You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.3
9th Maths Algebra Exercise 3.3 Question 1.
Check whether p(x) is a multiple of g(x) or not.
p(x) = x3 – 5x2 + 4x – 3, g(x) = x – 2
Solution:
p(x) = x3 – 5x2 + 4x – 3; g(x) = x – 2
Let g(x) = 0
x – 2 = 0
x = 2
p(2) = 23 – 5(22) + 4(2) – 3
= 8 – 5 × 4 + 8 – 3 = 8 – 20 + 5 = -7 ≠ 0
⇒ p(x) is not a multiple of g(x)
9th Maths Exercise 3.3 Question 2.
By remainder theorem, find the remainder when, p(x) is divided by g(x) where,
(i) p(x) = x3 – 2x2 – 4x – 1; g(x) = x + 1
(ii) p(x) = 4x3 – 12x2 + 14x – 3; g(x) = 2x – 1
(iii) p(x) = x3 – 3x2 + 4x + 50; g(x) = x – 3
Solution:
(i) p(x) = x3 – 2x2 – 4x – 1; g(x) = x + 1
Let g(x) = x + 1
x + 1 = 0
x = -1
P(-1) = (-1)3 – 2(-1)2 – 4(-1) – 1
= -1 -2 × 1 + 4 – 1
= -4 + 4 = 0
∴ Remainder = 0.
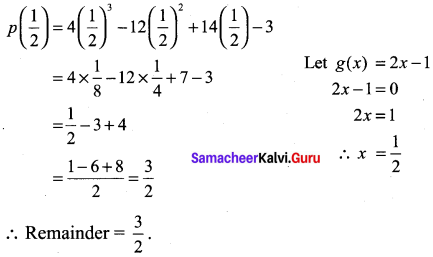
(ii) p(x) = 4x3 – 12x2 + 14x – 3; g(x) = 2x – 1
(iii) p(x) = x3 – 3x2 + 4x + 50 ; g(x) = x – 3
Let g(x) = x – 3
x – 3 = 0
x = 3
p(3) = 33 – 3(32) + 4(3) + 50
= 27 – 27 + 12 + 50
= 62
∴ Remainder = 62.
9th Maths 3.3 Question 3.
Find the remainder when 3x3 – 4x2 + 7x – 5 is divided by (x + 3)
Solution:
(3x3 – 4x2 + 7x – 5) + (x + 3)
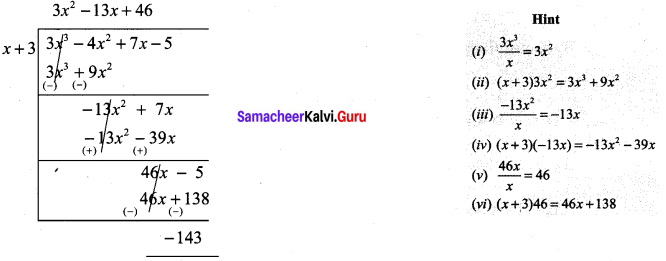
The remainder is -143.
9th Class Maths Exercise 3.3 Solution Question 4.
What is the remainder when x2018 + 2018 is divided by x – 1.
Solution:
x2018 + 2018 is divided by x – 1
Let g(x) = x – 1 = 0
x = 1
p(x) = x2018 + 2018
p(1)= 12018 + 2018
= 1 + 2018 = 2019
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Chapter 3 Question 5.
For what value of k is the polynomial p(x) = 2x3 – kx2 + 3x + 10 exactly divisible by (x – 2).
Solution:
Let g(x) = x – 2 = 0
x = 2
Since p(x) is exactly divisible by (x – 2)
p(2) = 2(23) – k(22) + 3(2)+ 10
= 16 – 4k + 6 + 10
= 32 – 4k = 0
= -k = -32
k= \(\frac{32}{4}\) = 8.
Ex 3.3 Class 9 Samacheer Question 6.
If two polynomials 2x3 + ax2 + 4x – 12 and x3 + x2 – 2x + a leave the same remainder when divided by (x – 3), find the value of a. and also find the remainder.
Solution:
Let f(x) = 2x3 + ax2 + 4x – 12 and g(x) = x3 + x2 – 2x + a
When f(x) is divided by x – 3, the remainder is f(3).
Now f(3) = 2(3)3 + a(3)2 + 4(3) – 12 = 54 + 9a + 12 – 12
f(3) = 9a + 54 …………. (1)
When g(x) is divided by x – 3, the remainder is g(3).
Now g(3) = 33 + 32 – 2(3) + a = 27 + 9 – 6 + a
g(3) = a + 30 ……….. (2)
Since, the remainder’s are same (1) = (2)
Given that f(3) = g(3)
That is 9a + 54 = a + 30
9a – a = 30 – 54 ⇒ 8a = -24 ∴ a = -3
Substituting a = -3 in f(3), we get
f(3) = 9(-3) + 54 = -27 + 54
f(3) = 27
∴ The remainder is 27.
9th Class Math 3.3 Exercise Solution Question 7.
Determine whether (x – 1) is a factor of the following polynomials:
(i) x3 + 5x2 – 10x + 4
(ii) x4 + 5x2 – 5x + 1
Solution:
(i) Let P(x) = x3 + 5x2 – 10x + 4
By factor theorem (x – 1) is a factor of P(x), if P(1) = 0
P(1) = 13 + 5(12) – 10(1) + 4 = 1 + 5 – 10 + 4
P(1) = 0
∴ (x – 1) is a factor of x3 + 5x2 – 10x + 4
(ii) Let P(x) = x4 + 5x2 – 5x + 1
By/actor theorem, (x – 1) is a factor of P(x), if P( 1) = 0
P(1) = 14 + 5 (12) – 5(1) + 1 = 1 + 5 – 5 + 1 = 2 ≠ 0
∴ (x – 1) is not a factor of x4 + 5x2 – 5x + 1
Class 9th Maths Exercise 3.3 Question 8.
Using factor theorem, show that (x – 5) is a factor of the polynomial 2x3 – 5x2 – 28x + 15
Solution:
LetP(x) = 2x3 – 5x2 – 28x + 15
By factor theorem, (x – 5) is a factor of P(x), if P(5) = 0
P(5) = 2 (5)2 – 5 (5)2 – 28 (5) + 15
= 2 × 125 – 5 × 25 – 140 + 15
= 250 – 125 – 140 + 15 = 265 – 265 = 0
∴ (x – 5) is a factor of 2x3 – 5x2 – 28x + 15
Class 9 Maths Exercise 3.3 Solutions Question 9.
Determine the value of m, if (x + 3) is a factor of x3 – 3x2 – mx + 24.
Solution:
Let P(x) = x3 – 3x2 – mx + 24
By using factor theorem,
(x + 3) is a factor of P(x), then P (-3) = 0
P(-3) = (-3)3 -3 (-3)2 – m (-3) + 24 = 0
⇒ -27 – 3 × 9 + 3m + 24 = 0 ⇒ 3m = 54 – 24
⇒ m = \(\frac{30}{3}\) = 10
Exercise 3.3 Class 9 Maths Question 10.
If both (x – 2) and (x – \(\frac{1}{2}\)) are the factors of ax2 + 5x + b, then show that a = b.
Solution:
Let P(x) = ax2 + 5x + b
(x – 2) is a factor of P(x), if P(2) = 0
P(2) = a(2)2 + 5(2) + b = 0
4a + 10 + b = 0
4 a + b = – 10 …………….. (1)
(x – \(\frac{1}{2}\)) is a factor of P(x), P(\(\frac{1}{2}\)) = 0
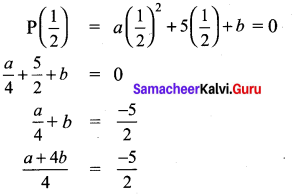
2a + 8b = -20
a + 4b = – 10 ……………… (2)
From (1) and (2)
4a + b = – 10 …………. (1)
a + 4b = – 10 ………… (2)
(1) and (2) ⇒ 4a + b = a + 4b
3a = 3b
∴ a = b. Hence it is proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 9 Maths Solutions Question 11.
If (x – 1)divides the polynomial kx3 – 2x2 + 25x – 26 without remainder, then find the value of k.
Solution:
Let P(x) = kx3 – 2x2 + 25x – 26
By factor theorem, (x – 1) divides P(x) without remainder, P (1) = 0
P(1) = k(1)3 -2 (1)2 + 25 (1) – 26 = 0
k – 2 + 25 – 26 = 0
k – 3 =0
k = 3
Class 9th Math Exercise 3.3 Question 12.
Check if (x + 2) and (x – 4) are the sides of a rectangle whose area is x2 – 2x – 8 by using factor theorem.
Solution:
Let P(x) = x2 – 2x2 – 8
By using factor theorem,(x + 2) is a factor of P(x), if P (-2) = 0
P(-2) = (-2)2 – 2 (-2) – 8 = 4 + 4 – 8 = 0
and also (x -4) is a factor of P (x), if P (4) = 0
p (4) = 42 – 2(4) – 8 = 16 – 8 – 8 = 0
∴ (x + 2), (x – 4) are the sides of a rectangle whose area is x2 – 2x – 8.