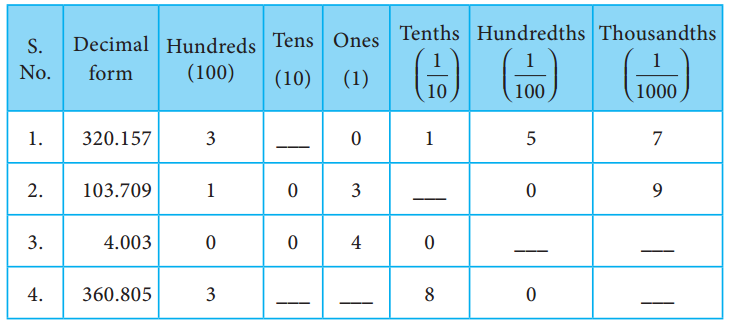
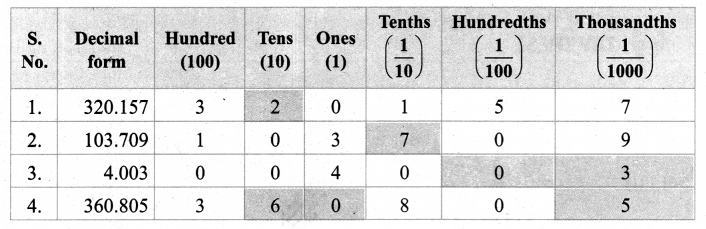
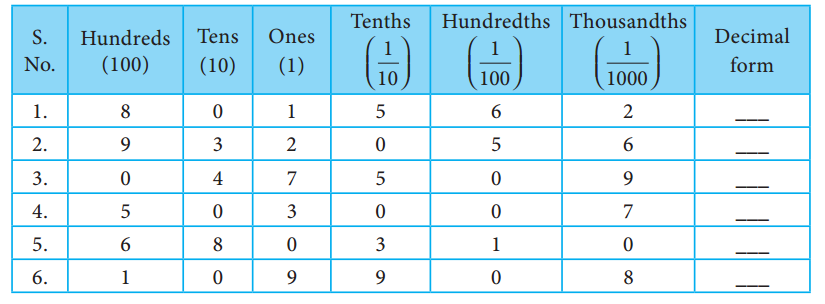
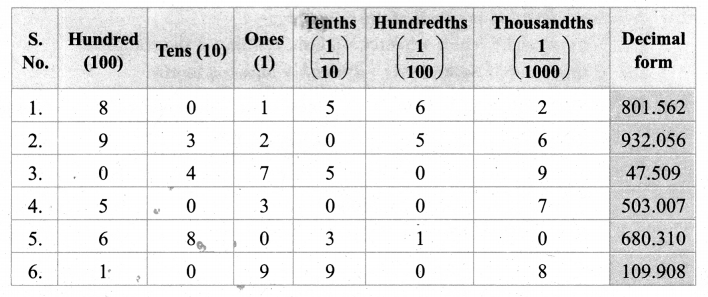
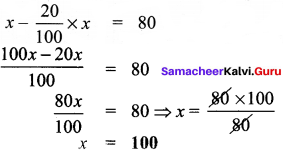
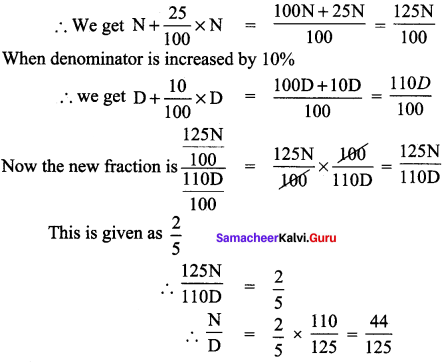
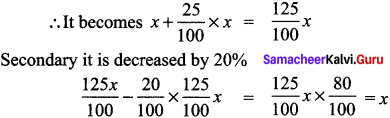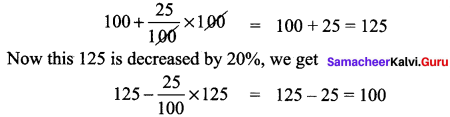Students can Download Social Science Geography Term 3 Chapter 2 Exploring Continents (Africa, Australia and Antarctica) Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Geography Solutions Term 3 Chapter 2 Exploring Continents (Africa, Australia and Antarctica)
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Geography Exploring Continents (Africa, Australia and Antarctica)Textual Evaluation
![]()
I. Choose the best answer:
Question 1.
The southernmost tip of Africa is …………..
(a) Cape Blanca
(b) Cape Agulhas
(c) Cape of Good Hope
(d) Cape Town
Answer:
(b) Cape Agulhas
Question 2.
The manmade canal through an isthmus betw een Egypt and Sinai Peninsula is
(a) Panama Canal
(b) Aswan Canal
(c) Suez Canal
(d) Albert Canel
Answer:
(c) Suez Canal
![]()
Question 3.
In respect of the Mediterranean climate, consider the following statements and choose the correct answer.
(1) The average rainfall is 15 cm
(2) The summers are hot and dry; winters are rainy.
(3) Winters are cool and dry; Summers are hot and wet
(4) Citrus fruits are grown
(a) 1 is correct
(b) 2 and 4 are correct
(c) 3 and 4 are correct
(d) All are correct
Answer:
(b) 2 and 4 are correct
Question 4.
The range which separates the west and east flowing rivers in Australia is
(a) Great Dividing Range
(b) Himalayan range
(c) Flinders range
(d) Mac Donnell range
Answer:
(a) Great Dividing Range
Question 5.
Kalgoorile is famous for …………….. mining.
(a) Diamond
(b) Platinum
(c) Silver
(d) Gold
Answer:
(d) Gold
![]()
II. Fill in the Blanks:
- Atlas Mountain is located in …………….. continent.
- …………….. is the first Indian research station in Antarctica.
- ………….. is the highest peak of Africa.
- A temperature grass land of Anustralia is called …………..
- ………….. is the first indian research station in Antarctica.
Answer:
- North – west Africa
- Mt. Kilimanjaro
- Eucalyptus
- Downs
- Dakshin Gangotri
II. Match the following:
- Pinnacle – Equatorial forest
- Krill – salt lake
- Ostrich – small red fish
- Lake Eyre – flightless bird
- Jewel of the earth – Pointed limestone pillars
Answer:
- Pinnacle – Pointed limestone pillars
- Krill – small red fish
- Ostrich – flightless bird
- Lake Eyre – salt lake
- Jewel of the earth – Equatorial forest
![]()
IV. Let us learn:
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Aurora is a curtain of color lights appear in the sky.
Reason (R): They are caused by magnetic storms in the upper atmosphere.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation for A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation for A
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) R is true but A is false
Answer:
(a) Both A and R is individually true and R is the correct explanation for A
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : A geological feature of Africa is the Great Rift Valley.
Reason (R): A Rift valley is a large crack in the earth’s surface formed by tectonic activity.
(a) Both A and R is individually true and R is the correct explanation for A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation for A
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) R is true but, A is false
Answer:
(a) Both A and R is individually true and R is the correct explanation for A
V. Answer in brief:
Question 1.
Why Africa is called a “Mother Continent”?
Answer:
Africa is nicknamed as the ‘Mother Continent’ as it was the oldest inhabited continent on Earth.
Question 2.
What are the important rivers of Africa?
Answer:
The important rivers of Africa are R. Nile, R. Congo or Zaire, R. Niger, R. Zambezi, R. Orange and R. Limpopo.
Question 3.
Name the physical division of Australia.
Answer:
The Physical divisions of Australia are –
- The Great Western Plateau
- The Central Low lands
- The Eastern High lands
![]()
Question 4.
Write about the nature of Antarctica continent.
Answer:
- Antarctica is a unique continent. It does not have a native population.
- There is no country in Antarctica.
- It is the coldest continent with a permanent cover of ice.
- It is the only continent called white continent.
![]()
Question 5.
Mention any four economic activities of Australia.
Answer:
Agriculture, forestry, fishing mining, manufacturing, trade and services are the major economic activities of Australia.
VI. Distinguish between:
Question 1.
Sahel and Sahara
Answer:
1. Sahel:
- Sahel is a semi-arid tropical Savanna region.
- It covers an area of 3.0 million sq km.
- It is largely a semi-arid belt of barren, sandy and rocky land.
2. Sahara:
- The world-famous Sahara desert is located in the northern part of Africa.
- It has an area of .9.2 million sq kms.
- It consists of many topographical features such as Mountain, plateaus, ergs, oases, sand and gravel covered plains, salt flats, basins and depressions.
Question 2.
Western Antarctica and Eastern Antarctica.
Answer:
1. Western Antarctica:
- The West Antarctica faces the Pacific Ocean.
- The Antarctic Peninsula which points towards the South America shows that it is the continuation of the Andes mountain range.
2. Eastern Antarctica:
- The East Antarctica faces the Atlantic and the Indian Oceans.
- The Mt. Erebus in this region is an active volcano located in the Ross Island.
![]()
Question 3.
Great Barrier Reef and Artesian Basin.
Answer:
1. Great Barrier Reef:
- Great Barrier Reef is located in the north east of Australia.
- It is formed by the tiny coral polyps..
- It is about 2300 kms long.
2. Artesian Basin:
- The Artesian Basins are regions on the earth’s surface where water gushes out like a fountain.
- It is found in the arid and semi – arid parts of Queensland.
- It extents for 1.7 million square km.
VII. Give reasons:
Question 1.
Egypt is called the gift of the Nile.
Answer:
- Nile is the life line of Egypt
- Without Nile the Egypt would have been a desert
- So Egypt in the gift of the Nile.
![]()
Question 2.
Deserts are found in the western margins of continents.
Answer:
- Most of the world deserts are located in the western margins of continents in the subtropics because the prevailing winds in the tropics are tropical easterly winds.
- The tropical easterly winds become dry by the time they reach the western margins of continent and so they bring no rainfall.
Question 3.
Antarctica is called the continent of scientists.
Answer:
- Scientists of any country are free to conduct experiments and collect data from Antarctica.
- Hence it is called ‘continent of Science’.
![]()
VIII. Answer in a paragraph each:
Question 1.
Give an account on mineral wealth of Australia.
Answer:
- Minerals are the largest export item of Australia.
- It contributes about 10 percent of country’s GDP.
- Australia is the world’s leading producer of bauxite, limonite, rutile and zircon.
- The Second largest producer of gold, lead, lithium, manganese ore and zinc, the third largest producer of iron ore and uranium and they fourth largest producer of black coal.
- The coal belts of the country stretches from New Castle to Sydney on the South Eastern Coast.
- Iron ores are found mainly in southern and Western Australia.
- Petroleum and natural gas is obtained from Bass Strait and west of Brisbane.
- Uranium is mined in northern territory at Ram jungle and Queensland.
- Gold is mined in the western desert at Kalgoorlie and Koolgarlie.
- Lead, Silver, Zinc, Manganese, Tungsten, Nickel and copper are also mined in parts of Australia.
Question 2.
Describe the flora and fauna of Antarctica
Answer:
Flaora and Fauna:
- Since the temperature is below freezing point almost throughout the year, no major vegetation is found in this continent.
- Simple plants like algae, mosses, liverworts, lichens and microscopic fungi can survive and grow in Antarctica.
- Some algae live in the snow, while other plants grow on the coastal rocky land that is ice free.
- A few species of plants, such as plankton, algae and mosses are seen in and around, Antarctica’s fresh and saltwater lakes.
- Small red fish called krill are found in large shoals .It is the food for many warm blooded sea animals.
- The blue whale is the largest animal which feeds on plankton. All these animals and birds have a thick layer of fat called blubber which helps them to withstand the cold condition.
- Penguin birds in Antarctica cannot fly. They have webbed feet and flipper instead of wings. Small invertebrates are the only land animals which lives in the continent.
![]()
Question 3.
Name the physical divisions of Africa and explain any one.
Answer:
1. Africa consists of mixture of land forms such as mountains, plateaus and plains. The following are the 8 major physical divisions of Africa.
- Sahara
- Sahel
- Savanna
- The Great Rift Valley and the Great Lakes of Africa
- East African Highlands
- Swahili Coast
- The Congo Basin or Zaire Basin
- Southern Africa
2. Southern Africa.
- Most part of the Southern Africa is a plateau region.
- Drakensberg Mountain is found in the eastern portion of the escarpment.
- It extends from north east to south west for 1125 km.
- Its highest peak is.Thabana Ntlenyana (3482m).
- This region is covered with grasslands known as‘Veld’.
- Kalahari Desert lies in the south and Namib Desert is along the south -west shore of Africa.
- Kalahari Desert in this region is not actually a desert but, a bushy scrubland situated between the Orange and Zambezi Rivers.
![]()
XI. Map skill:
Question 1.
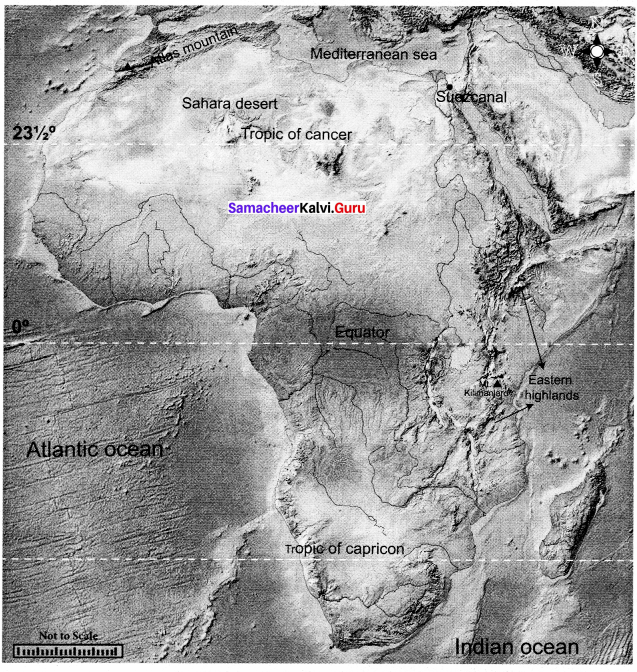
Mark the following on the outline map of Africa and Australia.
Answer:
Africa:
Equator, Atlas Mountain, Sahara, Eastern highlands, Mediterranean Sea, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Suez Canal, Mount Kilimanjaro,
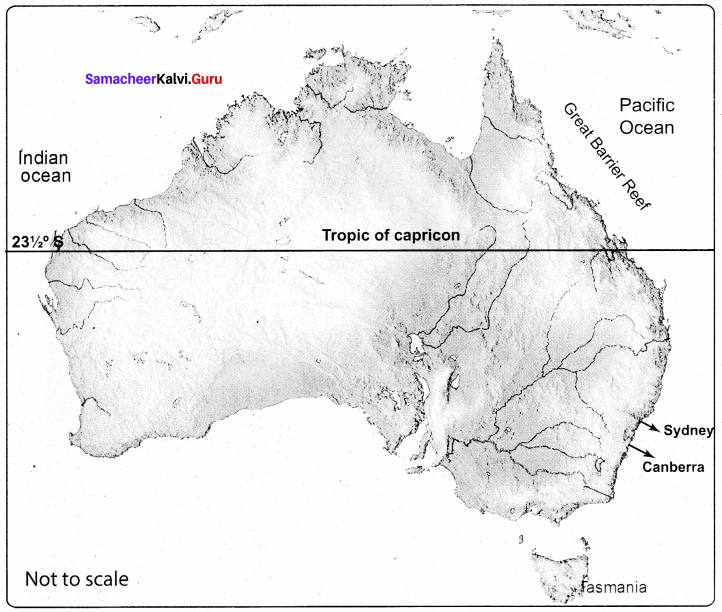
Australia:
Great Dividing Range , Great barrier reef, Tasmania, tropic of Capricorn, pacific ocean. Great Australian Sandy Desert. Indian ocean, Sydney, Canberra.
X. Activity:
Question 1.
Find out the hemisphere and season during December for the following countries.
Answer:
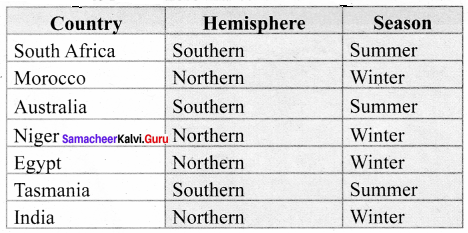
Question 2.
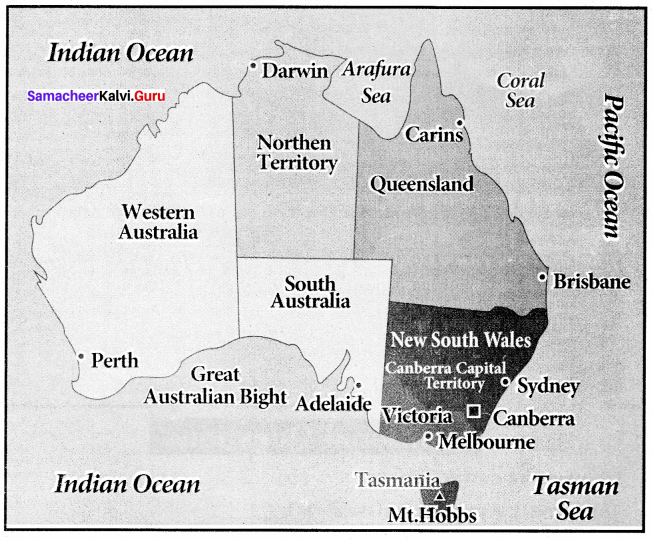
Label the name of the different states of Australia in the following map
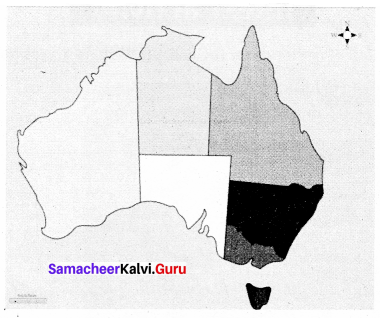
Answer:
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Geography Chapter 2 Exploring Continents (Africa, Australia and Antarctica) Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The second largest continent of the world is …………..
(a) Asia
(b) Africa
(c) Europe
(d) South Africa
Answer:
(b) Africa
Question 2.
The only continent through which Tropic of Capricorn and Tropic of Cancer pass is ………….. in Indian ocean took place in the year 2004.
(a) Asia
(b) Australia
(c) Africa
(d) Europe
Answer:
(c) Africa
Question 3.
Africa is located in all the ………….. hemisphere.
(a) three
(b) two
(c) four
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) four
![]()
Question 4.
Henry M. Stanley used the term ………….. to refer to Africa
(a) Land of rising sun
(b) Land of Thousand lakes
(c) Dark continent
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) Dark continent
Question 5.
The continent of Africa consists of ………….. countries.
(a) 48
(b) 54
(c) 36
(d) 60
Answer:
(b) 54
Question 6.
The term ‘Maghreb’ refers to ………….. of Africa.
(a) North Western countries
(b) West part
(c) Central part
(d) Eastern part
Answer:
(a) North Western countries
![]()
Question 7.
Sahara desert is located in the ………….. part of Africa.
(a) Eastern
(b) Western
(c) Southern
(d) Northern
Answer:
(d) Northern
Question 8.
The Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic ocean are separated by ………….. moutain.
(a) Atlas
(b) Himalayas
(c) Rocky
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Atlas
![]()
Question 9.
The African Great Lakes consist of ………….. major lakes.
(a) 5
(b) 7
(c) 6
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 7
Question 10.
Kalahari desert situated between the Orange and ………….. Rivers.
(a) Nile
(b) Congo
(c) Amazon
(d) Zambezi
Answer:
(d) Zambezi
![]()
Question 11.
Father of African rivers is …………..
(a) Cango
(b) Nile
(c) Niger
(d) Zambezi
Answer:
(b) Nile
Question 12.
Southern Africas ‘River of Life’ is …………..
(a) Cango
(b) Zambezi
(C) Nile
(d) Zaire
Answer:
(b) Zambezi
![]()
Question 13.
The Chief cash crop of Africa is …………..
(a) Cotton
(b) Jute
(c) Tea
(d) Sugarcane
Answer:
(a) Cotton
Question 14.
Australia’s largest physical division is …………..
(a) The Great Western Plateau
(b) The Central Low lands
(c) The Eastern High lands
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) The Great Western Plateau
![]()
Question 15.
Mt. Kosciuszko is located in the …………..
(a) Melbourne
(b) Perth
(c) New South Wales
(d) Adelaide
Answer:
(c) New South Wales
Question 16.
Tasmania gets rain throughout the year from …………..
(a) Trade winds
(b) Monsoon winds
(c) westerly winds
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) westerly winds
Question 17.
The Cash Crop of Australia is …………..
(a) Cotton
(b) Tea
(c) Wool
(d) Jute
Answer:
(c) Wool
![]()
Question 18.
Australia is highly dependent on ………….. transport.
(a) road
(b) train
(c) air
(d) water
Answer:
(a) road
Question 19.
There is no native population in …………..
(a) Asia
(b) Africa
(c) Australia
(d) Antarctica
Answer:
(d) Antarctica
![]()
Question 20.
Artesian basins are common in …………..
(a) Africa
(b) Australia
(c) Antarctica
(d) South America
Answer:
(b) Australia
II. Fill in the blanks:
- The second most populous continent after Asia is …………..
- In Africa the Prime Meridian Passes near ………….. the capital of Ghana.
- The major island of Africa is ……………
- Sahara is one of the largest ………….. in the world.
- ………….., an extinct volcano in chad, is the highest point in the sahara.
- Sahara’s deepest point is ………….. in Egypt.
- Sahel means ……………
- In Africa tropical dry grasslands are known as …………..
- One of the largest plains in Savanna is …………..
- ………….. plain is called the open Air Zoo.
- The largest fresh water body in Africa is …………..
- The first largest fresh water is ………….. in USA.
- Lake Victoria is the source of river …………..
- The longest and deepest fresh water lake in the world is ……………
- Swahili coast is located along the shores of ……………
- The world’s first largest river basin is ………….. in South America.
- The second largest river basin in the world is the ………….. in Africa.
- Southern Africa region is c covered with grasslands known as ……………
- The Gift of the Nile is ……………
- The longest river in the world is ……………
- The world famous waterfall Victoria is formed by the river ……………
- Southern Africa’s ‘River of Life’ is river ……………
- A hot and dry dusty local wind blowing from the Sahara desert to Guinea coast is called …………..
- A hot local wind blowing from Sahara to Mediterranean Sea is called …………..
- Ghana is the Chief Producer of ……………
- The most populous country of Africa is …………..
- Australia is the largest ………….. and smallest ………….. in the world
- Australia was discovered by …………. an English Seaman in 1770 .
- The Tropic of ………….. cuts the Australia continent into two equal halves.
- The capital of Australia is ……………
- ………….. is the largest monolith rock in the world.
- The largest desert in Australia is the ……………
- The largest Salt Lake ………….. lies in the central low lands of Australia.
- The Eastern Highlands are also known as ………….. in Australia.
- The Great. Barrier Reef is formed by the ……………
- The longest river in Australia is ……………
- The plants and trees in Australia are called ……………
- The people who work in the sheep station in Australia are known as ……………
- The indigenous people of Australia are called …………..
- Tasmania is known as the ………….. Island.
- ………….. are rearing in Southern Australia.
- The densely populated region is ………….. part of Australia.
- The Mt. Erebus an active volcano is located in the ………….. Island.
- The largest piece of ice on the surface of Earth is …………..
- The largest glacier in the world in ………….. located in …………..
Answers:
- Africa
- Accra
- Antarctica
- hot deserts
- Mount Koussi
- Qattara
- broder or margin
- savanna
- Serengeti
- Serengeti
- Lake Victoria
- Lake superior
- Nile
- Tanganyika
- East Africa
- Amazon
- Congo
- Veld
- Egypt
- River Nile
- Zambezi
- Zambezi
- Harmattan
- Sirocco
- Cocoa
- Nigeria
- island/continent
- Captain James Cook
- Capricorn
- Canberra
- Ayers rock or Uluru
- Great Victoria Desert
- Lake Eyre
- Great Dividing Range
- Tiny coral polyps
- River Murray
- Xerophytes
- Jackroos
- Aborigines
- Apple
- Merino
- Southeastern
- Ross
- Antarctica
- Lambert glacier, Antarctica
![]()
III. Match the following:
Question 1.
- Dark Continent – a) Explorer
- David Livingstone – b) Evergreen Forest
- Atlas mduntain – c) Sheep rearing
- Congo Basin – d) Africa
- Karoo – e) Young fold mountain
Answer:
- d
- a
- e
- b
- c
Question 2.
- Captain James Cook – a) New South Wales
- Uluru – b) Australian river
- Mt. Kosciuszko – c) Swamp forests
- Lachlan – d) Monolitic rock
- Melaleuca – e) Australia
Answer:
- e
- d
- a
- b
- c
Question 3.
- Antarctica – a) largest animal
- White continent – b) Largest Research station
- Blue whale – c) India
- Mcmurdo – d) Continent of Science
- Bharathi – e) Antarctica
Answer:
- d
- e
- a
- b
- c
![]()
IV. Let us learn :
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : H.M. Stanley called Africa Dark continent.
Reason (R) : In the beginning the interior of Africa was largely unknown to people.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are individually true and R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) R is true but A is false
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : The great Barrier Reef is one of the natural wonders of the world.
Reason (R) : The Great Barrier Reef is formed by the tiny coral polyps.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are individually true and R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) R is true but A is false
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A
![]()
V. Answer in brief :
Question 1.
Explain the term‘Maghreb’.
Answer:
The north-western African countries of Morocco, Algeria, Libya, Mauritania and Tunisia are collectively called ‘Maghreb’, which means west in Arabic language.
Question 2.
Write a note on Atlas Mountains.
Answer:
- Atlas Mountain lies in the north- west of Africa.
- It is a young fold mountain.
- It separates the Mediterranean sea and Atlantic ocean.
- The highest point is Mount Toubkal (4167m).
Question 3.
Where do we find Savanna grasslands in Africa?
Answer:
- Savanna grassland is found in the regions just north and south of the rain forests that lie along the equator.
- Trees are the main features of the landscape in some parts of the savanna, while tall grass covers the other areas.
- The Serengeti Plain is one of the largest plains in Savanna.
- This is called the ‘Open Air Zoo’.
![]()
Question 4.
Nile is known as the Father of African Rivers. Give reasons.
Answer:
- River Nile is known as the Father of African Rivers.
- It is the largest river in the world with a length of 6650 km.
- White Nile and the Blue Nile join together to form the River Nile at Khartoum, in Sudan.
- It flows towards and drains into the Mediterranean-sea.
Question 5.
Write about the animals of Africa.
Answer:
- There are over one million species of animals in Africa including both the heaviest (elephants) and the tallest (giraffes) land animals on the earth.
- White Rhinoceros, Western Green Mamba, Zebra, African Elephants, chimpanzee, gorilla, Hippopotamus and Giraffe are the major animals of Africa.
- Bonobo, Wild Dogs, hyena and Lemur are the typical animals of Africa.
Question 6.
Name the major tribes of Africa.
Answer:
Afar, Fatwa, Bushmen, Dinka, Masai, Pygmies, Zulu, Tswan, and Efe are the major tribes of Africa.
Question 7.
Mention the political division of Australia.
Answer:
There are six states and two Union Territory in Australia They are:
- New South Wales
- Queensland
- South Australia
- Tasmania
- Victoria
- Western Australia
- Northern Territory
- Capital Territory (Canberra).
![]()
Question 8.
Mention the important cities of Australia.
Answer:
- Canberra is the capital of Australia.
- Sydney, Brisbane, Adelaide, Hobart, Melbourne, Perth and Darwin are the other important cities of Australia.
Question 9.
Why is Ayers rock one of the natural wonders of Australia?
Answer:
- Ayers rock or Uluru is the largest monolith rock in the world.
- It is found in the central part of The Great Western Plateau region.
- It is 863 meters high above the sea level.
- The pointed limestone pillars called Pinnacles are common in this region.
Question 10.
What is meant by Xerophytes?
Answer:
- The plants and trees in Australia are adapted to dry conditions.
- They can survive for long period without water.
- They are called Xerophytes.
![]()
Question 11.
Write about the fauna of Australia.
Answer:
- Australia has almost 400 mammal species and about 140 species of marsupials.
- These are the animals that carry their young ones in their pouches.
- Kangaroo is the national animal of Australia.
- Koala, platypus Wallaby and Dingo are the other important animals of Australia.
- The bird species like the laughing kookaburra, emu, and rainbow lorikeet are the major birds of Australia.
Question 12.
What are Merino sheep.
Answer:
- In Australia sheep farming is common in the temperate grassland.
- Merino sheep are rearing in southern Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and New South Wales.
- Sheep industry is a well developed industry in Australia.
- The wool is described as the ‘Cash Crop’ in Australia.
Question 13.
Mention the important industries A frica.
Answer:
- Food and beverage manufacturing industry is the primary industry in Australia.
- Finance, ship building, information and technology, mining, insurance, aviation and telecommunication industries are the other important industries.
![]()
Question 14.
Mention the living creatures of Antarctica Continent.
Answer:
- Small red fish called krill are found in large shoals .It is the food for many warm blooded sea animals.
- The living creatures of this region are includes whales, seals, walrus and sea birds like penguins, albatross, polar Skua and Stout.
- The blue whale is the largest animal which feeds on plankton.
VI. Distinguish between:
Question 1.
River Congo and River Niger
Answer:
1. River Congo:
- It is the second largest river of Africa.
- Its rises in the highlands of North Eastern Zambia .
- Its length is about 4700km.
- Drains into the Atlantic Ocean
2. River Niger:
- It is one of the major rivers in West Africa.
- It rises from the highlands of Guinea.
- It flows for about 4184 km.
- Drains into the Gulf of Guinea on the Atlantic Ocean.
Question 2.
Equatorial climate and Mediterranean climate (Africa).
Answer:
1. Equatorial climate (Africa):
- It is found in the equatorial region covering the Congo River basin and east African highlands.
- Temperature and rainfall are high all the year round in this region.
2. Mediterranean climate (Africa):
- It is found in the north-western and south western tips of Africa.
- These regions get rainfall in winters while in summers it is hot and dry.
![]()
Question 3.
Waterways and Airways (Africa).
Answer:
1. Waterways (Africa):
- Africa has trade routes between Asia and Australia in the east, Europe in the north and America in’the west.
- The major sea ports of Africa are Durban, Dar es Salaam and Mogadishu on the Indian Ocean, Port Said, and Alexandria, on the Mediterranean Sea, Cape Town, Algiers and Abidjan on the Atlantic Ocean.
2. Airways (Africa):
- They connect the capital cities of Africa and the other parts of the world.
- The major international airports of the continent are Cairo, Johannesburg, Nairobi, Dakar, Addis- Ababa, Casablanca, Durban, Douala and Logos.
VII. Give Reasons :
Question 1.
Kilimanjaro summit will be ice -free by 2025.
Answer:
- The glaciers on the top of Kilimanjaro have been disappearing since 20th centuries.
- If this trend continues. Kilimanjaro summit will be .ice -free by 2025.
![]()
Question 2.
The name of Swahili to the people of Swahili Coast.
Answer:
- Swahili Coast region extents from Somalia to Mozambique.
- It was a region where the Africans and Arabs mixed to create a unique culture referred to as Swahili Culture.
- People of this coast are also called as ‘Swahili’.
Question 3.
Roadways and Railways in Africa are poorly developed.
Answer:
- Roadways and Railways in Africa are poorly developed due to the presence of many barriers.
- It is very difficult to lay the roads and rails across the deserts and the dense forests.
- South Africa, Kenya, Egypt, Libya. Morocco and Nigeria have roadways and railways to some extent.
Question 4.
Australia was the last continent to be discovered.
Answer:
- Australia was the last of all the continents to be discovered.
- It was due to its remoteness.
Question 5.
Antarctica is the coldest continent.
Answer:
- Antarctica is the coldest continent in the world.
- It is located in the polar region.
- It has a permanent cover of ice.
![]()
Question 6.
Antarctica is the only white continent.
Answer:
- Antarctica is the only continent called white continent.
- It has a permanent cover of ice.
- In some places its ice cap is 4,000 metres deep.
Question 7.
The extraction of minerals does not take place in Antarctica.
Answer:
- The international agreement on the continent of Antarctica does not permit the extraction of minerals.
- Hence the extraction of minerals does not take place.
![]()
VIII. Answer in a paragraph each :
Question 1.
Write about the mineral wealth of Antarctica Continent.
Answer:
- Scientific studies show that the Antarctic continent is to be rich in gold, platinum, nickel, copper and petroleum.
- Traces of chromium, lead, molybdenum, tin, uranium, and zinc are also seen.
- The possible resources of this region also include silver, platinum, iron ore, cobalt, manganese and titanium.
- Coal and hydrocarbons have been explored in minimal non-commercial quantities.
Question 2.
Explain the term Aurora
Answer:
- A natural Curtain of combination of bright pink, red and green color light that appears in the sky near the north and south magnetic poles is called Aurora.
- The effect is caused by the interaction of charged particles from the sun with atoms in the upper atmosphere.
- It is also called Aurora Australis or Southern Lights in the South Pole and Aurora Borealis or Northern Lights in the North Pole.
- These amazing colours appear in the earth’s sky, especially in the high latitudinal countries like Alaska in the north and New Zealand of Falkland in the south.
![]()
Question 3.
What type of climatic Pattern is experienced by Australia?
Answer:
- Australia contains the second largest area of extremely arid land in the world.
- The Tropic of Capricorn divides the Australia into two equal parts.
- The Northern half is in the warm tropical zone and the southern half is in the cool temperate zone.
- The north coastal region experiences monsoon type of climate and there is a heavy rainfall during summer.
- The east coastal region receives good rainfall from south east trade wind.
- The hot desert climate extends from central lowlands to western shores.
- The rainfall in this region is less than 25cm per annum.
- Mediterranean type of climate prevails in the southern tip of Australia in the region around Perth and Adelaide.
- Tasmania gets rain throughout the year from westerly winds.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the location and size of Africa.
Answer:
- Africa is the second largest and second most populous continent after Asia.
- It stretches from 37°21 ’North latitude to 34° 51 ’ South latitude and from 17°33’ West longitude to 51 °27 ’ East longitude.
- It spreads over an area of about 30.36 million square kilometres (20.2% of the world’s land area).
- The equator passes through the middle of Africa and cuts into two equal halves.
- It is the only continent through which the major latitudes such as Tropic of Cancer, Equator and Tropic of Capricorn pass.
- Its north-south extent is 7623 km and east-west extent is 7260 km.
- The Prime Meridian passes this continent.
- Africa is located in all the four hemispheres.
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Geography Chapter 2 Exploring Continents (Africa, Australia and Antarctica) Intext activity
Question 1.
On the outline map of Africa draw the courses of main rivers and name them.
Answer:
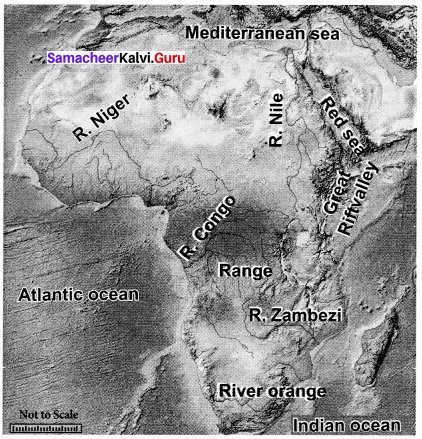
Question 2.
There are eight deserts in Australia. List them out with the help of Atlas.
Answer:
- Central Desert
- Gibson Desert
- Great Sandy Desert
- Great Victoria Desert
- Little Sandy Desert
- Simpson Desert
- Strzelecki Desert
- Tanami Desert