You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science History Solutions Term 2 Chapter 1 Educational Development in India
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Educational Development in India Textbook Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer
Educational Development In India 8th Standard Question 1.
The word ‘Veda’ is derived from ………
(a) Sanskrit
(b) Latin
(c) Prakrit
(d) Pauli
Answer:
(a) Sanskrit
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 8th Social Science Question 2.
Which of the following was an important center for the learning in the ancient period?
(a) Gurukula
(b) Viharas
(c) Pauli
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Gurukula
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 8th Social Question 3.
Nalanda, the oldest university in India was located in –
(a) Uttar Pradesh
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Bihar
(d) Punjab
Answer:
(c) Bihar
<img src=”https://samacheerkalviguru.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/SamacheerKalvi.Guru_.png” alt=”Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 10 Environmental Economics” width=”224″ height=”19″ />
Question 4.
When did the UNESCO declare Takshashila as world heritage site?
(a) 1970
(b) 1975
(c) 1980
(d) 1985
Answer:
(c) 1980
Question 5.
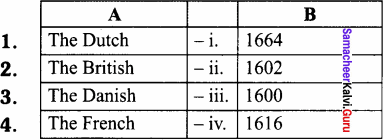
Which European country were the first to start Modern System of Education in India?
(a) British
(b) Danish
(c) French
(d) Portuguese
Answer:
(d) Portuguese
Question 6.
Which of the following Charter Act made a provision for an annual grant one lakhs Rupees for the promotion of Education in India?
(a) Charter Act of 1813
(b) Charter Act of 1833
(c) Charter Act of 1853
(d) Charter Act of 1858
Answer:
(a) Charter Act of 1813
Question 7.
Which of the following Commission recommended to constitute the University Grants Commission?
(a) Sergeant Report, 1944
(b) Radhakrishnan Commission, 1948
(c) Kothari Commission, 1964
(d) National Education Policy, 1968
Answer:
(b) Radhakrishnan Commission, 1948
Question 8.
In which year the New Education Policy was introduced in India?
(a) 1992
(b) 2009
(c) 1986
(d) 1968
Answer:
(c) 1986
II. Fill in the Blanks
- The word ‘Veda’ means ………
- Taxila ruins were discovered by ………..
- ………. was the first ruler to establish a madrasa at Delhi.
- The New Education Policy was revised in ………….
- ……….. is the primary vehicle for implementing the provisions of the Right to Education Act of (RTE) 2009.
- Mid – day meal program was introduced in schools in ………
Answers:
- Knowledge
- Archaeologist Alexander Cunningham
- Iltutmish
- 1992
- SSA (Sarva Shiksha Abhiyanj
- 1956
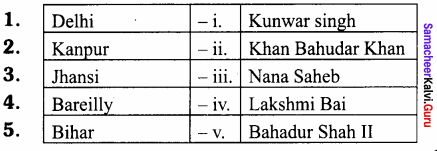
III. Match the following
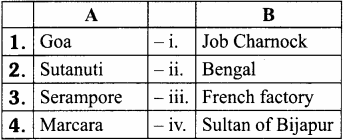
- I – Tsing – Saraswathi Mahal
- Francis Xavier – Magnacarta of Indian Education
- Wood’s Despatch – Western Education in Madras
- Sarafoji II – University at Kochin
- Sir Thomas Munroe – Chinese scholar
Answer:
- I – Tsing – Chinese scholar
- Francis Xavier – University at Kochin
- Wood’s Despatch – Magnacarta of Indian Education
- Sarafoji II – Saraswathi Mahal
- Sir Thomas Munroe – Western Education in Madras
IV. State True or False
- The writings of Charaka and Sushrutha were the sources of learning of medicine.
- Temples were the centers of learning and played an active role in the promotion of knowledge.
- The Jataka tales tell us that the kings and society took an active interest in promoting education.
- Women education in India was not prevalent during the medieval period.
- The RMSA scheme was implemented during tenth Five Year Plan.
Answer:
- True
- True
- True
- True
- False
V. Consider the following statements and tick the appropriate answer
Question 1.
(i) The Nalanda University was founded in fifth century C.E
(ii) In ancient India teachers had complete autonomy in all aspects from selection of students to designing their syllabi
(iii) In ancient times the teacher was called Kanakkayar.
(iv) The famous college during the Chola period was Kandhalur salai.
(a) i and ii are correct iii and iv are correct
(b) ii and iv are correct
(c) iii and iv are correct
(d) i, ii and iii are correct
Answer:
(d) i, ii and iii are correct
Question 2.
Find out the Correct pair –
(a) Maktabs – Secondary School
(b) Macaulay’s Minutes of 1835 – English education
(c) Operation Blackboard – Secondary Education Commission
(d) Salabhogam – Lands were given to temples
Answer:
(b) Macaulay’s Minutes of 1835
VI. Answer the following in one or two sentences
Question 1.
Write about the importance of Gurukulas.
Answer:
- Teaching was oral and students remembered and meditated upon what was taught in the Gurukulas Guru / Acharya.
- Many of these Gurukulas were named after the sages. Situated in forests, in serve and peaceful surroundings, hundreds of students used to learn together in Gurukulas.
- This was known as ‘Gurukula System’ of education.
Question 2.
Name the most notable universities that evolved in ancient India.
Answer:
The most notable universities the emerged during that period were situated at –
- Taxila
- Nalanda
- Valabhi
- Vikramshila
- Odantapuri
- Jagaddala
Question 3.
Write a short note on Taxila.
Answer:
- Taxila was an ancient Indian city, which is now in north – western Pakistan.
- It is an important archaeological site and the UNESCO declared it as a world heritage site in 1980.
- Its fame rested on the university where Chanakya is said to have composed his Arthashastra.
Question 4.
Mention the education centres flourished in Cholas period?
Answer:
- Rajaraja Chaturvedimangalam – Vedic College (Ennayiram in Former South Arcot District)
- Tirubuvanai – Vedic College (Pondicherry)
- Viravajendra – Medical School (Tiruvaduthurai)
Question 5.
Expand SSA and RMSA.
Answer:
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA)
- Rastriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA)
Question 6.
What do you know about RTE.?
Answer:
Right to Education (RTE) provides for free and compulsory education to all the children from the age of 6 to 14 years.
VII. Answer the following
Question 1.
What were the sources of .education in ancient India?
Answer:
Education in Ancient India:
- The historical Sources provide the information that from very early times, the tradition on teaching and learning had been in vogue in India.
- The concept of Education might have originated from the Vedas.
- The literal meaning the Sanskrit word ‘Veda’ is knowledge and the word derived from the word Vid, which means ‘to know’.
Gurukula System in ancient India :
- In ancient India, both formal and informal education existed.
- There were people in homes, villages and temples who guided young children in imbibing pious ways of life.
- Teaching was oral and students remembered and meditated upon what was taught in the Gurukulas Guru / Acharya.
Question 2.
Write a paragraph about the education under the British rule.
Answer:
History of education in British rule can be divided into four periods.
- From the early days of the British rule upto 1813.
- Period from 1813 – 1853
- Period from 1854 – 1920
- Period from 1921 – 1947
1. From the early days of the British Rule:
- The Company’s charter was renewed in 1813, which compelled the company to assume responsibility for the education of Indian’s, though on a very limited scale.
- Missionaries, non-missionaries like Raja Ram Mohan Roy of Bengal, Pachyappar of Madras, W. Frazer of Delhi contributed to the cause of education.
2. Period from 1813 – 1853:
- The second period was also marked by great educational controversies concerning the issues of educational policy, medium of instruction and method of spreading education.
- These controversies were partially set at rest by Macaulay’s Minutes of 1835.
- It also encouraging English education for the upper classes.
3. Period from 1854 – 1920:
- The Third phase of British – influenced education may be called the period of an All India Educational Policy.
- It commenced with Sir Charles Wood’s Despatch in 1854.
4. Period from 1921 – 1947 :
- This period may be called provincial autonomy.
- The Act of 1935 ushered a new era of educational advancement through the country.
- After the Second World War, a very important plan for educational development, known as the Sergeant Report (1944) was prepared.
Question 3.
Describe the National Policy on Education.
Answer:
1. The First National Educational Policy of 1968,marked a significant step in the history of education in post independent India.
2. It aimed to promote national progress, culture and to strengthen national integration.
3. In 1986, the Government of India introduced a New Education Policy.
4. The aim of New Education Policy (NEP) was to transfer a static society into a vibrant one with a commitment to development and change. It emphasized an equal opportunities for marginalized – sections of the country and the removal of disparity through scholarships, adult education and open universities, especially for rural India.
5. The New Education Policy called for a child – centered approach in primary education.
6. This policy launched operation of Blackboard to improve primary schools nationwide.
7. The New Education Policy was revised again in 1992.
8. It envisaged the formulation of National Curriculum Framework, emphasis on in – service education,improvement of facilities and streamlining of the evaluation system at the secondary stage.
Question 4.
Give a detailed account on education under Cholas.
Answer:
The Chola Period :
- The Chola Period was the most brilliant and creative period in the Tamil Literature.
- Tamil education enjoyed a greater connection with religion and temple.
- Free education was given to people.
- The curriculum and syllabi had a theoretical background.
- From the inscription of that period, we. can now gain knowledge about the qualification of teacher, method of teaching etc.
The education centres flourished in Chola’s Period:
- Rajaraja Chaturvedimangalam Vedic College (Ennayiram in Former South Arcot District).
- Tirubuvanai Vedic College (in Pondicherry)
- Viravajendra Medical School (in Tiruvaduthurai).
VIII. HOTs
Question 1.
How does the flagship programme of SSA achieve Universal Elementary Education?
Answer:
The Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) is the Government of India’s flagship programme that was launched in 2000 – 01 to achieve Universal Elementary Education (UEE). SSA is now the primary vehicle for implementing the provisions of the Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act (2009) (RTE). Right To Education (RTE) provides for free and compulsory education to all the children from the age of 6 to 14 years. The SSA initiates a variety of innovation and activities related to schools.
IX. Mark the following places on the outline map of India
1. Nalanda
2. Taxila
3.Valabhi
4. Kanchi
5. Vikramshila
6. Delhi
7. Lucknow
8. Allahabad
9. Cochin
10. Calcutta
11. Madras
12. Chidambaram
Answer:
X. Project and Activity
Question 1.
Collect the pictures of ancient educational centres and prepare an album.
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students.
Question 2.
Find out the historic importance of Nalanda, Taxila and prepare a power point presentation on it.
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students.
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Educational Development in India Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
……… is derived from Sanskrit word
(a) Latin
(b) Prakrit
(c) Veda
(d) Pali
Answer:
(c) Veda
Question 2.
In 1986 …………. policy was introduced in India.
(a) New Education Policy
(b) New Agricultural Policy
(c) New Industrial Policy
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) New Education Policy
Question 3.
………. Program was introduced in School in 1956.
(a) Educational
(b) Mid-day-meal
(c) Free Books Scheme
(d) Free Cycle
Answer:
(b) Mid-day-meal
Question 4.
………… means knowledge.
(a) Prakrit
(b) Pali
(c) Viharas
(d) Veda
Answer:
(d) Veda
Question 5.
Iltutmish was the first ruler to establish a ……… at Delhi.
(a) Madrasas
(b) School
(c) Dam
(d) Gurukulam
Answer:
(a) Madrasas
Question 6.
………. ‘Vid’ means:
(a) ‘Togo’
(b) ‘Toknow’
(c) ‘Torun’
(d) ‘Tostudy’
Answer:
(b) ‘To know’
Question 7.
Education is a continuous process of aquring and sharing of ………..
(a) Knowledge
(b) Skills
(c) Values
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 8.
The concept of ……….. might have originated from the Vedas.
(a) Information
(b) Distribution
(c) Education
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Education
Question 9.
……… was an ancient Indian city, which is now in north – western Pakistait.
(a) Jataka
(b) Alexander
(c) Nalanda
(d) Taxila
Answer:
(d) Taxila
Question 10.
The UNESCO declared it as a world heritage site in ……….
(a) 1980
(b) 1976
(c) 1986
(d) 1982
Answer:
(a) 1980
Question 11.
………. played a vital role in importing education and served the centers of learning.
(a) Church
(b) Temples
(c) Both‘a’and‘b’
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Temples
Question 12.
Chanakya is said to have composed his ……….
(a) Jataka Tales
(b) Taxila
(c) Arthashastra
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) Arthashastra
Question 13.
Archaeologist Alexandar Cunningham discovered its ruins in the mid ……….
(a) 15th Century
(b) 17th Century
(c) 18th Century
(d) 19th Century
Answer:
(d) 19th Century
Question 14.
In the later medieval era, the British came to India and introduced ……… education.
(a) Arabic
(b) Tamil
(c) English
(d) Spanish
Answer:
(c) English
Question 15.
…………. of Jaipur encouraged learning of scientific subjects.
(a) Maulana Sadruddin
(b) Ghaziuddin
(c) Ilthumis
(d) Raj a Jai Singh
Answer:
(d) Raja Jai Singh
Question 16.
Several Madrasas were set up by the ………. and nobles.
(a) Sultans
(b) Raja Jai Singh
(c) Maulana
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) Sultans
Question 17.
……… came to India for trade and established trading companies.
(a) Arabs
(b) Europeans
(c) Japanese
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Europeans
Question 18.
The first college offering degrees on a completion of a course was started in ……..
(a) Madras
(b) Culcutta
(c) Goa
(d) Cochin
Answer:
(c) Goa
Question 19.
Charter of Act in 1813 made a provision for an annual grant of sum of ………. for the promotion of education.
(a) 1 lakh rupees
(b) 2 lakhs rupees
(c) 10 thousand rupees
(d) 5 lakhs rupees
Answer:
(a) 1 lakh rupees
Question 20.
Gandhiji evolved a scheme popularly known as the ……… scheme of Basic National Education.
(a) Wood’s Despatch
(b) Wardha Scheme
(c) SSA Scheme
(d) Kothari Commission
Answer:
(b) Wardha Scheme
II. Fill in the blanks
- Free education at secondary level was introduced in ……….
- ……….. Rural College was established in 1975.
- The First National Educational Policy of ………… marked a significant step in the history of education in post – independent India.
- ……… program was introduced in school in 1956.
- The Annamalai University was founded at ……….. in 1929.
- The Madras University was founded in ……….
- The First University in Tamil Nadu under the British rule ……….
- Wood’s Dispatch of 1854 introduced the department of public instruction in …………
- ………….. came to Madurai during the time of Veerappa Nayak.
- The Maratha ruler ……….. collected the old records and kept them in the Saraswathi Mahal Library.
- ………….. the Governor of Madras Presidency in (1820 – 27).
- Pradran is an important center of ………. in the country.
- The curriculum and ………. had a theoretical background.
- In ancient times, the teacher was called as …………
- ………… period was the most brilliant and creative period in the Tamil literature
- ……………. Kings patronized Sanskrit in an exemplary way.
- The SSA is the Government of India flagship programme was launched in …………
- In 1948 …………. commission was appointed to present a report on university education.
- Free and compulsory primary education for all children up to the age of …………
- The family of Guru functioned as a domestic school or an ………..
- The ………. accounts given by Hiuen Tsang and I – Tsing.
Answer:
- 1964 – 64
- Gandhigram
- 1968
- Mid-day meal
- Chidambaram
- 1857
- The Madras University
- Madras Presidency
- Fernandez
- Sarfoji – II
- Sir Thomas Munroe
- higher education
- syllabi
- ‘Kanakkayar’
- The Chola
- The Pandya
- 2000 – 01
- Dr. Radhakrishnan
- 14 years
- Ashram
- Jataka tales
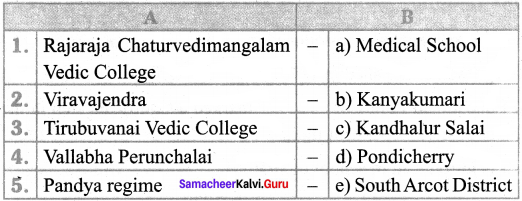
III. Match the following
Answer:
- e
- a
- d
- b
- c
IV. State True or False
- The word derived from the word vid, which means ‘to understand’.
- The Gurus and their students worked conscientiously together to become proficient in all aspects of learning.
- In ancient India, both formal and informal education existed.
- Taxila is an important archaeological site and the UNESCO declared it as a world heritage site in 1960.
- The New Nalanda University is envisaged as a centre of inter – civilisational dialogue.
- Women education in India was followed during the medival period.
- The Revered Dr. Middleton, started a missionary college at Calcutta, which become famous as the Bishop’s college.
- The fourth phase may be called the period of provincial autonomy.
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
V. Consider the following statements and Tick the appropriate answer
Question 1.
(i) The Chola’s period free education was given to people.
(ii) Thinnappalli Koodam was established during the Vijayanagar rule.
(iii) Pradran is an important center of higher education in the country.
(iv) Fernandez, who came to Madurai during the time of Veerappa Nayak, established a primary school.
(a) (i) & (ii) are Correct
(b) (ii) & (iii) are Correct
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii) are Correct
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv) are Correct
Answer:
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv) are Correct
Question 2.
Find out the wrong pair:
(a) Lord William – Western System of Education in India
(b) Sir Thomas Munroe – Creation of two school principal
(c) Fernandez – Printing press with Devanagari type
(d) Thirukkural – Stress the need for education
Answer:
(c) Fernandez – Printing press with Devanagari type
Question 3.
Find out the correct pair
(a) RMSA – College level
(b) SSA – Serva Shiksha Abhiyan
(c) Hiuen Tsang – Vidhyasathana
(d) The Pallava – ‘Kanakkayar’
Answer:
(b) SSA – Serva Shiksha Abhiyan
VI. Answer the following one or two sentences
Question 1.
What is the role of the Teacher?
Answer:
- Teachers had complete autonomy in all aspects from selection of students to designing their syllabi.
- When the teacher was satisfied with the performance of the students, the course concluded.
Question 2.
Who introduced Modern System of Educational in India?
Answer:
- The Portuguese were the first Europeans who started modem system of education in India.
- Francis Xavier, a Jesuit, started a University at Cochin.
- The first collage offering degrees on a completion of a course was started in Goa in (1575).
Question 3.
Write a short note on Wood’s despatch.
Answer:
- The Wood’s Despatch (1854) is called the ‘Magna Carta’ of English education in India because it was the first declaration of British education policy for educating the masses at all levels.
- But it resulted in the complete control on state education, divorcing it from Indian ideals and culture.
Question 4.
Write a short note on Jataka tales.
Answer:
The Jataka tales accounts given by Hiuen Tsang and I – Tsing (Chinese scholars) and other sources tell us that kings and society took an active interest in promoting education.
Question 5.
Write a few lines about Monasteries.
Answer:
Many monasteries and viharas were set up for monks and nuns to meditate, debate and discuss with the learned for their quest for knowledge during this period.
Question 6.
What are the characteristics of India’s traditional economy?
Answer:
India’s traditional economy was characterized by a blend of agriculture and handicrafts.
Question 7.
Write few Metal Industrial Centers found in India.
Answer:
- Certain centers of metal industry were quite well known.
- For example, Saurashtra was known for bell metal, Vanga for tin industry and Dacca was identified with muslin clothes.
Question 8.
Which is the oldest industry in India?
Answer:
Textile Industry was the oldest industry in India.
Question 9.
Write a short note on beginning of modern industries.
Answer:
- The process of industrialization started in India from the mid-19th Century.
- The beginning of modem industry is associated with the development in mainly plantations like jute, cotton and also steel.
Question 10.
Write a short note on self-reliance.
Answer:
- Another positive aspect of industrial growth is the attainment of the goal of self reliance.
- We have achieved self-reliance in machinery, plant and other equipment.
VII Answer the following in detail
Question 1.
Explain education in Medieval India.
Answer:
- The country was invaded by various foreign rulers and several traders from different part of the world.
- Besides, religion, society and culture, education in medieval India also experienced a new perspective.
- The aim of education during Muslim period (Medieval) was the illumination and extension of knowledge.
- In the eleventh century, the Muslim rulers established elementary and secondary schools.
- They founded primary schools (maktabs) in which students learnt reading, writing and basic Islamic prayers.
- And secondary schools (madrasas) were established to teach advanced language skills. Several madrasas were set up by the Sultans and nobles.
- The main objective of these madrasas was to train and educate the scholars who would become eligible for the civil service.
- Iltutmish was the first ruler to establish a madrasas at Delhi during his rule. Gradually many madrasas came into existence.
- In the later medieval era, the British came to India and introduced English education with the coming of the European missionaries, Western education made firm advances in the country.
- Various universities and thousands of colleges were formed and popularity of education increased.
Question 2.
Explain the Educational Development in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
- The pattern of education in Tamil Nadu was not merely reading and understanding of books but listening to learned persons.
- The Thirukkural stresses the need for education and warns the dangers of illiteracy.
- In ancient times, the school was called (Palli) and the teacher was a Kanakkayar.
- Hiuen Tsang gives a graphic picture about Kanchi Buddhist centre and Kanchi, was considered as the main centre of learning.
- The Chola period was the most brilliant and creative period in the Tamil literature.
- Tamil education enjoyed a greater connection with religion and temple. Free education was given to people.
- The curriculum and syllabi had a theoretical background.
Education Centres flourished in Cholas period :
- Rajaraja Chaturvedimangalam was the famous seat of a Vedic College (Ermayiram in Former South Arcot District).
- Tirubuvanai Vedic College (in Pondicherry).
- Viravajendra Medical School (in Thiruvaduthurai).
Education Development in Pandya’s Kings:
- The Pandya Kings patronised Sanskrit in an exemplary way.
- It is revealed in the copper plates.
- The educational institutions of that period were called as (Ghatigai, Salai and Vidhyasathana).
- Lands were given to teacher. They were known as Salabhogam (Eg. Vallabha Perunchalai at Kanyakumari).
- The famous college during the Pandya regime was Kandhalur Salai.
- Mutts occupied a significant place in the promotion of education.
Vijayanagar Rule:
- Learning flourished under the Vijayanagar rule.
- Many educational institution were established under their patronage.
Nayak Rule:
- Thinnappalli Koodam was established during the Nayak Rule.
Question 3.
Explain educational development in modern period.
Answer:
- Fernandez, who came to Madurai during the time of Veerappa Nayak, established a primary school.
- Tha Maratha ruler Sarfoji II collected the old records and kept them in the Saraswathi Mahal Library.
- He also had a printing press with Devanagari type, which was located at Tanjore.
- Pradran is an important center of higher education in the country.
- Sir Thomas Munroe the Governor of Madras Presidency (1820 – 27) was highly responsible for the introduction of Western education in Madras Presidency.
- The Education Commission of Munroe recommended the creation of two principal schools (Collectorate and Tahsildare Schools) in each district.
- In 183 5 Lord William passed a resolution favouring the introduction of western system of education in India.
- Wood’s Despatch of 1854 introduced the department of public instruction in Madras Presidency. Grant – in – aid was given to all schools.
- The Madras University was founded in 1857. It was the first University in Tamil Nadu under the British rule.
- In 1882 the Local Boards Act was passed. The Board was empowered to open new schools and to get grants from the government.
- In 1938, all subjects except English were taught in Tamil in Schools.
- The Annamalai University was founded at Chidambaram in 1929. This was the next step in the development of higher education.