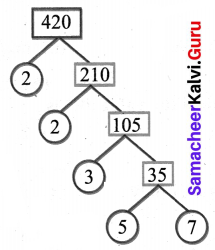
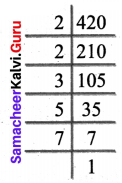
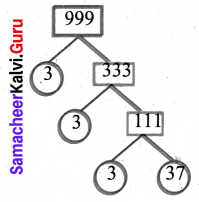
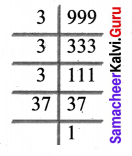
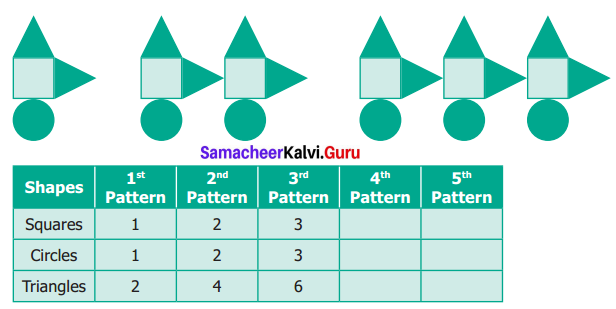
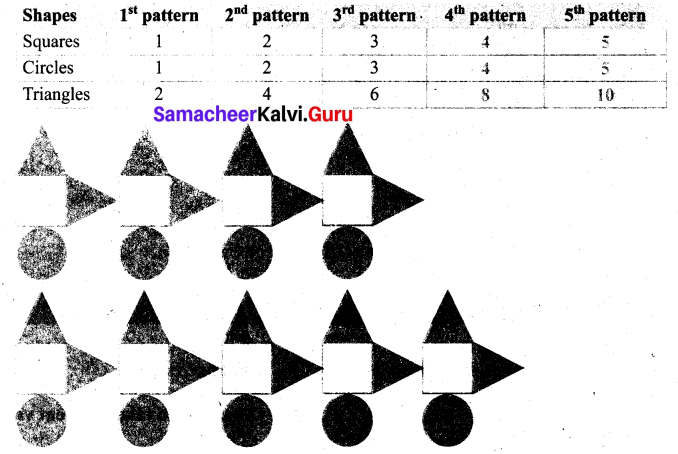
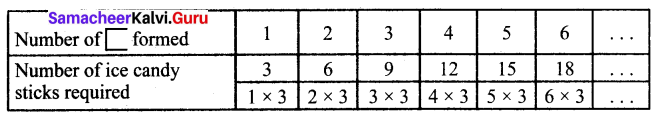
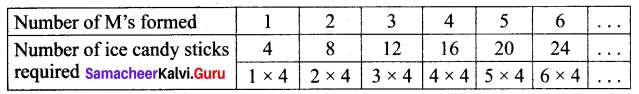
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 3 Chapter 5 Plants in Daily Life
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Plants in Daily Life Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
One of the following birds is an example of plant pollinator
(a) Duck
(b) Parrot
(c) Humming bird
(d) Dove
Answer:
(c) Humming bird
Question 2.
Natural Mosquito repellant is
a. Nutmag
b. Bamboo
c. Ginger
d. Neem
Answer:
d. Neem
Question 3.
Which of the following is not a root?
(a) Potato
(b) Carrot
(c) Radish
(d) Turnip
Answer:
(a) Potato
Question 4.
Which of the following medicinal plants has anticancer properties?
a. Amla
b. Tulasi
c. Turmeric
d. Aloe
Answer:
a. Amla
Question 5.
Which is the national tree of India?
(a) Neem tree
(b) Jack tree
(c) Banyan tree
(d) Mango tree
Answer:
(c) Banyan tree
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks :
- In every year October _______ is celebrated as world food day.
- _______ is an example of textile fibre.
- I am the state tree of Tamilnadu. Who am I _______ ?
- The juice of the leaves of _______ plant relieves cough and bronchitis.
- The edible seeds of leguminous plants are called _______
Answers:
- Sixteenth
- Cotton
- Palm tree
- Tulasi
- Pulses
![]()
III. True or False – If False, give the correct answer :
Question 1.
Plants grown for decorative purposes are called as softwood.
Answer:
False. Plants grown for decorative purposes are called Ornamental plants.
Question 2.
Silkworm eats mulberry leaves.
Answer:
True.
Question 3.
Cauliflower is used for ornamental purpose.
Answer:
False. Jasmine is used for ornamental purpose.
Question 4.
Cotton cloth is not suitable for summer season.
Answer:
False. Cotton cloth is suitable for summer season.
Question 5.
Sugarcane is used as bio fuel.
Answer:
True.
![]()
IV. Match the following :
Question 1.
- Fibre yielding plant – Chloramine
- Hardwood – Spice
- Neem – Hemp
- Clove – Cereals
- Millet – Teakwood
Answer:
- Fibre yielding plant – Hemp
- Hardwood – Teakwood
- Neem – Chloramine
- Clove – Spice
- Millet – Cereals
![]()
V. Analogy :
Question 1.
mango : fruit:: maize : _______
Answer:
cereals.
Question 2.
coconut: fibre :: rose : _______
Answer:
ornamental.
Question 3.
Bees: Polinate insect:: earthworms : _______
Answer:
Natural manure
![]()
VI. Give Very Short Answer:
Question 1.
What is food?
Answer:
Any nutritious substance that people or animals eat or drink or that plants absorb in order to maintain life and growth is called Food.
Question 2.
What are the medicinal plants?
Answer:
Plants that have ingredients which can be used in drug preparation are known as medicinal plants. (Eg.) Tulsi, Neem etc.
Question 3.
How hardwoods differ from softwoods?
Answer:
Hardwoods:
- Present in angiosperms (flowering plants)
- It is used to prepare furniture, decks, flooring and wooden construction.
- Example: Teak, Jackfruit.
Softwoods:
- Present in gymnosperm (non-flowering plants)
- It is used to produce plywood, wooden boxes, medium-density fibreboard (MDF) and paper making.
- Example: Katampu, Pine
Question 4.
What is spice?
Answer:
Spices are the aromatic parts of tropical plant traditionally used to flavour food. Bark, roots, leaves, flowers or stems of certain plants primarily used for flavouring colouring or preserving food.
(Eg.) roots – vetiver,
leaves – curry leaves
seeds – fenugreek
flower bud – clove
Question 5.
Name any three medicinal plants, which are available in your area?
Answer:
Neem tree, Tulsi tree, Amla tree are the medicinal plants.
Question 6.
What are the uses of timber?
Answer:
- A timer is used in the construction of buildings, making of furniture
- It is used in making fibreboard, paper making.
![]()
VII. Give Short Answer:
Question 1.
What is a symbiotic relationship?
Answer:
- The relationship between animals and plants, benefiting both of them is known as a symbiotic relationship.
- (Eg.) Silkworms – feeding on Mulberry leaves – produce silk fibres.
- Honey bee – feed on pollen and honey of plants – Agents of cross-pollination and form vegetables and fruits along with honey.
Question 2.
Write the uses of neem?
Answer:
- Neem leaf is used for leprosy, eye disorders, intestinal worms, stomach upset, skin ulcer, diseases of heart and blood vessels, fever, diabetes and liver problem.
- Neem flowers can be used to treat intestinal worm.
- Neem oil is rich in vitamin E and fatty acid. It helps to improve skin elasticity.
Question 3.
Name any five plants and their parts that we eat.
Answer:
- Carrot, Beetroot and radish – Taproots
- Potato, Ginger, Turmeric – Underground stem
- Curry leaves, Coriander leaves – Leaves
- Drum stick – Leaves, Unripe fruit and bark.
- Paddy, Wheat, Maize and Ragi – Seeds
![]()
VIII. Answer in detail :
Question 1.
Write short notes on – Timber yielding plants.
Answer:
- The wood needed for the construction of buildings and making of furniture are obtained from certain plants.
- We use wood for these purposes due to their features like durability, stylish finishing and resistance to temperature changes.
- All commercial timbers are classified into two classes as Hardwoods and softwoods based essentially on their structure.
i. Hardwoods:
Hardwoods are angiosperms (flowering plants), the largest group of land plants. High-quality furniture, decks, flooring and wooden construction are being made only using hardwood. Example: Teak, Jackffuit.
ii. Softwoods:
Softwoods come from gymnosperm (non-flowering plants) trees. Certain angiosperms also yield softwood.
Softwoods have a wide range of applications such as making plywood, wooden boxes, medium-density Fibreboard (MDF) and paper making.
Example: Katampu, Pine.
Question 2.
Comment on the importance of plant-animal interaction.
Answer:
Animal – Plant interactions :
- Animals and birds play an important role in spreading seeds of various plants.
- The digestive enzymes in the digestive system of the birds soften the protective layer of the seeds and make it easier to germinate.
- If this natural relationship between animals and plants are affected, it shows its impact on the economy too.
![]()
IX. Questions based on Higher Order Thinking Skills :
Question 1.
Desert does not have water. Why? Give the reason?
Answer:
- Most deserts get less than 10 inches of rainfall each year.
- The evaporation rate is higher than the rainfall.
- In the desert, there is little water available for plants (cactus-like) and other organisms.
- Cactus like plants and animals living in such areas are adapted to save water and to endure drought.
(Eg.) Cactus Camel etc.
Question 2.
Kavitha said, “Palm tree is a tall tree, so it gives hardwood”! Do you agree with her statement (or) not? Explain Why?
Answer:
No. I don’t agree with her statement.
- Palm tree is technically neither hardwood nor softwood.
- It comes from a separate family known as Arecaceae.
- It has significantly different cellular structure from either soft or hardwoods
Question 3.
Look at the diagram given below and answer the following questions,
a. Soil fertility is increased by bacteria. How?

Answer:
Bacteria like Pseudomonas are used to fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil for agriculture. So they increase the soil fertility.
b. Honey bees are essential for the reproduction of the plants. Why?

Answer:
- Bees are the best pollinators. Bright colour of flower, smell and honey attract honey bees.
- The bees go from one flower to another they leave the pollen grains from their legs.
- It results in cross pollination takes place and the formation of vegetable and fruit. So honey bees are essential for the reproduction of the plants.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Plants in Daily Life Intext Activities
Activity 1
Question 1.
Tabulate the names of vegetables, Cereals and pulses you know.
| S.No. | Vegetables | Cereals | Pulses |
| 1. | |||
| 2. | |||
| 3. | |||
| 4. | |||
| 5. |
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students themselves
![]()
Activity 2
Question 1.
How do Rava, Maida, Sago and Vermicelli are made? Discuss with your friends.

Answer:
Activity to be done by the students themselves
Activity 3
Question 1.
Ask your parents about the medicinal uses of plants such as Phylanthus, Vallarai, Black nightshade, Tippili, Vettiver, Thuthuvalai and make a write up. What are the other plants used for medicinal purpose in your area?
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students themselves
![]()
Activity 4
Question 1.
Take a small quantity of cotton swap. Hold in between your thumb and fore finger. Now, gently Start pulling out the cotton, while continuously twisting the Fibres.
Are you able to make a yam?

The process of making yam from Fibres is called Spinning.
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students themselves
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Plants in Daily Life Additional Questions
I. Choose the appropriate answer:
Question 1.
From the earliest time ______ have been the staple food of India.
i. Rice
ii. Millet
iii. Oats
iv. Pulses.
(a) i and ii
(c) i and iv
(b) ii and iii
(d) i and iii
Answer:
(a) i and ii
Question 2.
Rava uppuma is made of
(a) Paddy
(b) Wheat
(c) Millet
(d) Sorghum
Answer:
(b) Wheat
Question 3.
For making rope, fibres are obtained from _______ free.
(a) Neem
(b) Mango
(c) Coconut
(d) Jack fruit
Answer:
(c) Coconut
Question 4.
The wealth of any country largely depends upon its
(a) Educational development
(b) Agricultural development
(c) Industrial development
(d) Political development
Answer:
(b) Agricultural development
Question 5.
________ are the best for pollinations.
(a) Housefly
(b) Mosquito
(c) Birds
(d) Honeybees
Answer:
(d) Honeybees
Question 6.
Carpentry works depend on
(a) Medicinal plants
(b) Fibre plants
c) Ornamental plants
(d) Timber plants
Answer:
(d) Timber plants
Question 7.
We obtain _______ from plants for making tyre, seats etc.
(a) Plastic
(b) Rubber
(c) Pencil
(d) Wood
Answer:
(b) Rubber
Question 8.
Neem coated urea releases _______ gradually and helps the plants.
(a) Oxygen
(b) Carbon
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Sulphur
Answer:
(c) Nitrogen
![]()
II. Fill up the blanks:
- Plants, based on their economic values and uses, may be broadly classified into _______ categories.
- The heartbeat of an Indian kitchen is _______
- We get food from roots is _______
- _______ are secured in Pods.
- India is the _______ largest producer of fruits and vegetables.
- Some medicinal plants like _______ are used to produce medicines.
- For making mattresses _______ is used.
- _______ alone accounts for over 50% of raw jute production.
- Hardwoods are _______ the largest group of land plants.
- To decorate houses we are planting climber plant like _______
- _______ are economically useful for us in silk production.
- _______ are used to fix nitrogen in the soil for agriculture.
- Indian scientists have made a _______ formulation from the Palak to cure Osteoarthritis.
Answers:
- six
- Spices
- Carrot
- Pulses
- Second
- Fungi
- Silk cotton
- West Bengal
- Angiosperms
- Mullai
- Silkworms
- Blue gree algae
- Nano
![]()
III. True or False. If False, give the correct statement:
Question 1.
The useful Hardwoods and Softwoods are given by fibre plants.
Answer:
False. The useful hardwoods and softwoods are given by timber plants.
Question 2.
In the cabbage the edible part is leaves.
Answer:
True.
Question 3.
Spices are aromatic parts of tropical plants traditionally used to flavour the food.
Answer:
True.
Question 4.
Cardamom and black pepper are pulses.
Answer:
False. Cardamom and black pepper are spices.
Question 5.
In turmeric, the Rhizome part is used to help body to fight foreign invaders.
Answer:
True.
Question 6.
The process of making yam from fibres is called yam production.
Answer:
False. The process of making yam from fibres is called spinning.
Question 7.
Hibiscus trees are used to decorate houses.
Answer:
False. Hibiscus shrubs are used to decorate houses.
Question 8.
Plants and algae living in coral reefs are the food for variety of fishes.
Answer:
True.
![]()
IV. Analogy:
Question 1.
Tomato : Vegetable :: Wheat: _______
Answer:
Pulses
Question 2.
Roots as food : Beetroot:: Stem as food : _______
Answer:
Potato
Question 3.
Spices : Cardamom :: Medicinal plant: _______
Answer:
Amla
Question 4.
Protect from scurvy : Amla :: Bronchitis, expectorant: _______
Answer:
Tulsi
Question 5.
Leaf fibres : Agave :: Husk fibres : _______
Answer:
Coconut.
Question 6.
Hardwoods: angiosperm
Soft woods : _______
Answer:
Gymnosperm.
Question 7.
Shrubs : Crape Jasmine :: Climbers : _______
Answer:
Allamanda.
Question 8.
Fix nitrogen in the soil: Pseudomonas :: Produce bio-fuel: _______
Answer:
Jatropha.
![]()
V. Match the following :
A.
| i. | Plants as food | (a) | Curry leaves |
| ii. | Spice yielding plant | (b) | Phylanthus |
| iii. | Medicinal plant | (c) | Paddy |
| iv. | Fibre yeilding plant | (d) | Carnation |
| v. | Ornamental plant | (e) | Coconut |
Answer:
i – c
ii – a
iii – b
iv – e
v – d.
B.
| i. | Root as food | (a) | Yam |
| ii. | Leaves as food | (b) | Banana flower |
| iii. | Stems as food | (c) | Apple |
| iv. | Flowers as food | (d) | Beetroot |
| v. | Fruits as food | (e) | Cabbage |
Answer:
i – d
ii – e
iii – a
iv – b
v – c.
![]()
VI. Give Short Answer:
Question 1.
Define – Economic botany.
Answer:
Economic botany is the study of the relationship between people and plants and the uses of plants in the economy.
Question 2.
Name the plant from which we get cordage or rope?
Answer:
Fibres got from coconut stem, stalk of the compound leaf and husk fibres of the coconut are the sources from which cordage or rope is processed.
Question 3.
Define – Cereals.
Answer:
Cereals are edible components of grain of cultivated grass.
Example : Rice, Wheat, Bajra, Millet.
Question 4.
Why do we consider cotton as cash crop?
Answer:
- Cotton give textile fibres used for making garments or dress materials or fabric.
- 80% cotton is used in making fabrics or cotton mixed fabrics.
- Because of its large scale cultivation, manufacture and industry if is a commercially very important plant. So known as cash crop.
Question 5.
Name some medicinal plants.
Answer:
The medicinal plants are Phyllanthus, Vallarai, Black nightshade, Tippili, Vetiver, Thuthuvalai, Neem and Tulsi.
Question 6.
What are the specialities of Teak Wood?
Answer:
- Teak is a hardwood, durable and strong.
- Teak central wood is deposited with gum, resin oil etc and so strong that it can’t be destroyed by termites and other insects.
- Doors, windows, roof and railway sleeper wood and cots are made out of it.
Question 7.
Classify the Fibre yielding parts based on the plant parts.
Answer:
- Plant Fibres include seed hairs – Cotton.
- Stem Fibres – Flax, jute.
- Leaf Fibres – Agave.
- Husk Fibres – Coconut.
Question 8.
Name some states in which jute crop is grown.
Answer:
Jute crop is grown in seven states – West Bengal, Assam, Odisha, Bihar, UttarPradesh, Tripura and Meghalaya.
Question 9.
Classify the Ornamental plants.
Answer:
- Shrubs – Hibiscus, Crape Jasmine and Crotons
- Climbers – Mullai, Allamanda and Bougainvilleam
- Trees – Golden shower tree, Mandarai, Delonix tree
Question 10.
How pollination takes place by insects?
Answer:
Bright colured flowers, smell and honey attract insects. As the insects go from one flower to another they leave the pollen grains from their body. This results in cross pollination.
Question 11.
Define – Osteoarthritis.
Answer:
Osteoarthritis is a joint disease affecting joints and knee in old age and any age people. Pala spinach is used to cure the disease.
![]()
VII. Answer in detail :
Question 1.
Classify the plants as food with example.
1. Vegetables
2. Cereals
3. Pulses
Plants also give us coffee, tea, sugar and raw materials for oil.
1. Vegetables: We get vegetables from different parts of the plants.
Roots : eg : Beetroot, Carrot.
Leaves : eg : Curry Leaves, Cabbage.
Stems : eg : Potato, Yam.
Flowers : eg : Banana flower, Cauliflower.
Fruits : eg : Amla, Guava.
2. Cereals : Cereals are edible components of grain of cultivated grass.
Example : Rice, Wheat, Bajra, Millet.
3. Pulses : (i) Pulses are edible seeds of plants legume family. Pulses are secured in pods.
(ii) Example : Bengal gram, Green mung bean.
4. Spices : Spices are aromatic parts of tropical plants traditionally used to flavour the food. Spices come from the bark1 or roots of certain plants, leaves, flowers, or stems of plants primarily used for flavoring, coloring or preserving food.
Spices used in India : Following spices are included in a variety of Indian dishes Cardamom, black pepper, curry leaves, fenugreek, fennel, ajwain, bay leaves, cumin, coriander seeds, turmeric, cloves, ginger, nutmeg, and cinnamon.
Question 2.
Give any five medicinal plants and their medicinal use.
Answer:
Here is a list of plants that have the highest medicinal value.
| Plant Name | Parts used | Medicinal use |
| Amla | Fruit | Cure Vitamin “C” deficiency diseases like Scurvy. Improve immunity. |
| Tulsi | Leaves, Seed | Cough, cold, bronchitis, expectorant. |
| Aloe | Leaves | Laxative, wound healing, skin bums and ulcer. |
| Neem | Bark, leaf and seed | Skin diseases |
| Turmeric | Rhizome | Helps body to fight foreign invaders |
![]()
Question 3.
Give other uses of plants.
Answer:
- Maintain soil fertility – Plants maintain soil fertility. Plants like blue green algae and bacteria like Pseudomonas are also extensively used to fix nitrogen in the soil for agriculture.
- Prevent soil erosion – Plants when grown in dense will prevent soil erosion. This is prevented by plants if grown around.
- Bio-fuels – Some plants are also grown for the sake of bio-fules. Plant fuel is less toxic as it does not emit harmful gases and also less expensive. Ex : Jatropha. Even the plant waste is used to generate electricity. Ex : Sugar mills.
- Rubber and Natural Plastic – Natural plastics and rubber are also produced from plants.
- Neem oil coated Urea – Neem coated urea releases nitrogen gradually and helps the plants to absorb maximum nitrogen. It reduces the impact of urea on the environment.