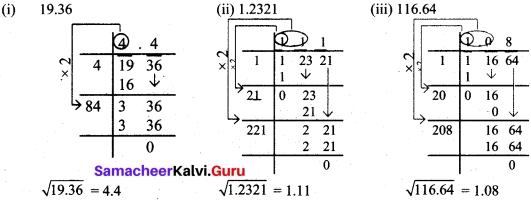
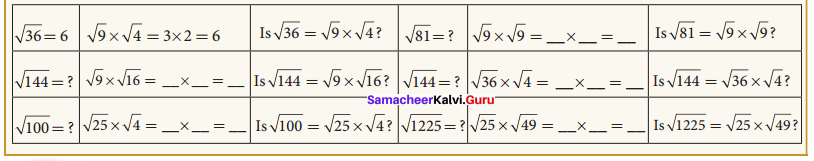
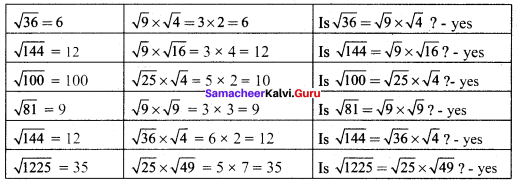
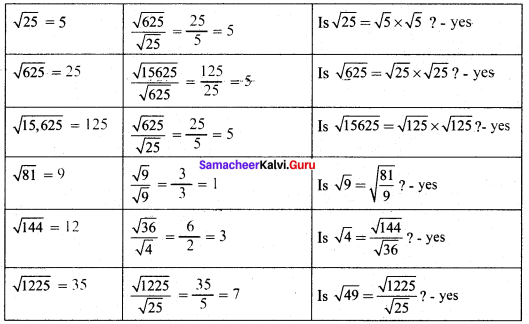
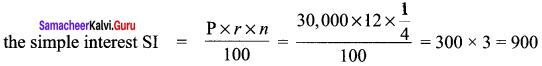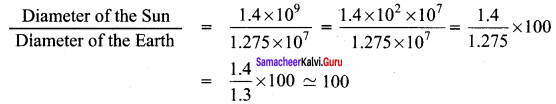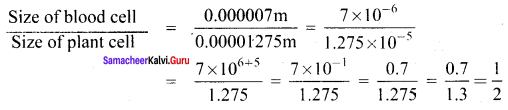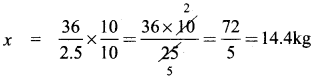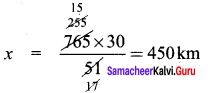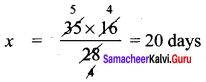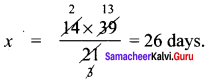Students can Download Maths Chapter 1 Numbers Ex 1.3 Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Solutions Term 3 Chapter 1 Numbers Ex 1.3
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) The ones digits in the cube of 73 is……….
(ii) The maximum number of digits in the cube of a two digit number is……….
(iii) The cube root of 540 × 50 is………..
(iv) The cube root of 0.000004913 is………..
(v) The number to be added to 3333 to make it a perfect cube is………….
Solution:
(i) 7
(ii) 6
(iii) 30
(iv) 0.017
(v) 42
Question 2.
Say True or False:
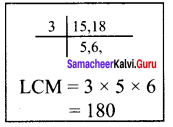
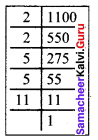
(i) The cube of 0.0012 is 0.000001728.
(ii) The cube root of 250047 is 63.
(iii) 79570 is not a perfect cube.
Solution:
(i) false
(ii) true
(iii) true
![]()
Question 3.
Show that 1944 is not a perfect cube.
Solution:
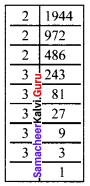
1994 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3
= 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3
= 2³ × 3³ × 3 × 3
There are two triplets to make further triplets we need one more 3.
∴ 1944 is not a perfect cube.
Question 4.
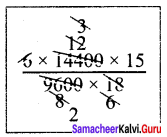
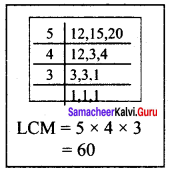
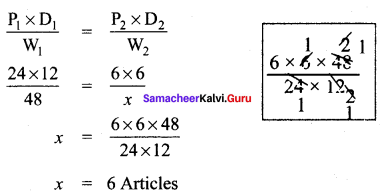
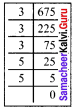
Find the cube root of 24 × 36 × 80 × 25.
Solution:
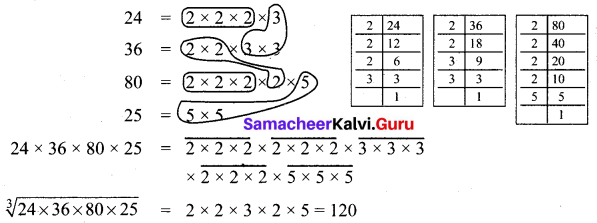
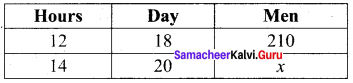
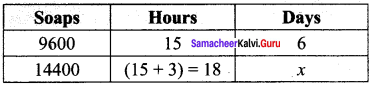
Question 5.
Find the smallest number by which 10985 should be divided so that the quotient is a perfect cube.
Solution:

We have 10985 = 5 × 13 × 13 × 13
= 5 × 13 × 13 × 13
Here we have a triplet of 13 and we are left over with 5.
If we divide 10985 by 5, the new number will be a perfect cube.
∴ The required number is 5.
Question 6.
Find two smallest perfect square numbers which when multiplied together gives a perfect cube number.
Solution:
Consider the numbers 22 and 42
The numbers are 4 and 16.
Their product 4 × 16 = 64
64 = 4 × 4 × 4
∴ The required square numbers are 4 and 16
Question 7.
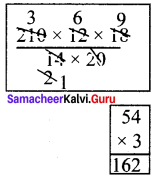
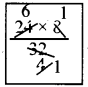
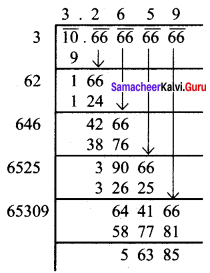
If the cube of a squared number is 729, find the square root of that number.
Solution:
729 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3
(729)1/3 = 3 × 3 = 9
∴ The cube of 9 is 729.
9 = 3 × 3 [ie 3 is squared to get 9]
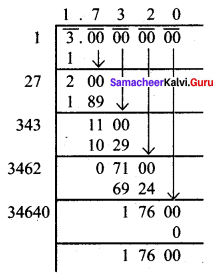
we have to find out √3, √3 = 1.732
![]()
Question 8.
What is the square root of cube root of 46656?
Solution:
We have to find out \(\sqrt{(\sqrt[3]{46656})}\)
First we will find \(\sqrt[3]{46656}\)

\(\sqrt[3]{46656}\) = (2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3)1/3
\(\sqrt[3]{46656}\) = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3
\(\sqrt[3]{46656}\) = 2² × 3² = 36
Now \(\sqrt{(\sqrt[3]{46656})}\) = \(\sqrt{36}\) = \(\sqrt{2^2×3^2 }\) = 2 × 3 = 6
∴ The required is 6.
Question 9.
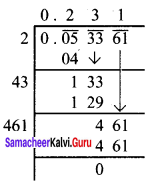
Find the cube root of 729 and 6859 by prime factorisation.
Solution:
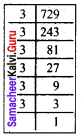
(i) \(\sqrt[3]{729}\) = \(\sqrt[3]{3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3}\)
= 3 × 3
\(\sqrt[3]{729}\) = 9
(ii) \(\sqrt[3]{6859}\) = \(\sqrt[3]{19 × 19 × 19 }\)
\(\sqrt[3]{6859}\) = 19
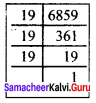
![]()
Question 10.
Find the smallest number by which 200 should be multiplied to make it a perfect cube.
Solution:
We find 200 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 5 × 5
Grouping the prime factors of 200 as triplets, we are left with 5 × 5
We need one more 5 to make it a perfect cube.
So to make 200 a perfect cube multiply both sides by 5.
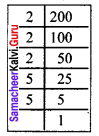
200 × 5 = (2 × 2 × 2 × 5 × 5) × 5
1000 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 5 × 5 × 5
Now 1000 is a perfect cube.
∴ The required number is 5.