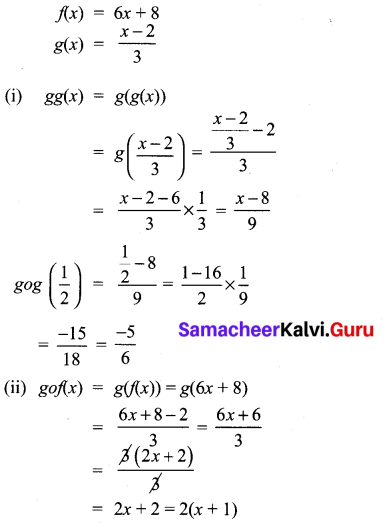
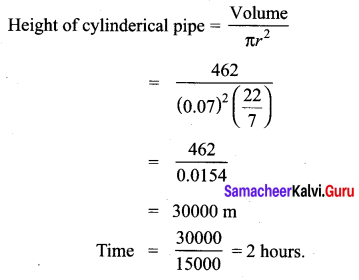
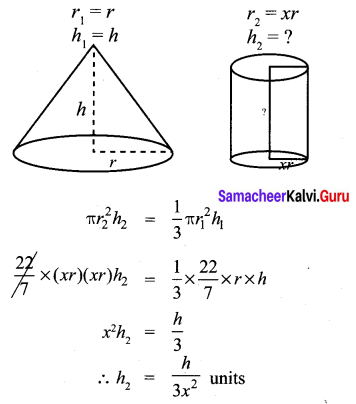
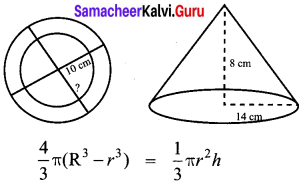
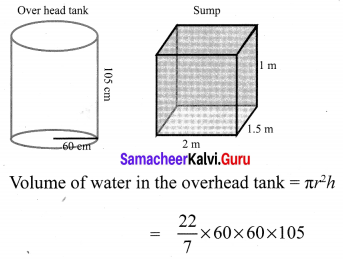
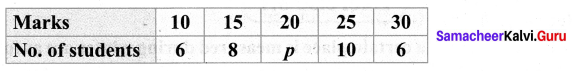
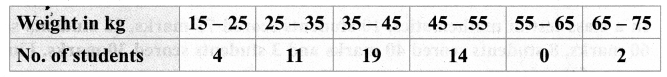
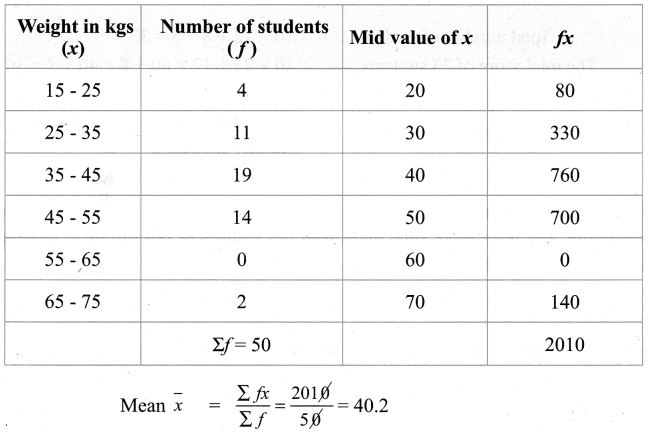
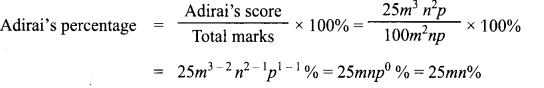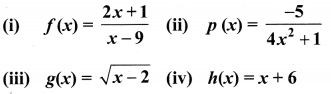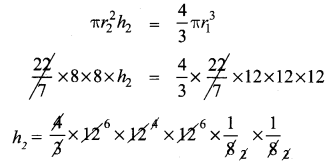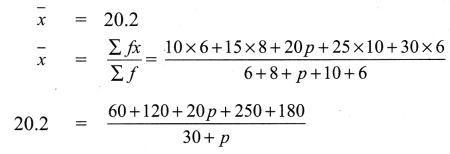You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Binomial Theorem, Sequences and Series Ex 5.1
11th Maths Exercise 5.1 Question 1.
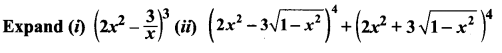
Solution:
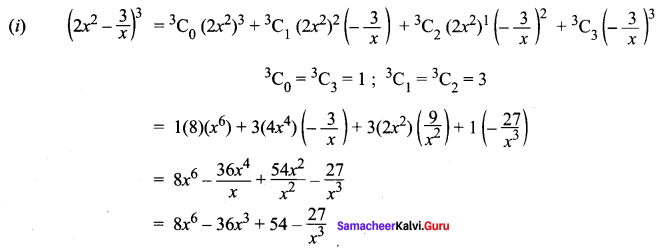
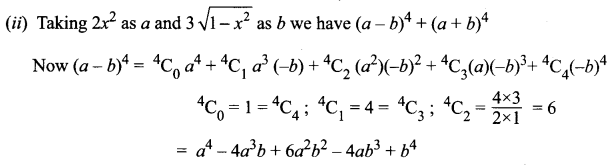
Similarly (a + b)4 = a4 + 4a3b + 6a2b2 + 4ab3 + b4
∴ (a – b)4 + (a + b)4 = 2 [a4 + 6a2b2 + b4]
Substituting the value of a and b we get
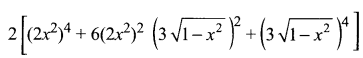
= 2[16x8 + 6(4x4)(9(1 – x2)) + 81(1 – x2)2]
= 2[16x8 + 216x4(1 – x2) + 81(1 – x2)2]
= 2[16x8 + 216x4 – 216x6 + 81 + 81x4 – 162x2]
= 2[16x8 – 216x6 + 297x4 – 162x2 + 81]
= 32x8 – 432x6 + 594x4 – 324x2 + 162
11th Maths Exercise 5.1 Samacheer Kalvi Question 2.
Compute
(i) 1024
(ii) 994
(iii) 97
Solution:
(i) 1024 = (100 + 2)4 = (102 + 2)4
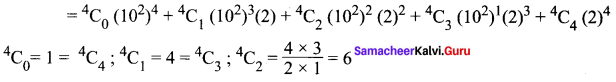
= 1(108) + 4(106)(2) + 6(104)(4) + 4(102)(8) + 16
= 100000000 + 8000000 + 240000 + 3200 + 16
= 108243216
(ii) 994 = (100 – 1)4 = (102 – 1)4
![]()
= 1(108) + 4(106)(-1) + 6 (104)(1) + 4( 104)(-1) + (-1)4
= 100000000 – 4000000 + 60000 – 400 + 1
= 100060001 – 4000400 = 96059601
(iii) 97 = (10 – 1)7
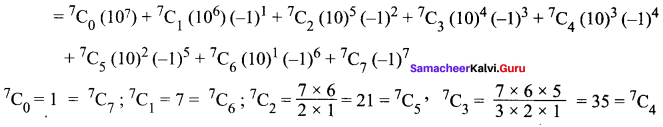
= 1(10000000) + 7(1000000)(-1) + 21(100000)(1) + 35(10000)(-1) + 35(1000)(1) + 21(100)(-1) + 7(10)(1) + 1(-1)
= 10000000 – 7000000 + 2100000 – 350000 + 35000 – 2100 + 70 – 1
= 12135070 – 7352101 = 4782969
Sequences And Series Solutions Question 3.
Using binomial theorem, indicate which of the following two number is larger: (1.01)1000000, 10000.
Solution:
(1.01)1000000 = (1 + 0.01)1000000
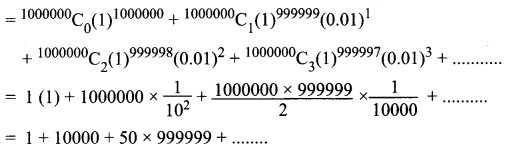
which is > 10000
So (1.01)1000000 > 10000 (i.e.) (1.01)1000000 is larger
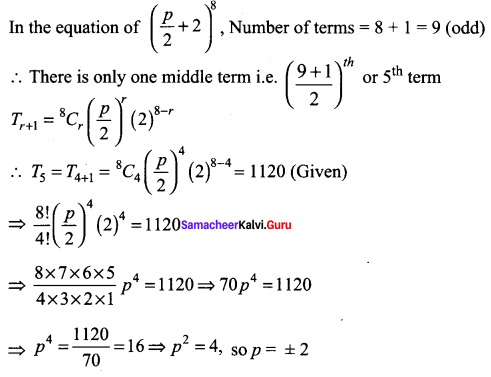
11 Maths Samacheer Kalvi Question 4.
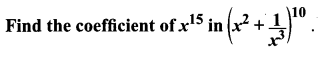
Solution:
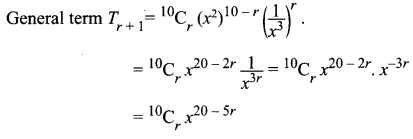
To find coefficient of x15 we have to equate x power to 15
i.e. 20 – 5r = 15
20 – 15 = 5r ⇒ 5r = 5 ⇒ r = 5/5 = 1
So the coefficient of x15 is 10C1 = 10
Ex 5.1 Class 11 Question 5.

Solution:
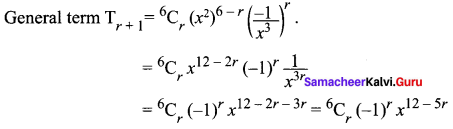
To find coefficient of x6
12 – 5r = 6
12 – 6 = 5r ⇒ 5r = 6 ⇒ r = 6/5 which is not an integer.
∴ There is no term involving x6.
To find coefficient of x2
12 – 5r = 2
5r = 12 – 2 = 10 ⇒ r = 2
![]()
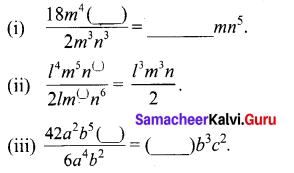
Question 6.
![]()
Solution:
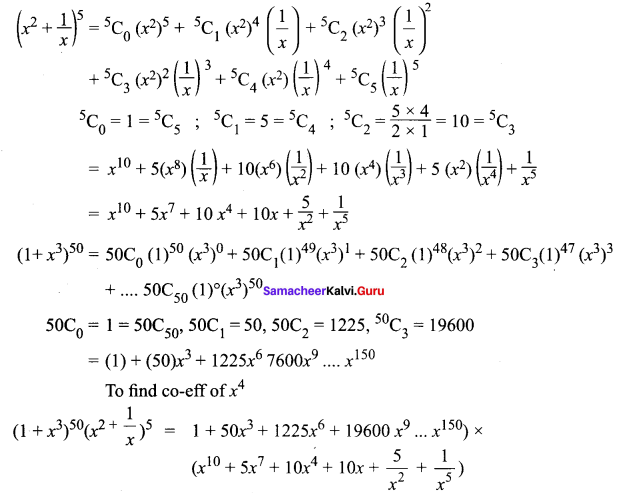
when multiplying these terms, we get x4 terms

∴ The co-eff of x4 is 26325
Ex 5.1 Class 11 Question 7.

Solution:
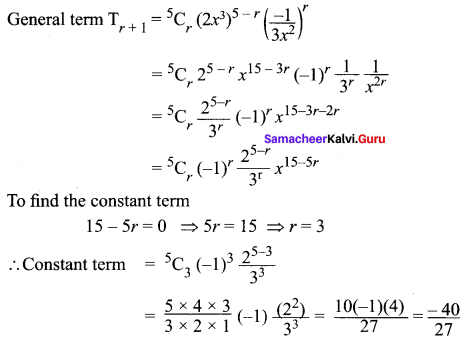
Chapter 5 Class 11 Maths Question 8.
Find the last two digits of the number 3600.
Solution:
3600 = 32 × 300 = (9)300 = (10 – 1)300
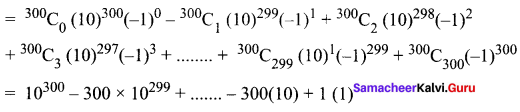
All the terms except last term are ÷ by 100. So the last two digits will be 01.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Question 9.
If n is a positive integer, show that, 9n + 1 – 8n – 9 is always divisible by 64.
Solution:
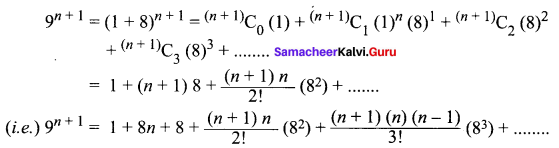
∴ 9n + 1 – 8n – 9 = 64 [an integer]
⇒ 9n + 1 – 8n – 9 is divisible by 64
Class 11 Maths Binomial Theorem Question 10.
If n is an odd positive integer, prove that the coefficients of the middle terms in the expansion of (x + y)n are equal.
Solution:
Given n is odd. So let n = 2n + 1, where n is an integer.
The expansion (x + y)n has n + 1 terms.
= 2n + 1 + 1 = 2(n + 1) terms which is an even number.

⇒ The coefficient of the middle terms in (x + y)n are equal.
Class 11 Ex 5.1 Question 11.
If n is a positive integer and r is a non – negative integer, prove that the coefficients of xr and xn – r in the expansion of (1 + x)n are equal.
Solution:
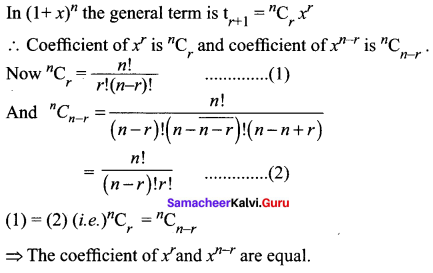
Class 11 Maths Chapter 5 Exercise 5.1 Question 12.
If a and b are distinct Integers, prove that a – b is a factor of an – bn, whenever n is a positive integer. [Hint: write an = (a – b + b)n and expand]
Solution:

= (a – b)[an integer]
⇒ an – bn is divisible by (a – b)
Chapter 5 Maths Class 11 Question 13.
In the binomial expansion of (a + b)an, the coefficients of the 4th and 13th terms are equal to each other, find n.
Solution:
In (a + b)n general term is tr + 1 = nCr an – r br
So, t4 = t3 + 1 = nC3 = nC12
⇒ n = 12 + 3 = 15
We are given that their coefficients are equal ⇒ nC3 = nC12 ⇒ n = 12 + 3 = 15
[nCx = nCy ⇒ x = y (or) x + y = n]
Class 11 Chapter 5 Maths Question 14.
If the binomial coefficients of three consecutive terms in the expansion of (a + x)n are in the ratio 1 : 7 : 42, then find n.
Solution:
In (a + x)n general term is tr + 1 = nCr
So, the coefficient of tr + 1 is nCr
We are given that the coefficients of three consecutive terms are in the ratio 1 : 7 : 42.
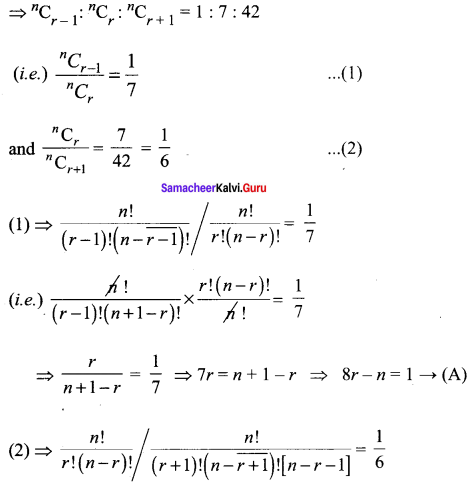
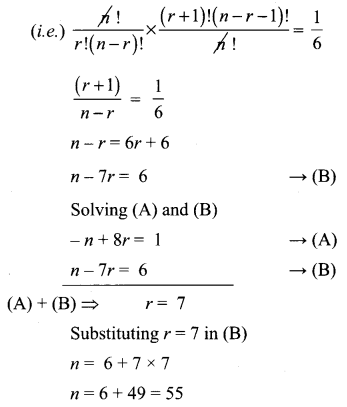
Class 11 Maths Chapter 5 Question 15.
In the binomial coefficients of (1 + x)n, the coefficients of the 5th, 6th and 7 terms are in AP. Find all values of n.
Solution:

⇒ (n – 1)(n – 14) = 0
∴ n = 7 , 14
Question 16.
![]()
Solution:
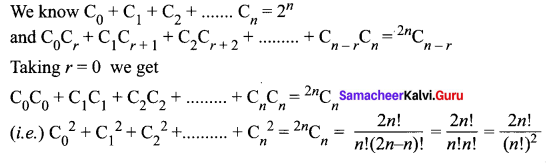
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Binomial Theorem, Sequences and Series Ex 5.1 Additional Questions Solved
Question 1.
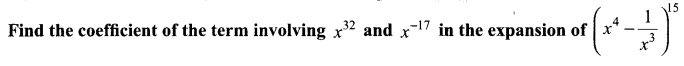
Solution:
Let Tr + 1 be the term in which x32 and x-17 occurs,
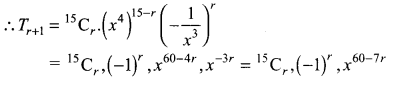
(i) Since x32 occurs in this term
∴ Exponent of x = 32
⇒ 60 – 7r = 32 ⇒ 7r = 28
r = 28 ÷ 7 = 4
∴ Coefficient of the term containing x32 = 15C4 (-1)4 = 1365
(ii) Since x-17 occurs in this term .
∴ Exponent of x = -17
⇒ 60 – 7r = -17 ⇒ 7r = 77, ∴ r = 11
![]()
Question 2.
Find a positive value of m for which the coefficient of x2 in the expansion of (1 + x)m is 6.
Solution:
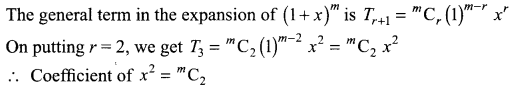
Also, coefficient of x2 in the expansion of (1 + x)m is 6
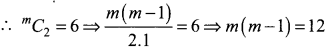
⇒ m (m – 1) = 4.3 ⇒ m = 4
Question 3.
In the binomial expansion of (1 + a)m + n, prove that the coefficients of am and an are equal.
Solution:
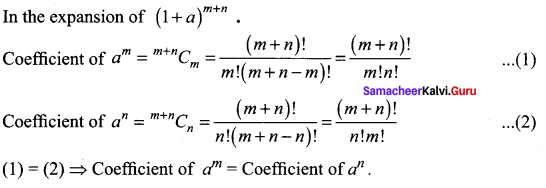
Question 14.
The coefficient of (r – 1)th, rth, and (r + 1)th terms in the expansion of (x + 1)n are in the ratio 1 : 3 : 5. Find both n and r.
Solution:
We know that co-effcients of (r – 1)th, rth and (r + 1)th terms in the expansion of (x + 1)n are nCr – 2: nCr – 1 and nCr respectively
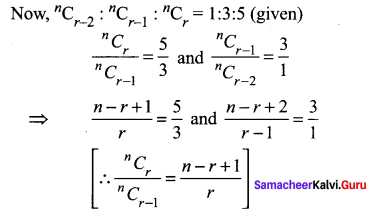
⇒ 3n – 8r + 3 = 0 and n – 4r + 5 = 0
Solving these for n, r we get,
n = 7 and r = 3
Question 5.
![]()
Solution:
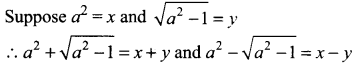
Using binomial theorem,
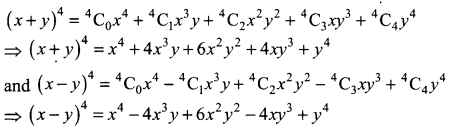
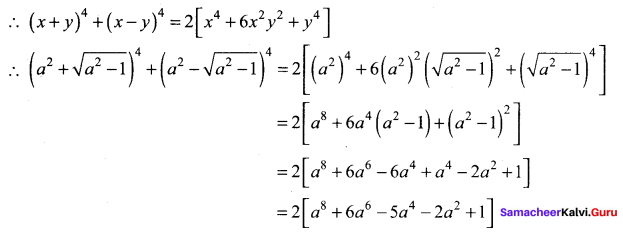
Question 6.
Show that the coefficient of the middle term in the expansion of (1 + x)2n is equal to the sum of the coefficients of the two middle terms in the expansion of (1 + x)2n – 1.
Solution:
In the expansion of (1 + x)2n,
Number of terms = 2n + 1, which is odd
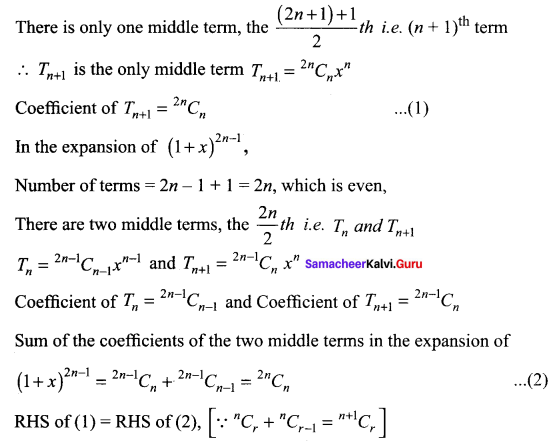
Question 7.
If three consecutive coefficients in the expansion of (1 + x)n are in the ratio 6 : 33 : 110, find n.
Solution:
Let the consecutive coefficients nCr, nCr + 1 and nCr + 2 be the coefficients of Tr + 1, Tr + 2 and Tr + 3 then nCr : nCr + 1 : nCr + 2 = 6 : 33 : 110
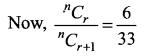
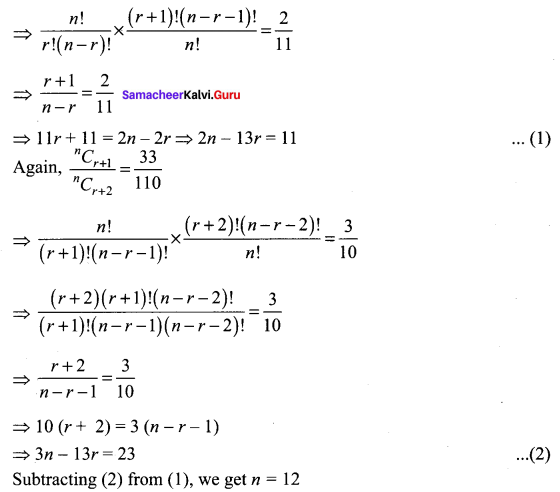
Question 8.
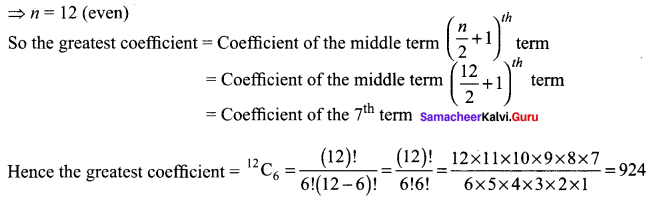
If the sum of the coefficients in the expansion of (x + y)n is 4096. Then find the greatest coefficient in the expansion.
Solution:
Given that, Sum of the coefficients in the expansion of (x + y)n = 4096
∴ nC0 + nC1 + nC2+…+ nCn = 4096
[∴ Sum of binomial coefficients in the expansion of (x + a)n is 2n]
⇒ 2n = 4096 = 212
Question 9.
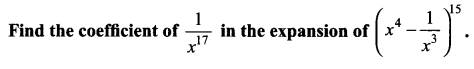
Solution:
The general term in the expansion of
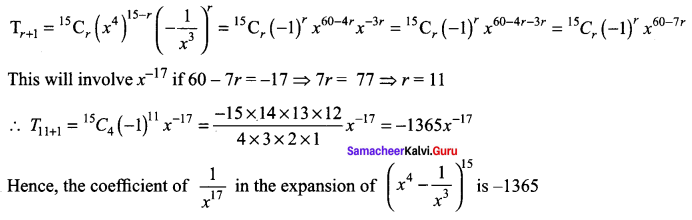
Question 10.

Solution: