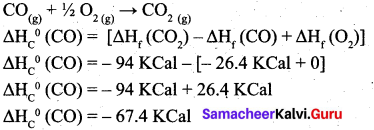
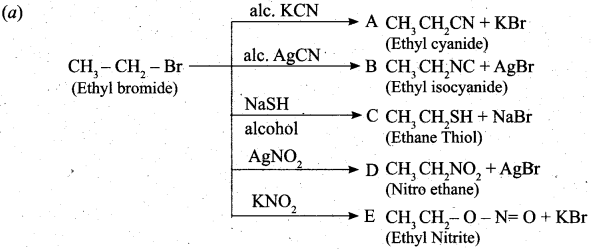
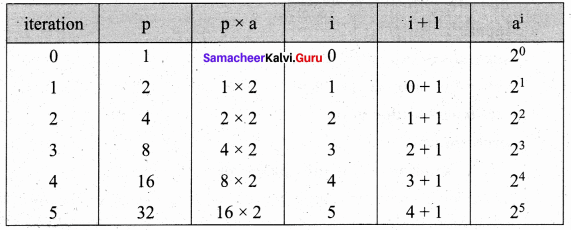
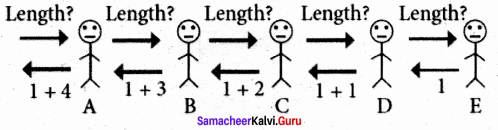
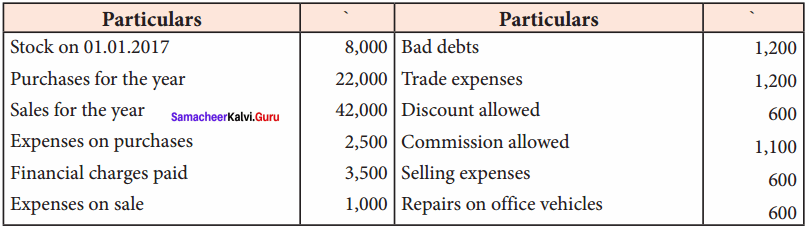
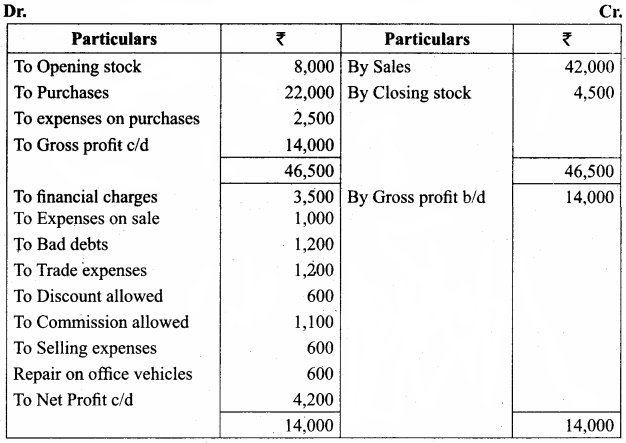
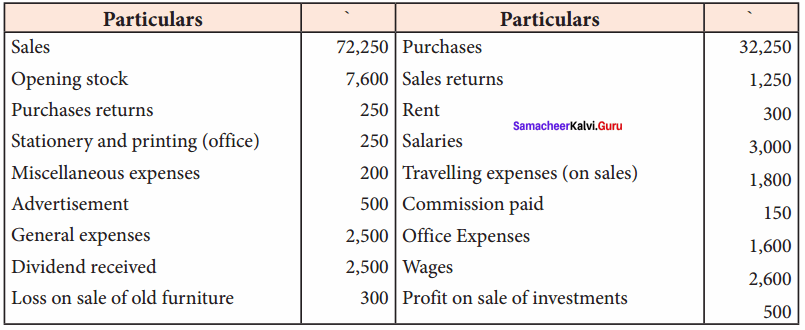
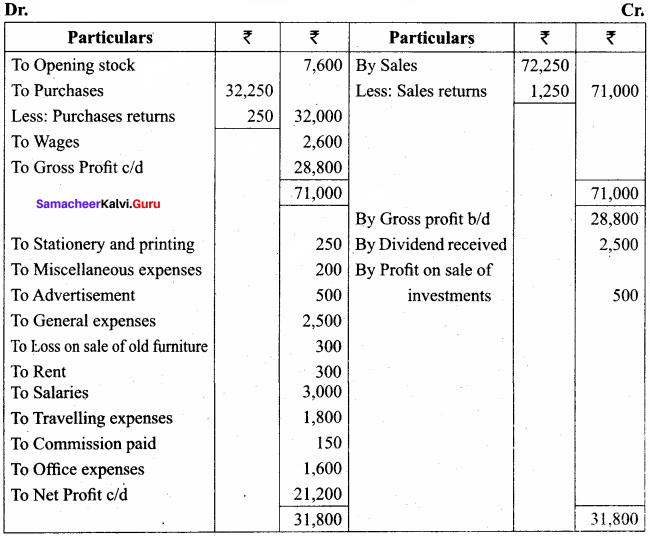
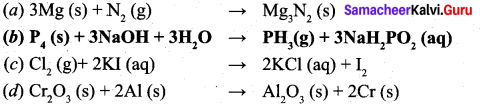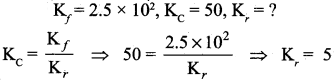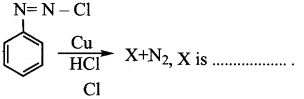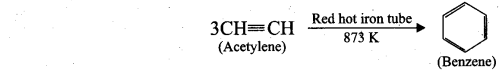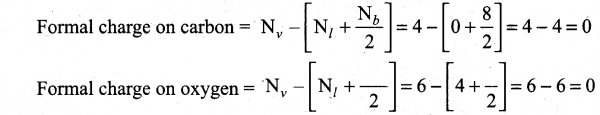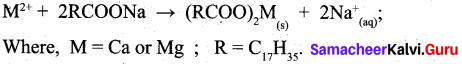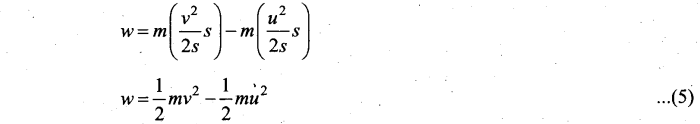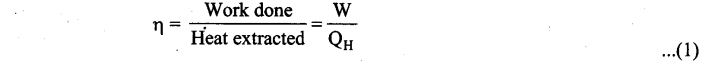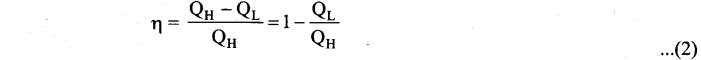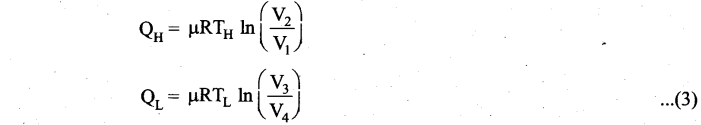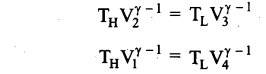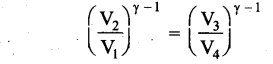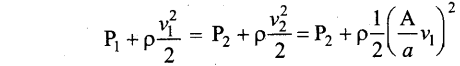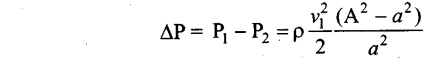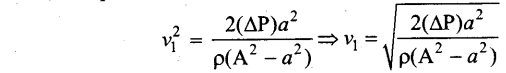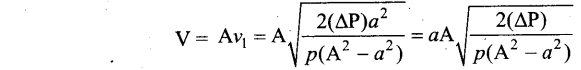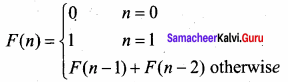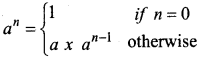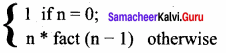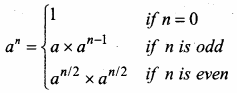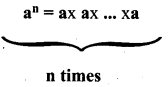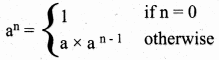Students can Download Computer Science Chapter 11 Functions Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 11 Functions
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Functions Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – 1
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
Which of the following header file defines the standard I/O predefined functions?
(a) stdio.h
(b) math.h
(c) string.h
(d) ctype.h
Answer:
(a) stdio.h
Question 2.
Which function is used to check whether a character is alphanumeric or not?
(a) isalpha()
(b) isdigit()
(c) isalnum()
(d) islower()
Answer:
(c) isalnum()
Question 3.
Which function begins the program execution?
(a) isalpha()
(b) isdigit()
(c) main()
(d) islower()
Answer:
(c) main()
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following function is with a return value and without any argument?
(a) x = display(int, int)
(b) x = display()
(c) y = display(float)
(d) display(int)
Answer:
(b) x = display()
Question 5.
Which is return data type of the function prototype of add(int, int);?
(a) int
(b) float
(c) char
(d) double
Answer:
(a) int
Question 6.
Which of the following is the scope operator?
(a) >
(b) &
(c) %
(d) ::
Answer:
(d) ::
PART – 2
II. Answer to all the questions
Question 1.
Define Functions.
Answer:
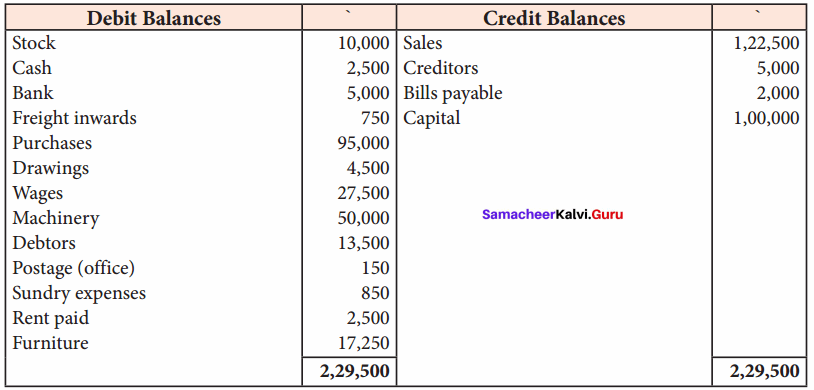
A large program can typically be split into small sub – programs (blocks) called as functions where each sub-program can perform some specific functionality. Functions reduce the size and complexity of a program, makes it easier to understand, test and check for errors.
Question 2.
Write about strlen() function.
Answer:
The strlen() takes a null terminated byte string source as its argument and returns its length. The length does not include the null(\0) character.
Question 3.
What are importance of void data type? void type has two important purposes:
Answer:
- To indicate the function does not return a value.
- To declare a generic pointer.
![]()
Question 4.
What is Parameter and list its types?
Answer:
Arguments or parameters are the means to pass values from the calling function to the called function. The variables used in the function definition as parameters are known as formal parameters. The constants, variables or expressions used in the function call are known as actual parameters.
Types : Default arguments and Constant Arguments.
Question 5.
Write a note on Local Scope.
Answer:
- A local variable is defined within a block. A block of code begins and ends with curly braces { }.
- The scope of a local variable is the block in which it is defined.
- A local variable cannot be accessed from outside the block of its declaration.
- A local variable is created upon entry into its block and destroyed upon exit.
PART – 3
III. Answer to all the questions
Question 1.
What is Built – in functions?
Answer:
C++ provides a rich collection of functions ready to be used for various tasks. The tasks to be performed by each of these are already written, debugged and compiled, their definitions alone are grouped and stored in files called header files. Such ready – to – use sub programs are called pre – defined functions or built – in functions.
Question 2.
What is the difference between isupper() and toupper() functions?
Answer:
isupper():
- This function is used to check the given character is uppercase.
- This function will return 1 if true otherwise 0.
toupper():
- This function is used to convert the given character into its uppercase.
- This function will return the upper case equivalent of the given character. If the given character itself is in upper case, the output will be the same.
Question 3.
Write about strcmp() function.
Answer:
The strcmp() function takes two arguments: string1 and string2. It compares the contents of string1 and string2 lexicographically.
The strcmp() function returns a:
- Positive value if the first differing character in string1 is greater than the corresponding character in string2. (ASCII values are compared)
- Negative value if the first differing character in string1 is less than the corresponding character in string2.
- 0 if string1 and string2 are equal.
![]()
Question 4.
Write short note on pow() function in C++.
Answer:
The pow() function returns base raised to the power of exponent. If any argument passed to pow() is long double, the return type is promoted to long double. If not, the return type is double. The pow() function takes two arguments:
- base – the base value
- exponent – exponent of the base
Example:
cout << pow(5, 2);
Output:
25
Question 5.
What are the information the prototype provides to the compiler?
Answer:
The prototype above provides the following information to the compiler:
- The return value of the function is of type long.
- Fact is the name of the function.
- The function is called with two arguments:
- The first argument is of int data type.
- The second argument is of double data type, int display(int, int) // function prototype//.
The above function prototype provides details about the return data type, name of the function and a list of formal parameters or arguments.
Question 6.
What is default arguments? Give example.
Answer:
In C++, one can assign default values to the formal parameters of a function prototype. The Default arguments allows to omit some arguments when calling the function.
1. For any missing arguments, complier uses the values in default arguments for the called function.
2. The default value is given in the form of variable initialization.
Example : void defaultvalue(int n1 = 10, n2 = 100);
3. The default arguments facilitate the function call statement with partial or no arguments.
Example :
- defaultvalue (x, y);
- defaultvalue (200, 150);
- defaultvalue (150);
- defaultvalue (x, 150);
4. The default values can be included in the function prototype from right to left, i.e., we cannot have a default value for an argument in between the argument list.
Example:
- void defaultvalue (int n1=10, n2);//invalid prototype.
- void defaultvalue (int n1, n2 = 10);//valid prototype.
PART – 4
IV. Answers to all the questions
Question 1.
Explain Call by value method with suitable example.
Answer:
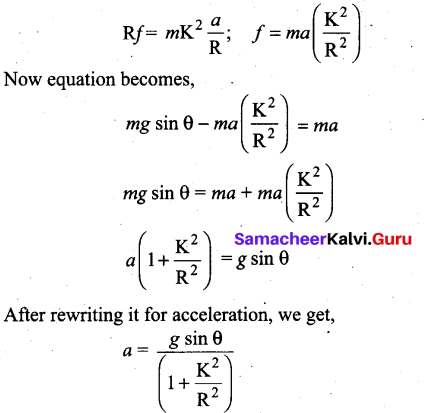
This method copies the value of an actual parameter into the formal parameter of the function. In this case, changes made to formal parameter within the function will have no effect on the actual parameter.
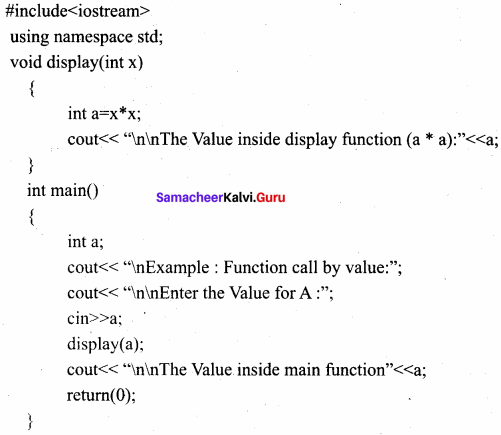
Output:
Example : Function call by value
Enter the Value for A : 5
The Value inside display function (a * a) : 25
The Value inside main function 5
Question 2.
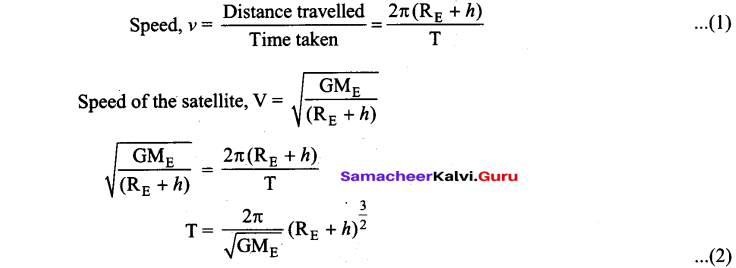
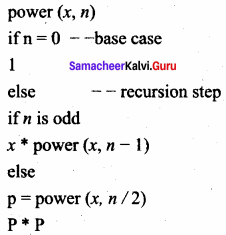
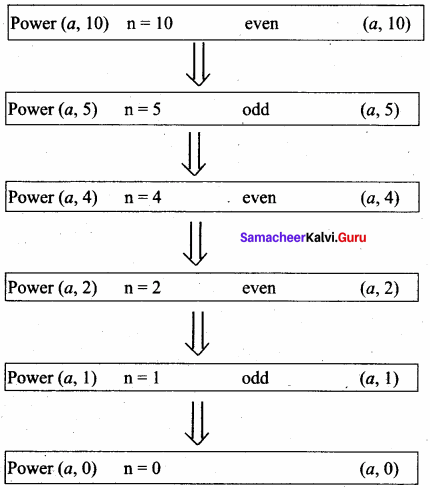
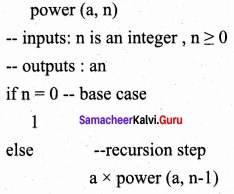
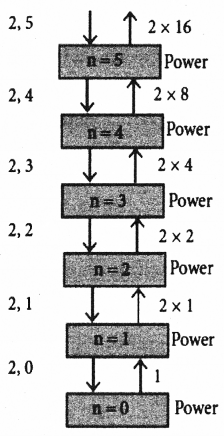
What is Recursion? Write a program to find GCD using recursion.
Answer:
A function that calls itself is known as recursive function. And, this technique is known as recursion.

Output:
Enter two numbers: 81 153
gcd : 9
Question 3.
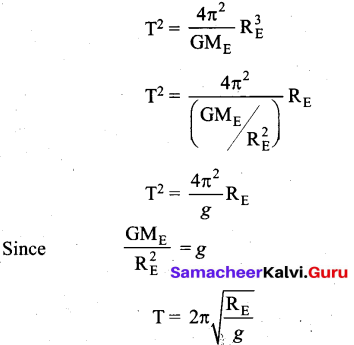
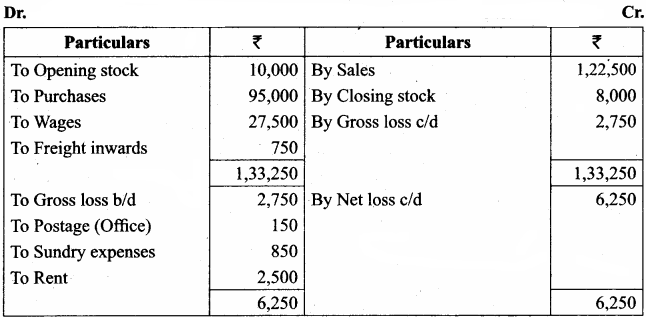
What are the different forms of function return? Explain with example.
Answer:
The return statement:
Returning from the function is done by using the return statement. The return statement stops execution and returns to the calling function. When a return statement is executed, the function is terminated immediately at that point. The return statement is used to return from a function. It is categorized as a jump statement because it terminates the execution of the function and transfer the control to the called statement.
Syntax:
return expression/variable;
Example : retum(a + b); retum(a);
return; // to terminate the function
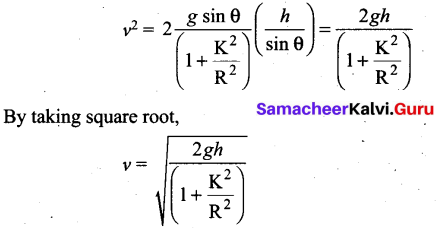
The Returning values:
The functions that return no value is declared as void. The data type of a function is treated as int, if no data type is explicitly mentioned. For example,
For Example:
int add (int, int);
add (int, int);
In both prototypes, the return value is int, because by default the return value of a function in C++ is of type int.
Returning Non – integer values:
A string can also be returned to a calling statement.

Output:
Example: Function with Non Integer Return Chennai
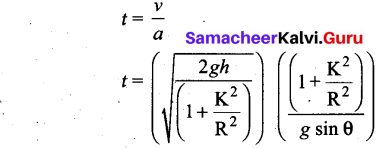
The Returning by reference:
#include
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int n 1 = 150;
int &n 1 ref = n1;
cout << “\nThe Value of N1 = “<< n1 << “and n 1 Reference =”<< n 1 ref;
n 1 ref++;
cout << “\n After nl increased the Value of N1 =”<< n1;
cout << “and n 1 Reference = ”<< n 1 ref;
retum(0);
}
Output:
The Value of N1 = 150 and nl Reference =150
After n1 increased the Value of N1 = 151 and n1 Reference =151
![]()
Question 4.
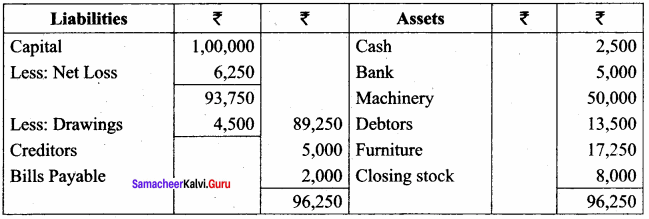
Explain scope of variable with example.
Answer:
Scope refers to the accessibility of a variable.
There are four types of scopes in C++
- Local Scope
- Function Scope
- File Scope
- Class Scope
1. Local Scope:
- A local variable is defined within a block. A block of code begins and ends with curly braces {}.
- The scope of a local variable is the block in which it is defined.
- A local variable cannot be accessed from outside the block of its declaration.
- A local variable is created upon entry into its block and destroyed upon exit;
Example:
int main( )
{
int a,b; //Local variable
}
2. Function Scope:
- The scope of variable within a function is extended to the function block and all sub-blocks therein.
- The lifetime of a function scope variable is the lifetime of the function block.
Example:
int. sum(intx, int y); //x and y has function scope.
3. File Scope:
- A variable declared above all blocks and functions (including main()) has the scope of a file.
- The lifetime of a file scope variable is the lifetime of a program.
- The file scope variable is also called as global variable.
Example:
#include
using namespace std;
int x,y; //x and y are global variable
void main()
{
……..
}
4. Class Scope:
- Data members declared in a class has the class scope.
- Data members declared in a class can be accessed by all member functions of the class.
Example:
Class example
{
int x,y; //x and y can be accessed by print() and void():
void print();
Void total();
};
Question 5.
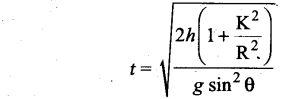
Write a program to accept any integer number and reverse it.
Answer:

Output:
Enter number : 1 2 3
Reverse number: 3 2 1
Samacheer kalvi 11th Computer Science Functions Additional Questions and Answers
PART – 1
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
………………. is the name of the function.
(a) Pre – defined
(b) Built – in
(c) Library
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 2.
………………. is used to check whether the given character is an alphabet or not.
(a) isalnum()
(b) isalpha()
(c) isalph()
(d) isal()
Answer:
(b) isalpha()
Question 3.
The strcpy() function takes two arguments of ……………….
(a) target and source
(b) upper and lower
(c) base and exponent
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) target and source
![]()
Question 4.
………………. takes a null terminated byte string source as its argument and returns its length.
(a) strcpy()
(b) strlen()
(c) strcmp()
(d) strcat()
Answer:
(b) strlen()
Question 5.
The pow() function takes the two arguments of ……………….
(a) target and source
(b) upper and lower
(c) base and exponent
(d) source and exponent
Answer:
(c) base and exponent
Question 6.
………………. is the name of the function.
(a) fact
(b) task
(c) arguments
(d) none of these
Answer:
(d) none of these
Question 7.
The C++ program always have main() function to begin the program execution.
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) null
Answer:
(a) 1
Question 8.
Arguments are also called as ……………….
(a) variable
(b) constant
(c) function
(d) parameters
Answer:
(d) parameters
Question 9.
In C++ the arguments can be passed to a function in ………………. ways.
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) 7
Answer:
(a) 2
Question 10.
Inline functions execute faster but requires more ……………….
(a) variables
(b) pointers
(c) memory
(d) functions
Answer:
(c) memory
PART – 2
II. Very Short Answers
Question 1.
Write about reusability.
Answer:
- Few lines of code may be repeatedly used in different contexts. Duplication of the same code can be eliminated by using functions which improves the maintenance and reduce program size.
- Some functions can be called multiple times with different inputs.
Question 2.
What is user – defined functions?
Answer:
C++ also provides the facility to create new functions for specific task as per user requirement. The name of the task and data required (arguments) are decided by the user and hence they are known as User-defined functions.
Question 3.
What is constant arguments and write its syntax?
Answer:
The constant variable can be declared using const keyword. The const keyword makes variable , value stable. The constant variable should be initialized while declaring. The const modifier enables to assign an initial value to a variable that cannot be changed later inside the body of the function.
Syntax:
(const )
![]()
Question 4.
What are the advantages of inline functions?
Answer:
Advantages of inline functions:
- Inline functions execute faster but requires more memory space.
- Reduce the complexity of using STACKS.
Question 5.
What is function scope?
Answer:
Function Scope:
- The scope of variables declared within a function is extended to the function block, and all sub – blocks therein.
- The life time of a function scope variable, is the life time of the function block. The scope of.
PART – 3
III. Short Answers
Question 1.
What is divide and conquer?
Answer:
Divide and Conquer
- Complicated programs can be divided into manageable sub programs called functions.
- A programmer can focus on developing, debugging and testing individual functions.
- Many programmers can work on different functions simultaneously.
Question 2.
Define library functions.
Answer:
C++ provides a rich collection of functions ready to be used for various tasks. The tasks to be performed by each of these are already written, debugged and compiled, their definitions alone are grouped and stored in files called header files. Such ready – to – use sub programs are called pre – defined functions or built – in functions or Library Functions.
Question 3.
What is isdigit()? Give example.
Answer:
This function is used to check whether a given character is a digit or not. This function will return 1 if the given character is a digit, and 0 otherwise.
Example:
using namespace std;
#include
#include int main( )
{
char ch;
cout << “\n Enter a Character:”; cin >> ch;
cout << “\n The Return Value of isdigit(ch) is << isdigit(ch);
}
Output – 1
Enter a Character: 3
The Return Value of isdigit(ch) is : 1
Output – 2
Enter a Character: A
The Return Value of isdigit(ch) is :0
Question 4.
Write a program using pow() and sin() function.
Answer:
The pow() function returns base raised to the power of exponent. The sin() function takes a single argument in radians.
#include
#include using namespace std;
int main ()
{
double base, exponent, result;
base = 5;
exponent = 4;
result = pow(base, exponent);
cout << “pow(“ << base << “A” << exponent <<”) =” << result;
double x = 25;
result = sin(x);
cout << “\nsin(“<< x <<”)=”<<result;
return 0;
}
Output:
pow (5^4) = 625
sin (25) = – 0.132352
Question 5.
What is return statement with example?
Answer:
The return statement stops execution and returns to the calling function. When a return statement is executed, the function is terminated immediately at that point. The return statement is used to return from a function. It is categorized as a jump statement because it terminates the execution of the function and transfer the control to the called statement.
Example:
return(a + b); return(a);
return; // to terminate the function
![]()
Question 6.
What is scope resolution operation?
Answer:
- The scope operator reveals the hidden scope of a variable. The scope resolution operator (::) is used for the following purposes.
- To access a Global variable when there is a Local variable with same name. An example using Scope Resolution Operator.
PART – 4
IV. Explain in Detail
Question 1.
Explain about generating random numbers with suitable program.
Answer:
The srand() function in C++ seeds the pseudo random number generator used by the rand() function. The seed for rand() function is 1 by default. It means that if no srand() is called before rand(), the rand() function behaves as if it was seeded with srand( 1). The srand() function takes an unsigned integer as its parameter which is used as seed by the rand() function. It is defined inor header file.
#include
#include using namespace std; int main()
{
int random = rand(); /* No srand() calls before rand(), so seed = 1*/
cout << “\nSeed = 1, Random number =” << random;
srand(10);
/* Seed= 10 */
random = rand();
cout << “\n\n Seed =10, Random number =” << random;
return 0;
}
Output:
Seed = 1, Random number = 41
Seed =10, Random number 71
Question 2.
Explain about Inline functions with a suitable program.
Answer:
An inline function looks like normal function in the source file but inserts the function’s code directly into the calling program. To make a function inline, one has to insert the keyword inline in the function header.
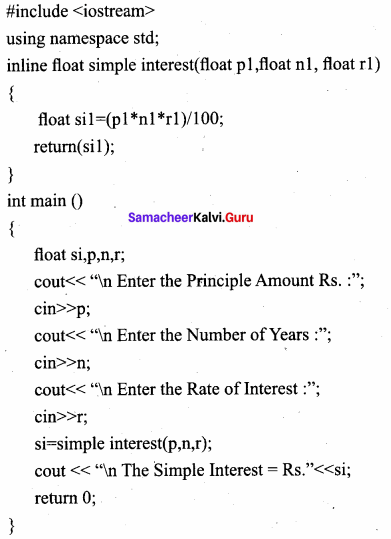
Output:
Enter the Principle Amount Rs. :60000
Enter the Number of Years : 10
Enter the Rate of Interest :5
The Simple Interest = Rs. 30000
Question 3.
Write about function prototype.
Answer:
C++ program can contain any number of functions. But, it must always have only one main() function to begin the program execution. We can write the definitions of functions in any order as we wish. We can define the main() function first and all other functions after that or we can define all the needed functions prior to main(). Like a variable declaration, a function must be declared before it is used in the program. The declaration statement may be given outside the main() function
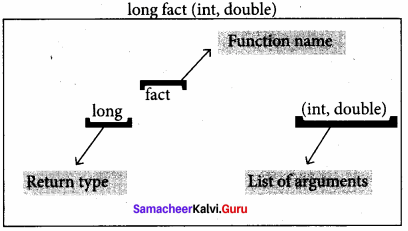
The prototype above provides the following information to the compiler:
- The return value of the function is of type long.
- Fact is the name of the function.
- The function is called with two arguments:
- The first argument is of int data type.
- The second argument is of double data type, int display(int, int)//function prototype//
The above function prototype provides details about the return data type, name of the function and a list of formal parameters or arguments.
![]()
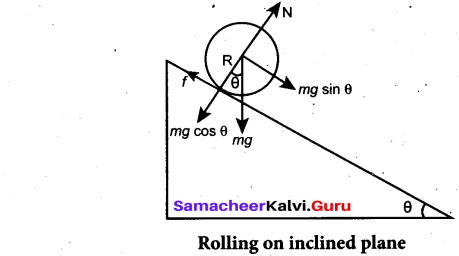
Question 4.
Explain about address method.
Answer:
This method copies the address of the actual argument into the formal parameter. Since the address of the argument is passed, any change made in the formal parameter will be reflected back in the actual parameter.
#include
using namespace std;
void display(int & x) //passing address of a//
{
x = x*x;
cout << “\n\n The Value inside display function (n1 x n1) :”<< x ;
}
int main()
{
intn 1;
cout << “\n Enter the Value for N1 cin >> n1;
cout << “\n The Value of N1 is inside main function Before passing:” << n1;
display(n1);
cout << “\n The Value of N1 is inside main function After passing (n1 x n1):”<< n1; retum(O);
}
Output:
Enter the Value for N1 : 45
The Value of N1 is inside main function Before passing : 45
The Value inside display function (n1 x n1) : 2025
The Value ofNl is inside main function After passing (n1 x n1): 2025
![]()
Question 5.
Given data: Principal amount Rs. 50000
Number of years 5
Rate of interest 7
To find the simple interest of the above mentioned given data. Write a C++ program using inline functions.
Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
inline float simple interest(float p1, float n 1, float r 1)
{
float sil=(pl*nl*rl)/100;
retum(sil);
}
int main ()
{
float si,p,n,r;
cout << “\n Enter the Principle Amount Rs. :”; cin >> p;
cout << “\n Enter the Number of Years :”; cin >> n;
cout << “\n Enter the Rate of Interest :”; cin >> r;
si = simple interest(p, n, r);
cout << “\n The Simple Interest = Rs.” << si;
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter the Principle Amount Rs. : 50000
Enter the Number of Years : 5
Enter the Rate of Interest : 7
The Simple Interest = Rs. 17500