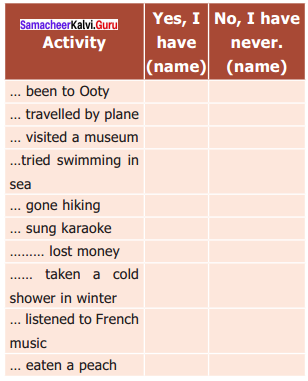
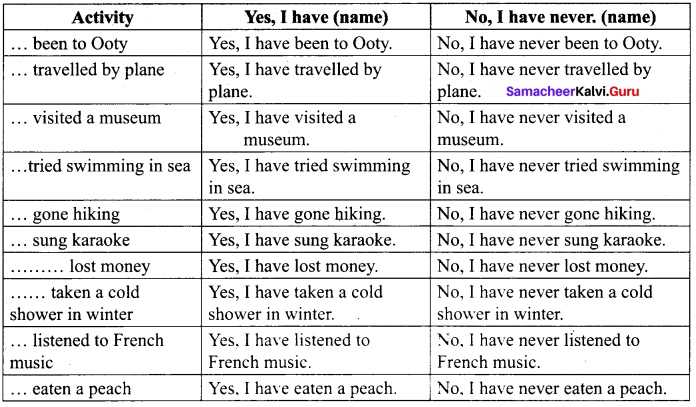
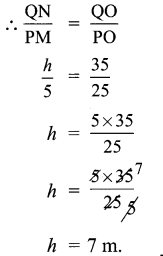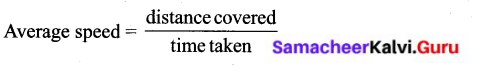You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Economics Solutions Chapter 1 Understanding Development: Perspectives, Measurement and Sustainability
Understanding Development: Perspectives, Measurement and Sustainability Textual Exercise
I. Choose the correct answer.
9th Economics Samacheer Book Question 1.
Assertion (A): Development increases the quality of life.
Reason (R): People will have higher incomes, better education, better health and nutrition, less poverty. .
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is correct and (R) is false
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
Expand The Following Ppp And Hdi Question 2.
The term‘Human resources’ refers to ……
(a) investment on poor people
(b) expenditure on agriculture
(c) investment on assests
(d) collective abilities of people
Answer:
(d) collective abilities of people
Expand The Following Nnp And Pci Question 3.
For comparing development between countries, their …… is considered to be one of the
most important attributes.
(a) growth
(b) income
(c) expenditure
(d) savings
Answer:
(b) income
Expand The Following Hdi Question 4.
……. is considered a true measure of national income.
(a) GNP
(b) GDP
(c) NNP
(d) NDP
Answer:
(c) NNP
Expand The Following Nnp Question 5.
The …… income is also called per capita income.
(a) average
(b) total
(c) people
(d) monthly
Answer:
(a) average
Expand Nnp And Pci Question 6.
Which one of the following country is not a G-8 country?
(a) Japan
(b) Canada
(c) Russia
(d) India
Answer:
(d) India
Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 Let’s Discuss Answers Question 7.
Which one of the following country is not a member of SAARC?
(a) India
(b) Pakistan
(c) China
(d) Bhutan
Answer:
(c) China
Class 9th Sst Economics Chapter 1 Question 8.
Assertion (A) : The Net Product (NNP) is considered as a true measure of national output.
Reason (R): It is also known as national income.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is correct and (R) is false
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
Sustainability Meaning In Tamil Question 9.
Assertion (A): Human resource is necessary for the progress of any country.
Reason (R): Investment in education and health of people can result in a high rate of returns in the future for a country.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is correct and (R) is false
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
Question 10.
The Human Development Index (HDI) does not take into account the following dimension in its calculation.
(a) Gender
(b) Health
(c) Education
(d) Income
Answer:
(a) Gender
Question 11.
Among the following states which state have the literacy rate (2011) higher than national average?
(a) Andhra Pradesh
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Tamil Nadu
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Tamil Nadu
Question 12.
Sex-ratio means …..
(a) the ratio between adult-male and adult female in a population
(b) the ratio between female and male in a population
(c) the relationship between male of female
(d) the number of females per thousand males
Answer:
(b) the ratio between female and male in a population
Question 13.
Inter-generational equality is ensured under the process of
(a) Industrial progress
(b) Economic development
(c) Sustainable development
(d) Economic growth
Answer:
(b) Economic development
Question 14.
Find the odd one.
(a) Solar energy
(b) Wind energy
(c) Paper
(d) Natural gas
Answer:
(c) Paper
Question 15.
……….. is the state with highest installed solar capacity in India.
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) West Bengal
(c) Kerala
(d) Andhra Pradesh
Answer:
(a) Tamil Nadu
Question 16.
……. resources are those which will get exhausted after years of use.
(a) Natural
(b) Renewable
(c) Non-Renewable
(d) New
Answer:
(c) Non-Renewable
Question 17.
Thermal plant emits large quantity of ……, which pollutes the environment.
(a) Oxygen
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Carbon
(d) Carbon dioxide
Answer:
(d) Carbon dioxide
II. Fill in the blanks
1. Economic progress of any country is known as ………
2. The head quarters of HRD Ministry is in ……..
3. The state having the highest literacy rate in India is ……….
4. Human Development Report of the world prepared and released by …….
5. Groundwater is an example of ……. resource.
6. The book An Uncertain Glory was written by ……..
Answers:
1. economic development
2. New Delhi
3. Kerala
4. UNDP
5. renewable
6. Prof. Amartya Sen
III. Match the following

Answers:
1. (d)
2. (c)
3. (b)
4. (a)
IV. Give Short answers
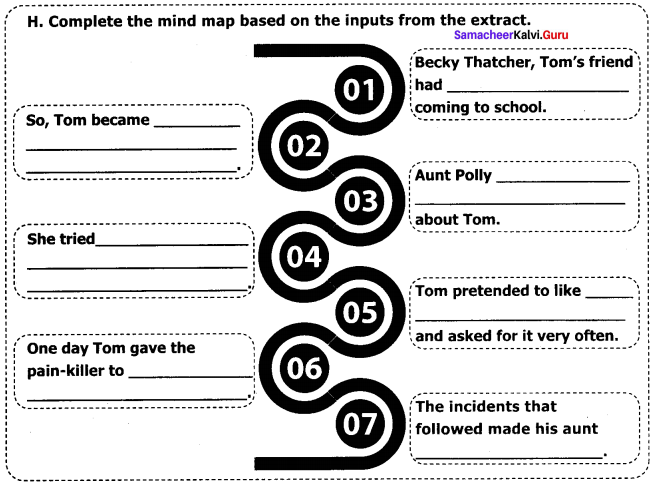
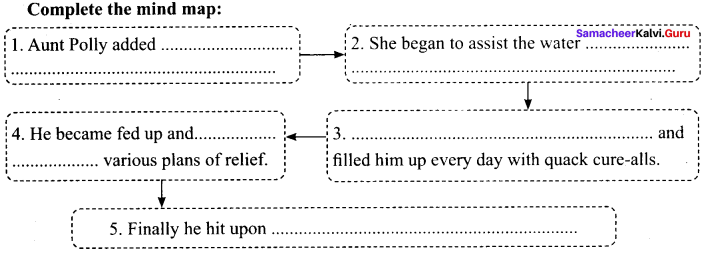
Question 1.
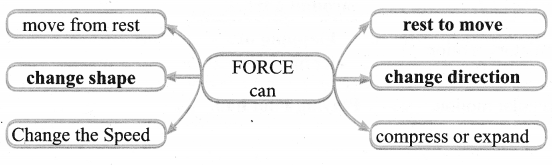
What do you mean by development?
Answer:
- The word ‘development’ refers to the progress of a particular field (or) a particular person.
- Similarly the economic progress of a country is known as ‘economic development’.
- However, the interpretation of the concept development keeps On changing from time to time, from person to person.
Question 2.
What are the indicators of development?
Answer:
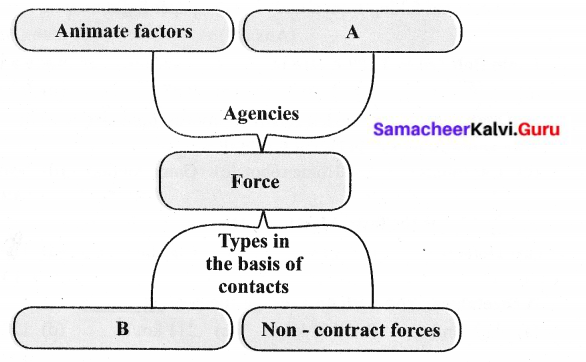
The major indicators to measure the level of economic development are Net National Product (NNP), Per Capita Income (PCI), Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) and Human Development
Index (HDI).
Question 3.
Why NNP is not considered as an useful measure to compare a country’s development with other countries?
Answer:
- For measuring a country’s development, its income is considered to be one of the most
important factors. - NNP is considered as a true measure of National output.
So NNP is not considered as an useful measure to compare a country’s development with
other countries.
Question 4.
Why human resources is considered as the foremost resource of any country?
Answer:
- Human Resource is necessary for the progress of any country.
- The ‘Human Resources’ refers to the collective abilities of people, which can be utilised in the production sector.
So human resource is considered as the foremost resource of any country.
Question 5.
Expand the following:
1. PPP
2. HDI
Answer:
1. PPI – Purchasing Power Parity
2. HD – Human Development Index.
Question 6.
Expand the following:
1. NNP
2. PCI.
Answer:
1. NNP – Net National Product
2. PCI – Per Capita Income
Question 7.
What is‘Solar Power’?
Answer:
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity either directly using photovoltaic cells (or) indirectly using concentrated solar power.
V. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
Discuss the policies for sustainable development.
Answer:
- India depends on thermal and hydro power plants to meet its power needs. Both these sources have an adverse environmental impact.
- Thermal power plants emit large quantities of carbon dioxide, which pollute the
environment. - Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity either directly
using photovoltaic cells or indirectly using concentrated solar power. - Solar panels absorb the sunlight as a source of energy to generate electricity. A solar electric system can reliably produce electricity for our home and offices.
- These distributed solar systems are often installed by home and business owners to reduce their electricity costs. Solar power in India is a fast-developing industry.
- Tamil Nadu is the state with highest installed solar capacity in India.
- Tamil Nadu is one of the leading solar power producing states in India. As on 31 July 2017, the total installed capacity in Tamil Nadu is 1,697 MW.
Question 2.
Describe in detail about environmental policies in India.
Answer:
- Environmental policies in India have been evolved considerably over the past three decades.
- These policies have covered a wide range of issues such as air, water pollution, waste management and biodiversity conservation.
- India faces challenges in economic development, which has to be achieved with limited resources, minimum externalities and in the presence of an uncertain climate.
- One of the approaches to overcome this challenge is through the path of sustainable development.
- The Supreme Court of India has interpreted and introduced new changes in environmental protection through a series of directions and judgements.
Question 3.
Differentiate between renewable and non-renewable resources.
Answer:

Question 4.
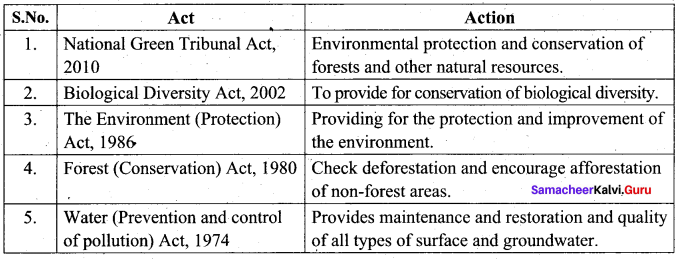
Mention any five environmental acts and their action.
Answer:
VI. Projects and Activities.
List the various ways in which the problems of garbage and emissions are being dealt with around the world.
Plastic bags, broken glass, obsolete cell phone (or) used battery cells, they are all used products that require appropriate disposal to limit their harm to the environment.
The various ways in which the problem of garbage and emissions are being dealt:
- Collection
- transportation
- dumping
- recycling (or) sewage treatment.
Various waste disposal problems:
- Production of too much waste.
- Most of the waste is toxic.
- Landfills are a problem as well.
- Regulations are based on vested interests.
- Reliance of dying technologies to reduce and recycle waste.
- Some of the technologies marked as ‘green’ are not true in actual sense.
You can do this project with the help of your teacher.
VII. HOTS
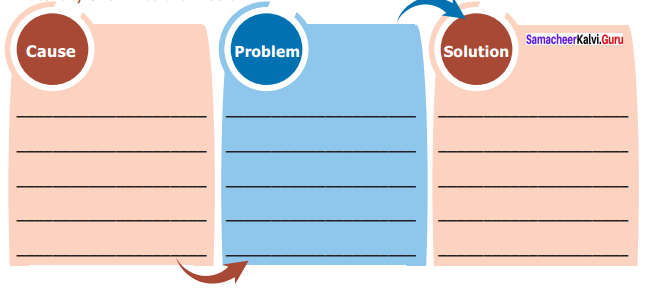
Write in detail what kind of environmental problems you face in your locality.
Location: Velachery – Chennai.
Problem: “Despite being one of the fastest growing localities with several up market malls and hotels living in Velachery still face basic problems such as
(a) Overflowing sewage
(b) Poor drainage
(c) The under ground water-breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
(d) There is always fear of contamination of drinking water.
(e) Everytime it pours in the city, most of Velachery drowns.
The above mentioned problems are the dominant ones in Velachery.
VIII. Life Skill.
Question 1.
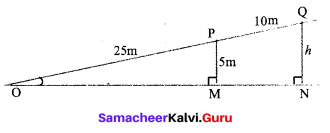
How is the Per Capita income calculated?
Answer:
The average income is calculated by dividing the country’s total income by its total population. The average income is also called per capita income. Calculations on the per capita income of all countries are calculated only in the US dollar in order to compare International level.
Understanding Development: Perspectives, Measurement and Sustainability Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): The term ‘economic development’ refers to the overall growth of all sectors of
the economy.
Reason (R): By adoption of new technologies.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is correct and (R) is false
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
Question 2.
This is also known as National Income.
(a) NNP
(b) GDP
(c) PCI
(d) PPP
Answer:
(a) NNP
Question 3.
This is not a G8 country.
(a) Russia
(b) Canada
(c) France
(d) Nepal
Answer:
(d) Nepal
Question 4.
This is one among the ‘BRICS’ countries.
(a) China
(b) Afghanistan
(c) Nepal
(d) Pakistan
Answer:
(a) China
Question 5.
The enrolment for higher education in the highest in ……… in India.
(a) Kerala
(b) Tamil Nadu
(e) West Bengal
(d) Maharashtra
Answer:
(b) Tamil Nadu
Question 6.
This is a renewable resource.
(a) Metals
(b) Glass
(c) Wind energy
(d) Diesel
Answer:
(c) Wind energy
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. Every, human being has an ……… of his (or) her own to achieve progress in life.
2. Countries with higher income are considered to be ………
3. ………. became the third largest economy in terms of PPP.
4. ………. can be divided into renewable resources and non-renewable resources.
5. ……. absorb the sunlight as a source of energy to generate electricity.
Answers:
1. Ambition
2. More developed
3. India
4. Natural resources
5. Solar panels
III. Match the following

1. (d)
2. (a)
3. (b)
4. (c)
IV. Give short answers.
Question 1.
What leads to development?
Answer:
If our thinking turns towards progress and about the ways to achieve the many goals for progress, it leads to development.
Question 2.
For comparing the development of various countries, total income is not an useful measure. How?
Answer:
Since the countries have different populations comparing total income will not be suggestive of what an average person is likely to earn. So, for comparing the development of various countries total income is not an useful measure.
Question 3.
Define Purchasing Power Parity.
Answer:
Purchasing Power Parity is defined as the number of units of a country’s currency required to buy the same amount of goods and services in the domestic market as one dollar would buy in the U.S.
Question 4.
What do you mean by Human Resource Development?
Answer:
Human Resource Development means the development of a person’s physical and mental abilities through education, health care and training.
Question 5.
Why do we say that investment in education and health of people can result in a high rate
of returns?
Answer:
If a child is invested with good education and health, he or she may turn to be very productive in future in the form of higher earnings and greater contribution to the society. Therefore that, investment in education and health of people can result in a high rate of returns
Question 6.
What is the end result of Development?
Answer:
- Development increases the quality of life.
- People will have higher incomes, better education, better health and nutrition, less poverty and more equality of opportunity.
V. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
Describe sustainability of Development.
Answer:
Sustainable economic development is taken to mean development without damaging the environment and not compromising with the needs of the future generation.
The consequences of environmental degradation do not respect national or state boundaries. Sustainability of development is comparatively a new area of knowledge in which scientists, economists, philosophers and other social scientists are working together.
Natural resources can be divided into renewable resources and non-renewable resources.
Groundwater is an example of a renewable resource. The question arises as to how sustainable development is possible if the resources are over-used rather than getting replenished. Non-renewable resources get exhausted after certain number of years of extracting and using them and they cannot be replenished.
To achieve real sustainability, we need to balance economic, social and environmental sustainability in equal harmony.
In general, the question of development or progress is continuous. At all times, as a member of society and as individuals, we need to ask where we want to go, what we wish to become and what our goals are.