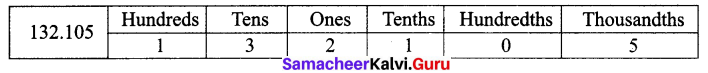
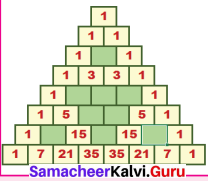
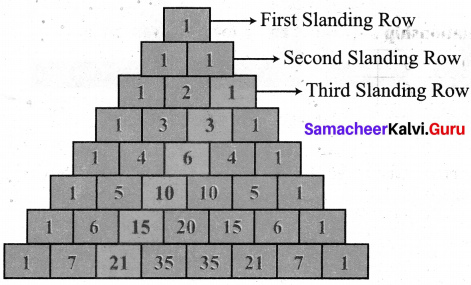
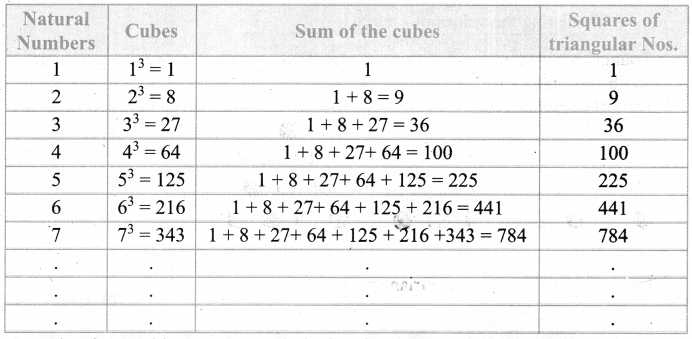
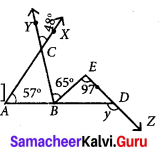
Students can Download Maths Chapter 1 Number System Additional Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Maths Solutions Term 2 Chapter 1 Number System Additional Questions
Additional Questions and Answers
Exercise 1.1
Question 1.
Express as rupees using decimals.
(i) 4 paise
(ii) 4 rupees 4 paise
(iii) 44 rupees 44 paise
(iv) 50 paise
(v) 625 paise
Solution:
We know that 100 paise = ₹ 1
1 paise = ₹ \(\frac { 1 }{ 100 } \)
(i) 4 paise = ₹ 4 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 100 } \) = ₹ \(\frac { 4 }{ 100 } \) = ₹ 0.04
(ii) 4 rupees 4 paise = ₹ 4 + ₹ 0.04 = ₹ 4.04
(iii) 44 rupees 4 paise = ₹ 44 + 44 paise = ₹ 44 + ₹ \(\frac { 44 }{ 100 } \) = ₹ 44 + ₹ 0.44 = ₹ 44.44
(iv) 625 paise = 600 paise + 25 paise = ₹ 6 + ₹ \(\frac { 25 }{ 100 } \) = ₹ 6 + ₹ 0.25 = ₹ 6.25
![]()
Question 2.
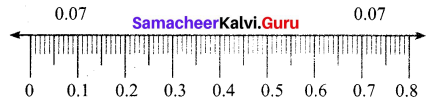
Express 7 cm in metre and kilometer.
Solution:
7 cm = \(\frac { 7 }{ 100 } \) m = 0.07 m
7 cm = \(\frac { 7 }{ 10000 } \) km = 0.00007 km
Question 3.
Write the following decimal numbers in the expanded form.
(i) 30.04
(ii) 3.04
(iii) 300.04
Solution:
(i) 30.04 = 3 × 10 + 0 × 1 + 0 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 } \) + 4 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 100 } \) = 3 × 10 + \(\frac { 4 }{ 100 } \)
(ii) 3.04 = 3 × 1 + 0 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 } \) + 4 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 100 } \) = 3 × 1 + \(\frac { 4 }{ 100 } \)
(iii) 300.04 = 3 × 100 + 0 × 10 + 0 × 1 + 0 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 } \) + 4 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 100 } \) = 3 × 100 + \(\frac { 4 }{ 100 } \) = 3 × 100 + \(\frac { 4 }{ 100 } \)
Question 4.
Write the place value of 2 in the following decimal numbers.
(i) 2.47
(ii) 26.89
(iii) 36.28
Solution:
(i) 2.47 Place value of 2 in 2.47 is ones.
(ii) 26.89 Place value of 2 in 26.89 is Tens.
(iii) 36.28 Place value of 2 in 36.28 is tenths
![]()
Exercise 1.2
Question 1.
Explain the following as fractions.
(i) Ajar containing 3.6 litres of milk.
(ii) A cup containing 9.63 mg of medicine.
Solution:
(i) 3.6 = 3 + \(\frac { 6 }{ 10 } \) = 3 + \(\frac { 3 }{ 5 } \) = 3 \(\frac { 3 }{ 5 } \) litre of milk
(ii) 9.63 = 9 + \(\frac { 6 }{ 10 } \) + \(\frac { 3 }{ 100 } \) = \(\frac { 900+60+3 }{ 100 } \) = \(\frac { 963 }{ 100 } \) mg of medicine
Question 2.
Convert into decimal.
(i) Three hundred three and nine hundredths.
(ii) Six and fifty five thousands
Solution:
(i) Three hundred three and nine hundredths
= 303 + \(\frac { 9 }{ 100 } \) = 303 + 0 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 } \) + 9 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 100 } \) = 303.09
(ii) Six and fifty five thousands
6 + \(\frac { 55 }{ 100 } \) = 6 + \(\frac { 5 }{ 100 } \) + \(\frac { 5 }{ 1000 } \) = 6 + \(\frac { 0 }{ 10 } \) + \(\frac { 5 }{ 100 } \) + \(\frac { 5 }{ 1000 } \) = 6.055
Question 3.
Find the decimal form of (i) 194 + 20 + 3 + \(\frac { 7 }{ 10 } \) + \(\frac { 2 }{ 100 } \)
(ii) 111 + 11 + 1 + \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 } \) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 1000 } \)
Solution:
(i) 194 + 20 + 3 + \(\frac { 7 }{ 10 } \) + \(\frac { 2 }{ 100 } \) = 217 + 7 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 } \) + 2 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 100 } \) = 217.72
(ii) 111 + 11 + 1 + \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 } \) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 1000 } \) = 123 + 1 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 } \) + 0 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 100 } \) + 1 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 1000 } \) = 123.101
![]()
Exercise 1.3
Question 1.
Maya bought 5 kg 300 g bananas and 3 kg 250 kg oranges. Diya bought 4 kg 800 g apples and 4 kg 150 g of mangoes. Who bought more fruits.
Solution:
Total fruits bought by Maya = 5 kg 300 g + 3 kg 250 g = 8 kg 550 g = 8.550 kg
Total fruits Diya bought = 4 kg 800 g + 4 kg 150 g = 8 kg 950 g = 8.950 kg
Comparing the whole number parts, they are equal.
Comparing thet tenths place we get 9 > 5.
∴ 8.950 kg > 8.550 kg
∴ Diya bought more fruits.
Question 2.
Which is greater 28 km or 42.6 km.
Solution:
Comparing the whole number part 42 > 28.
42.6 km is greater than 28 km.
![]()
Exercise 1.4
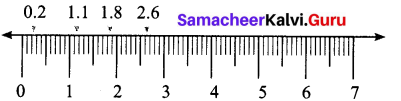
Question 1.
Show that the following numbers in a number line.
(i) 0.2
(ii) 1.8
(iii) 1.1
(iv) 2.6
Solution:
![]()
Question 2.
Write the decimal numbers represented by the points A, B, C, D, E and F.
Solution:
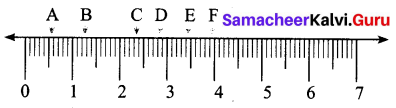
A (0.5); B (1.2); C (2.3); D (2.8); E (3.4); F (3.9)