You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 7 Mensuration Ex 7.2
9th Maths Exercise 7.2 Samacheer Kalvi Question 1.
Find the total surface area and the lateral surface area of a cuboid whose dimensions are
(i) length = 20 cm,
breadth = 15 cm,
height = 8 cm
Solution:
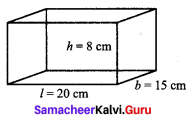
(i) (a) Total surface Area of cuboid = 2(lb + bh + hl) sq. units
= 2(20 × 15 + 15 × 8 + 8 × 20)
= 2(300 + 120 + 160) = 2 × 580
(b) Lateral surface area of a cuboid = 2h(l + b) sq. units
= 2 × 8 (20 + 15) = 16 × 35 = 560 cm2
9th Maths Mensuration Exercise 7.2 Question 2.
The dimensions of a cuboidal box are 6 m × 400 cm × 1.5 m. Find the cost of painting its entire outer surface at the rate of ₹ 22 per m2
Solution:
l × b × h = 6 m × 400 cm × 1.5 m
l = 6m,
b = 4 m,
h = 1.5 m
∴ Total surface area of the cuboid = Outer surface area
= 2(lb + bh + hl) = 2((6 × 4) + (4 × 1.5) + (1.5 × 6))
= 2(24 + 6 + 9) = 2(39) m2
Cost of painting 1 m2 = ₹ 22
Cost of painting 78 m2 = 78 × 22 = ₹ 1716
10th Maths Exercise 7.2 Samacheer Kalvi Question 3.
The dimensions of a hall is 10 m × 9 m × 8 m. Find the cost of white washing the walls and ceiling at the rate of ₹ 8.50 per m2.
Solution:
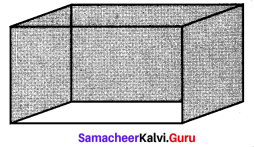
Dimensions of a hall 10m × 9m × 8m
l = 10 m
b = 9m
h = 8 m
White washing to be done for the area of the surface
= 2 (lh + bh) + lb
= 2 (10 × 8 + 9 × 8) + 10 × 9
= 2 (80 + 72) + 90 = 2 × 152 + 90
= 304 + 90 = 394 m2
Cost of white washing per m2 = ₹ 8.50
Cost of white washing 394 m2 = 394 × 8.50
Total cost = ₹ 3349
9th Maths Exercise 7.2 Question 4.
Find the TSA and LSA of the cube whose side is
(i) 8 m
(ii) 21 cm
(iii) 7.5 cm
Solution:
(i) side of a cube = 8m
TSA of the cube = 6a2 = 6 × 64 = 384 m2
LSA of the cube = 4a2= 4 × 64 = 256 m2
(ii) side a 21 cm
TSA = 6a2 = 6 × 21 × 21 = 2646 cm2.
LSA = 4a2 = 4 × 21 × 21 = 1764 cm2.
(iii) side a = 7.5 cm
TSA = 6a2 = 6 × 7.5 × 7.5 cm2 = 337.5 cm2
LSA = 4a2 = 4 × 7.5 × 7.5 cm2 = 225 cm2
9th Maths 7.2 Question 5.
If the total surface area of a cube is 2400 cm2 then, find its lateral surface area.
Solution:
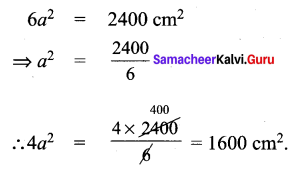
9th Standard Maths Exercise 7.2 In Tamil Question 6.
A cubical container of side 6.5 m is to be painted on the entire outer surface. Find the area to be painted and the total cost of painting it at the rate of ₹ 24 per m2.
Solution:
a = 6.5 m
6a2 = 6 × 6.5 × 6.5 = 253.5 m2
Area to be painted = 253.5 m2
Cost of painting 1 m2 = ₹ 24
∴ Cost of painting 253.5 m2 = 253.5 × 24 = ₹ 6084
9th Maths Exercise 7.2 In Tamil Question 7.
Three identical cubes of side 4 cm are joined end to end. Find the total surface area and lateral surface area of the new resulting cuboid.
Solution:
a = 4 cm
TSA of the cuboid = 2(lb + bh + hl)
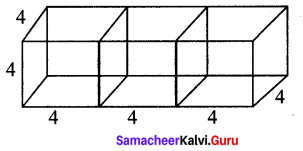
l = 12 cm
b = 4 cm
h = 4 cm
∴ TSA = 2(12 × 4 + 4 × 4 + 4 × 12)
= 2(48 + 16 + 48) = 2 × 112 = 224 cm2
LSA = 2h(l + b) = 2 × 4(12 + 4) = 8 × 16 = 128 cm2