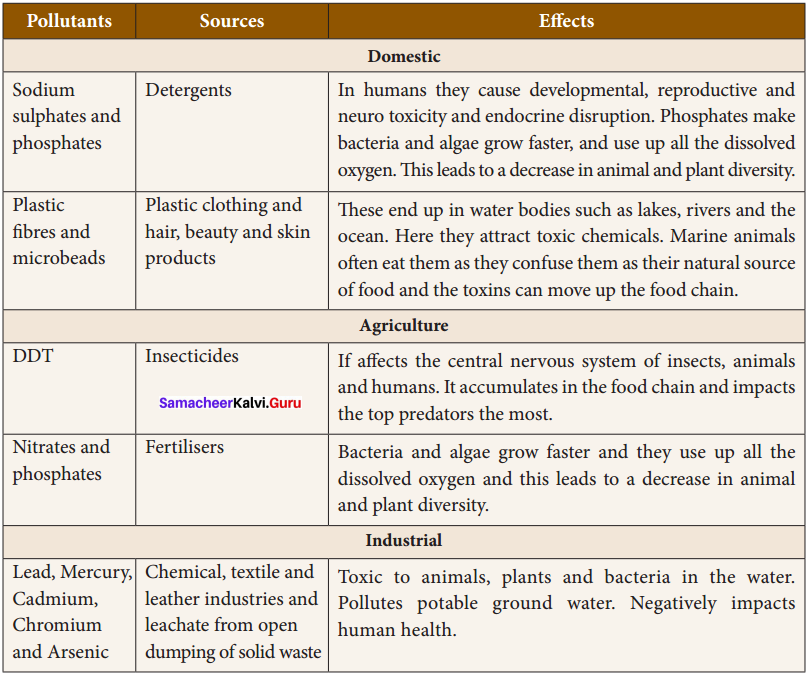
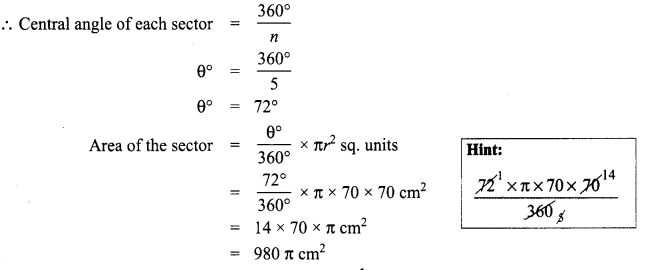You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Civics Solutions Term 2 Chapter 2 Human Rights and UNO
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Civics Human Rights and UNO Textbook Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer
Human Rights And Uno 8th Standard Question 1.
After the Second World War ……………. has taken several measures to protect the human rights.
(a) UNO
(b) Supreme Court
(c) International Court of Justice
(d) None
Answer:
(a) UNO
Human Rights And Uno 8th Standard Samacheer Kalvi Question 2.
In 1995 women from all over the world gathered at ……………..
(a) Beijing
(b) New York
(c) Delhi
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Beijing
Human Rights Lesson Class 8 Question 3.
The National Human Rights Commission was constituted in ………………
(a) 1990
(b) 1993
(c) 1978
(d) 1979
Answer:
(b) 1993
Human Rights Class 8th Question 4.
The UNO declared 1979 as the International year of ……………..
(a) Girl Child
(b) Children
(c) Women
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Women
Human Rights 8th Standard Notes Question 5.
When is Human Rights Day observed?
(a) 9th December
(b) 10th December
(c) 11th December
(d) 12th December
Answer:
(b) 10th December
8th Standard Social Human Rights Notes Question 6.
Which one is known as modern International Magna Carta of Human rights?
(a) UDHRC
(b) NHRC
(c) SHRC
(d) International year for women
Answer:
(a) UDHRC
Human Rights 8th Standard Question 7.
Who can be appointed as the chairperson of the National Human Rights Commission?
(a) Retired judge of high court
(b) Any retired Chief Justice of the Supreme Court.
(c) Any person appointed by the president.
(d) Retired Chief Judge of any court.
Answer:
(c) Any person appointed by the president.
Human Rights 8th Std Notes Question 8.
How many articles does the Universal Declaration of Human Rights contain?
(a) 20
(b) 30
(c) 40
(d) 50
Answer:
(b) 30
Human Rights And Uno Question 9.
What is the tenure of the Chairperson of the National Human Rights Commission?
(a) 5 years or upto 62 years of age
(b) 5 years or upto 65 years of age
(c) 6 years or upto 65 years of age
(d) 5 years or upto 70 years of age
Answer:
(d) 5 years or upto 70 years of age
Question 10.
Where is the headquarters of the National Human Rights Commission?
(a) Delhi
(b) Mumbai
(c) Ahmedabad
(d) Kolkata
Answer:
(a) Delhi
II. Fill in the Blanks
- Each individual has ………….. to lead a dignified life.
- Human Rights are ………….. rights.
- The State Human Rights commission was formed on ……………
- Article 24 of Indian Constitution prohibits ……………
- United Nations Organisation was established in the year ……………
Answer:
- Right
- Fundamental rights
- 17th April 1997
- Child Labor
- 24th October 1945
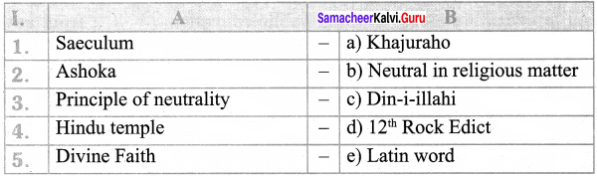
III. Match the following:
- Eleanor Roosevelt – world’s first charter of human rights
- The Cyrus Cylinder – 1997
- Eve Teasing Act – freedom from slavery
- Child help line – Human Rights Commission
- Civil right – right to vote
- Political right – 1098
Answer:
- Eleanor Roosevelt – Human Rights Commission
- The Cyrus Cylinder – world’s first charter of human rights
- Eve Teasing Act – 1997
- Child help line – 1098
- Civil right – freedom from slavery
- Political right – right to vote
IV. State True or False
- Human rights and civil rights are the same.
- Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen was proclaimed in India.
- The Human Right Act of 1993 provides the creation of National Human Rights Commission.
- National Human Rights Commission has empowered to give punishment to the victims.
- ………….. was empowered to setup commission for the promotion of Human rights at National and State level.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- True
- ECOSOC
V. Consider the following statements and tick the appropriate answer
Question 1.
Find the wrong statement
(a) National Human Rights Commission is a statutory body.
(b) National Human Rights Commission is a constitutional body.
(c) National Human Rights Commission is an independent body.
(d) National Human Rights Commission is a multilateral institution.
Answer:
(b) National Human Rights Commission is a constitutional body.
Question 2.
Which of the following statement is not correct about the National Human Rights Commission?
(a) It was established in 1993.
(b) In the cases of human rights violation, the Commission has no rights to punish the culprit.
(c) The Chairperson and members are of this Commission are appointed by the Supreme Court of India.
(d) The Commission sends its annual report to the Central Government and State Governments.
Answer:
(c) The Chairperson and members are of this Commission are appointed by the Supreme Court of India.
Question 3.
Assertion (A) : Human Rights day is observed on 10th December
Reason (R) : It commemorates Eleanor Roosevelt’s birthday.
(a) A is correct but R does not explain A
(b) A is correct but R explains A
(c) A and R are correct
(d) A and R are Wrong
Answer:
(a) A is correct but R does not explain A
Question 4.
Consider the following statements
- The State Human Rights Commission is a multi-member body.
- The State Human Rights Commission consists of a chairperson and three members.
Which of the statements given above is /are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both a and b
(d) None
Answer:
(a) 1 only
VI. Answer the following in one or two sentences
Question 1.
What are Human Rights?
Answer:
- Human rights are rights inherent to all human beings regardless of race, sex, nationality, ethnicity, language and religion.
- Human rights include freedom from slavery and torture, freedom of opinion and expression and fair trial. The right to life work and education.
Question 2.
Bring out the importance of UDHR.
Answer:
- One of the greatest achievements of United Nations is the creation of human rights law.
- To advance this goal, the UN established a Commission of Human Rights.
- it is also known as modem International Magna Carta of Human Rights.
- It is the most translated document in the world.
Question 3.
What does Article 45 of Indian Constitution provide?
Answer:
Article 45 of Indian Constitution provides that the state shall endeavor to provide early childhood care and education for all children until they complete the age of six years.
Question 4.
Write about Right to Education Act.
Answer:
Article 21A provides that the state shall provide free and compulsory education to all children aged six to fourteen years.
Question 5.
State any three legislation passed to safeguard the welfare of women.
Answer:
- The Hindu Widow Remarriage Act 1856
- The Hindu Marriage Act 1955.
- The Hindu Succession Act 1956.
Question 6.
Mention some of the political rights.
Answer:
The freedom of expression, and peaceful assembly, the right to take part in the government of one’s country, the right to vote, the freedom of speech and obtain information.
Question 7.
Name the five primary categories of Human Rights.
Answer:
- Civil Rights
- Political Rights
- Social Rights
- Economic Rights
- Cultural Rights
VII. Answer the following in detail:
Question 1.
Distinguish between Human rights and Civil rights.
Answer:
Human Rights:
- Human Rights belong to everyone, everywhere, regardless of nationality, sexuality, gender, race, religion or age.
- Human rights are considered universal to all human beings and universsal in all countries.
- No nation may rightfully deprive human rights to an individual.
- Human rights are basic rights inherent with birth.
Civil Rights:
- Civil rights are those rights that one enjoys by virtue of citizenship in a particular nation or state.
- Civil rights vary greatly from country to the country’s or government to government. It is related to the constitution.
- Different nations can grant or deny different civil rights and liberties.
- Civil rights are creation of the society.
Question 2.
Describe any five basic characteristics of Human rights.
Answer:
- Inherent – they are not granted by any person or authority.
- Fund ntal – they are fundamental rights because without them, the life and dignity of man will be meaningless.
- Inalienable – they cannot be taken away from the individual.
- Indivisible – they can’t be denied even when other rights have already been enjoyed.
- Universal – they are universal. They apply irrespective of one’s origin or status. They are enforceable without national border.
Question 3.
What are the measures taken by the government to protect the children?
Answer:
- The child is considered as an important national asset.
- The future of a nation depends on how its children mature and develop.
- So protection of children from all kinds of exploitation and abuses has become the main objective of our society.
- There are laws in India protecting the rights of the children.
(a) Right to Education Act:
Article 21A provides that the state shall provide free and compulsory education to all children aged six to fourteen years.
(b) The Child Labour Act (Prohibition and Regulation Act 1986):
It provides no child who has not completed 15 years of age can be employed.
(c) The Juvenile Justice Act 2000 (Care and Protection of Children):
This Act tries to protect children deprived of adequate care and to reform the children by adopting child friendly approach.
(d) POCSO A I 2012:
Protection of children from Sexual Offences Act regards the best interest of the child as being paramount importance in’every state.
VIII. HOTs
Question 1.
To whom does the Universal Declaration of Human Rights apply? Why is it important to you?
Answer:
To each individual, regardless of gender, race, religion or cultural background. Because it protects and promotes your individual rights.
IX Project and Activity
Question 1.
Make a list of 10 rights that you enjoy, and the responsibilities that you have.
Answer:
Rights :
- Right to life
- Right to family life
- Right to education
- Right to personal freedom
- Right to religious freedom
- Right to freedom of movement
- Freedom of press
- Right to equality
- Right to justice
- Freedom to form associations
Responsibilities:
- Support and defend the constitution
- Stay informed of the issues affecting your community.
- Participate in the democratic process.
- Respect and obey federal, state and local laws.
- Respect the rights, beliefs, and opinion of others.
- Participate in your local community.
- Serve on a jury when called upon.
- Defend the country if the need should arise.
- Pay income and other taxes honestly and on time, to federal, state and local authorities.
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Civics Human Rights and UNO Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
After the ……………. war, UNO has taken several measures to protect the human rights.
(a) First world
(b) Second world
(c) Third world
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Second world
Question 2.
In ………….. women from all over the world gathered at Beijing.
(a) 1994
(b) 1995
(c) 1999
(d) 1996
Answer:
(b) 1995
Question 3.
The ………….. commission was constituted in 1993.
(a) State Human Rights
(b) Local Human Rights
(c) National Human Rights
(d) Union Human Rights
Answer:
(c) National Human Rights
Question 4.
The ………….. declared 1979 as the International year of women.
(a) UNO
(b) UNESCO
(c) UDHRC
(d) SHRC
Answer:
(a) UNO
Question 5.
………….. is celeberated on 10th December every year.
(a) Valentine’s day
(b) Human Freedom Day
(c) Human Rights Day
(d) World Environment Day
Answer:
(c) Human Rights Day
Question 6.
………….. of Human Rights contain 30 Articles.
(a) Universal Declaration
(b) National Declaration
(c) State Declaration
(d) District Declaration
Answer:
(a) Universal Declaration
Question 7.
The ………….. was formed on 17th April 1997.
(a) Universal Human Rights Commission
(b) State Human Rights Commission
(c) District Human Rights Commission
(d) Local Human Rights Commission
Answer:
(b) State Human Rights Commission
Question 8.
………….. was established in the year 1945.
(a) UNESCO
(b) SHRC
(c) NHRC
(d) UNO
Answer:
(d) UNO
Question 9.
………….. are related to individuals and society.
(a) Human Liberty
(b) Human Rights
(c) Human Freedom
(d) Petition of Right
Answer:
(b) Human Rights
Question 10.
One of the greatest achievements of ………….. is the creation of Human Rights Law.
(a) India
(b) United Kingdom
(c) United Nation
(d) All the above
Answer:
(c) United Nation
Question 11.
Expand form of UDHR …………..
(a) United Declaration of Human Rights
(b) Universal Declaration of Human Rights
(c) Universal Development of Health Rights
(d) Universal Declaration of Health Rights
Answer:
(b) Universal Declaration of Human Rights
Question 12.
UDHR was adopted by the UN General Assemly in ……………
(a) 1948
(b) 1949
(c) 1950
(d) 1947
Answer:
(a) 1948
Question 13.
………….. refers to the basic rights afforded by law of the government to every person.
(a) Human Rights
(b) Freedom Rights
(c) Civil Rights
(d) Fundamental Rights
Answer:
(c) Civil Rights
Question 14.
………….. are exercised in the formation and administration of a government.
(a) Civil rights
(b) Political rights
(c) Social rights
(d) Economic rights
Answer:
(b) Political rights
Question 15.
The civil and Political rights are directly related to ………….. democracy.
(a) modem
(b) classical
(c) tradition
(d) all the above
Answer:
(a) modern
Question 16.
………….. rights are those rights necessary for an adequate standard of living ncluding the rights in education and health etc.
(a) Economic
(b) Civil
(c) Political
(d) Social
Answer:
(d) Social
Question 17.
The convention on the rights of the Rights of the child was proclaimed by UN on …………..
(a) 20th November 1989
(b) 20th December 1989
(c) 20th October 1989
(d) 20th September 1989
Answer:
(a) 20th November 1989
Question 18.
………….. provides no child who has not completed 15 years of age can be employed.
(a) POCSO Act
(b) Right to Education Act
(c) The Child Labour Act
(d) The Juvenile Justice Act
Answer:
(c) The Child Labour Act
Question 19.
UNO has declared ………….. as International.year of women.
(a) 1979
(b) 1978
(c) 1980
(d) 1961
Answer:
(b) 1978
Question 20.
………….. has declared 1979 as the International year of children.
(a) POCSO
(b) UDHRC
(c) UNO
(d) NHRC
Answer:
(c) UNO
II. Fill in the blanks:
- ………….. are basic rights inherent with birth.
- A ………….. means every human being below the age of 18 years.
- ………….. was adopted by UN General Assembly in 1948.
- In 1995 the …………… world conference of women, held in Beijing.
- Indian Constitution Article 39 (F) provides for …………… to develop in healthy manner.
- ………….. rights includes the rights to life, liberty, freedom from slavery and arbitrary arrest.
- The United Nations Organisation was drafted in …………….
- A set of basic right and freedom has deep roots in ……………. and ……………. countries.
- There are 30 Articles incorporated in the ……………..
- …………….. the great, the first king of Ancient Persia.
- UNO was established on …………….. 1945.
- …………….. during the Second World War made clear that previous efforts to protect body.
- Expand form of ECOSOC ……………
- NHRC is an …………… and …………… body.
- NHRC is Multi member body which consists of a …………… and other members.
- NHRC has ……………… division.
- The State Human Rights Commission of ………….. was formed on 17th April 1997.
- State Human Rights Commission consists of ……………. members including Chairperson.
- The headquarter of NHRC is located at …………….
Answer:
- Human Rights
- Child
- UDHR
- fourth
- Children
- Civil
- 1945
- European and American
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights
- Cyrus
- 24th October
- rocities
- The Economic and Social Council
- Independent statutory and non-constitutional
- Chairperson
- Five
- Tamil Nadu
- three
- New Delhi
III. Match the following:
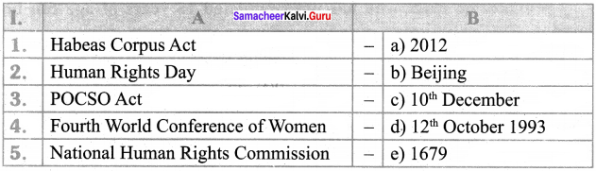
Answer:
- e
- c
- a
- b
- d
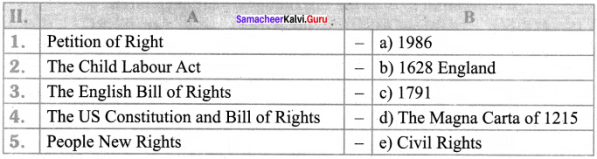
Answer:
- b
- a
- e
- c
- d
IV. State True or False
- Every year 18th November is observed as the Human Rights Day.
- The Headquarters of National Human Rights Commission is situated in Mumbai.
- The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) was adopted by the UN General Assembly in 1948.
- Human Rights are related to individual and society.
- There are 45 Articles incorporated in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
- Indian Constitution Article 39(f) provides for Children to develop in healthy manner.
- 1098 Child Line is India’s First 24 hours free emergency phone service for children in need if assistance.
- The National Human Rights Commission’s Chairperson and other members appointed for 6 years.
- The child is considered as an important national asset.
- UNO has declared 1979 as the international year of women.
- UNO has declared 1978 as international year of women.
Answer:
- False
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
V. Consider the following statements and Tick (✓) the appropriate answer
Question 1.
Find the Correct Statement:
(i) Human Rights are inherent, inalienable, interdependent and indivisible.
(ii) In 1996 the fourth world conference of women, held in Beijing.
(iii) The Dowry Prohibition Act 1961.
(iv) The UNO has declared 1979 as the International Year of Children.
(a) (i), (ii) & (iii) are Correct
(b) (i), (ii) & (iv) are Correct
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv) are Correct
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv) are Correct
Answer:
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv) are Correct
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : Indian Constitution Article 39(f) provides for Children to develop in healthy manner.
Reason (R) : The child is considered as an important national assets.
(a) A is correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) A is correct but R is wrong
(c) A is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A
(d) A is incorrect but R is correct
Answer:
(a) A is correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 3.
Which of the following is correctly matched?
(a) The Eve Teasing Act – 1998
(b) The Hindu Succession Act – 1956
(c) The Hindu Re – Marriage Act – 1958
(d) The Hindu Marriage Act – 1856
Answer:
(b) The Hindu Succession Act – 1956
Question 4.
Which of the following is not correctly matched?
(a) The Dowry Prohibition Act – 1961
(b) The Hindu Marriage Act – 1955
(c) Indecent Representation Act – 1998
(d) Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act – 2005
Answer:
(c) Indecent Representation Act – 1998
VI. Answer in one or two sentences:
Question 1.
List out the Four basic characteristics of Human Rights.
Answer:
- Inherent
- Fundamental
- Indivisible
- Universal
Question 2.
What do you meant by human rights?
Answer:
Human rights belong to everyone, everywhere, regardless of nationality, sexuality, gender, race, religion or age.
Question 3.
What are Civil Rights?
Answer:
Civil Rights are those rights that one enjoys by virtue of citizenship in a particular nation or state.
Question 4.
Write a short note on National Human Rights Commission.
Answer:
- The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) of India was established on 12th October, 1993.
- It is an independent statutory and non – constitutional body.
- Its headquarter is located in New Delhi.
Question 5.
Who are them members of National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)?
Answer:
NHRC is a multi member body which consists of a Chairperson and other members. They are –
- Chairperson (Retired) Chief Justice of India, Judge of Supreme Court, Judge of High Court, 2 members having practical knowledge relating to Human Rights and Deemed members.
- Chairpersons of National Commission for Minorities, Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes and Women.
Question 6.
Write a few lines about the State Human Rights Commission of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
- The State Human Rights of Tamil Nadu was formed on 17th April, 1997.
- It function at the state level.
- It consists of three members including a chairperson.
Question 7.
Expand POCSO and NHRC.
Answer:
- POCSO : Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act.
- NHRC : National Human Rights Commission
Question 8.
Define Child Rights.
Answer:
According to Article 1 of the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child 1989, ‘a child means every human being below the age of eighteen years’.
VII. Answer the following in detail:
Question 1.
Explain the various kinds of Human Rights.
Answer:
These rights are broadly classified into five primary categories. They are as follows:
1. Civil Rights:
The term civil rights refers to the basic rights afforded by laws of the government to every person.
2. Political Rights:
- Political rights are exercised in the formation and administration of a government.
- The civil and political rights are directly related to modem democracy.
- It includes the freedom of expression and peaceful assembly, the right to take part in the government of one’s country, the right to vote, the freedom of speech and obtain information.
3. Social Rights:
- It is necessary for an individual to fully participate in the society.
- Social rights are those rights necessary for an adequate standard of living including the right to education, health care, food, clothing, shelter and social security.
4. Economic Rights:
- The right to participate in an economy that benefits all and to desirable work.
- Economic rights guarantee every person to have condition under which they are able to meed their needs.
- This includes the rights to employment and fair wage, the reasonable limitation of working hours etc.
5. Cultural Rights:
The rights to freedom of religion and to speak the language and to practice the cultural life of the community, the right to share in scientific advancement, and right to the protection of moral and material interest.
Question 2.
Discuss about the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR)
Answer:
1. One of the greatest achievements of United Nations is the creation of human rights law.
2. To advance this goal, the UN established a Commission on Human Rights.
3. The Commission guided by Eleanor Roosevelt’s (Wife of former US President Franklin D Roosevelt) forceful leadership captured the world’s attention.
4. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) was adopted by the UN General Assembly in 1948.
5. It is a milestone document in the history of Human rights.
6. The Declaration was proclaimed by the UN General Assembly in Paris, France on 10th December 1948 (General Assembly Resolution 217A).
7. In remembrance of every year 10th December is observed as the Human rights Day and its regular observance commenced from 1950.
8. It is also known as modem International Magna Carta of Human Rights.
9. Its principles have been incorporated into the Constitutions of most of the (more than 185) nations.
10. DHR has been translated into more than 500 languages.
11. It is the most translated document in the world.