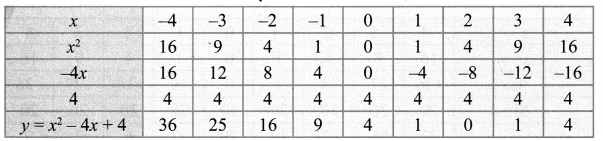
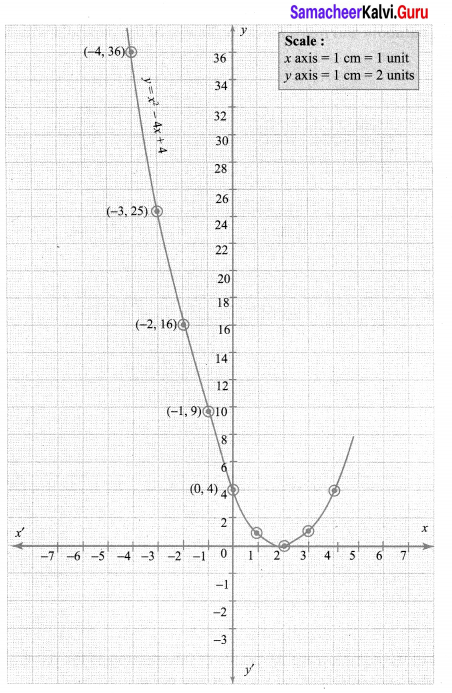
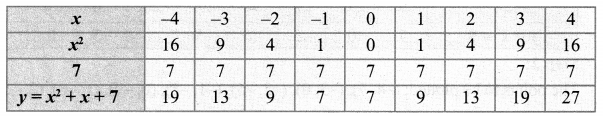
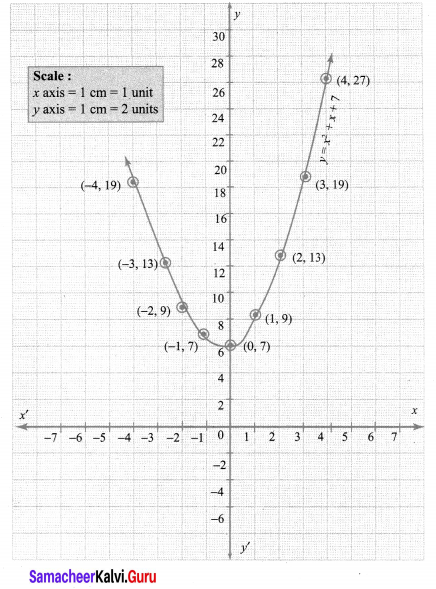
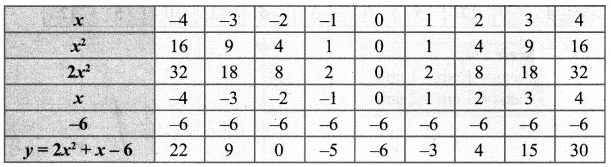
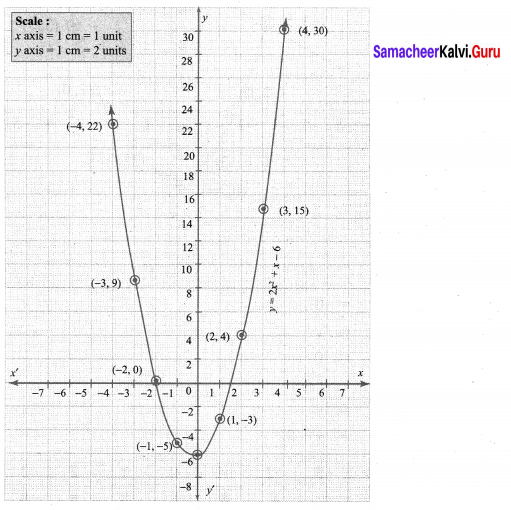
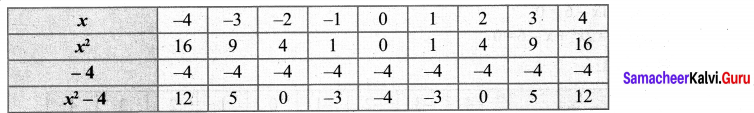
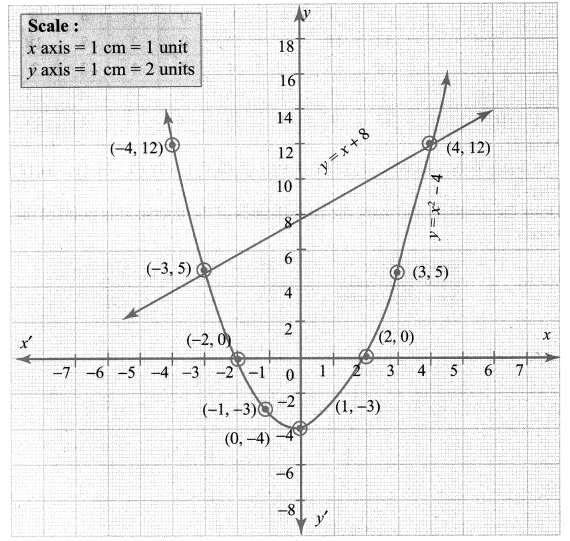
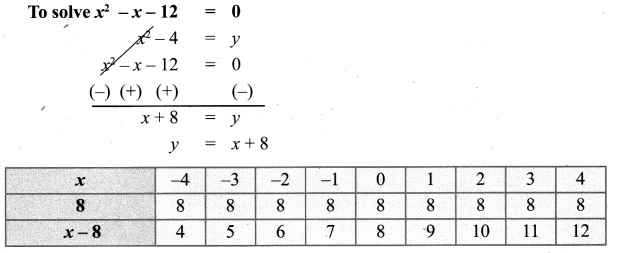
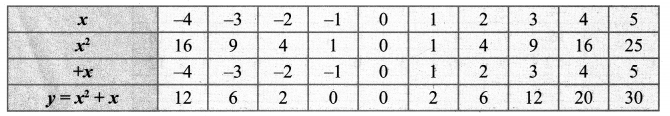
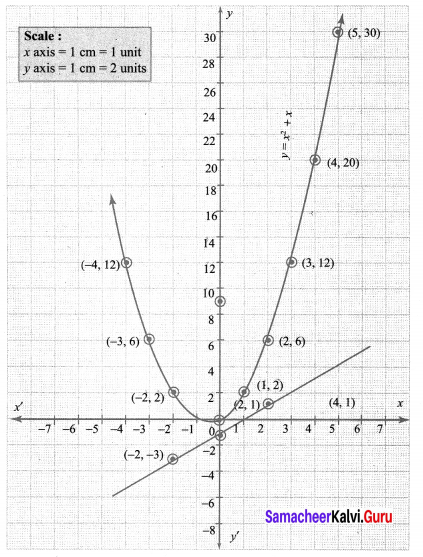
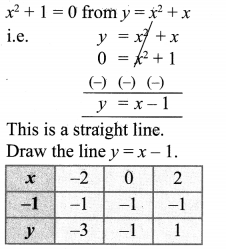
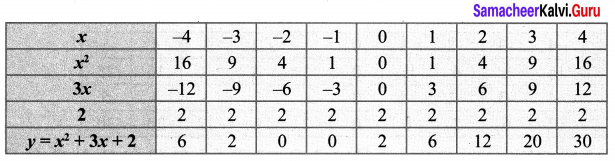
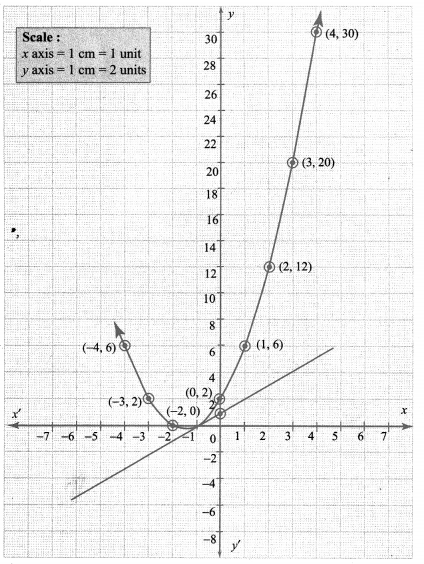
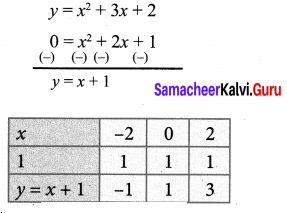
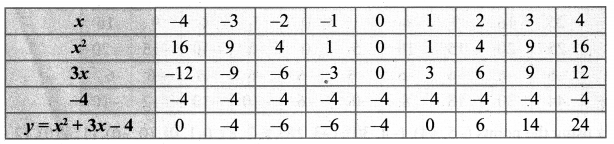
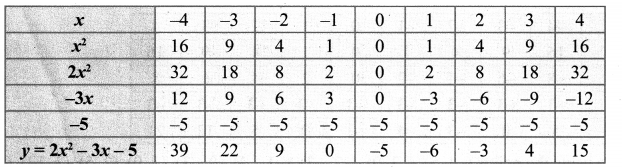
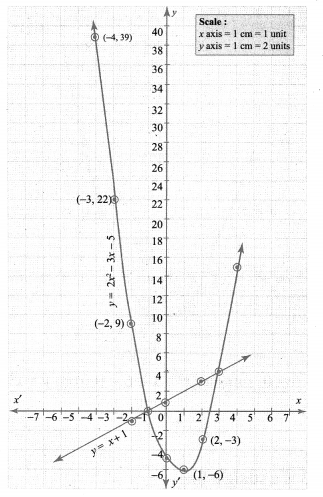
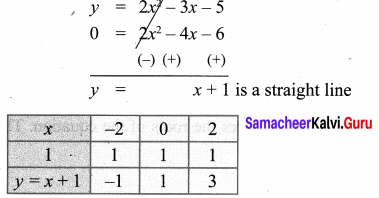
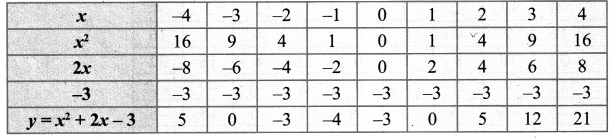
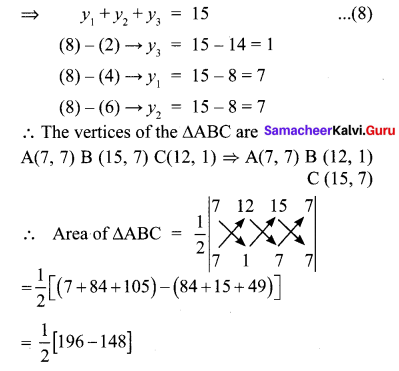
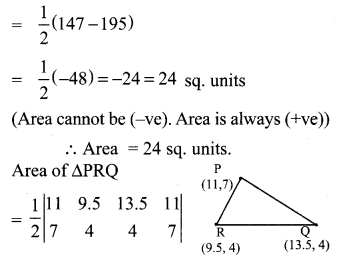
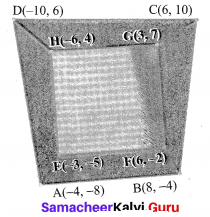
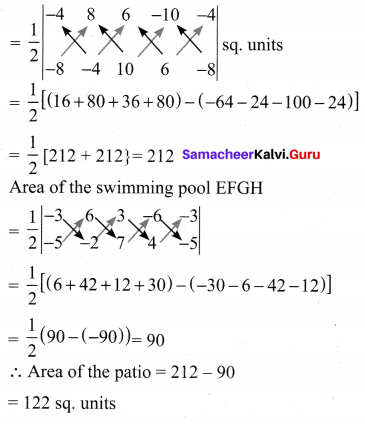
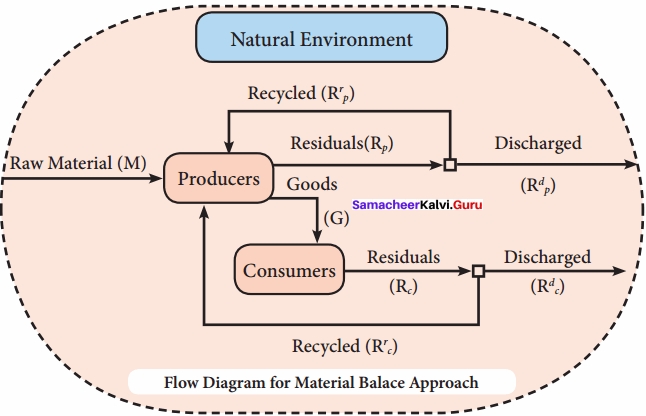
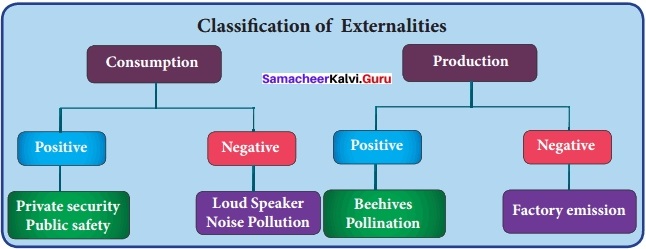
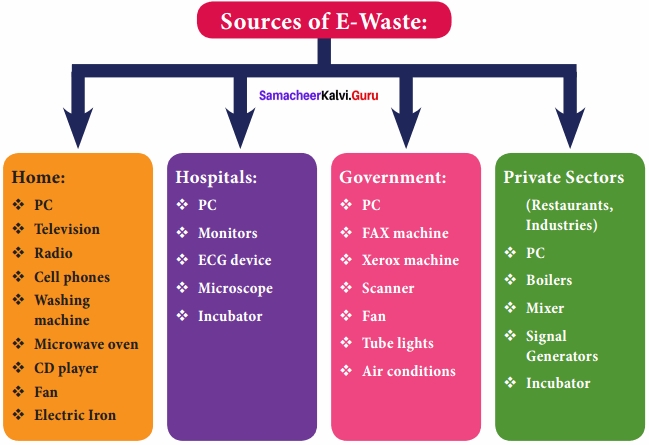
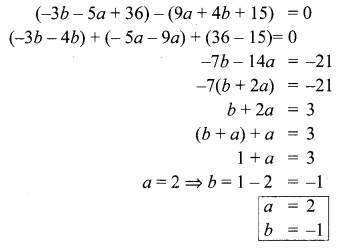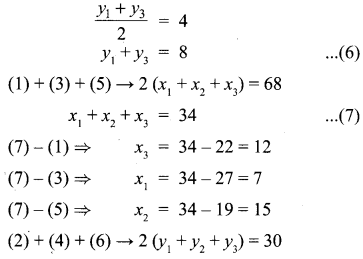You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.1
Exercise 3.1 Class 10 Maths Samacheer Question 1.
Solve the following system of linear equations in three variables
(i) x + y + z = 5; 2x – y + z = 9; x – 2y + 3z = 16
(ii) \(\frac { 1 }{ x } \) – \(\frac { 2 }{ y } \) + 4 = 0; \(\frac { 1 }{ y } \) – \(\frac { 1 }{ z } \) + 1 = 0; \(\frac { 2 }{ z } \) + \(\frac { 3 }{ x } \) = 14
(iii) x + 20 = \(\frac { 3y }{ 2 } \) + 10 = 2z + 5 = 110 – (y + z)
Solutions:
(i) x + y + z = 5 ………….. (1)
2x – y + z = 9 …………. (2)
x – 2y + 3z = 16 …………. (3)
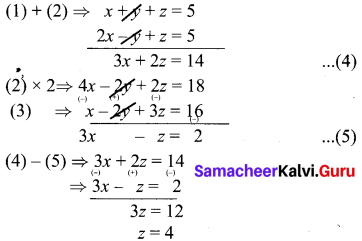
Substitute z = 4 in (4)
3x + 2(4) = 14
3x + 8 = 14
3x = 6
x = 2
Substitute x = 2, z = 4 in (1)
2 + y + 4 = 5 ⇒ y = -1
x = 2, y = -1, z = 4
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solution Book Pdf Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
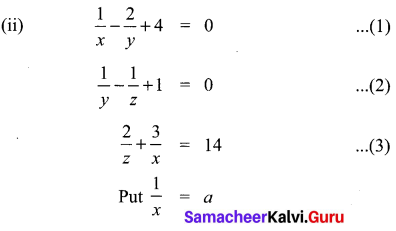
\(\frac{1}{y}\) = b
\(\frac{1}{z}\) = c in (1), (2) & (3)
a – 2b + 4 = 0 ⇒ a – 2b = -4 …………. (1)
b – c + 1 = 0 ⇒ b – c = -1 ……….. (2)
2c + 3a = 14 ⇒ 2c + 3a = 14 …………. (3)
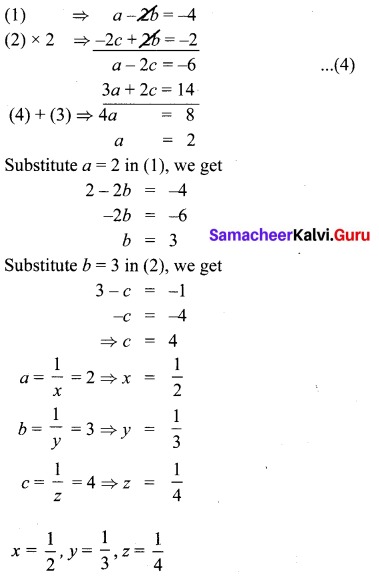
(iii) x + 20 = \(\frac { 3y }{ 2 } \) + 10 = 2z + 5 = 110 – (y + z)
x = \(\frac { 3y }{ 2 } \) – 10 …………. (1)
2z + 5 = 110 – (y + z)
2z = 105 – y – z
y = 105 – 3z ………….. (2)
Substitute (2) in (1), x = \(\frac { 315 }{ 2 } \) – \(\frac { 9z }{ 2 } \) – 10
= 2z + 5 – 20
∴ 315 – 9z – 20 = 4z – 30
13 z = 315 – 20 + 30
= 325
z = \(\frac { 325 }{ 13 } \) = 25
x + 20 = 2z + 5
x + 20 = 50 + 5
x = 35
Substitute z = 25 in (2)
y = 105 – 3z = 105 – 75 = 30
y = 30
x = 35, y = 30, z = 25
The system has unique solutions.
10th Maths Exercise 3.1 Question 2.
Discuss the nature of solutions of the following system of equations
(i) x + 2y – z = 6 ; -3x – 2y + 5z = -12 ; x – 2z = 3
(ii) 2y + z = 3 (-x + 1); -x + 3y -z = -4 3x + 2y + z = – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)
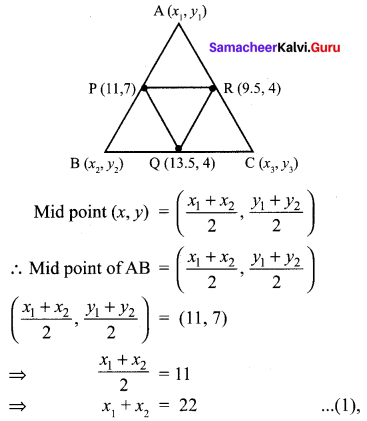
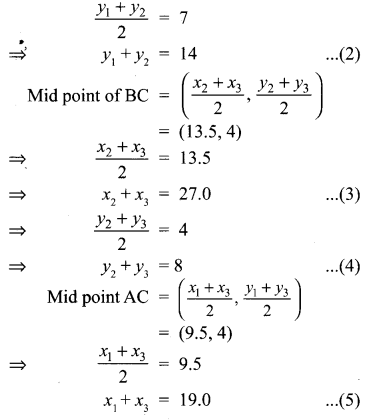
(iii) \(\frac { y+z }{ 4 } \) = \(\frac { z+x }{ 3 } \) = \(\frac { x+y }{ 2 } \); x + y + z = 27
Solution:
(i) x + 2y – z = 6 …………. (1)
-3x – 2y + 5z = -12 ……… (2)
x – 2z = 3 …………… (3)
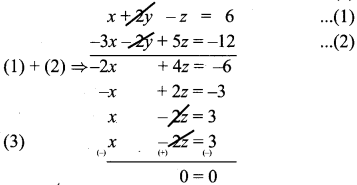
We see that the system has an infinite number of solutions.
(ii) 2y + z = 3(-x + 1);
-x + 3y – z = -4;
3x + 2y + z = –\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)
2y + z + 3x = 3 ⇒ 3x + 2y + z = 3 ………….. (1)
-x + 3y – z = -4 …………. (2)
3x + 2y + z = –\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) ………………. (3)
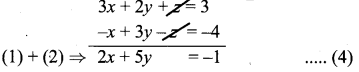
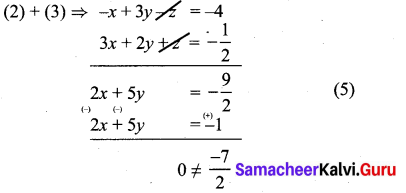
This is a contradiction. This means the system is inconsistent and has no solutions.
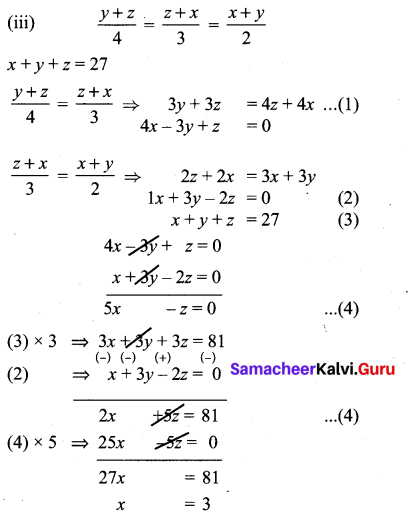
Sub. x = 3 in (4) ⇒ 5(3) – z = 0
15 – z = 0
-z = -15
z = 15
Sub, x = 3, z = 15 in (3)
x + y + z = 27
3 + y + 15 = 27
y = 27 – 18 = 9
x = 3, y = 9, z = 15
∴ The system has unique solutions.
Ex 3.1 Class 10 Samacheer Question 3.
Vani, her father and her grand father have an average age of 53. One-half of her grand father’s age plus one-third of her father’s age plus one fourth of Vani’s age is 65. Four years ago if Vani’s grandfather was four times as old as Vani then how old are they all now?
Solution:
Let Vani’s age be x
Let Vani’s father’s age be y
Let Vani’s grand father’s age be z.
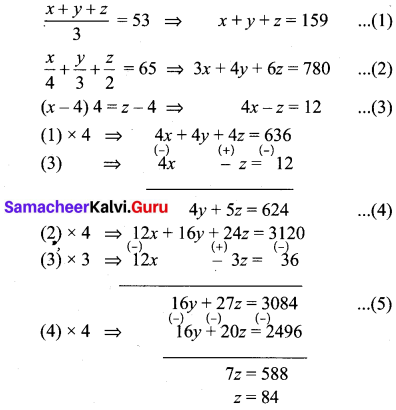
Sub, z = 84 in (3), we get
4x – 84 = 12
4x = 96
x = 24
Sub, x = 24, z = 84 in (1) we get
24 + y + 84 = 159
y = 159 – 108
= 51
∴ Vani’s age = 24 years
Her father’s age =51 years
Her grand father’s age = 84 years.
10th Maths Exercise 3.1 Samacheer Kalvi Question 4.
The sum of the digits of a three-digit number is 11. If the digits are reversed, the new number is 46 more than five times the former number. If the hundreds digit plus twice the tens digit is equal to the units digit, then find the original three digit number?
Solution:
Let the number be 100x + 10y + z.
Reversed number be 100z + 10y + x.
x + y + z = 11 …………… (1)
100z + 10y + x = 5(100x + 10y + z) + 46
100z + 10y + x = 500x + 50y + 5z + 46
499x + 40y – 95z -46 ………….. (2)
x + 2y = z
x + 2y – z = 0 ……………. (3)
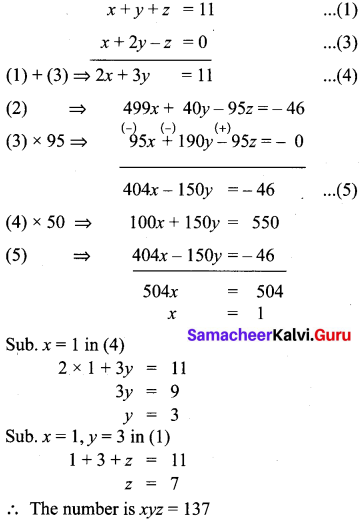
10th Maths Algebra Exercise 3.1 Solutions Question 5.
There are 12 pieces of five, ten and twenty rupee currencies whose total value is ₹105. When first 2 sorts are interchanged in their numbers its value will be increased by ₹20. Find the number of currencies in each sort.
Solution:
Let x, y and z be number of currency pieces of 5,10,20 rupees
x + y + z = 12 ………. (1)
5x + 10y + 20z = 105 ………… (2)
10x + 5y + 20z = 125 …………. (3)
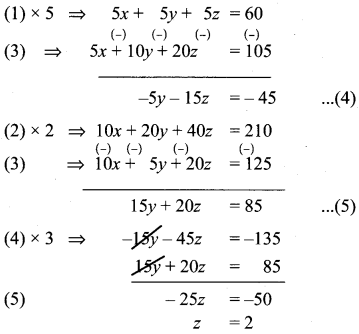
Sub, z = 2 in (5), we get
15y + 20 × 2 = 85
15y = 45
y = 3
Sub; y = 3, z = 2 in (1)
x + y + z = 12
x = 7
∴ The solutions are
the number of ₹ 5 are 7
the number of ₹ 10 are 3
the number of ₹ 20 are 2