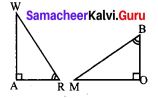
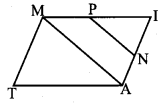
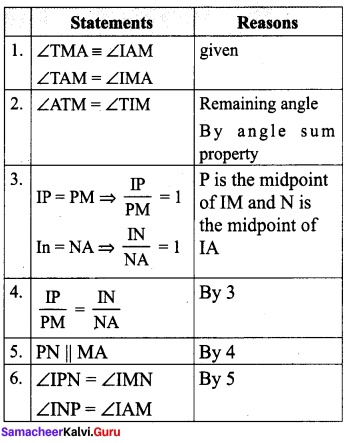
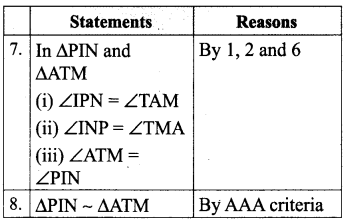
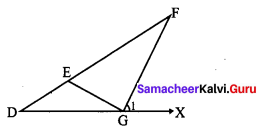
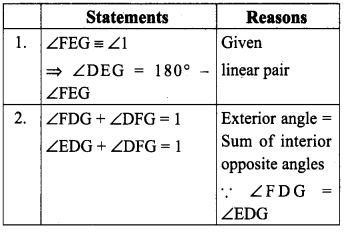
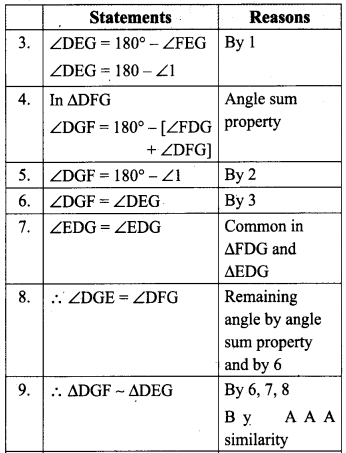
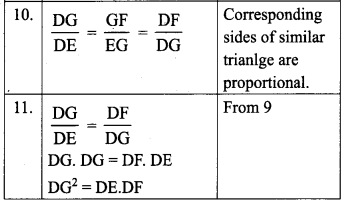
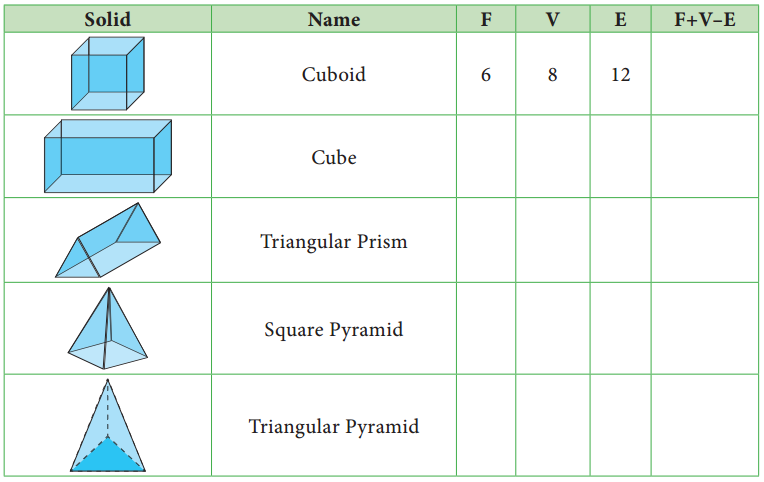
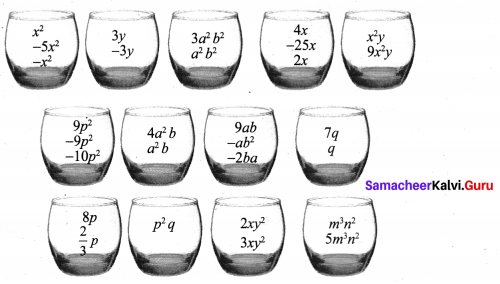
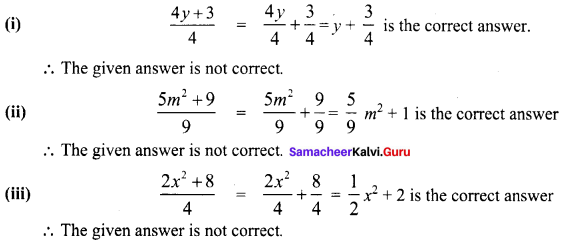
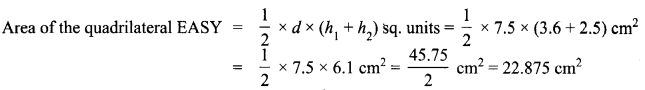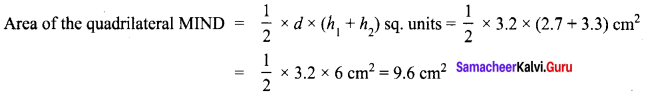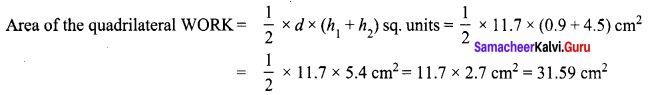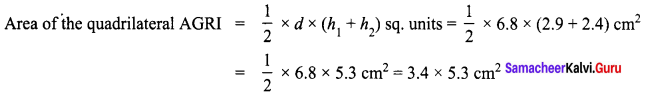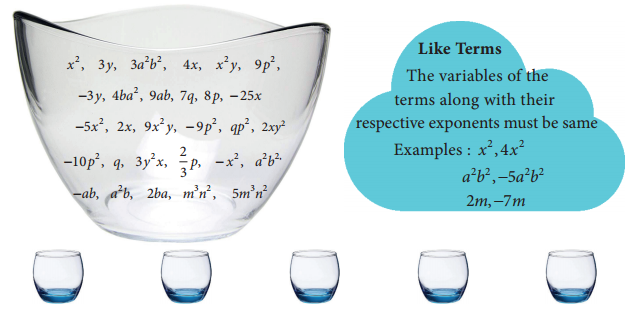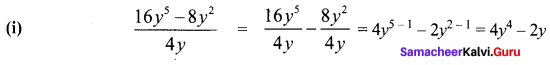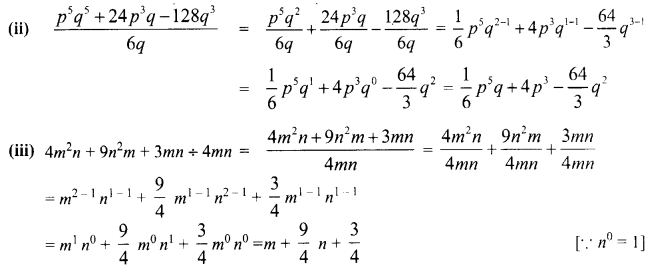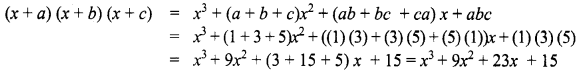Students can Download Maths Chapter 5 Information Processing Ex 5.3 Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
![]()
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Solutions Term 1 Chapter 5 Information Processing Ex 5.3
MISCELLANEOUS QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Shanthi has 5 chudithar sets and 4 Frocks. In how many possible ways, can she wear either a chudithar or a frock ?
Solution:
Shanthi his 5 chudidhar sets and 4 frocks.
She wear either chudidhar or a frock.
∴ Total possible ways = 5 + 4 = 9 ways
Question 2.
In a Higher Secondary School, the following types of groups are available in XI standard
I. Science Group:
(i) Physics, Chemistry, Biology and Mathematics
(ii) Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics and Computer Science
(iii) Physics, Chemistry, Biology and Home Science
II. Arts Group:
(i) 1. Accountancy, Commerce, Economics and Business Maths
(ii) 2. Accountancy, Commerce, Economics and Computer Science
(iii) 3. History, Geography, Economics and Commerce
III. Vocational Group:
(i) Nursing – Biology, Theory, Practical I and Practical II
(ii) Textiles and Dress Designing – Home Science, Theory, Practical I and Practical II
In how many possible ways, can a student choose the group?
Solution:
The student either select any one of science group in 3 ways or any of the arts group in 3 ways or any of the vocational group in 2 ways.
∴ Total possible ways = 3 + 3 + 2 = 8 ways
![]()
Question 3.
An examination paper has 3 sections, each with five instructed to answer one question from each section. In can the questions be answered?
Solution:
The tree diagram for this may be

∴ Number of possible ways to select one questions from each of 3 sections is 3 × 5 = 15 ways.
Question 4.
On a sports day, students must take also part in one of the one track events 100m Running and 4 × 100 m Relay. He must take part of any of the field events Long Jump, High Jump and Javelin Throw. In how many different ways can the student take part in the given events?
Solution:
Number of track events ⇒ (100m running, 4 × 100 m Relay) 2.
Number of field events ⇒ (Long jump, High jump, Javelin Throw) 3.
Students can take part in the given events in 2 × 3 = 6 ways.
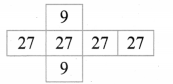
Question 5.
The given spinner is spun twice and the two numbers got are used to form a 2 digit number. How many different 2 digits numbers are possible?

Solution:
On the first spin we get any of the five numbers to form ones place then insecond spin the number got will fill 10’s place.
∴ Number of ways = 5 × 5 = 25 ways.
Removing the repetitions (11, 22, 33, 44, 55) once we get 25 – 5 = 20 ways.
20 different two digit numbers are possbile
![]()
Question 6.
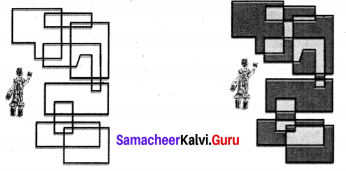
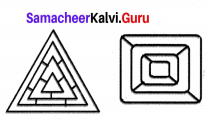
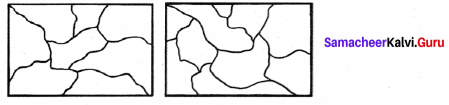
Colour the following pattern with as few colours as possible but make sure that no two adjacent sections are of the same colour.

Solution:


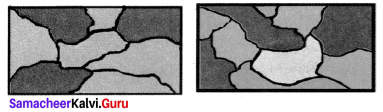
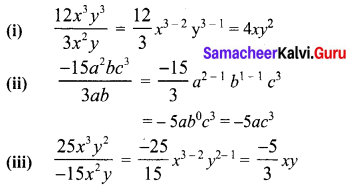
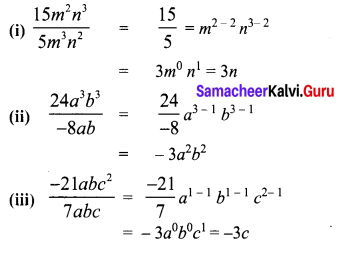
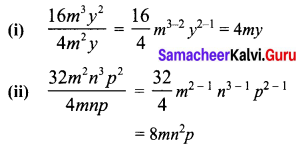
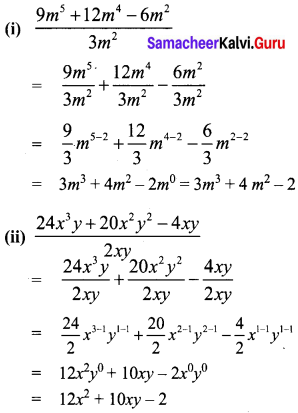
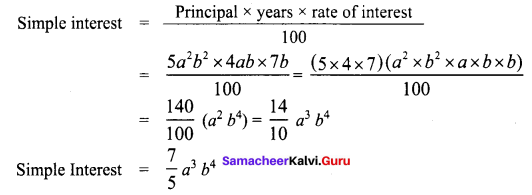
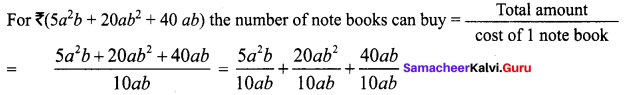
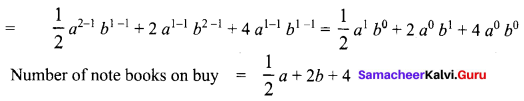
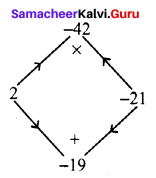
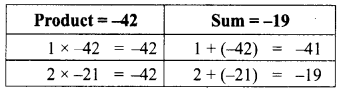

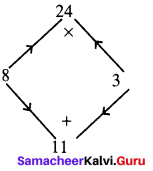
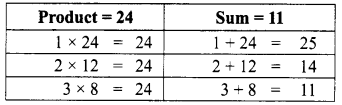
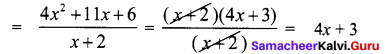
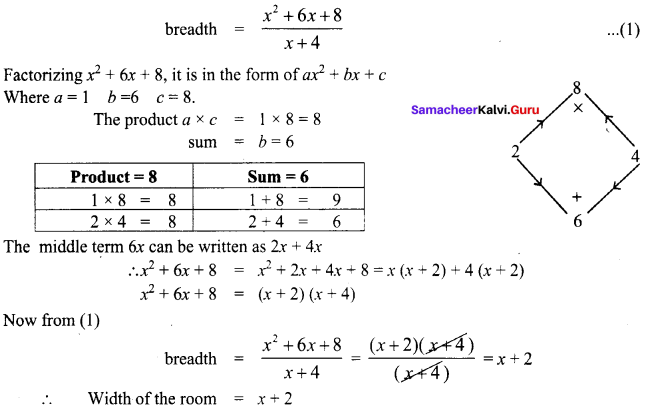
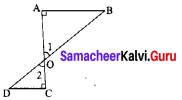
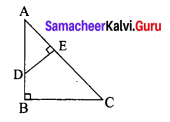
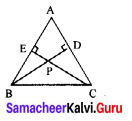
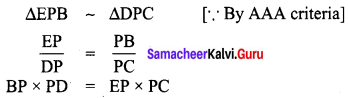
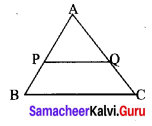
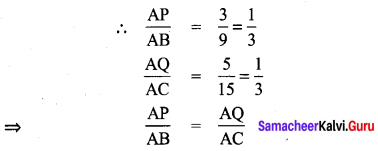

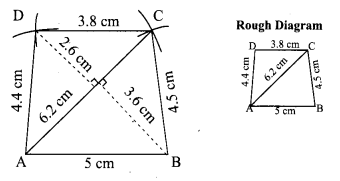
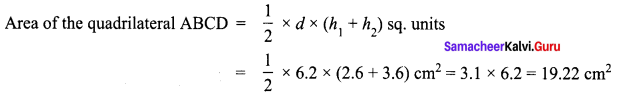
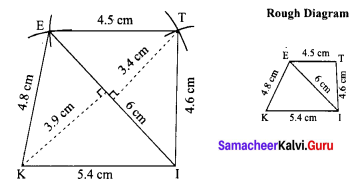

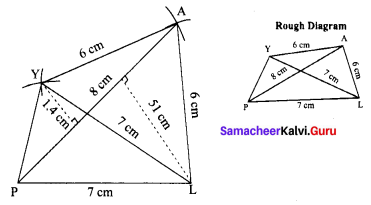

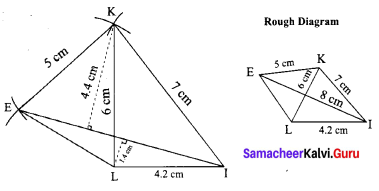
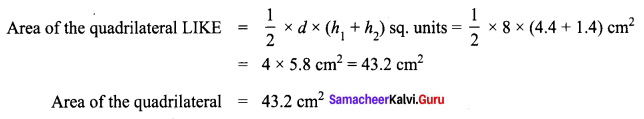
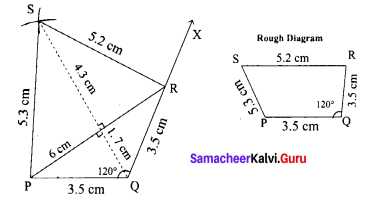
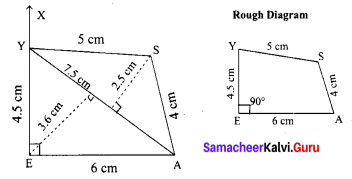
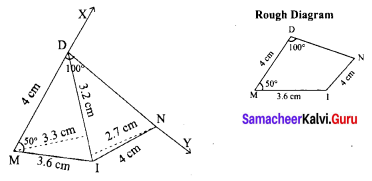
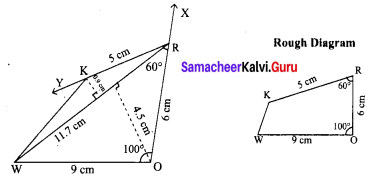
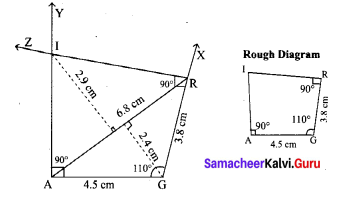
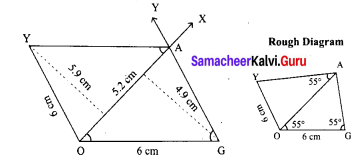
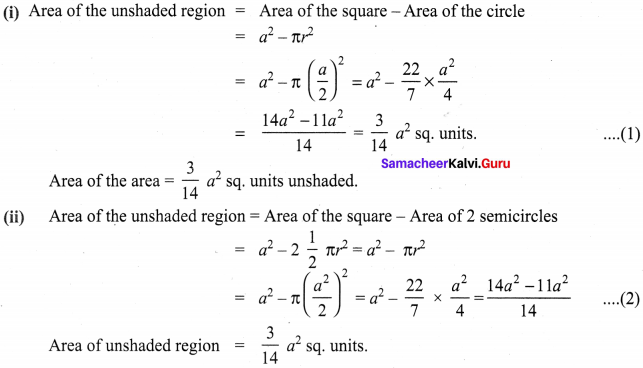
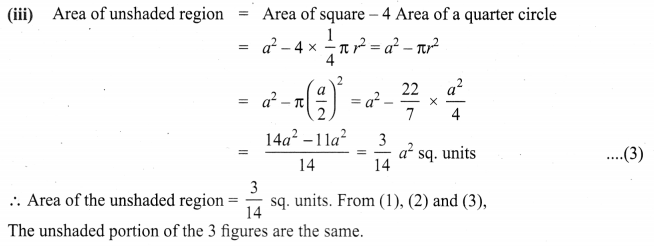
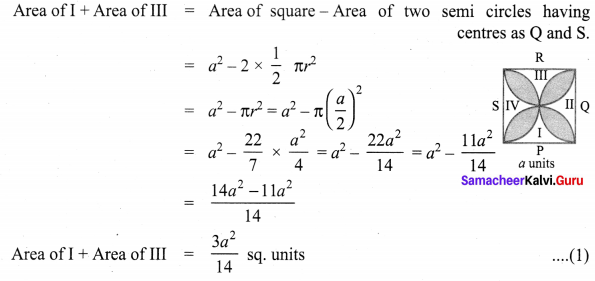
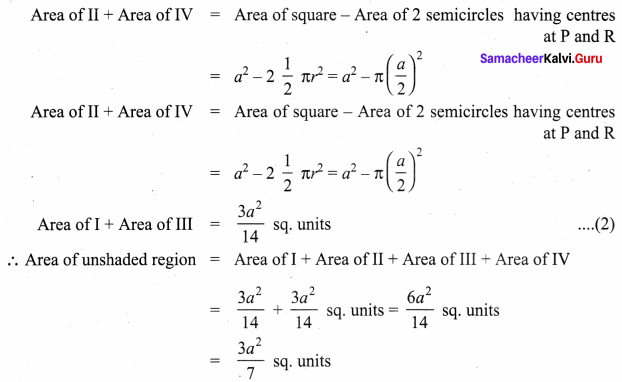
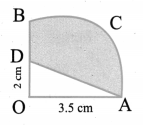
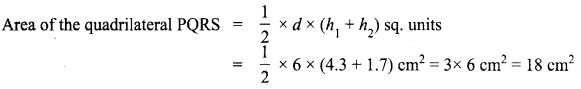 Area of the quadrilateral PQRS = 18 cm2
Area of the quadrilateral PQRS = 18 cm2