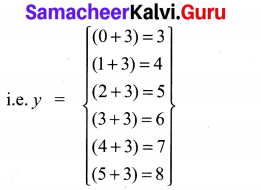
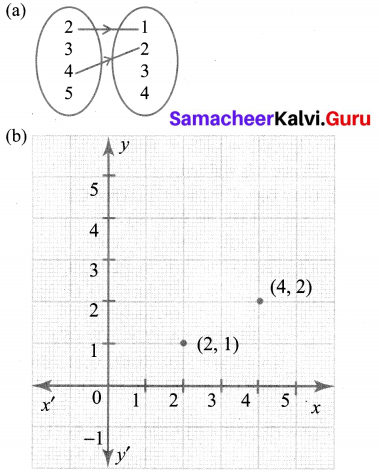
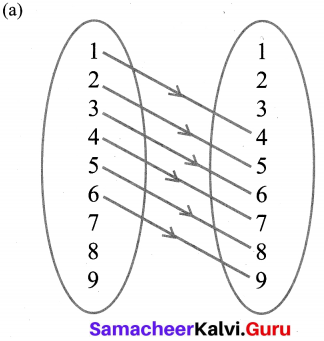
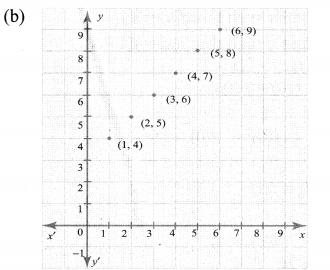
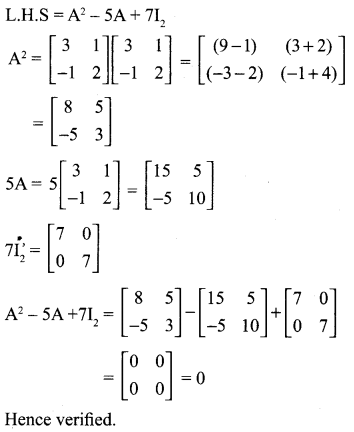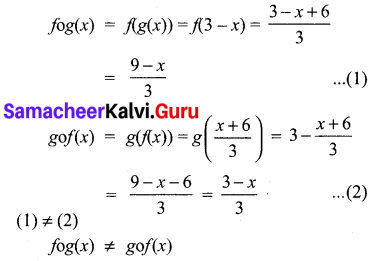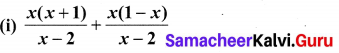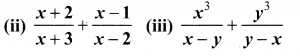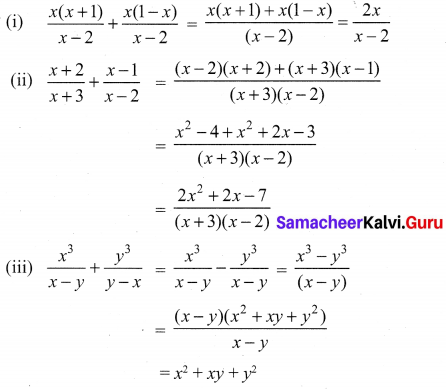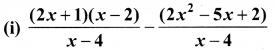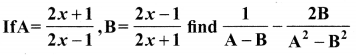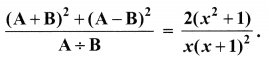You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.18
10th Maths Exercise 3.18 Answers Question 1.
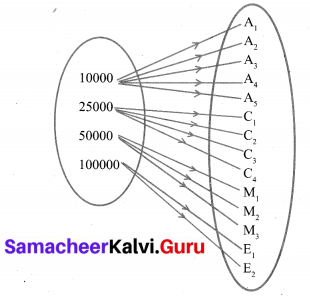
If A is of order p × q and B is of order q × r what is the order of AB and BA?
Solution:
If A is of order p × q [∵ p × q q × r = p × r]
the order of AB = p × r [∵ q × r p × q = r ≠ p]
Product of BA cannot be defined/found as the number of columns in B ≠. The number of rows in A.
10th Maths Exercise 3.18 Question 2.
If A is of order p × q and B is of order q × r what is the order of AB and BA?
Answer:
Order of A = a × (a + 3)
Order of B = b × (17 – b)
Given: Product of AB exist
a + 3 = b
a – b = – 3 ….(1)
Product of BA exist
17 – b = a
– a – b = -17
a + b = 17 ………(2)
(1) + (2) ⇒ 2a = 14
a = \(\frac { 14 }{ 2 } \) = 7
Substitute the value of a = 7 in (1)
7 – b = -3 ⇒ -b = -3 -7
-b = -10 ⇒ b = 10
The value of b = 7 and b = 10
Ex 3.18 Class 10 Question 3.
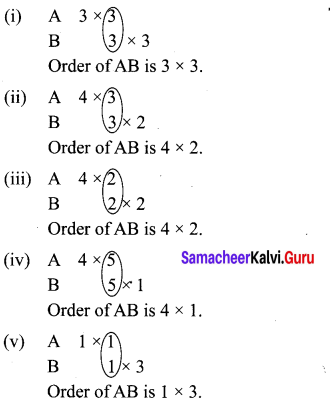
Find the order of the product matrix AB if
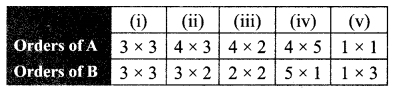
Solution:
10th Maths Exercise 3.18 Samacheer Kalvi Question 4.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll}{2} & {5} \\ {4} & {3}\end{array}\right]\), B = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}{1} & {-3} \\ {2} & {5}\end{array}\right]\) find AB, BA and check if AB = BA?
Solution:
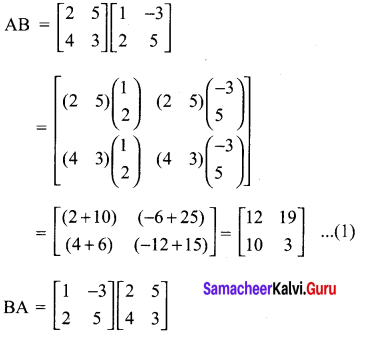
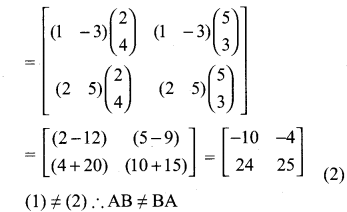
Exercise 3.18 Class 10 Question 5.
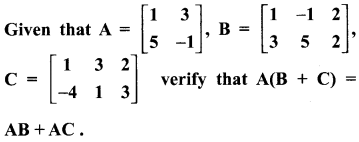
Solution:
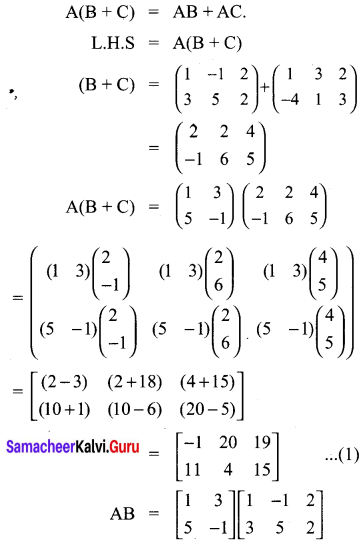
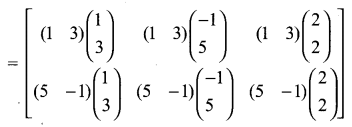
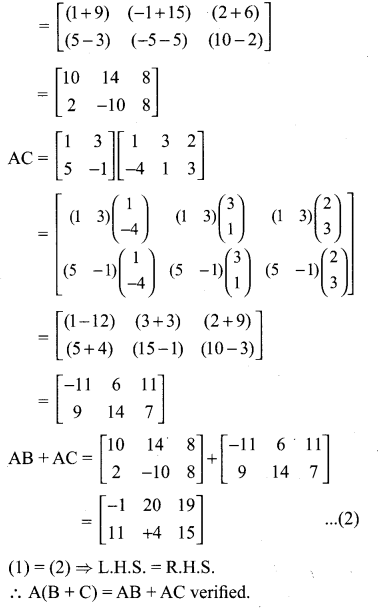
Ex 3.18 Class 10 Samacheer Question 6.
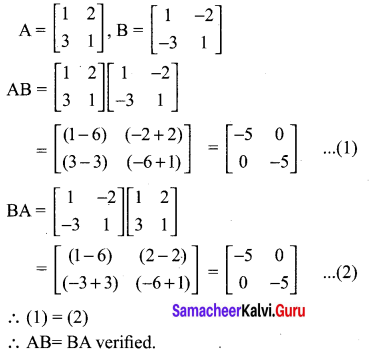
Show that the matrices A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll}{1} & {2} \\ {3} & {1}\end{array}\right]\), B = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}{1} & {-2} \\ {-3} & {1}\end{array}\right]\) satisfy commutative property AB = BA
Solution:
10th Maths Exercise 3.18 In Tamil Question 7.
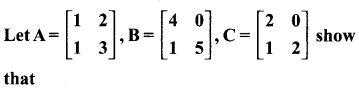
(i) A(BC) = (AB)C
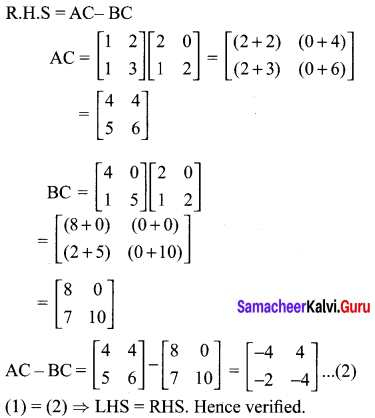
(ii) (A – B)C = (AC – BC)
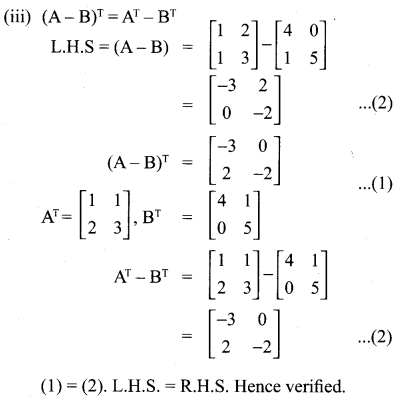
(iii) (A- B)T = AT – BT
Solution:
(i) A(BC) = (AB)C
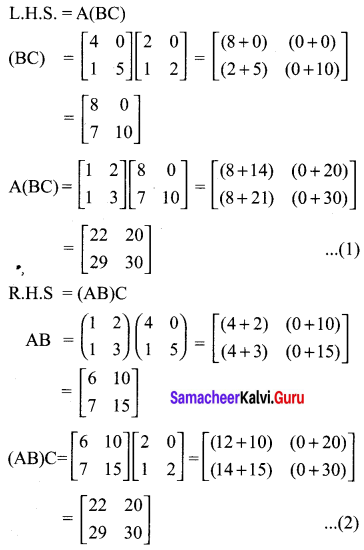
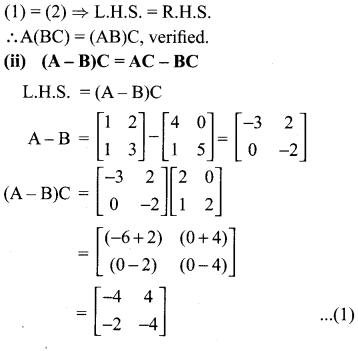
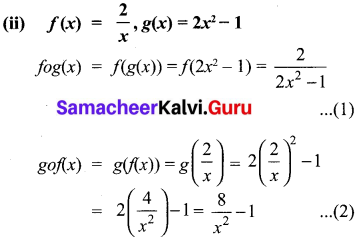
10th New Syllabus Maths Exercise 3.18 Question 8.
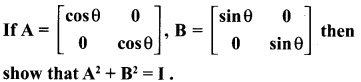
Solution:
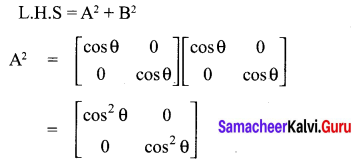
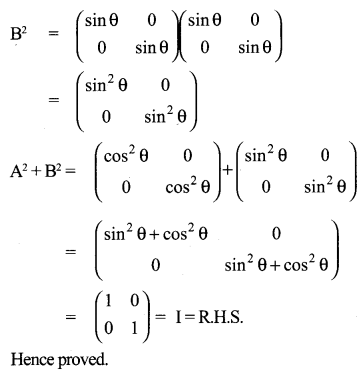
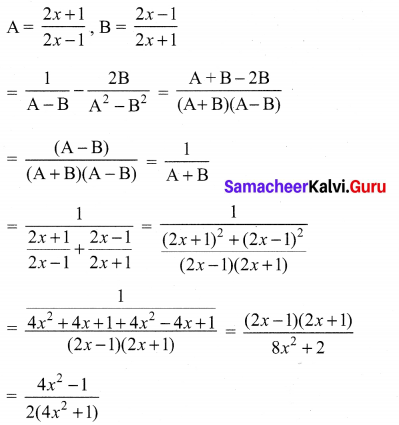
10th Maths Exercise 3.18 3rd Sum Question 9.
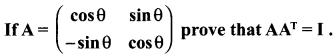
Solution:
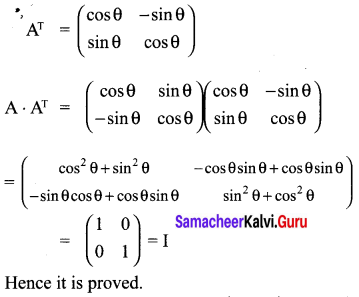
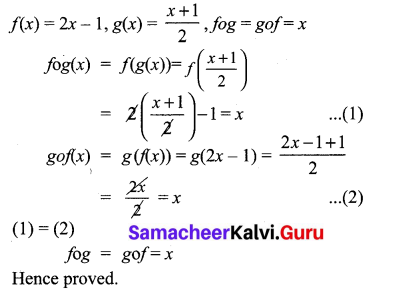
10th Maths 3.18 Question 10.
Verify that A2 = I when A = \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}{5} & {-4} \\ {6} & {-5}\end{array}\right)\)
Solution:

Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Graph Question 11.
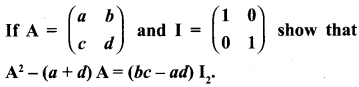
Solution:
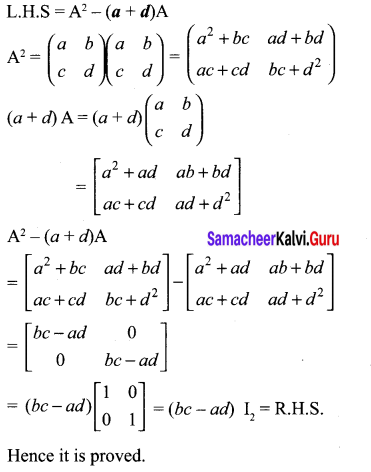
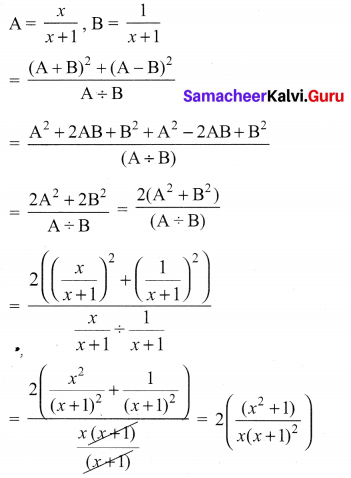
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 10th Maths Question 12.
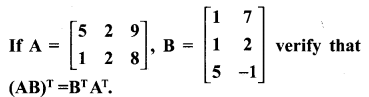
Solution:
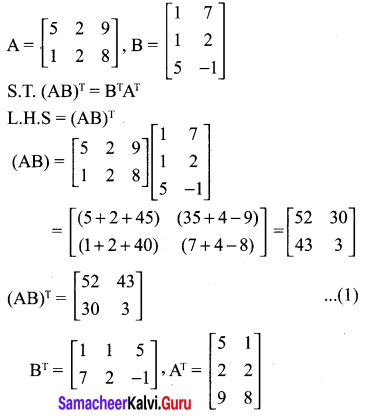

Samacheerkalvi.Guru 10th Maths Question 13.
If A = \(\) show that A2 – 5A + 7I2 = 0.
Solution: