact result when the same arguments are passed. For example the mathematical function sin (0) always results 0. This means that every time you call the function with the same arguments, you will always get the same result. A function can be a pure function provided it should not have any external variable which will alter the behaviour of that variable. Let us see an example:

The above function square is a pure function because it will not give different results for same input.
There are various theoretical advantages of having pure functions. One advantage is that if a function is pure, then if it is called several times with the same arguments, the compiler only needs to actually call the function once. Lt’s see an example:

If it is compiled, strlen (s) is called each time and strlen needs to iterate over the whole of ‘s’. If the compiler is smart enough to work out that strlen is a pure function and that ‘s’ is not updated in the loop, then it can remove the redundant extra calls to strlen and make the loop to execute only one time. From these what we can understand, strlen is a pure function because the function takes one variable as a parameter, and accesses it to find its length. This function reads external memory but does not change it, and the value returned derives from the external memory accessed.
Question 35 (a).
Explain selection sort.
Answer:
The selection sort is a simple sorting algorithm that improves on the performance of bubble sort by making only one exchange for every pass through the list. This algorithm will first find the smallest elements in array and swap it with the element in the first position of an array, then it will find the second smallest element and swap that element with the element in the second position, and it will continue until the entire array is sorted in respective order. This algorithm repeatedly selects the next-smallest element and swaps in into the right place for every pass. Hence it is called selection sort.
Pseudo code:
- Start from the first element i.e., index-0, we search the smallest element in the array, and replace it with the element in the first position.
- Now we move on to the second element position, and look for smallest element present in the sub-array, from starting index to till the last index of sub – array.
- Now replace the second smallest identified in step-2 at the second position in the or original array, or also called first position in the sub array.
- This is repeated, until the array is completely sorted.
Let’s consider an array with values {13, 16, 11, 18, 14, 15}
Below, we have a pictorial representation of how selection sort will sort the given array.
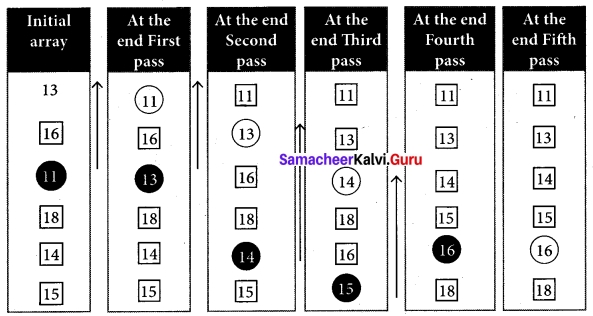
In the first pass, the smallest element will be 11, so it will be placed at the first position. After that, next smallest element will be searched from an array. Now we will get 13 as the smallest, so it will be then placed at the second position.
Then leaving the first element, next smallest element will be searched, from the remaining elements. We will get 13 as the smallest, so it will be then placed at the second position.
Then leaving 11 and 13 because they are at the correct position, we will search for the next smallest element from the rest of the elements and put it at third position and keep doing this until array is sorted. Finally we will get the sorted array end of the pass as shown above diagram.
[OR]
(b) Explain operators in python.
Answer:
Operators:
In computer programming languages operators are special symbols which represent computations, conditional matching etc. The value of an operator used is called operands. Operators are categorized as Arithmetic, Relational, Logical, Assignment etc. Value and variables when used with operator are known as operands.
(i) Arithmetic operators:
An arithmetic operator is a mathematical operator that takes two operands and performs a calculation on them. They are used for simple arithmetic. Most computer languages contain a set of such operators that can be used within equations to perform different types of sequential calculations.
Python supports the following Arithmetic operators.
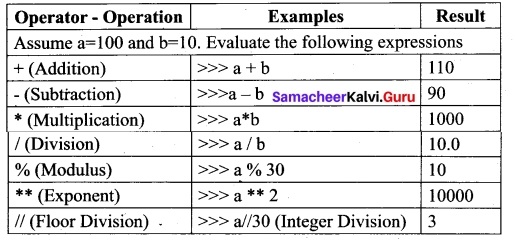
Program To test Arithmetic Operators:
#Demo Program to test Arithmetic Operators
a = 100
b = 10
print (“The Sum = “, a + b)
print (“The Difference = “, a – b)
print (“The Product. = “, a * b)
print (“The Quotient = “, a / b)
print (“The Remainder = “, a % 30)
print (“The Exponent = “, a ** 2)
print (“The Floor Division =”, a // 30)
#ProgramEnd
Output:
The Sum = 110
The Difference = 90
The Product = 1000
The Quotient = 10.0
The Remainder = 10
The Exponent = 10000
The Floor Division = 3
(ii) Relational or Comparative operators
A Relational operator is also called as Comparative operator which checks the relationship between two operands. If the relation is true, it returns True; otherwise it returns False.
Python supports following relational operators
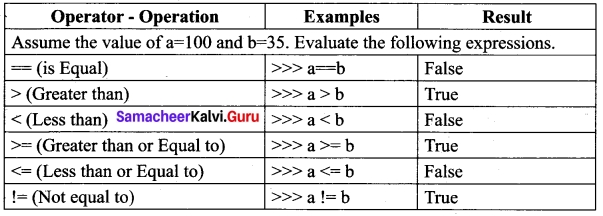
Program To test Relational Operators:
#Demo Program to test Relational Operators
a = int (input(“Enter a Value for A:”))
b = int (input(“Enter a Value for B:”))
print (“A = “, a ,” and B = “, b)
print (“The a==b = “, a == b)
print (“The a > b = “, a > b)
print (“The a < b = “, a < b)
print (“The a >= b = “, a >= b)
print (“The a <= b = “, a <= 0)
print (“The a != b = “, a!=b)
#Program End
Output:
Enter a Value for A: 35
Enter a Value for B:56
A = 35 and B = 56
The a==b = False
The a > b = False
The a < b = True
The a >= b = False
The a <= b = False
The a != b = True
![]()
(iii) Logical operators
In python, Logical operators are used to perform logical operations on the given relational expressions. There are three logical operators they are and, or and not.
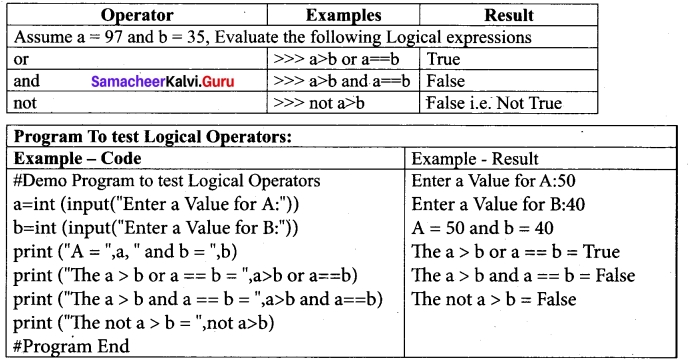
(iv) Assignment operators:
In Python, = is a simple assignment operator to assign values to variable. Let a = 5 and b = 10 assigns the value 5 to a and 10 to b these two assignment statement can also be given as a, b = 5, 10 that assigns the value 5 and 10 on the right to the variables a and b respectively. There are various compound operators in Python like +=, -=, *=, /=, %=, **= and //= are also available.
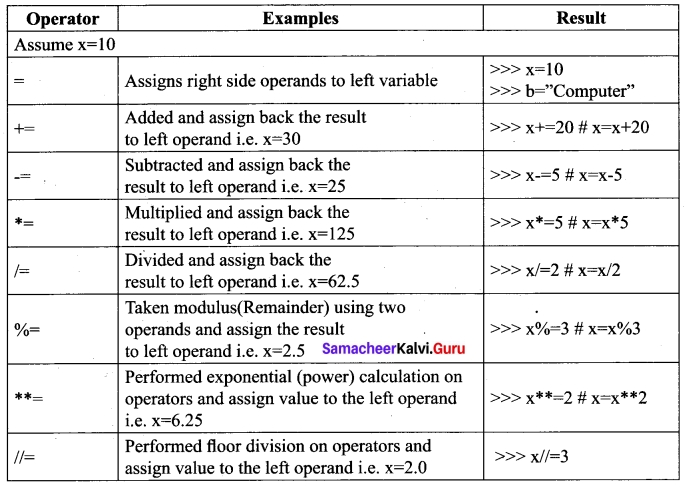
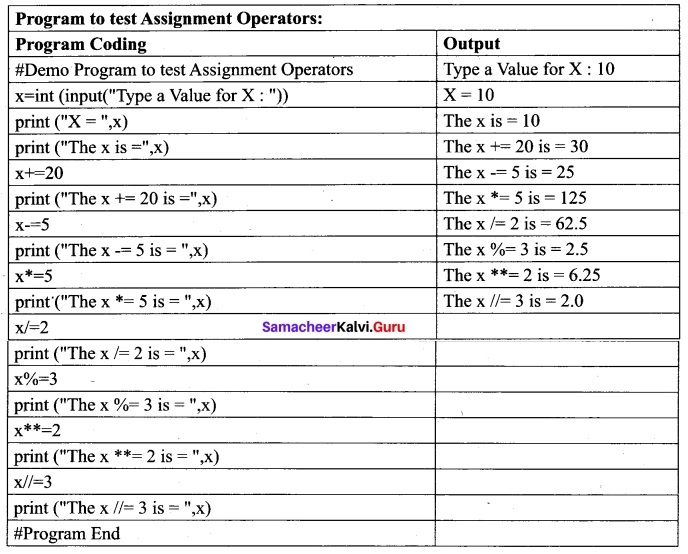
(v) Conditional operator:
Ternary operator is also known as conditional operator that evaluate something based on a condition being true or false. It simply allows testing a condition in a single line replacing the multiline if-else making the code compact.
The Syntax conditional operator is,
Variable Name = [on_true] if [Test expression] else [on_false]
Example:
min = 50 if 49 < 50 else 70 # min = 50 min = 50 if 49 > 50 else 70 # min = 70
Program to test Conditional (Ternary) Operator:
# Program to demonstrate conditional operator.
a, b = 30, 20
# Copy value of a in min if a < b else copy b
min = a if a < b else b print (“The Minimum of A and B is “,min) # End of the Program Output: The Minimum of A and B is 20
![]()
Question 36 (a).
Write a python script with SQL to display the name and grade of students who have born in the year 2001. Answer:
Querying a Date Column In this example we are going to display the name and grade of students who have born in the -year 2001
Example: import sqlite3
connection = sqlite3.connect (“Academy.db”)
cursor = connection.cursor ( )
cursor.execute(“SELECT Rollno,sname FROM student
WHERE(Birth_date >= 2001-01-01′ AND Birth_date <= ‘2001-12-01’)”)
result = cursor.fetchall( )
print(*result,sep=”\n”)
Output:
(5, ‘VARUN’)
[OR]
(b) Write a python program to display-
1
1 2
1 2 3
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Answer:
Program to illustrate the use nested loop -for within while loop
i = 1
while (i <= 6): for j in range (1, i): print (j,end=’\t’) print (end-\n’) i + = 1
Output
1
1 2
1 2 3
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Question 37 (a).
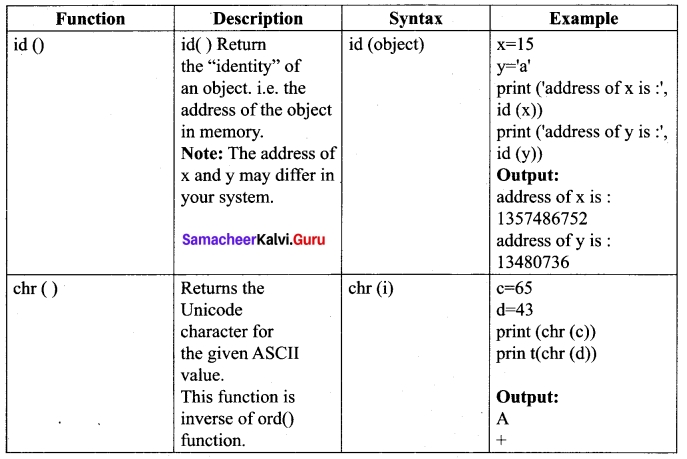
Explain the following built in functions.
(a) id ()
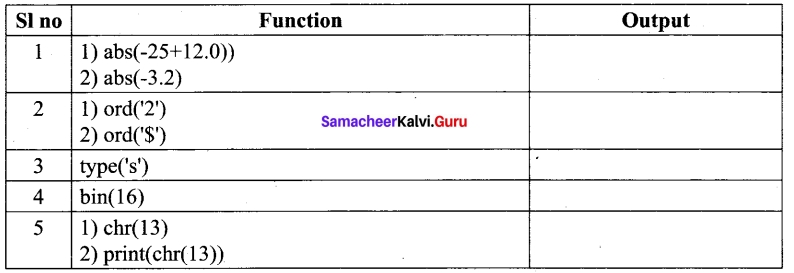
(b) Chr ()
(c) round ()
(d) type ()
(e) pow ()
Answer:
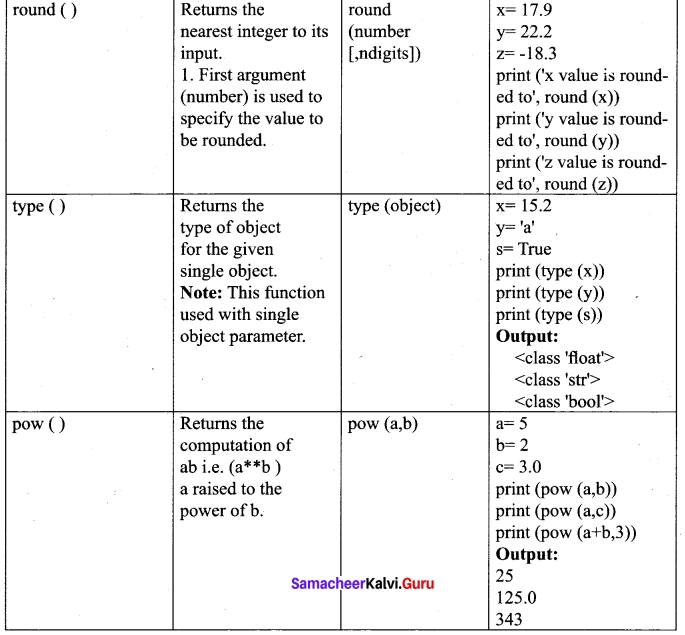
![]()
[OR]
(b) Explain how to delete elements from a list.
Answer:
Deleting elements from a list There are two ways to delete an element from a list viz. del statement and remove() function, del statement is used to delete known elements whereas remove() function is used to delete elements of a list if its index is unknown. The del statement can also be used to delete entire list.
Syntax:
del List [index of an element]
# to delete a particular element
del List [index from : index to]
# to delete multiple elements
del List
# to delete entire list
Example:
>>> MySubjects = [‘Tamil’, ‘Hindi’, ‘Telugu’, ‘Maths’]
>>> print (MySubjects)
[‘Tamil’, ‘Hindi’, ‘Telugu’, ’Maths’]
>>> del MySubjects[1]
>>> print (MySubjects)
[‘Tamil’, ‘Telugu’, ‘Maths’]
In the above example, the list MySubjects has been created with four elements, print statement shows all the elements of the list. In >>> del MySubjects[1] statement, deletes an element whose index value is 1 and the following print shows the remaining elements of the list.
Example:
>>> del MySubjects [1 :3]
>>> print(My Subjects)
[‘Tamil’]
In the above codes, >>> del MySubjects [1 : 3] deletes the second and third elements from the list. The upper limit of index is specified within square brackets, will be taken as -1 by the python.
Question 38 (a).
Explain various data model.
Answer:
- A data model describes how the data can be represented and accessed from a software after complete implementation
- It is a simple abstraction of complex real world data gathering environment.
- The main purpose of data model is to give an idea as how the final system or software will look like after development is completed.
Types of Data Model
Following are the different types of a Data Model
- Hierarchical Model
- Relational Model
- Network Database Model
- Entity Relationship Model
- Object Model
1. Hierarchical Model:
Hierarchical model was developed by IBM as Information Management System.
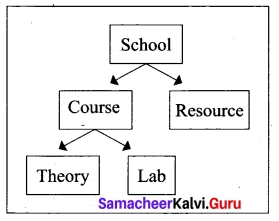
In Hierarchical model, data is represented as a simple tree like structure form. This model represents a one-to-many relationship i.e. parent – child relationship.
One child can have only one parent but one parent can have many children. This model is mainly used in IBM Main Frame computers.
2. Relational Model:
The Relational Database model was first proposed by E.F. Codd in 1970 . Now a days, it is the most widespread data model used for database applications around the world.
The basic structure of data in relational model is tables (relations). All the information’s related to a particular type is stored in rows of that table. Hence tables are also known as relations in a relational model. A relation key is an attribute which uniquely identifies a particular tuple (row in a relation (table)).
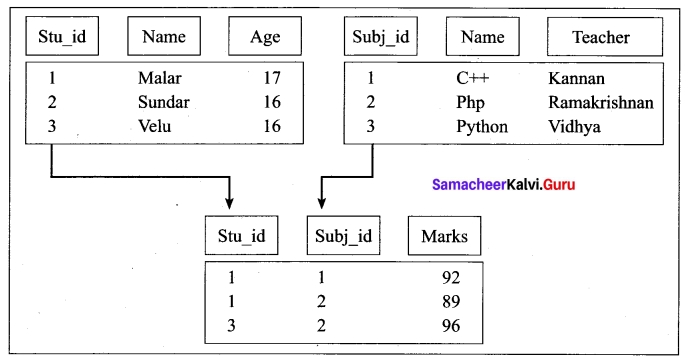
![]()
3. Network Model:
Network database model is an extended form of hierarchical data model. The difference between hierarchical and Network data model is:
- In hierarchical model, a child record has only one parent node,
- In a Network model, a child may have many parent nodes. It represents the data in many to – many relationships.
This model is easier and faster to access the data
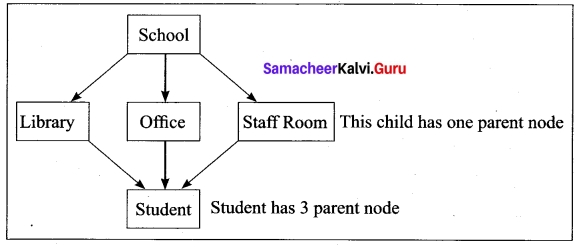
School represents the parent node
Library, Office and Staff room is a child to school (parent node)
Student is a child to library, office and staff room (one to many relationship)
4. Entity Relationship Model.
In this database model, relationship are created by dividing the object into entity and its characteristics into attributes.
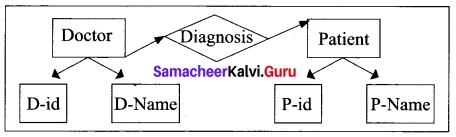
It was developed by Chen in 1976. This model is useful in developing a conceptual design for the database. It is very simple and easy to design logical view of data. The developer can easily understand the system by looking at ER model constructed.
Rectangle represents the entities. E.g. Doctor and Patient
Ellipse represents the attributes E.g. D-id, D-name, P-id, P-name. Attributes describes the characteristics and each entity becomes a major part of the data stored in the database. Diamond represents the relationship in ER diagrams
E.g. Doctor diagnosis the Patient.
5. Object Model
Object model stores the data in the form of objects, attributes and methods, classes and Inheritance. This model handles more complex applications, such as Geographic information System (GIS), scientific experiments, engineering design and manufacturing. It is ‘ used in file Management System. It represents real world objects, attributes and behaviors. It provides a clear modular structure. It is easy to maintain and modify the existing code.
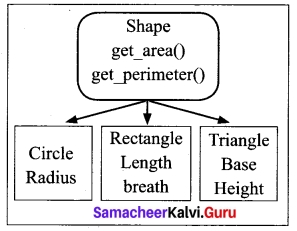
An example of the Object model is Shape,
Circle, Rectangle and Triangle are all objects in this model.
- Circle has the attribute radius.
- Rectangle has the attributes length and breadth.
- Triangle has the attributes base and height.
- The objects Circle, Rectangle and Triangle inherit from the object Shape.
[OR]
(b) Explain creating a New Normal CSV file with syntex and program.
Answer:
Creating A New Normal CSV File
When you have a set of data that you would like to store inside a CSV file, it’s time to do the opposite and use the write function.
The csv.writer() method returns a writer object which converts the user’s data into delimited strings on the given file-like object. The writerow() method writes a row of data into the specified file.
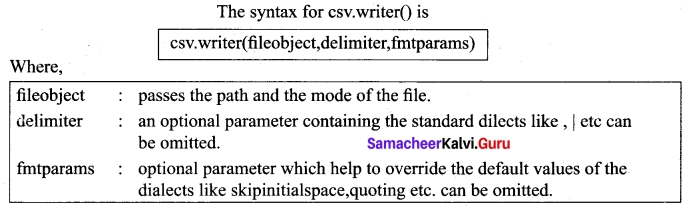
![]()
You can create a normal CSV file using writer() method of csv module having default delimiter comma (,)
Here’s an example.
The following Python program converts a List of data to a CSV file called “Pupil.csv” that uses, (comma) as a value separator.

When you open the “Pupil.csv” file with a text editor, it will show the content as follows.
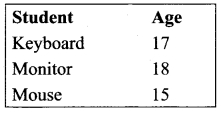
In this program, csv.writer() method converts all the data in the list “csvData” to strings and create the content as file like object. The writerows () method writes all the data in to the new CSV file “Pupil.csv”.