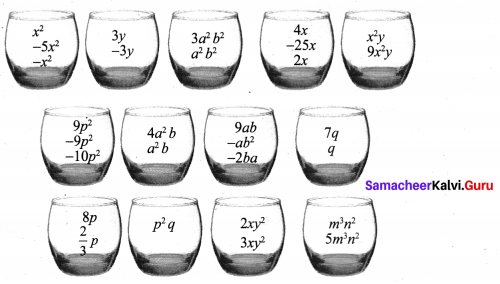
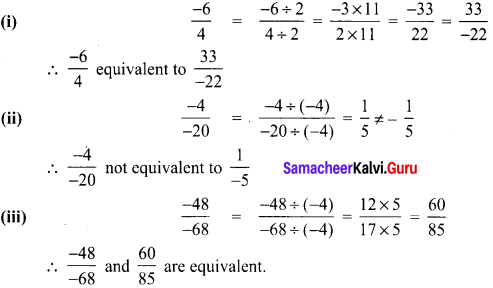
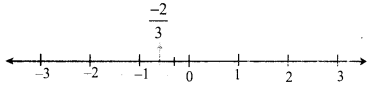
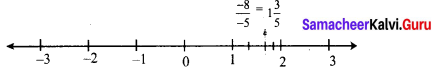
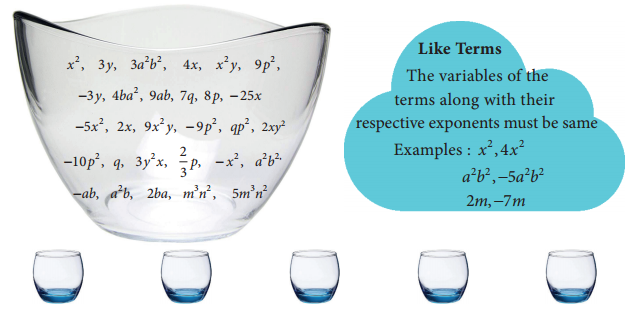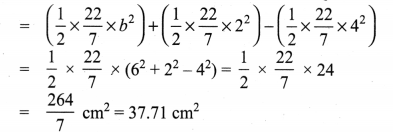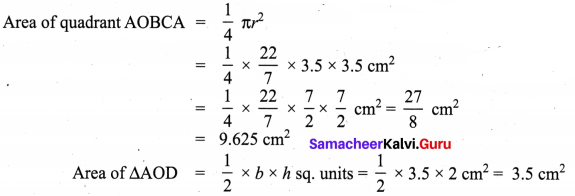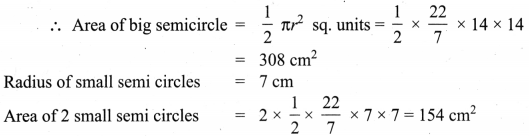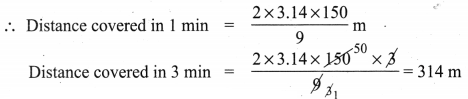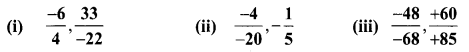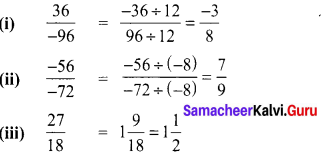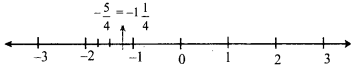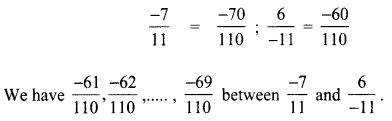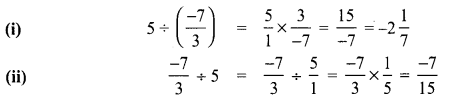Students can Download Maths Chapter 2 Measurements Intext Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
![]()
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Solutions Term 1 Chapter 2 Measurements Intext Questions
Try this Page No. 35
Question 1.
\(\frac{22}{7}\) and 3.14 are rational numbers. Is ‘π’ a rational number? Why?
Solution:
\(\frac{22}{7}\) and 3.14 are rational numbers n has non-terminating and non -repeating decimal expansion. So it is not a rational number. It is an irrational number.
![]()
Try this Page No. 38
Question 1.
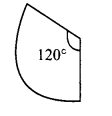
The given circular figure is divided into six equal parts. Can we call the parts as sectors? Why?
Solution:
No, the equal parts are not sectors. Because a sector is a plane surface that is enclosed between two radii and the circular arc of the circle.
Here the boundaries are not radii.
![]()
Try these Page No. 38
Question 1.
Fill the central angle of the shaded sector (each circle is divided into equal sectors)
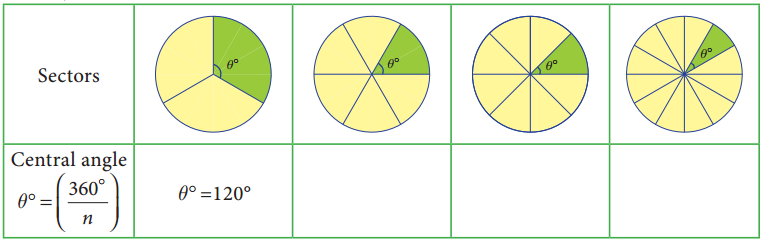
Try this Page No. 44
Question 1.
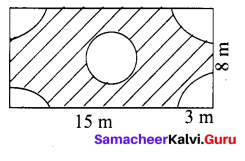
If the radius of a circle is doubled, what will the area of the new circle so formed?
Solution:
If r = 2r1 ⇒ Area of the circle = πr2 = π(2r1)2 = π4r12 = 4πr12
Area = 4 × old area.
![]()
Try this Page No. 49
Question 1.
All the sides of a rhombus are equal. Is it a regular polygon?
Solution:
For a regular polygon all sides and all the angles must be equal. But in a rhombus all the
sides are equal. But all the angles are not equal
∴ It is not a regular polygon.
![]()
Try this Page No. 53
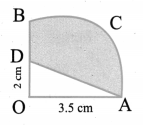
Question 1.
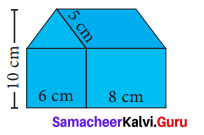
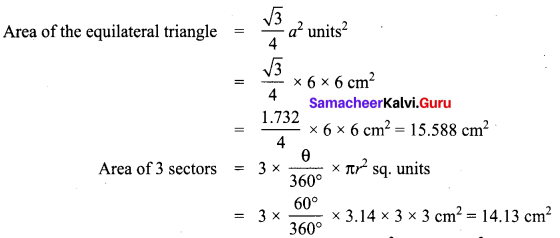
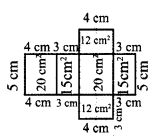
In the above example split the given mat as into two trapeziums and verify your answer.
Solution:
Area of the mat = Area of I trapezium + Area of II trapezium

∴ Cost per sq.feet = ₹ 20
Cost for 28 sq. feet = ₹ 20 × 28 = ₹ 560
∴ Total cost for the entire mat = ₹ 560
Both the answers are the same.
![]()
Try these Page No. 54
Question 1.
Show that the area of the unshaded regions in each of the squares of side ‘a’ units are the same in all the cases given below.
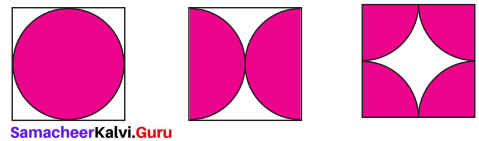
Solution:
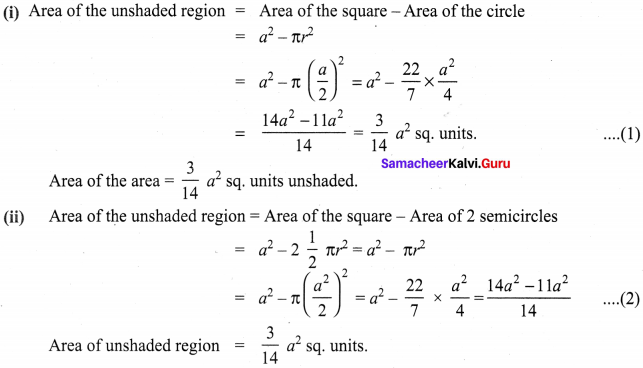
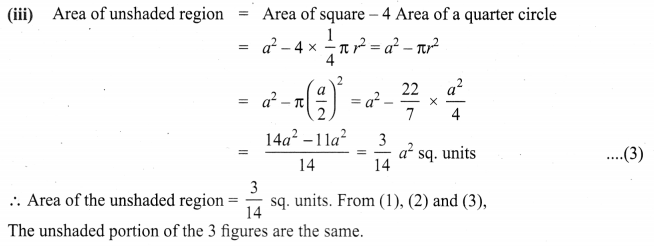
![]()
Question 2.
If π = \(\frac{22}{7}\), show that the area of the unshaded part of a square of side ‘a’ units is approximately \(\frac{3}{7}\) a2 sq. units and that of the shaded part is approximately \(\frac{4}{7}\) a2 sq. units for the given figure.

Solution:
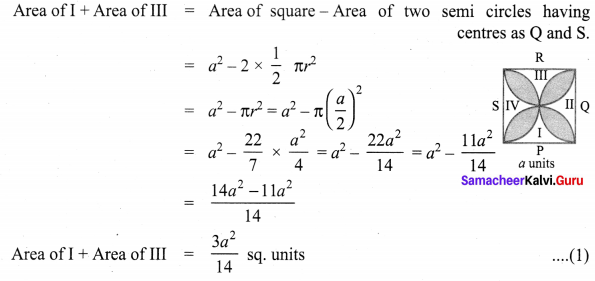
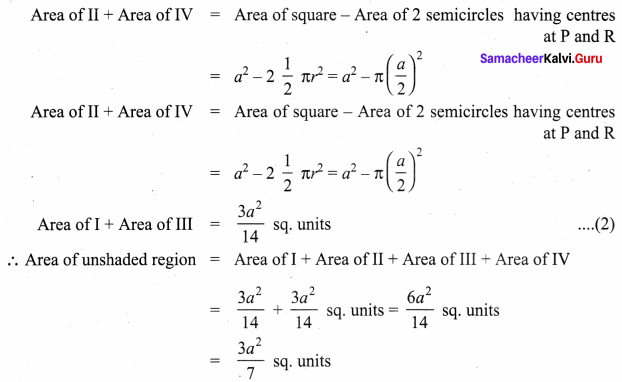

Try this Page No. 57
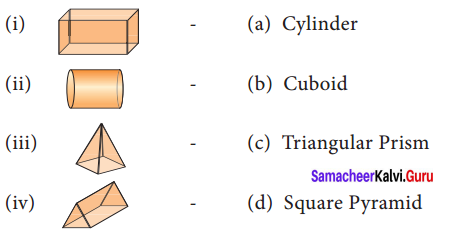
Question 1.
List out atleast three objects in each category which are in the shape of cube, cuboid,
cylinder, cone and sphere.
Solution:
(i) Cube – dice, building blocks, jewel box.
(ii) Cuboid – books, bricks, containers.
(iii) Cylinder – candles, electric tube, water pipe.
(iv) Cone – Funnel, cap, ice cream cone
(v) Sphere – ball, beads, lemon.
![]()
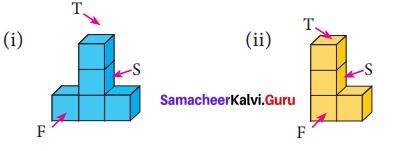
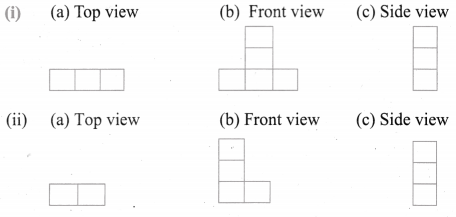
Try this Page No. 58
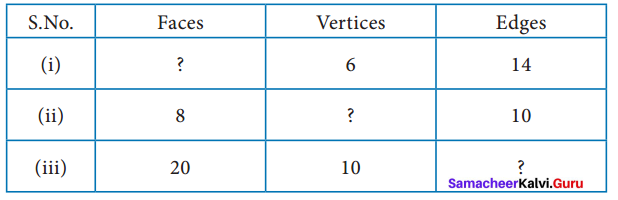
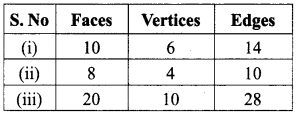
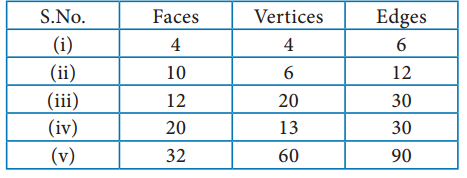
Question 1.
Tabulate the number of faces(F), vertices(V) and edges(E) for the following polyhedron. Also find F + V – E
Solution:
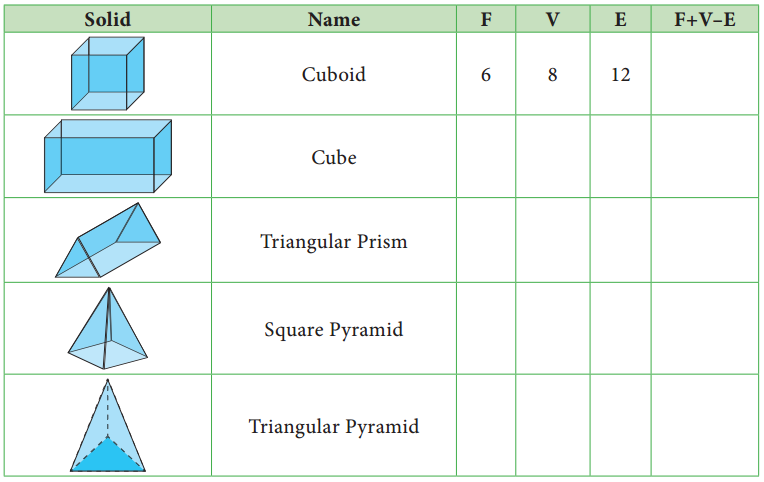
From the table F + V – E = 2 for all the solid shapes.
![]()
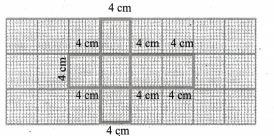
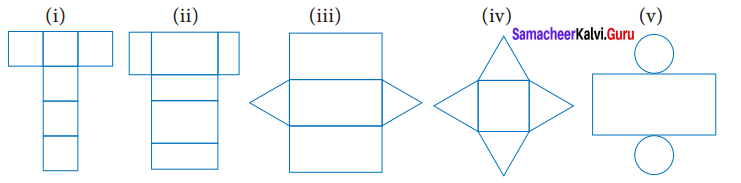
Try this Page No. 58
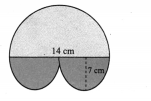
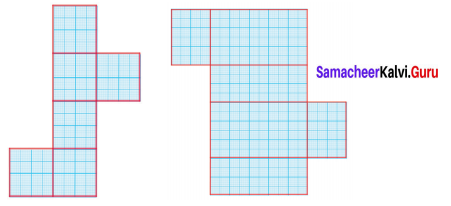
Question 1.
Find the area of the given nets.
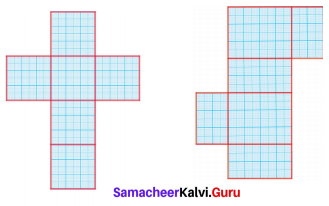
Solution:
Area = 6 × Area of a square of side 6 cm
= 6 × (6 × 6) cm2
= 216 cm2
(ii) Area = Area of 2 rectangles of side (8 × 6) cm2 + Area of 2 rectangles of side (8 × 4) cm2 + Area of 2 rectangles of side (6 × 4) cm2
= (8 × 6) + (8 × 4) + (6 × 4)cm2
= 48 + 32 + 24 cm2
= 104 cm2