You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Solutions Term 1 Chapter 4 Matter
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Matter Text Book Exercises
I. Choose the best answer
(a) Atoms
(b) Molecules
(c) Ions
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
8th Science Matter Around Us Question 2.
The liquid metal used in thermometers is –
(a) Copper
(b) Mercury
(c) Silver
(d) Gold
Answer:
(b) Mercury
8th Science Matter Around Us Book Back Answers Question 3.
The Pictorial symbol for water given by the alchemists was –
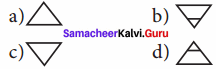
Answer:
![]()
Matter Around Us Class 8 Answers Question 4.
Which one of the element name not derived from planet?
(a) Plutonium
(b) Neptunium
(c) Uranium
(d) Mercury
Answer:
(d) Mercury
8th Science Matter Around Us Question Answer Question 5.
Symbol of Mercury is –
(a) Ag
(b) Hg
(c) Au
(d) Pb
Answer:
(b) Hg
8th Science Guide Matter Around Us Question 6.
A form of non – metal which has high ductility is –
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Oxygen
(c) Chlorine
(d) Carbon
Answer:
(d) Carbon
8th Class Matter Around Us Lesson Question 7.
Which one of metal possess low tensile strength?
(a) Silver
(b) Copper
(c) Zinc
(d) Aluminium
Answer:
(c) Zinc
Matter Around Us Class 8 Questions And Answers Question 8.
The property which allows metals to be hammered into their sheets is –
(a) Ductility
(b) Malleability
(c) Conductivity
(d) Tensile strength
Answer:
(b) Malleability
Matter Around Us Lesson In 8th Class Question 9.
The non – metal which conduct current is –
(a) Carbon
(b) Oxygen
(c) Aluminium
(d) Sulphur
Answer:
(a) Carbon
Matter Around Us Class 8 Textbook Question 10
Pencil lead contains –
(a) Graphite
(b) Diamond
(c) Aluminium
(d) Sulphur
Answer:
(a) Graphite
II. Fill in the blanks
- The element which possess character of both metals and non – metals are called ……………..
- The symbol of Tungsten ……………..
- Melting point of most metal is …………….. than non – metal.
- Water contains …………….. and …………….. element.
- …………….. is the used in semiconductor industry.
Answer:
- Metalloids
- W
- Higher
- Hydrogen, oxygen
- Silicon / Germanium
III. True or False, if false correct the statement
Matter Around Us Class 8 Pdf Question 1.
Metals are generally good conductors of electricity, but not good conductors of heat.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement:
Metals are generally good conductors of heat and electricity.
Matter Around Us Class 8 Pdf Download Question 2.
Gallium metal is in solid state at or just above room temperature.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement:
Gallium (Ga) become liquid at or just above room temperature.
Matter Around Us Class 8 Textbook Pdf Question 3.
Compounds can be made up of one atom.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement:
A compound is formed due to the chemical combination of two or more elements.
Matter Around Us Class 8 Samacheer Question 4.
Coal can be drawn into wires.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement:
Coal cannot be drawn into wires, because they are non- metals since non – metals are brittle and non – ductile. So, they cannot be drawn into wires.
Matter Around Us Class 8 Samacheer Kalvi Question 5.
Zinc is highly ductile in nature.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement:
Zinc is neither ductile nor malleable at room temperature.
IV. Match the substance given in column A with their use given in Column B
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Solution Question 1.
| A | B | ||
| 1. | Iron | (A) | For making wires |
| 2. | Copper | (B) | Sewing needle |
| 3. | Tungsten | (C) | As a fuel for ignition in rocket. |
| 4. | Boron | (D) | Making the filament of a bulb |
Answer:
- B
- A
- D
- C
Kalvi Guru 8th Science Question 2.
| 1. | Atom | (A) | building block of matter |
| 2. | Element | (B) | atoms of different kinds |
| 3. | Compound | (C) | atoms of the same kind |
| 4. | Molecule | (D) | smallest unit of a substance |
(a) 1 – A, 2 – C, 3 – B, 4 – D
(b) 1 – C,2 – A, 3 – B, 4 – D
(c) 1 – D, 2 – C, 3 – B, 4 – A
(d) 1 – B, 2 – C, 3 – A, 4 – D
Answer:
- A
- C
- B
- D
8th Science Matter Around Us Guide Question 3.
Identify the state of matter based on the arrangement of the molecules.
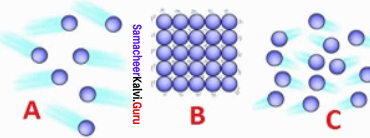
(a) A – gas, B – solid, C – liquid
(b) A – Liquid, B – solid, C – Gas
(c) A – gas, B – solid, C – liquid
(d) A – Liquid, B – Gas, C – Solid
Answer:
(a) A – gas, B – solid, C – liquid
V. Very Short Answer Questions
Matter Around Us 8th Class Question 1.
What is ductility?
Answer:
Metals can be drawn into thin wires. This property of metals is called ductility.
Example : Copper wires.
Matter Around Us Class 8 Answer Key Question 2.
Write the constituent elements and their symbols for the following compounds
- Carbon monoxide
- Washing soda
Answer:
| Compound | Symbols | Constituent elements |
| Carbon monoxide | (CO) | Carbon and oxygen |
| Washing soda | (Na2CO3) | Sodium, carbon and oxygen |
8th Standard Matter Around Us Question Answer Question 3.
Write the symbols for these elements
- Oxygen
- Gold
- Calcium
- Cadmium
- Iron
Answer:
| S.No | Element | Symbols |
| (i) | Oxygen | O |
| (ii) | Gold | Au |
| (iii) | Calcium | Ca |
| (iv) | Cadmium | Cd |
| (v) | Iron | Fe |
Question 4.
Name two soft metals that can be cut with a knife.
Answer:
Sodium (Na) and Potassium (K) are soft metals those metals can be cut with a knife.
Question 5.
Which non – metal is essential for our life and all living beings inhale it during breathing?
Answer:
Oxygen is essential for our life and all living beings inhale it during breathing.
Question 6.
Why are bells made of metals?
Answer:
On being hit, metals produce a typical sound. They are said to be sonorous. This property is being made used in making bells.
Question 7.
What does a chemical symbol represent?
Answer:
A chemical symbol is a shorthand method of representing an element.
Symbol of an element signifies:
- Name of the element.
- One atom of the element for example,
- The symbol O stands for the element of oxygen.
- One atom of oxygen.
Question 8.
Give two examples for metalloids.
Answer:
Boron and silicon.
Question 9.
Mention any three compounds that exist in liquid state.
Answer:
- Water
- Hydro chloric Acid
- Nitric Acid
Question 10.
Write three properties of metalloids.
Answer:
Properties of metalloids:
Metalloids are all solid at room temperature.
- They can form alloys with other metals
- Some metalloids, such as silicon and germanium, can act as electrical conductors under the specific conditions, thus they are called semiconductors.
- Silicon for example appears lustrous, but is not malleable nor ductile (it is brittle – a characteristic of some non – metals). It is a much poorer conductor of heat and electricity than the metals
VI. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Can you store pickle in an aluminium utensil? Explain.
Answer:
No, we cannot store the lemon pickle in aluminium utensil because aluminium is a metal and lemon is acidic. The acids react with metals to give hydrogen which would spoil the food and makes it unfit to use.
Question 2.
Tabulate four points of difference between metals and non – metals.
Answer:
| Property | Metal | Non – metal |
| Physical state at room temperature | Usually solid | Solid, liquid or gas. |
| Malleability | Good | Poor – usually soft or brittle. |
| Ductility | Good | Poor – usually soft or brittle. |
| Boiling point | Usually high | Usually low |
Question 3.
Define tensile strength.
Answer:
Metals have the capacity to withstand strain without breaking. This property is called tensile strength. It is the property that owes the use of iron for the construction of railway tracks.
Question 4.
Why are utensils made up of aluminium and brass?
Answer:
- The cooking utensils are made up of aluminium and brass because they are good conductors of heat.
- Aluminium will form a layer of protective oxide that prevents further reaction. Also aluminium is also relatively cheap and that is why it is used widely in making utensils.
Question 5.
Define a Alchemy.
Answer:
Alchemy was form of chemistry studied in the middle age, which was concerned with trying to discover ways to change ordinary metals into gold.
Question 6.
Name the elements for following symbols.
- Na
- W
- Ba
- Al
- U
Answer:
- Na – Sodium
- W – Tungsten
- Ba – Barium
- Al – Aluminium
- U – Uranium.
Question 7.
Name six common non – metals and write their symbols.
Answer:
| S.No | Non – metals | Symbols |
| 1. | Sulphur | S |
| 2. | Carbon | c |
| 3. | Oxygen | 0 |
| 4. | Hydrogen | H |
| 5. | Helium | He |
| 6. | Nitrogen | N |
Question 8.
Answer:
Mention any four compounds and their uses.
Answer:
Compounds and their uses:
|
Common Name |
Chemical Name | Constituents | Uses |
| Water | Hydrogen Oxide | Hydrogen and oxygen | For drinking and as solvent |
| Table salt | Sodium chloride | Sodium and chlorine | Essential component of our daily diet, preservative for meat and fish. |
| Sugar | Sucrose | Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen | Preparation of sweets, toffees and fruit juices. |
|
Baking soda |
Sodium bicarbonate | Sodium, hydrogen, carbon and oxygen | Fire extinguisher, preparation of baking powder and preparation of cakes and bread. |
Question 9.
Mention the metals that are used in jewellery.
Answer:
Silver and gold are used for making jewels and in decorative purposes
Question 10.
Mention the uses for the following compounds.
- Baking soda
- Bleaching powder
- Quick lime
Answer:
| S.No | Compounds | Uses |
| (i) | Baking soda | Fire extinguisher, preparation of baking powder and preparation of cakes and bread. |
| (ii) | Bleaching powder | As bleaching agent, disinfectant and sterilisation of drinking water. |
| (iii) | Quick lime | Manufacture of cement and glass. |
VII. Reason out
Question 1.
Give reasons for the following.
- Aluminum foils are used to wrap food items.
- Immersion rods for heating liquids are made up of metallic substances.
- A doctor prescribed a tablet to a patient suffering from iron deficiency. The tablet does not look like iron.
- Sodium and potassium are stored in kerosene.
- Mercury is used in thermometers.
Answer:
- Aluminium is malleable, soft and does not react with food items, so it is used to wrap food items.
- Metals are good conductor of heat and electricity, so immersion rods are made up of metallic substances.
- It doesn’t look like iron, iron tablets does not contains iron metal, rather it contains iron salts like ferrous sulphate, ferrous citrate etc.
- Sodium and potassium are very reactive, they react with air and water, so they are stored in kerosene.
- Mercury is used in thermometers and barometers because of its high density and uniform expansion at different temperature.
Question 2.
Why wires cannot be drawn from materials such as stone or wood?
Answer:
Wires cannot be drawn from materials such as stone or wood, is because these materials are non – conductors of electricity.
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Solutions Matter Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The most reactive metal is ……………..
(a) Iron
(b) Gold
(c) Zinc
(d) Potassium
Answer:
(d) potassium
Question 2.
The liquid metal at room temperature ……………..
(a) Mercury
(b) Bromine
(c) Sodium
(d) Gold
Answer:
(a) Mercury
Question 3.
Non – metals are ……………….
(a) Generally liquids
(b) Generally gases
(c) Generally solids and gases
(d) Generally gases and liquids
Answer:
(c) Generally solids and gases
Question 4.
The metal which is stored in kerosene
(a) phosphorous
(b) Magnesium
(c) Sodium
(d) Gold
Answer:
(c) sodium
Question 5.
The non – metal which is liquid at room temperature is
(a) Carbon
(b) Iodine
(c) Bromine
(d) Chlorine
Answer:
(c) Bromine
Question 6.
The metal which can be cut with a knife
(a) Sodium and potassium
(b) Barium and calcium
(c) Sodium and mercury
(d) Potassium and calcium
Answer:
(a) sodium and potassium
Question 7.
Which of the following is false for gases?
(a) They diffuse easily
(b) They have mass
(c) They do not mix well
(d) They are highly compressible
Answer:
(c) They do not mix well
II. Fill in the Blanks
- Atom or group of atoms having a charge are called ………………
- In chemistry each element is denoted by a ………………
- Metals and non – metals are used for making ……………., …………… and ……………..
- ……………. is so hard that it can scratch glass.
- The typical shine of metals is called …………….
- Metals are ……………. conductors of heat and electricity.
- Metalloids are ……………. at room temperature.
- A molecule of water is composed of an oxygen atom and ……………..
- Compounds obtained from non – living sources are called …………….
- All gases are …………….
Answer:
- Ions
- Symbol
- Tools, machines, cars
- Osmium
- Metallic lustre
- Good
- Solid
- Two hydrogen atoms
- Inorganic compounds
- Non – metals
III. True or False – if false give the correct statement
Question 1.
Sodium is a hard metal.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement:
Sodium is a soft metal, it can be cut with a knife.
Question 2.
Silver and copper are very good conductors of electricity.
Answer:
True.
Question 3.
Metals have high melting points.
Answer:
True.
Question 4.
Antimony has the highest tensile strength.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement:
Tungsten has the highest tensile strength.
Question 5.
The other name of potassium hydroxide is caustic potash.
Answer:
True.
IV. Match the following
Question 1.
| i | Softest metal | (a) | Copper |
| ii | Hardest metal | (b) | Sodium |
| iii | Hardest non – metal | (c) | Osmium |
| iv | Ductility | (d) | Diamond |
Answer:
i. b
ii. c
iii. d
iv. a
Question 2.
| i | Silica | (a) | Caustic potash |
| ii | Potassium hydroxide | (b) | Sand |
| iii | Sodium hydroxide | (c) | Calamine |
| iv | Zinc carbonate | (d) | Caustic soda |
Answer:
i. b
ii. a
iii. d
iv. c
V. Very short Answers
Question 1.
Which metal has the highest ductility?
Answer:
The most ductile metals is platinum.
Question 2.
Why do metals appear shiny?
Answer:
All metals are shiny. The typical shine of metals is called metallic lustre. All metals have typical metallic lustre. An exception is calcium.
Question 3.
Which metals are not solid at room temperature?
Answer:
Metals are solid under normal conditions of temperature and pressure. Mercury is liquid at room temperature.
Question 4.
Which metals are liquid at room temperature?
Answer:
Elements Cesium (Cs), Rubidium (Rb), Francium (Fr) and Gallium (Ga) become liquid at or just above room temperature.
Question 5.
State different states of matter with an example.
Answer:
Matter has three different states.
![]()
Question 6.
Why are metalloids called semimetals?
Answer:
Some elements neither fit with the metals or with non – metals. Such elements are called semi – metals. They exhibit the properties of metals as well as non – metals.
Question 7.
Name the two elements which are derived from the country.
Answer:
(i) Name : Americum
Symbol : Am
Country : America
(ii) Name : Europium
Symbol : Eu
Country : Europe
VII. Short Answer
Question 1.
Differentiate inorganic compounds and organic compounds.
Answer:
Inorganic compounds:
Compounds obtained from non – living sources such as rock, minerals etc.
Example:
Chalk, baking powder etc.
Organic compounds:
Compounds obtained from living sources such as plants and animals.
Example:
Protein, carbohydrates etc.
Question 2.
What is the significance of the symbol of an element? Ans. Symbol of an element signifies .
- Name of the element.
- One atom of the element.
Example : The symbol O stands for the element of oxygen. One atom of oxygen.
Question 3.
Tabulate the some important compounds that exist in gaseous state.
Answer:
| Compound | Constituent elements |
| Carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide | Carbon, Oxygen |
| Sulphur dioxide | Sulphur, Oxygen |
| Methane | Carbon, Hydrogen |
| Nitrogen dioxide | Nitrogen, Oxygen |
| Ammonia | Nitrogen, Hydrogen |
Question 4.
Answer:
The vapour had purple colour, so the element was given the name after the Greek iodides, which means violet.
Name : Iodine
Symbol : I
Name derived from : Violet (colour, Greek)
Question 5
Answer:
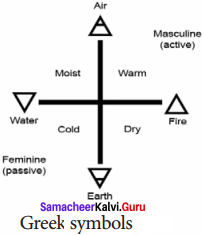
Write a note on Greem symbols.
Answer:
The symbols in form of the geometrical shapes were those used by the ancient Greeks to represent the four basic elements around us such as earth, air, fire and water.
Question 6.
Answer:
Compare the conductivity of metals and non – metals.
Metals:
- Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
- Silver and copper are very good conductor of electricity. However bismuth and tungsten are poor conductors.
Non – metals:
- Non – metals are bad conductor of electricity.
- Graphite (a form of carbon) is exception.
VIII. Long Answer
Question 1.
Write the physical properties of non – metals.
Answer:
Physical p roperties of non – metals:
1. Physical state:
Non – metals occur as solids, liquids or gases at normal temperature; for example sulphur, phosphorus occurs in solid state while bromine occurs in liquid state. Gases like oxygen, nitrogen, etc., occur in the gaseous state.

2. Hardness:
Non – metals are generally not hard except diamond, (a form of carbon)
3. Lustre:
Non – metals have a dull appearance; Graphite and iodine are exceptions as they are shiny and lustrous.
4. Density:
Non – Metals are generally soft and have low densities. The exception here is diamond (a form of carbon) which’is the hardest naturally occurring substance
5. Melting point and boiling point:
Non – metals have low melting point and boiling point. However, carbon, silicon and boron are exceptions.
6. Tensile strength:
Non – metals do not have tensile strength. However, carbon fibre (a form of carbon) is as tensile as steel.
7. Malleability:
Non – metals are non-malleable. If hammered, they form a powdery mass. Actually non – metals in solid state are brittle in nature.
8. Ductility:
Non – metals are not ductile. Carbon fibre is highly ductile.
9. Conductivity:
Non – Metals are generally bad conductor of electricity. Graphite (a form of carbon) is exception.
10. Sonorous:
Non – metals do not produce sound (non – sonorous) when hit.
Question 2.
Write the uses of metals.
Answer:
Metal:
- Iron, is used for making bridges, engine parts, iron – sheet and bars.
- Copper is used for making electrical wires, coins and statue.
- Silver and gold are used for making jewels, in decorative purposes and photography.
- Mercury is used in thermometers and barometers because of its high density and uniform expansion at different temperature.
- Aluminium is used in electrical wires, cables and in aerospace industries.
- Lead is used in automobile batteries, X – ray machines.

Question 3.
Write the uses of non – metals.
Answer:
- Diamond (a form of carbon) is used for making jewels, cutting and grinding equipments. Graphite is used in making pencil lead.
- Sulphur is used in the manufacturing of gun powder and vulcanization of rubber.
- Phosphorus is used in matches, rat poison etc.
- Nitrogen is used for manufacturing ammonia.
- Chlorine is used as a bleaching agent and in sterilizing water.
- Hydrogen is used as a rocket fuel and hydrogen flame is used for cutting and welding purposes, as well as a reducing agent.


Question 4.
Write a note on classification of compounds.
Answer:
Classsification compound:
Based on the origin of chemical constituents, compounds are classified as inorganic compounds and organic compounds.
1. Inorganic compounds:
Compounds obtained from non – living sources such as rock, minerals etc., are called inorganic compounds. Example: chalk, baking powder etc.
2. Organic compounds:
Compounds obtained from living sources such as plants, animals etc., are called organic compound. Example: Protein, carbohydrates, etc.
Both inorganic and organic compounds exists in all three states of matter ie., solids, liquids and gases.
IX. Cross word puzzle
In this crossword puzzle, names of 10 elements are hidden. Symbols of these are given below. Complete the puzzle.
Answer:
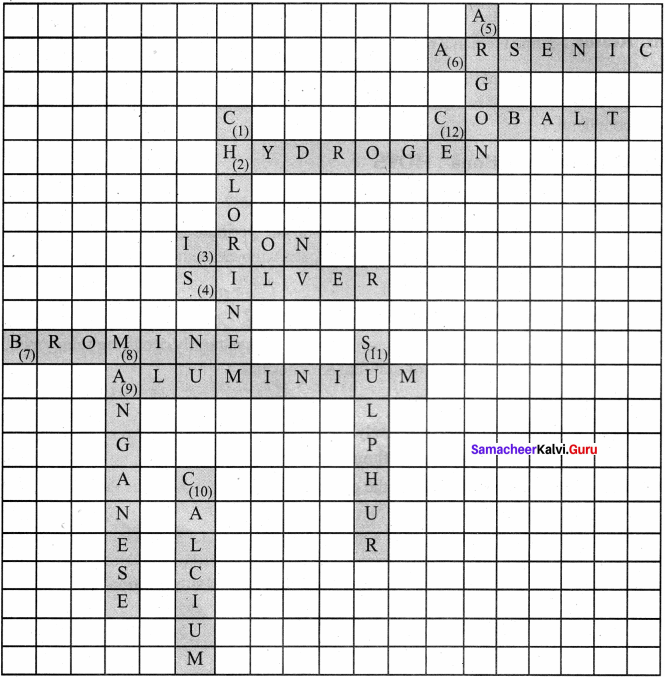
Across and down:
- Cl
- H
- Fe
- Ag
- Ar
- As
- Br
- Mn
- Al
- Ca
- S
- CO
X. Reason out
Question 1.
Sand is also known as silica.
Answer:
Reason : High purity sand almost entirely composed of silica.
Question 2.
Sulphur is used in vulcanization of rubber.
Answer:
Reason : Vulcanization of rubber is a process of improvement of the rubber elasticity and strength by heating it in the presence of sulphur.
Question 3.
Elements are called semi – metals.
Reason : Some elements neither fit with the metals nor with non – metals.
Question 4.
Mercury is the only metal that is liquid at room temperature.
Answer:
Reason : Mercury has a low melting point, and it is a poor electrical and thermal conductor.
XI. Creative questions : HOTS
Question 1.
Which letter is never used in any element symbol?
Answer:
The letter “J” is the only one not found on the periodic table. In some countries (eg: Norway, Poland, Sweden. Serbia, Croatia), the element iodine is known by the name jod.
Question 2.
What is the rarest natural element in the earth?
Answer:
Astatine is the rarest element on earth. Astatine is a naturally occurring semi – metal that results from the decay of uranium and thorium.
Question 3.
Explain why?
Answer:
- A gas fill a vessel completely?
- Camphor disappears without leaving any residue.
Answer:
- Because the molecules of the gas moves freely so it occupies the whole space the vessel.
- Camphor disappears after sometimes as its surface gains kinetic energy and gets directly converted into gas. The process of getting converted directly into gas without getting converted into liquid is called sublimation.