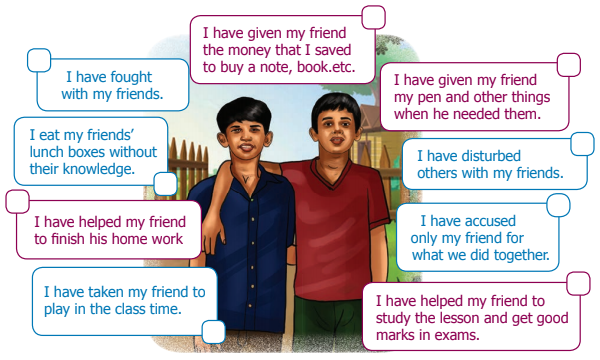
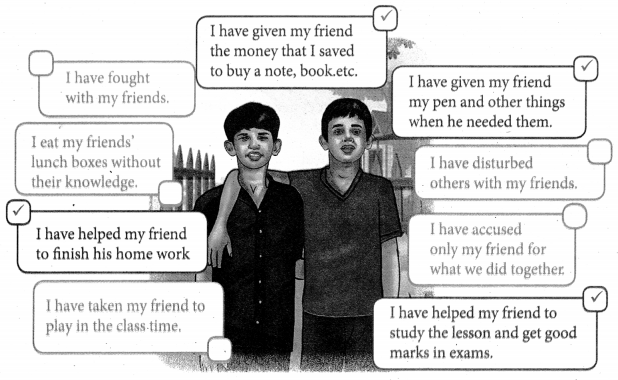
Students can Download English Lesson 2 The Mystery of the Cyber Friend Questions and Answers, Summary, Activity, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 8th English Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th English Solutions Term 3 Supplementary Chapter 2 The Mystery of the Cyber Friend
The Mystery Of The Cyber Friend Summary Read And Understand
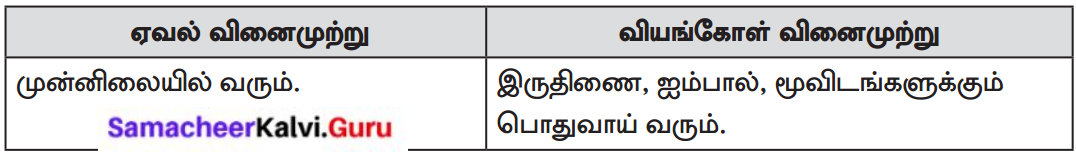
A. Say whether the following are ‘True’ or ‘False’.
- Shree spends most of the time on T.V.
- Shrees aunt stays with them.
- Chaitra is Shrees school friend.
- Chaitra gifted Shree a new camera phone.
- Shree went alone to the train station to meet Chaitra.
- A fraud middle aged man pretended to be Chaitra. Name the speaker.
Answer:
- False
- True
- False
- False
- False
- True
B. Name the speaker.
Answer:
| S. No. | Lines from the lesson | Speaker |
| 1. | “Do you do anything other than eating?” | Shree’s friend |
| 2. | “Are you feeling unwell?” | Shree’s aunt |
| 3. | “I don’t have a camera phone” | Shree |
| 4. | “I told you I am thirteen, the same age as you”. | Chaitra |
| 5. | “You are a brave pair!” | Policewoman |
C. Answer the following questions
The Mystery Of The Cyber Friend Questions And Answers Question 1.
Why did Shree’s parents buy her a computer?
Answer:
Shrees parents bought her a computer because they wanted her to learn computers.
The Mystery Of The Cyber Friend Question 2.
How did Shree make friends through computer?
Answer:
Two months ago, on her thirteenth birthday, Shree joined “Friends Net”. Through this net, she made friends.
The Mystery Of Cyber Friend Question 3.
What were the online activities given in this story?
Answer:
Chaitra tells lies to Shree, saying that she is studying in a school near to Shree’s school. She used a film stars picture as her profile. She asked Shree to come to the raiway station all alone.
The Mystery Of The Cyber Friend Book Back Answers Question 4.
How did Shree’s aunt save Shree from the man who pretended to be Chaitra?
Answer:
Shrees aunt accompanied her to the railway station. She informed the station manager about the new friend and asked him to help them. When she saw the man talking to Shree, she hit him with her handbag. He ran away into the crowded train.
Summary Of The Mystery Of The Cyber Friend Question 5.
How did the police find the man who pretended to be Chaitra?
Answer:
A Cyber crime officer went through Shrees computer within hours he found the man, who pretended to be Chaitra.
D. Based on your reading of the text, list out the merits and demerits of using a computer.
Answer:
| S. No. | Merits | Demerits |
| 1. | Multitasking | 1. Virus and Cyber attacks |
| 2. | Speed | 2. Online cyber crimes |
| 3. | Stores huge amount of data | 3. Destroys social life |
| 4. | Accuracy | 4. Too much of sitting |
| 5. | Data security | 5. Eye strain |
The Mystery Of The Cyber Friend Story Step To Success
8th English The Mystery Of The Cyber Friend Question 1.
The following series is provided and you need to answer the question accordingly.
ABCDEFGHIJKLMN| |OPRSTUVWXYZ
In this series find the letter which is fifth to the left from the thirteenth letter from your right.
(a) M
(b) I
(c) H
(d) J
Answer:
(c) H
The Mystery Of The Cyber Friend Summary In English Question 2.
Based on the above series of English alphabets, if every alternate alphabet starting from C is deleted than which of the following alphabet will seventh from the left side of the series?
(a) H
(b) K
(c) I
(d) G
Answer:
(b) K
The Mystery Of The Cyber Friend Mind Map Question 3.
If the above series is written in reverse order than what is the eleventh letter of the fifteenth letter from your left?
(a) V
(b) W
(c) D
(d) X
Answer:
(b) W
The Mystery of the Cyber Friend Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer.
The Mystery Of The Cyber Friend Lesson Plan Question 1.
Shree lives in an apartment in a small town called ___________ Junction.
(a) Thirupathi
(b) Katpadi
(c) Gudur
(d) Thiruvallur
Answer:
(b) Katpadi
Mystery Of The Cyber Friend Question 2.
They want her to learn ___________
(a) arts
(b) singing
(c) music
(d) computers
The Mystery Of The Cyber Friend Pdf Question 3.
After tiffin, shree likes to ___________
(a) read books
(b) watch TV
(c) play
(d) sleep
Answer:
(c) play
The Mystery Of The Cyber Friend In Tamil Question 4.
The computer also has ___________ net.
(a) Friends
(b) Visitors
(c) Chat
(d) Vice
Answer:
(a) Friends
Question 5.
Shree says that she got extra sugar with her ___________
(a) coffee
(b) milk
(c) tea
(d) juice
Answer:
(c) tea
Question 6.
She chats with her ___________ friends through Friends Net.
(a) school
(b) college
(c) office
(d) best
Answer:
(a) school
Question 7.
Chaitra ___________ Shree to accept her as a new friend.
(a) pleaded
(b) begged
(c) requested
(d) ordered
Answer:
(c) requested
Question 8.
Soon Shree gets a ___________ from Chaitra.
(a) message
(b) warning
(c) threatening
(d) gift
Answer:
(a) message
Question 9.
Chaitra offers to give Shree her old ___________
(a) photos
(b) phone
(c) paintings
(d) laptop
Answer:
(b) phone
Question 10.
Best friends should be of the same ___________
(a) size
(b) race
(c) age
(d) status
Answer:
(c) age
II. dentify the character and speaker:
- “Do you have many friends?”
- “I lost a few friends today”
- “Are you feeling unwell”.
- “Too much of school work”
- “Hello, Friend. How are you today?”
- “Great. Now can you send me a selfie?”
- “I have a new friend, Akka!”
- “But that’s the film actress I like so much, Madhoo.”
- “Don’t you dare come near my niece”
- “You are clever to confide in a trusted adult.”
Answer:
- Chaitra
- Shree
- Shree’s aunt
- Shree
- Chaitra
- Chaitra
- Shree
- Shree’s aunt
- Shree’s aunt
- Policewoman
III. Give Very Short Answers :
Question 1.
Who was Shree’s best friend?
Answer:
The computer was Shree’s best friend.
Question 2.
What does Shree like to play on the computer?
Answer:
Shree likes to play games on the computer.
Question 3.
When did Shree join the Friends Net?
Answer:
She joined the friends Net two months ago on her thirteenth birthday.
Question 4.
How was Chaitra’s profile?
Answer:
Chaitra’s profile was very pretty. She looked like a film star.
Question 5.
Did Shree see Chaitra’s school? Why?
Answer:
No, Shree couldn’t see Chaitra’s school because it was not there.
Question 6.
Why didn’t Shree eat her tiffin?
Answer:
She couldn’t eat her tiffin because she was eagerly waiting to talk to Chaitra.
Question 7.
Where did Chaitra want to meet Shree ?
Answer:
Chaitra wanted to meet Shree at the Railway Station.
Question 8.
What did chaitra promise to give Shree?
Answer:
Chaitra promised to give her an old camera phone.
Question 9.
Who came to meet Shree at the Railway Station?
Answer:
A man, who was her father’s age, came to meet Shree.
IV. Write Short Answers :
Question 1.
Where did Shree live and what were his parents?
Answer:
Shree lived in an apartment in a small town called Katpadi Junction. Her mother works in a jewelery shop. Her father works as a taxi driver.
Question 2.
What does Shree do everyday?
Answer:
After snacks and tea, Shree chats with her school friends through Friend Net. They tell each other what they did everyday.
Question 3.
Who stays with Shree’s Family? What do everyone calls her?
Answer:
Shree’s aunt stays with their family. Everyone calls her “Akka”. Most of the time, she sleeps in front of the TV.
Question 4.
What did Shree’s aunt tell about Chaitra?
Answer:
Shree’s aunt tells Shree that Chaitra’s profile is not her. It is the picture of her favourite actress Madhoo.
Question 5.
What happend to the imposter at the Railway Station?
Answer:
Shree’s aunt hit the imposter with her handbag. The Station Manager rushed to catch the man. But he disappeared into the crowded train.
V. Answer in Detail:
Question 1.
How was the Cyber friend of Shree caught by the police?
Answer:
Shree went to meet her friend Chaitra at the railway station. Her aunt accompanied her. She informed about the imposter to the Station Manager and requested him to help them. When they were waiting at the station, a man came towards Shree. He was of Shree’s father’s age. He tried to convince Shree and requested her to be his friend. Seeing him talking to her neice, Shree’s aunt hit him with her handbag. The Station Manager also rushed forward to catch him. But he disappeared in the crowded train. Later the Cyber Crime officer went through Shree’s computer. He found the man and nabbed him in Bengaluru.
VI. Rearrange the jumbled sentences :
Question A.
1. So they are pleased that she likes to use it.
2. Appa works as a taxi driver.
3. They want her to learn computers.
4. Shree lives in an apartment in a small town called Katpadi Junction.
5. Amma works in a jewellery shop.
Answer:
4. Shree lives in an apartment in a small town called Katpadi Junction.
5. Amma works in a jewellery shop.
2. Appa works as a taxi driver.
3. They want her to learn computers.
1. So they are pleased that she likes to use it.
Question B.
1. She watched her favourite old films.
2. Shrees aunt also stays with them.
3. She gives Shree hot dosas stuffed with spicy noodles.
4. Everyone calls her Akka.
5. Most of the time, she naps in the front of the TV.
Answer:
2. Shrees aunt also stays with them.
4. Everyone calls her Akka.
5. Most of the time, she naps in the front of the TV.
1. She watched her favourite old films.
3. She gives Shree hot dosas stuffed with spicy noodles.
Question C.
1. Within hours, the police find the man who pretended to be Chaitra.
2. They nab him from his office in Bengaluru.
3. They find out that he has been trying to befriend many young girls and boys on social media.
4. Shree decides to only have friends from her own school.
5. The next day, a cyber crime officer goes through Shrees computer.
Answer:
5. The next day, a cyber crime officer goes through Shrees computer.
1. Within hours, the police find the man who pretended to be Chaitra.
2. They nab him from his office in Bengaluru.
3. They find out that he has been trying to befriend many young girls and boys on social media.
4. Shree decides to only have friends from her own school.
VII. Comprehension.
Question 1.
The next morning, Shree looks for school near hers. But she cannot see one. It is a little strange that she hasn’t heard of any other school nearby. But Chaitra is nicer than all her other friends. She is Shrees special friend and nobody else’s friend.
(a) What did Shree look for?
Answer:
Shree looked for Chaitra’s School.
(b) Did she see the school?
Answer:
No, She did not see the school.
(c) What did Shree think about Chaitra?
Answer:
She thought that Chaitra was nicer than all her other friends.
(d) Whose friend is Chaitra?
Answer:
Chaitra is Shrees special friend.
Question 2.
But Shree doesn’t do her homework. Instead, she starts the computer, goes online and waits for her new friend to ping her. Soon she gets a message from Chaitra.
“Hello, friend. How are you today?”
(a) Does Shree do her homework?
Answer:
No, Shree doesn’t do her homework.
(b) What does Shree do, instead doing of her homework?
Answer:
Shree starts the computer, goes online and waits for her new friend to ping her.
(c) What does Shree get from Chaitra?
Answer:
Shree gets a message from Chaitra.
(d) What was the message?
Answer:
The message was “Hello Friend. How are you today?”
The Mystery of the Cyber Friend Summary
Section – I
Shree lived in an apartment with her father, mother and aunt. Her parents wanted her to learn computers. So they were pleased with her, when she used it. She used to find information for school projects and send e-mails. Two months ago, on her thirteenth birthday, she joined the “Friend Net” on the computer. She used to chat with her friends everyday. One day, a new friend requested her to accept her. Shree accepted her and chatted with her. Her name was Chaitra. She told Shree that she was studying in a school, which was near to her school. Shree considered her to be her special friend. On a Sunday, Ghaitra asked her to meet her at the railway station.
Her aunt saw Chaitra’s profile picture. She told Shree that it was actually the picture of her favourite heroine Madhoo. It was not the picture of Chaitra. Shree could not find any school near her school. Chaitra had also asked Shree to come to the Railway Station all alone. All these things, created suspicion in Shree about Chaitra.
Section – II
Shree was very confused and couldn’t focus on her homework. Shree informed about Chaitra to her aunt. The next day Shree’s aunt accompanied Shree to the railway station. She informed the station manager and waited to see who would come to see Shree. A man who was of her father’s age met her. He tried to convince Shree that he was an uncle and he would like to be her friend. Shree’s aunt hit the man with her handbag. The station manager tried to catch him, but he disappeared into the crowded train. They went to the police station. The policewoman praised them and told Shree to put up a poster about cycber security in her school.
Next day, a cyber crime officer went through Shree’s computer. Within hours, the police found the man, who pretended to be Chaitra. They nabbed him from his office in Bengaluru. They found that he had been trying to befriend many young girls and boys on social media. Shree waited eagerly to tell her friends about her frightening adventure with her cyber friend.