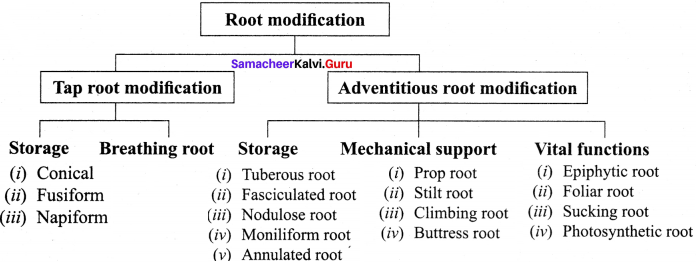
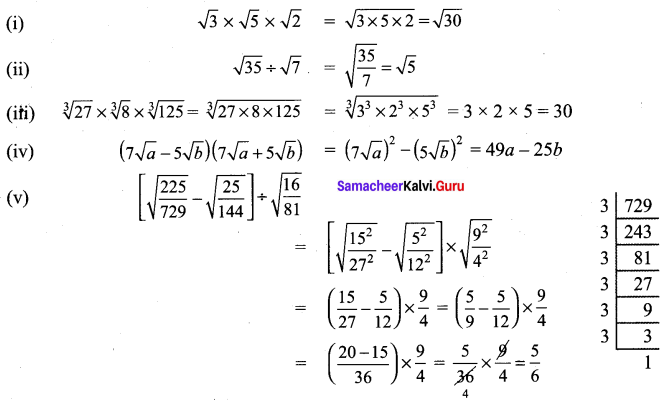
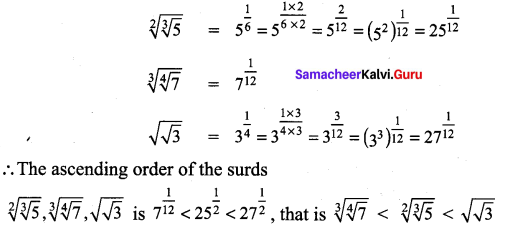
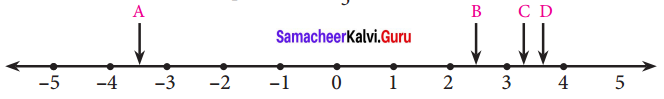
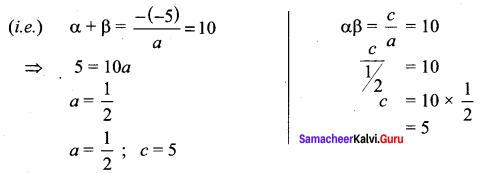
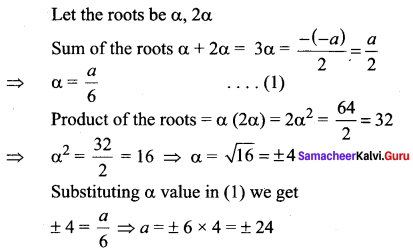
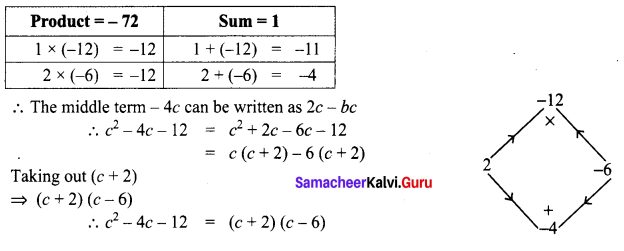
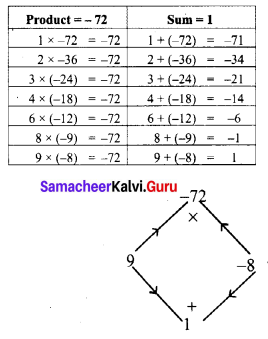
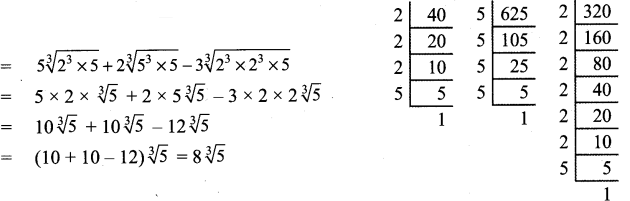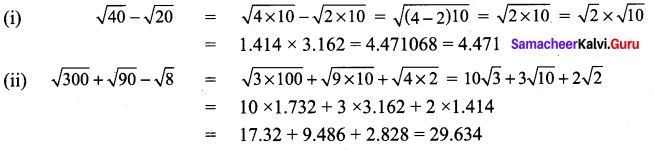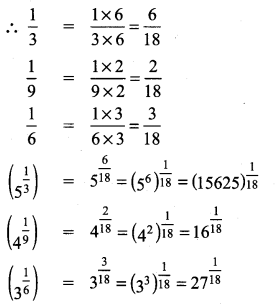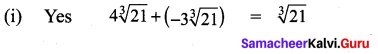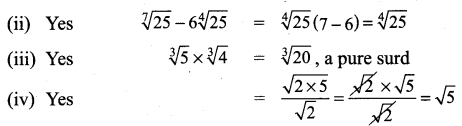Students can Download Tamil Chapter 1.3 திக்கெல்லாம் புகழுறும் திருநெல்வேலி Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Tamil Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Tamil Solutions Term 3 Chapter 1.3 திக்கெல்லாம் புகழுறும் திருநெல்வேலி
மதிப்பீடு
சரியான விடையைத் தேர்ந்தெடுத்து எழுதுக.
Question 1.
திருநெல்வேலி …………….. மன்னர்களோடு தொடர்பு உடையது.
அ) சேர
ஆ) சோழ
இ) பாண்டிய
ஈ) பல்லவ
Answer:
இ) பாண்டிய
Question 2.
இளங்கோவடிகள் …………………….. மலைக்கு முதன்மை கொடுத்துப் பாடினார்.
அ) இமய
ஆ) கொல்லி
இ) பொதிகை
ஈ) விந்திய
Answer:
இ) பொதிகை)
Question 3.
திருநெல்வேலி ………… ஆற்றின் கரையில் அமைந்துள்ளது.
அ) காவிரி
ஆ) வைகை
இ) தென்பெண்ணை
ஈ) தாமிரபரணி
Answer:
ஈ) தாமிரபரணி
பொருத்துக

Answer:

குறுவினா
Question 1.
தாமிரபரணி ஆற்றின் கிளை ஆறுகள் யாவை?
Answer:
தாமிரபரணி கிளை ஆறுகள் : பச்சையாறு, மணிமுத்தாறு, சிற்றாறு, காரையாறு, சேர்வலாறு, கடனாநதி.
Question 2.
கொற்கை முத்து பற்றிக் கூறுக.
Answer:
- கொற்கையில் விளைந்த பாண்டி நாட்டு முத்து உலகப் புகழ் பெற்றதாகும்.
- நற்றிணை, அகநானூறு முதலான சங்க இலக்கியங்கள் கொற்கை முத்தின் சிறப்பைக் கூறுகின்றன.
- கிரேக்க, உரோமாபுரி நாடுகளைச் சேர்ந்த யவனர்கள் முத்துக்களை விரும்பி வாங்கிச்சென்றனர்.
சிறுவினா
Question 1.
திருநெல்வேலிப் பகுதியில் நடைபெறும் உழவுத்தொழில் குறித்து எழுதுக.
Answer:
(i) திருநெல்வேலி மாவட்டப் பொருளாதாரத்தில் முதன்மையான பங்கு வகிப்பது உழவுத் தொழில். தாமிரபரணி ஆற்றின் மூலம் இங்கு உழவுத்தொழில் நடைபெறுகின்றது. இங்கு குளத்துப் பாசனமும் கிணற்றுப் பாசனமும்கூடப் பயன்பாட்டில் உள்ளன.
(ii) இரு பருவங்களில் நெல் பயிரிடப்படுகின்றது. மானாவாரிப் பயிர்களாகச் சிறுதானியங்கள், எண்ணெய்வித்துகள், காய்கனிகள், பருத்தி, பயறுவகைகள் போன்றவை பயிரிடப்படுகின்றன.
(iii) இராதாபுரம், நாங்குநேரி, அம்பாசமுத்திரம், தென்காசி போன்ற பகுதிகளில் பெருமளவில் வாழை பயிரிடப்படுகின்றது. இங்கு விளையும் வாழைத்தார்கள் -9 தமிழ்நாடு மட்டுமின்றி கர்நாடகம், கேரளம் போன்ற பிற மாநிலங்களுக்கும் அனுப்பப்படுகின்றன.
(iv) நெல்லிக்காய் உற்பத்தியில் தமிழகத்தில் நெல்லை மாவட்டமே முதலிடம் வகிக்கின்றது.
Question 2.
திருநெல்வேலிக்கும் தமிழுக்கும் உள்ள தொடர்பு குறித்து எழுதுக.
Answer:
திருநெல்வேலியும், தமிழும் :
(i) அகத்தியம் என்னும் முதல் தமிழ் இலக்கண நூலை எழுதியவர் அகத்தியர். இவர் திருநெல்வேலியிலுள்ள பொதிகை மலையில் வாழ்ந்தவர்.
(ii) சங்கப் புலவரான மாறோக்கத்து நப்பசலையார், நம்மாழ்வார், பெரியாழ்வார், குமரகுருபரர், திரிகூடராசப்பக் கவிராயர், கவிராசப் பண்டிதர் ஆகியோர் திருநெல்வேலிச் சீமையில் பிறந்து தமிழுக்குச் செழுமை சேர்ந்துள்ளனர்.
(iii) அயல்நாட்டு அறிஞர்களான ஜி.யு.போப், கால்டுவெல், வீரமாமுனிவர் போன்றோரையும் தமிழின்பால் ஈர்த்த பெருமைக்கு உரியது திருநெல்வேலி.
Question 3.
திருநெல்வேலி நகர அமைப்புப் பற்றிக் கூறுக.
Answer:
(i) பொருநை எனப்படும் தாமிரபரணி ஆற்றின் கரையில் அமைந்துள்ள நெல்லை மாநகரின் அமைப்பு சிறப்பானது.
(ii) நகரின் நடுவே நெல்லையப்பர் திருக்கோவில் அமைந்துள்ளது. கோவிலைச் சுற்றி நான்கு பக்கங்களிலும் மாட வீதிகள், அவற்றைச் சுற்றித் தேரோடும் வீதிகள், அழகுற அமைந்துள்ளன.
(iii) அரசரால் தண்டிக்கப்பட்டவர்கள் சிறை வைக்கப்பட்டதால் பெயர்பெற்ற காவற்புரைத் தெரு உள்ளது.
(iv) தானியங்களை விற்கும் வீதியான கூழைக்கடை (கூலம் – தானியம்), பொன் நாணயங்களை உருவாக்கும் பணியாளர்கள் வாழ்ந்த பகுதி அக்கசாலை, பெரு வணிகம் நடைபெற்ற இடமான பேட்டை என்னும் ஊர் உள்ளது.
(v) இத்தகு சிறப்பு மிகுந்த நகர அமைப்புகளைக் கொண்டு காலத்தால் புகழ்பெற்று நிற்கிறது திருநெல்வேலி நகரம்.
சிந்தனை வினா
மக்கள் மகிழ்ச்சியாக வாழ ஒரு நகரம் எவ்வாறு இருக்க வேண்டும் என்று நினைக்கிறீர்கள்?
Answer:
மக்கள் மகிழ்ச்சியாக வாழ ஒரு நகரம் :
(i) மக்கள் ஆண்டு முழுவதும் தண்ணீர் பஞ்சம் இன்றி வாழ உதவும் நீர்நிலைகளைப் பாதுகாக்க வேண்டும்.
(ii) மழைநீர் வீணாகக் கடலில் சென்று கலக்காமல் ஆங்காங்கு குளங்கள் இருக்க வேண்டும்.
(iii) அனைத்து வீடுகளிலும் மழைநீர் சேகரிப்புத் தொட்டி அமைத்திருக்க வேண்டும்.
(iv) மாணவர்கள் பள்ளிக்கு நீண்ட தூரம் செல்லாமல் மக்கள் தொகைக்கு ஏற்ப பள்ளிகள் மற்றும் கல்லூரிகள் இருக்க வேண்டும்.
(V) கோவில்கள் மற்றும் நூலகம் இருக்க வேண்டும்.
(vi) ஆங்காங்கு பூங்காக்கள் அமைத்து மரம் செடிகளை வளர்க்க வேண்டும். குழந்தைகள் விளையாடுவதற்கும், குழந்தைகள் முதல் பெரியவர்கள் வரை உடற்பயிற்சிக்கும் நடைப் பயிற்சிக்கும் உதவும்படி அமைக்க வேண்டும்.
(viii) சிறந்த போக்குவரத்து வசதிக்குச் சாலைகள் நன்கு அமைக்க வேண்டும்.
(ix) சிறந்த மருத்துவனைகள் இருக்க வேண்டும்.
(x) சாலையோரங்களில் மரங்கள் வளர்க்க வேண்டும்.
(xi) பலவகையான வணிகம் நடைபெற வேண்டும்.
(xii) மேற்கூறிய அனைத்தும் மக்களை மகிழ்ச்சியாக வாழ வைக்கும்.
கற்பவை கற்றபின்
Question 1.
உங்களுடைய மாவட்டத்தில் உள்ள சுற்றுலா இடங்கள் பற்றிய செய்திகளைத் தேடித் தொகுக்க.
Answer:
எனது மாவட்டத்தில் உள்ள சுற்றுலா இடங்கள் :
என்னுடைய மாவட்டம் சென்னை . இது நம் மாநிலத்தின் தலைநகரம் ஆகும். இங்கு பார்க்க வேண்டிய இடங்கள் பல உள்ளன. இங்குள்ள மெரினா கடற்கரை, உலகிலேயே மிக நீண்ட கடற்கரைகளில் இரண்டாவது இடத்தைப் பெறுகிறது. சென்னை வாசிகள் ஆசையோடு பொழுதுபோக்கி மகிழும் அருமையான திறந்த வெளி இடமாகும்.
ஆங்கிலக் கிழக்கிந்தியக் கம்பெனியரால் கட்டப்பட்டது புனித ஜார்ஜ் கோட்டை. இதன் வெளிப்புறத்தில் அகழி , அதனை சுற்றி மதில் சுவர்கள் உள்ளன. கோட்டையின் முன்பு மிகவும் உயரமான கொடிக்கம்பமும் உள்ளது.
அண்ணா அருங்காட்சியகம், பாரத ரத்னா டாக்டர் எம்.ஜி.ஆர். நினைவிடம் ஆகியவை மெரினா கடற்கரையில் அமைக்கப்பட்டுள்ளன. முதல் உலகப் போரில் தனது நாட்டிற்காக இன்னுயிரை ஈந்த வீரர்களுக்கு மரியாதை செலுத்தும் விதமாக போர் நினைவுச் சின்னம் கடற்கரைச் சாலையில் அமைக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது. இங்கு ஆண்டு தோறும் இராணுவ தினத்தின் போது மலர்வளையம் வைத்து அஞ்சலி செலுத்தப்படுகிறது.
எழும்பூரில் உள்ள அருங்காட்சியகம், இந்தியாவிலுள்ள பழமையான அருங்காட்சியகங்களில் இரண்டாவது இடத்தை வகிப்பது. இது 1851ல் நிறுவப்பட்டது. இது தேசிய மரபுச் செல்வங்களை காக்கும் கலைக் களஞ்சியமாக அமைந்துள்ளது.
வள்ளுவர் கோட்டம், தமிழ் மறையாம் திருக்குறளை உலகுக்கு அளித்த திருவள்ளுவரின் நினைவாக கட்டப்பட்ட கலைச் சின்னமாகும்.
சென்னை கிண்டியில் காந்தியடிகள், இராஜாஜி, காமராசர் நினைவாலயங்கள் உள்ளன. ஆசிய விளையாட்டு அரங்குகளின் அரசி’ எனப் போற்றப்படும் ஜவகர்லால் நேரு விளையாட்டு அரங்கம் உள்ளது.
அறிஞர் அண்ணா உயிரியல் பூங்கா வண்டலூரில் உள்ளது. வானவியல் பற்றிய த்துகளை நுண்ணிய ஒளி, ஒலி சாதனங்களைக் கொண்டு மக்களுக்குக் குறிப்பாக மாணவர்களுக்கு எளிய முறையில் கற்பிக்கும் இடமான கோளரங்கம், கோட்டூர்புரத்தில் உள்ளது.
காளிகாம்பாள் கோவில், கந்த கோட்டம், திருவல்லிக்கேணி பார்த்தசாரதி கோவில், மயிலாப்பூரில் உள்ள கபாலீஸ்வரர் கோவில், வடபழனியில் உள்ள முருகர் கோவில், திருவேற்காடு கருமாரியம்மன் கோவில், ஸ்ரீ மஹா ப்ரத்யங்கரா தேவி ஆலயம், கோயம்பேடு குறுங்காலீசுரவர் கோவில் என பல ஆன்மிகத்தலங்கள் நிறைந்தது எங்கள் சென்னை மாவட்டம்.
Question 2.
தமிழ்நாட்டில் உள்ள மாநகராட்சிகள் பற்றிய செய்திகளைத் தொகுக்க.
Answer:
தமிழ்நாட்டில் மொத்தம் 15 மாநகராட்சிகள் உள்ளன. அவைகளைப் பற்றிய செய்திகளை காண்போம்.
(i) சென்னை மாநகராட்சி
நகரம் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட நாள் : 29 செப்டம்பர் 1688
மாநகராட்சியாக மேம்படுத்தப்பட்ட நாள் : 29 செப்டம்பர் 1688
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்கள் : 15
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்களின் பெயர்கள் : திருவொற்றியூர், மணலி , மாதவரம், தண்டையார்பேட்டை, ராயபுரம், திரு.வி.க.நகர், அம்பத்தூர், அண்ணா நகர், தேனாம்பேட்டை, கோடம்பாக்கம், வளசரவாக்கம், ஆலந்தூர், அடையார், பெருங்குடி, சோளிங்கநல்லூர்.
வார்டுகளின் எண்ணிக்கை : 200
மக்கள் தொகை (2011 கணக்கெடுப்பின் படி) :86,96,010
(ii) கோயம்புத்தூர் மாநகராட்சி :
நகரம் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட நாள் : 1 நவம்பர் 1866
மாநகராட்சியாக மேம்படுத்தப்பட்ட ஆண்டு : 1981
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்கள் : 5
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்களின் பெயர்கள் : வடக்கு, கிழக்கு, தெற்கு, மேற்கு, மற்றும் மத்திய மண்டலம்.
வார்டுகளின் எண்ணிக்கை : 148
மக்கள் தொகை (2011 கணக்கெடுப்பின் படி) : 42,24,106
(iii) மதுரை மாநகராட்சி :
நகரம் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட நாள் : 1 நவம்பர் 1866
மாநகராட்சியாக மேம்படுத்தப்பட்ட ஆண்டு : 1971
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்கள் :4
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்களின் பெயர்கள் : வடக்கு, கிழக்கு, தெற்கு, மேற்கு.
வார்டுகளின் எண்ணிக்கை : 100
மக்கள் தொகை (2011 கணக்கெடுப்பின் படி) : 14,62,420
(iv) திருச்சிராப்பள்ளி மாநகராட்சி :
நகரம் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட நாள் : 1நவம்பர் 1866
மாநகராட்சியாக மேம்படுத்தப்பட்ட ஆண்டு : 1994
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்கள் : 4
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்களின் பெயர்கள் : ஸ்ரீரங்கம், அரியமங்கலம், பொன்மலை , K. அபிஷேகபுரம்
வார்டுகளின் எண்ணிக்கை : 65
மக்கள் தொகை (2011 கணக்கெடுப்பின் படி) : 10,21,717
(v) சேலம் மாநகராட்சி :
நகரம் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட நாள் : 1 நவம்பர் 1866
மாநகராட்சியாக மேம்படுத்தப்பட்ட ஆண்டு : 1994
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்கள் : 4
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்களின் பெயர்கள் : சூரமங்கலம், ஹஸ்தம்பட்டி, அம்மாபேட்டை, கொண்டலாம்பட்டி
வார்டுகளின் எண்ணிக்கை : 60
மக்கள் தொகை (2011 கணக்கெடுப்பின் படி) : 10,13,388
(vi) திருநெல்வேலி மாநகராட்சி :
நகரம் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட நாள் : 1நவம்பர் 1866
மாநகராட்சியாக மேம்படுத்தப்பட்ட ஆண்டு : 1994
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்கள் : 4
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்களின் பெயர்கள் : தச்சநல்லூர், பாளையம் கோட்டை, மேலப்பாளையம், திருநெல்வேலி
வார்டுகளின் எண்ணிக்கை : 55
மக்கள் தொகை (2011 கணக்கெடுப்பின் படி) : 4,74,838
(vii) திருப்பூர் மாநகராட்சி :
நகரம் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட நாள் : 1 டிசம்பர் 1947(பஞ்சாயத்து யூனியனாக)
மாநகராட்சியாக மேம்படுத்தப்பட்ட ஆண்டு : 2008
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்கள் : 4
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்களின் பெயர்கள் : வடக்கு, கிழக்கு, தெற்கு, மேற்கு.
வார்டுகளின் எண்ணிக்கை : 60
மக்கள் தொகை (2011 கணக்கெடுப்பின் படி) : 4,66,998
(viii) ஈரோடு மாநகராட்சி :
நகரம் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட ஆண்டு : 1871
மாநகராட்சியாக மேம்படுத்தப்பட்ட ஆண்டு : 2008
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்கள் : 4
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்களின் பெயர்கள் : சூரம்பட்டி, காசிபாளையம், வீரப்பன்சத்திரம், பெரிய சேமூர்.
வார்டுகளின் எண்ணிக்கை : 60
மக்கள் தொகை (2011 கணக்கெடுப்பின் படி) : 4,44,782
(ix) வேலூர் மாநகராட்சி :
நகரம் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட நாள் : 1 நவம்பர் 1866
மாநகராட்சியாக மேம்படுத்தப்பட்ட நாள் :1 ஆகஸ்ட் 2008
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்கள் : 4
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்களின் பெயர்கள் : காட்பாடி, வேலூர் கோட்டை, சத்துவாச்சாரி, செண்பகம்.
வார்டுகளின் எண்ணிக்கை : 60
மக்கள் தொகை (2011 கணக்கெடுப்பின் படி) : 4,21,327
(x) தூத்துக்குடி மாநகராட்சி :
நகரம் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட நாள் : 1நவம்பர் 1866
மாநகராட்சியாக மேம்படுத்தப்பட்ட நாள் : 5 ஆகஸ்ட் 2008
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்கள் : 4
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்களின் பெயர்கள் : வடக்கு, கிழக்கு, தெற்கு, மேற்கு.
வார்டுகளின் எண்ணிக்கை : 60
மக்கள் தொகை (2011 கணக்கெடுப்பின் படி) : 3,56,094
(xi) தஞ்சாவூர் மாநகராட்சி :
நகரம் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட நாள் : 1 நவம்பர் 1866
மாநகராட்சியாக மேம்படுத்தப்பட்ட ஆண்டு : 2014
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்கள் : 4
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்களின் பெயர்கள் : வடக்கு, கிழக்கு, தெற்கு, மேற்கு.
வார்டுகளின் எண்ணிக்கை : 62
மக்கள் தொகை (2011 கணக்கெடுப்பின் படி) : 2,22,943
(xii) திண்டுக்கல் மாநகராட்சி :
நகரம் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட நாள் : 1 நவம்பர் 1866
மாநகராட்சியாக மேம்படுத்தப்பட்ட ஆண்டு : 2014
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்கள் : 4
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்களின் பெயர்கள் : வடக்கு, கிழக்கு, தெற்கு, மேற்கு.
வார்டுகளின் எண்ணிக்கை :51
மக்கள் தொகை (2011 கணக்கெடுப்பின் படி) : 2,07,225
(xiii) நாகர்கோவில் மாநகராட்சி :
நகரம் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட நாள் : 1நவம்பர் 1866
மாநகராட்சியாக மேம்படுத்தப்பட்ட ஆண்டு : 2019
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்கள் : 4
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்களின் பெயர்கள் : வடக்கு, கிழக்கு, தெற்கு, மேற்கு.
வார்டுகளின் எண்ணிக்கை : 51
மக்கள் தொகை (2011 கணக்கெடுப்பின் படி) : 2,24,849
(xiv) ஓசூர் மாநகராட்சி :
நகரம் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட நாள் : 1நவம்பர் 1866
மாநகராட்சியாக மேம்படுத்தப்பட்ட ஆண்டு : 2019
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்கள் :4
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்களின் பெயர்கள் : வடக்கு, கிழக்கு, தெற்கு, மேற்கு.
வார்டுகளின் எண்ணிக்கை :51
மக்கள் தொகை (2011 கணக்கெடுப்பின் படி) : 1,16,821
(xv) ஆவடி மாநகராட்சி :
நகரம் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட நாள்
: 10 ஜனவரி 1955
மாநகராட்சியாக மேம்படுத்தப்பட்ட ஆண்டு : 2019
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்கள் : 4
நிர்வாக மண்டலங்களின் பெயர்கள் : வடக்கு, கிழக்கு, தெற்கு, மேற்கு.
வார்டுகளின் எண்ணிக்கை : 80
மக்கள் தொகை (2011 கணக்கெடுப்பின் படி) : 3,44,701
தெரிந்து தெளிவோம்
(i) முற்காலத்தில் திருநெல்வேலிக்கு வேணுவனம் என்னும் பெயரும் இருந்துள்ளது. மூங்கில் காடு என்பது அதன் பொருளாகும். மூங்கில் நெல் மிகுதியாக விளைந்தமையால் அப்பகுதிக்கு நெல்வேலி என்னும் பெயர் ஏற்பட்டிருக்கலாம் எனவும் கருதுவர்.
(ii) திருநெல்வேலிக்கு அருகிலுள்ள ஆதிச்சநல்லூர் என்னும் இடத்தில் நிகழ்த்தப்பட்ட அகழ்வாய்வில் இறந்தவர்களின் உடல்களைப் புதைக்கப் பழந்தமிழர்கள் பயன்படுத்திய முதுமக்கள் தாழிகள் கண்டெடுக்கப்பட்டுள்ளன. மேலும் தமிழரின் தொன்மைக்கும் நாகரிகச் சிறப்புக்கும் சான்றாக விளங்கும் தொல்பொருள்கள் இங்குக் கிடைத்துள்ளன. இவ்வூர் தற்போது தூத்துக்குடி மாவட்டத்தில் உள்ளது.
(iii) தாமிரபரணி ஆற்றின் மேற்குக் கரையில் திருநெல்வேலியும் கிழக்குக் கரையில்
பாளையங்கோட்டையும் அமைந்துள்ளன. இவ்விரு நகரங்களும் இரட்டை நகரங்கள் என அழைக்கப்படுகின்றன. பாளையங்கோட்டையில் அதிக அளவில் கல்வி நிலையங்கள் இருப்பதால் அந்நகரைத் தென்னிந்தியாவின் ஆக்ஸ்போர்டு என்பர்.
கூடுதல் வினாக்கள்
நிரப்புக.
1. பழந்தமிழகத்தை ஆண்ட மன்னர்கள் சேரர், சோழர், பாண்டியர்.
2. பாண்டியர்களின் தலைநகர் மதுரை.
3. பாண்டியர்களது இரண்டாவது தலைநகரமாக விளங்கிய நகரம் திருநெல்வேலி.
4. திருநெல்வேலிப் பகுதியை வளம் செழிக்கச் செய்யும் ஆறு தாமிரபரணி ஆகும்.
5. ‘திக்கெல்லாம் புகழுறும் திருநெல்வேலி’ எனப் பாடியவர் திருஞானசம்பந்தர்.
6. ‘தண்பொருநைப் புனல் நாடு’ என்று பாடியவர் சேக்கிழார்.
7. வேணுவனம் என்பதன் பொருள் மூங்கில் காடு.
8. தமிழகத்தில் நெல்லிக்காய் உற்பத்தியில் முதலிடம் வகிக்கும் மாவட்டம் திருநெல்வேலி.
9. தாமிரபரணி கடலோடு கலக்கும் இடத்தில் உள்ள துறைமுகம் கொற்கை.
10. முத்துப்படு பரப்பிற் கொற்கை முன்றுறை’ என்று பாடும் நூல் நற்றிணை
11. ‘கொற்கையில் பெருந்துறை முத்து எனப் பாடும் நூல் அகநானூறு.
12. காவற்புரை என்றால் சிறைச்சாலை.
13. தானியங்கள் விற்கப்படும் தெரு கூலக்கடைத் தெரு.
14. வணிகம் நடைபெறும் பகுதி பேட்டை என்று வழங்கப்பட்டது.
15. இரட்டை நகரங்கள் என்பவை திருநெல்வேலியும், பாளையங்கோட்டையும் ஆகும்.
16. தென்னிந்தியாவின் ஆஃஸ்போர்டு பாளையங்கோட்டை.
17. பாண்டிய மன்னன் நின்றசீர் நெடுமாறனை நெல்லை நகர மக்கள் எதிர்கொண்டு வரவேற்ற இடம் பாண்டியபுரம் என்று வழங்கப்படுகின்றன.
18. பாண்டிய மன்னனின் தேவியாகிய மங்கையர்க்கரசியை மகளிர் எதிர்கொண்டு வரவேற்ற இடம் திருமங்கை நகர் என்று வழங்கப்படுகின்றன.
19. தாமிரபரணி ஆற்றின் வேறு பெயர் தண்பொருநை .
20. திருநெல்வேலிக்கு அருகில் அகழ்வாய்வு நிகழ்த்தப்பட்ட இடம் ஆதிச்ச நல்லூர்.
21. இறந்தவர்களின் உடல்களைப் புதைக்கப் பழந்தமிழர்கள் பயன்படுத்தியவை முதுமக்கள் தாழிகள்.
விடையளி :
Question 1.
திருநெல்வேலி பற்றிக் குறிப்பு எழுதுக.
Answer:
(i) திருநெல்வேலி தமிழகத்தின் பழமையான நகரங்களுள் ஒன்று.
(ii) பழந்தமிழகத்தைச் சேர, சோழ, பாண்டியர் என்னும் மூவேந்தர் ஆண்டு வந்தனர்.
(iii) அவர்களுள் பாண்டியர்களின் தலைநகரமாக விளங்கியது மதுரை.
(iv) அவர்களது இரண்டாவது தலைநகரமாகத் திருநெல்வேலி விளங்கியது.
Question 2.
திருநெல்வேலியைப் பற்றி திருஞானசம்பந்தர் பாடியவற்றை எழுதுக.
Answer:
(i) ‘திக்கெல்லாம் புகழுறும் திருநெல்வேலி ‘ ‘எனத் திருநெல்வேலியின் சிறப்பைப் போற்றியுள்ளார்.
(ii) திருநெல்வேலியில் திங்கள் தோறும் திருவிழா நடைபெறும் என்பதை,
“திங்கள் நாள் விழா மல்கு திருநெல் வேலியுறை செல்வர் தாமே” என்று பாடியுள்ளார்.
Question 3.
குற்றாலமலையின் வளத்தைப் பாடியவர் யார்? என்னவென்று பாடியுள்ளார்?
Answer:
(i) குற்றால மலையின் வளத்தைப் பாடியவர் திரிகூட இராசப்பக் கவிராயர்.
(ii) “வானரங்கள் கனிகொடுத்து மந்தியொடு கொஞ்சும் மந்திசிந்து கனிகளுக்கு வான்கவிகள் கெஞ்சும்” என்று பாடியுள்ளார்.
Question 4.
திருநெல்வேலி மாவட்டத்தில் கோட்டைகள் பல இருந்தமைக்குச் சான்றாக விளங்கிய ஊர்கள் யாவை?
Answer:
(i) பாளையங்கோட்டை
(ii) உக்கிரன்கோட்டை
(iii) செங்கோட்டை.
Question 5.
பண்டைய வரலாற்றை நினைவூட்டும் திருநெல்வேலி மாவட்ட ஊர்கள் யாவை?
Answer:
(i) சேரன்மாதேவி
(ii) கங்கைகொண்டான்
(iii) திருமலையப்புரம்
{iv) வீரபாண்டியப் பட்டினம்
(V) குலசேகரன்பட்டினம்.