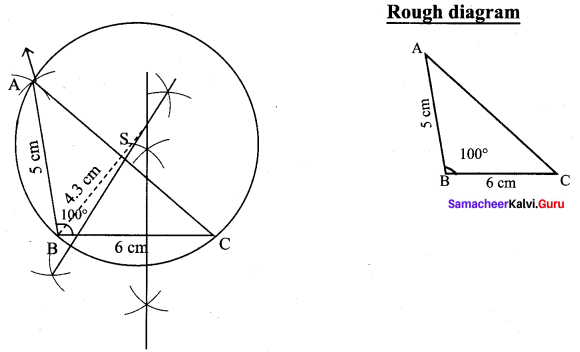
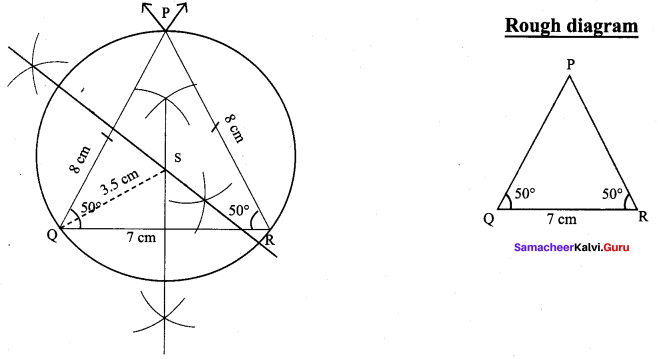
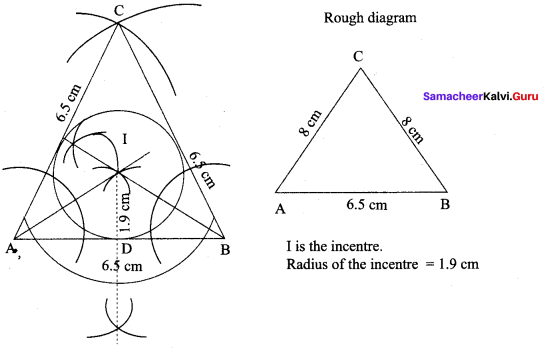
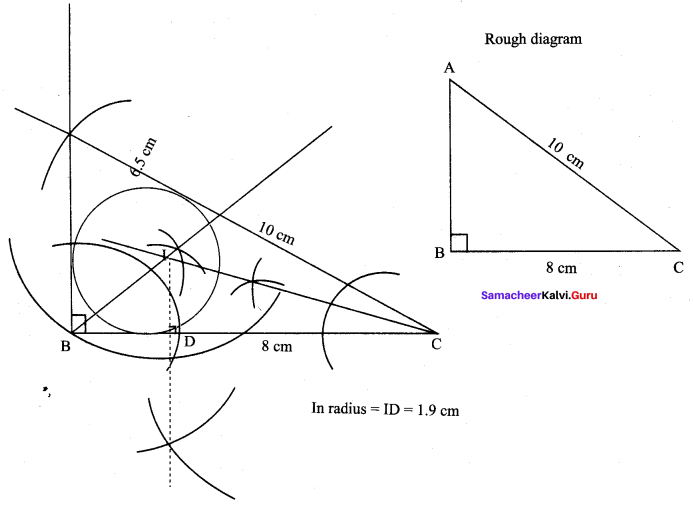
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Set Language Ex 1.1
Set Language Maths 9th Class Question 1.
Which of the following are sets?
(i) The Collection of prime numbers upto 100.
(ii) The Collection of rich people in India.
(iii) The Collection of all rivers in India.
(iv) The Collection of good Hockey players.
Solution:
(i) A = {2, 3, 5, 7,11, 13,17,19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89 and 97}
As the collection of prime numbers upto 100 is known and can be counted (well defined). Hence this is a set.
(ii) The collection of rich people in India. Rich people has no definition.
Hence, it is not a set.
(iii) A = {Cauvery, Sindhu, Ganga, }
Hence, it is a set.
(iv) The collection of good hockey players is not a well – defined collection because the criteria for determining a hockey player’s talent may vary from person to person.
Hence, this collection is not a set.
9th Maths Set Language Exercise 1.1 Question 2.
Listthe set of letters of the following words in Roster form.
(i) INDIA
(ii) PARALLELOGRAM
(iii) MISSISSIPPI
(iv) CZECHOSLOVAKIA
Solution:
(i) A = {I, N, D, A}
(ii) B = {P, A, R, L, E, O, G, M}
(iii) C = {M, I, S, P}
(iv) D = {C, Z, E, H, O, S, L, V, A, K, I}.
9th Maths Exercise 1.1 In Tamil Question 3.
Consider the following sets A = {0, 3, 5, 8} B = {2, 4, 6, 10} C = {12, 14, 18, 20}
(a) State whether True or false.
(i) 18 ∈ C
(ii) 6 ∉A
(iii) 14 ∉ C
(iv) 10 ∈ B
(v) 5 ∈ B
(vi) 0 ∈ B
(b) Fill in the blanks?
(i) 3 ∈ ___
(ii) 14 e ___
(iii) 18 ___ B
(iv) 4 ___ B
Solution:
(a) (i) True
(ii) True
(iii) False
(iv) True
(v) False
(vi) False,
(b) (i) A
(ii) C
(iii) ∉
(iv) ∈
9th Maths Exercise 1.1 Question 4.
Represent the following sets in Roster form.
(i) A = The set of all even natural numbers less than 20.
(ii) B = {y : y = \(\frac{1}{2 n}\), n ∈ N, n ≤ 5}
(iii) C = (x : x is perfect cube, 27 < x < 216}
(iv) D = {x : x ∈ Z, -5 < x ≤ 2}
Solution:
(i) A= {2,4, 6, 8,10, 12, 14,16, 18}
(ii) N = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}

(iii) C = {64, 125}
(iv) D = {-4,-3, -2, -1,0, 1, 2}
9th Maths Set Language Exercise 1.1 Solutions Question 5.
Represent the following sets in set builder form.
(i) B = The set of all Cricket players in India who scored double centuries in One Day Internationals.
(ii) C = { \(\frac{1}{2}, \frac{2}{3}, \frac{3}{4} \ldots . .\)}.
(iii) D = The set of all tamil months in a year.
(iv) E = The set of odd Whole numbers less than 9.
Solution:
(i) B = {x : x is an Indian player who scored double centuries in one day internationals}
(ii) C = {x : x = \(\frac{n}{n+1}\), n ∈ N}
(iii) D = {x : x is a tamil month in a year}
(iv) E = {x : x is odd number, x ∈ W, x < 9, where W is the set of whole numbers}.
Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Set Language Question 6.
Represent the following sets in descriptive form.
(i) P = {January, June, July}
(ii) Q = {7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29}
(iii) R= {x : x ∈ N,x< 5}
(iv) S = {x : x is a consonant in English alphabets}
Solution:
(i) P is the set of English Months begining with J.
(ii) Q is the set of all prime numbers between 5 and 31.
(iii) R is the set of all natural numbers less than 5.
(iv) S is the set of all English consonants.