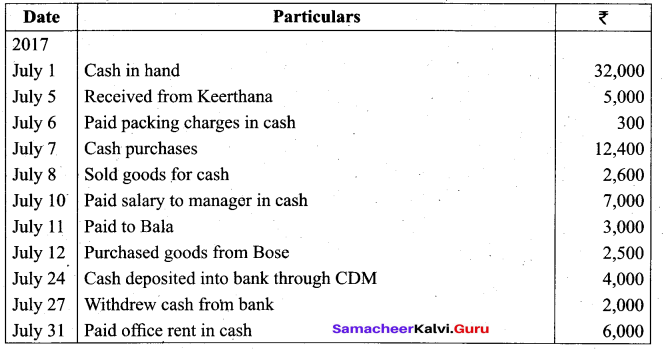
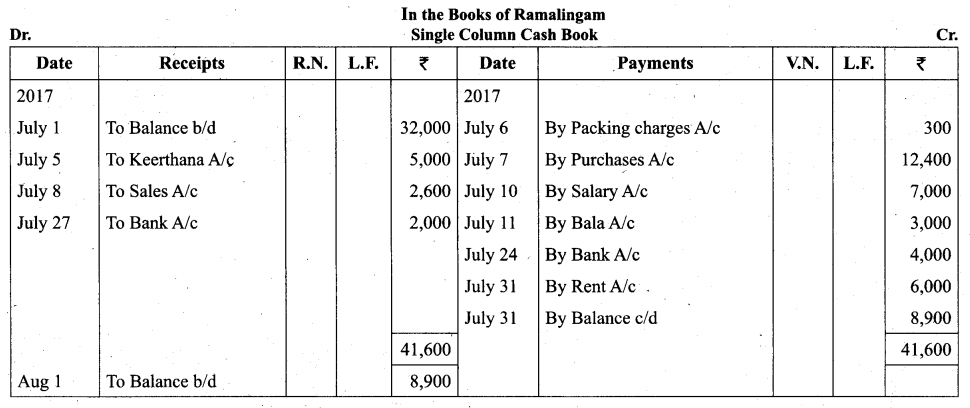
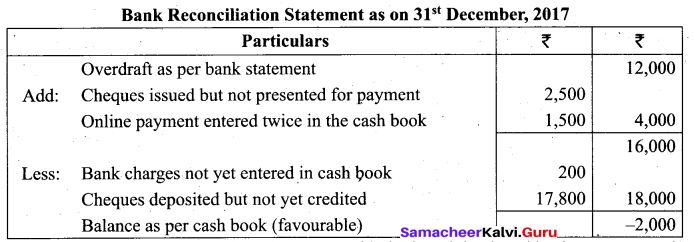
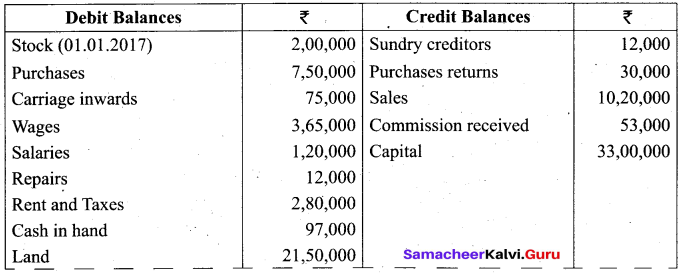
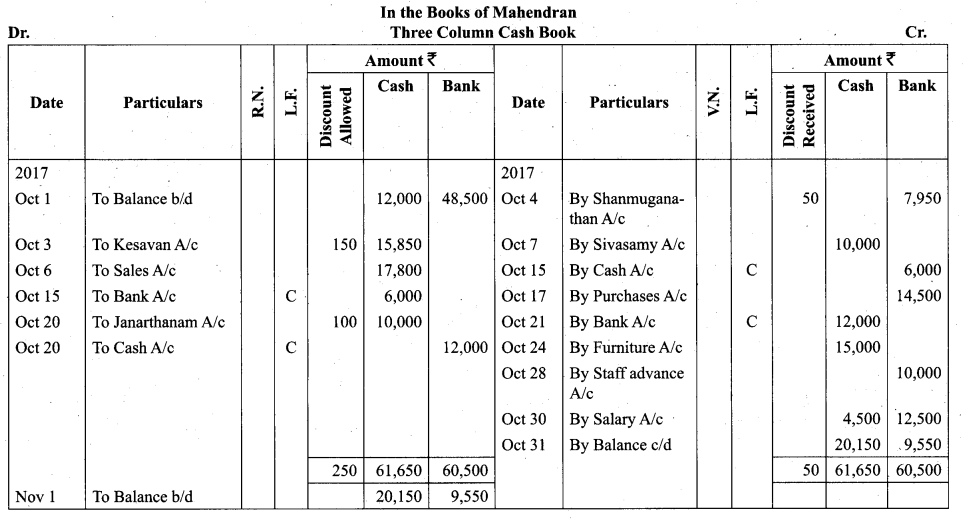
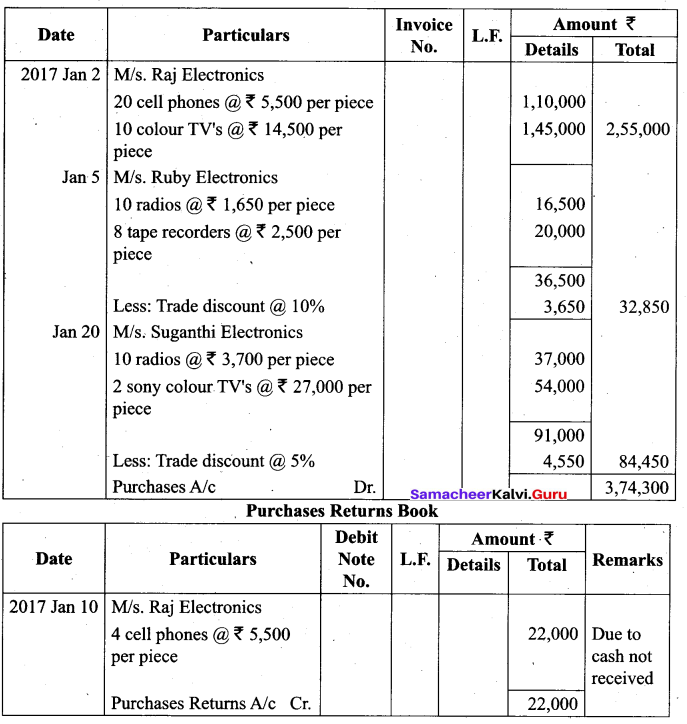
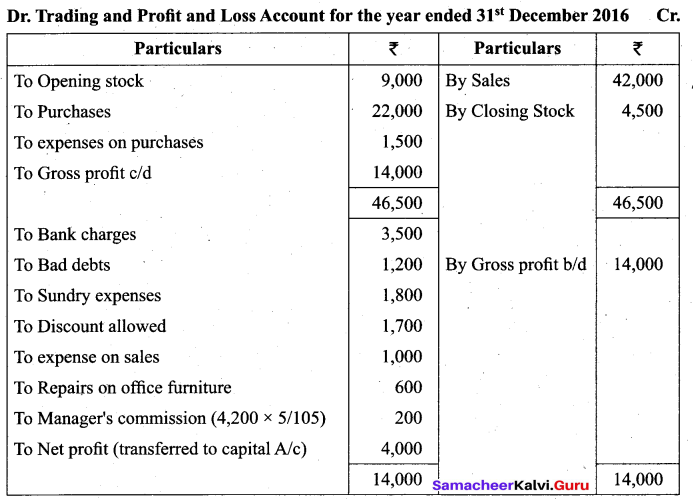
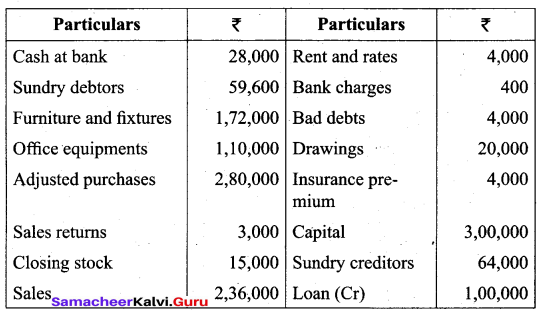
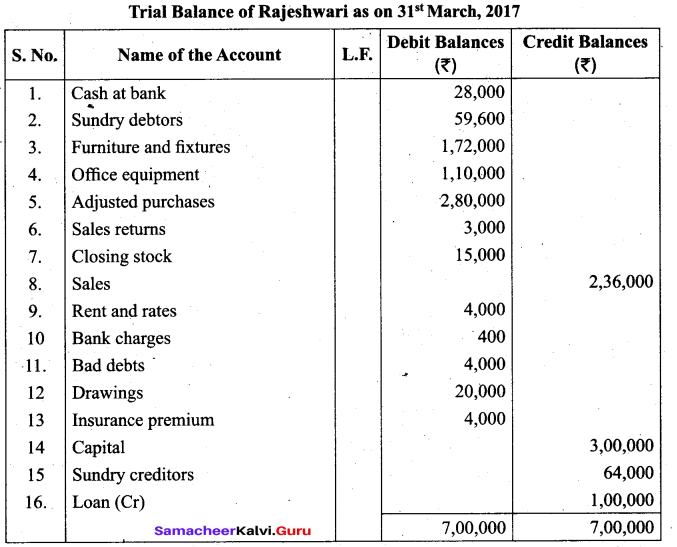
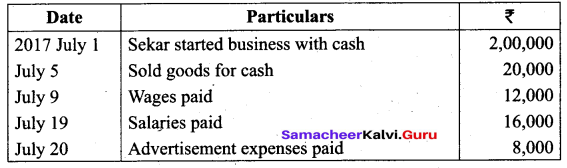
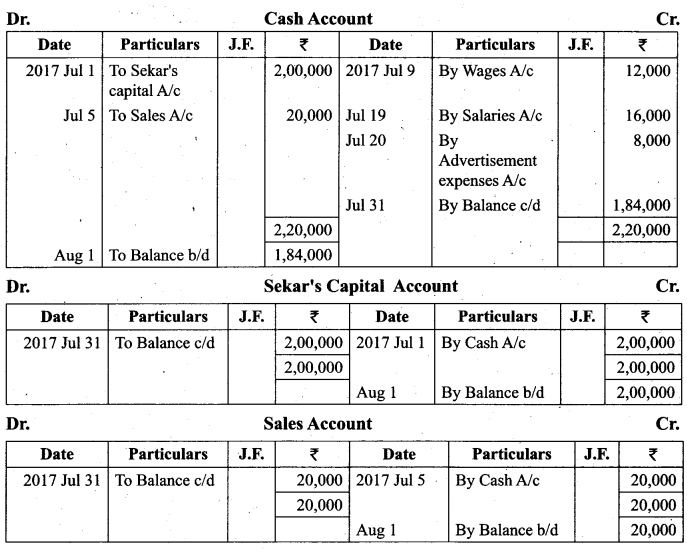
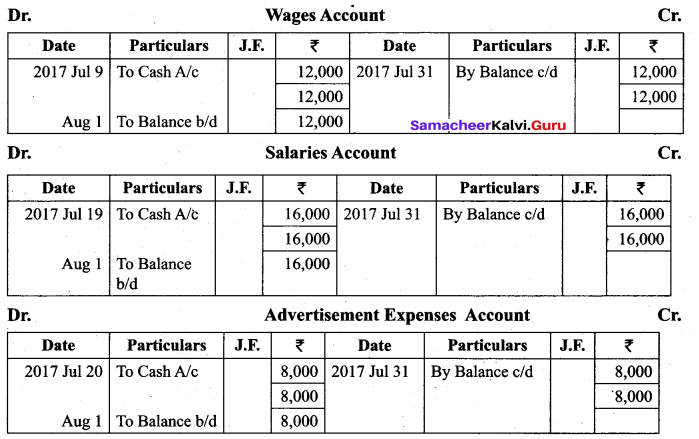
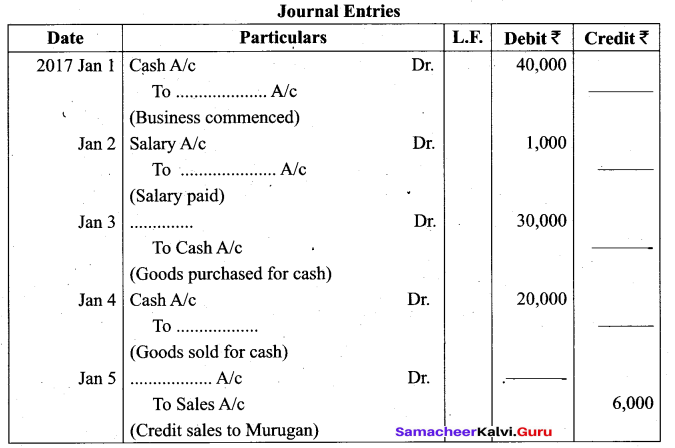
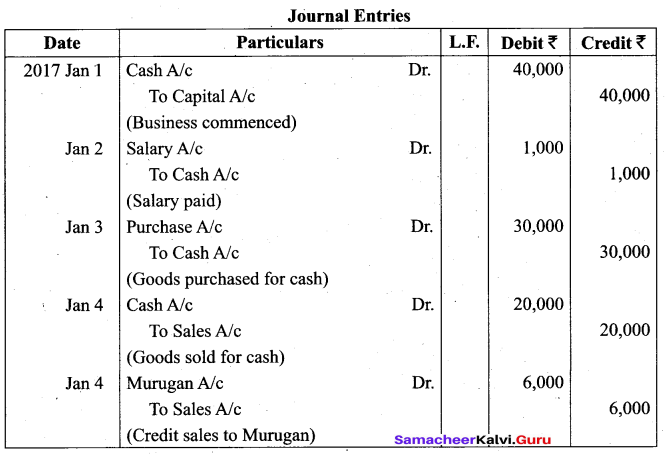
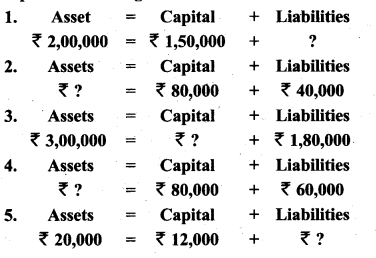
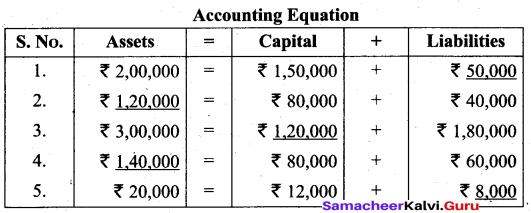
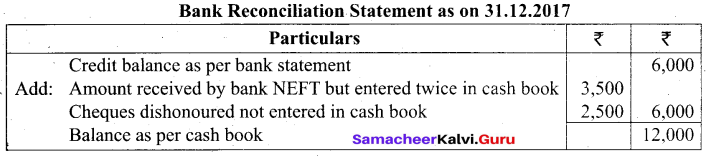
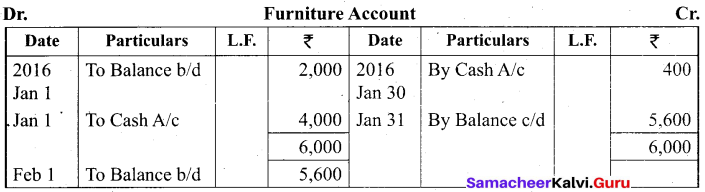
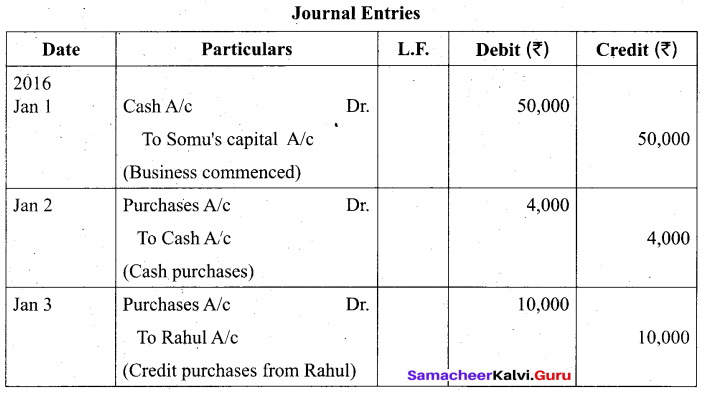
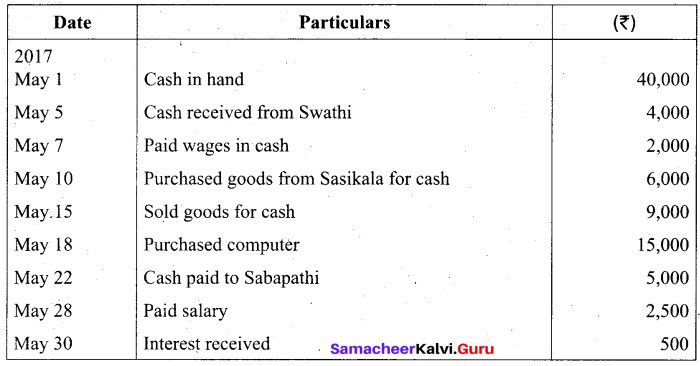
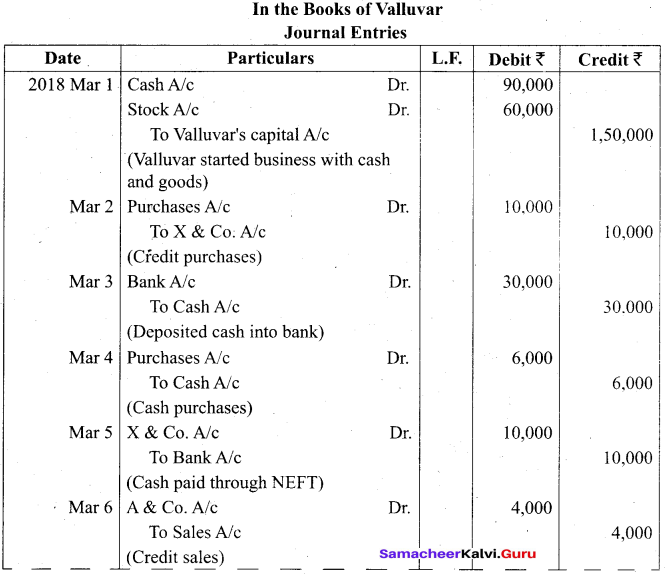
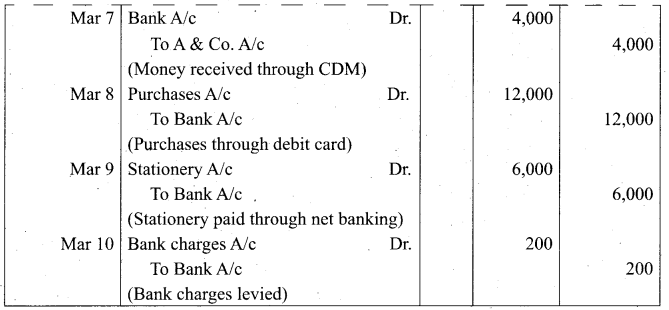
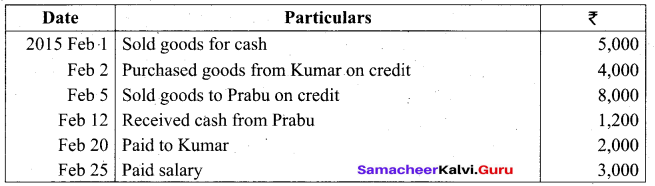
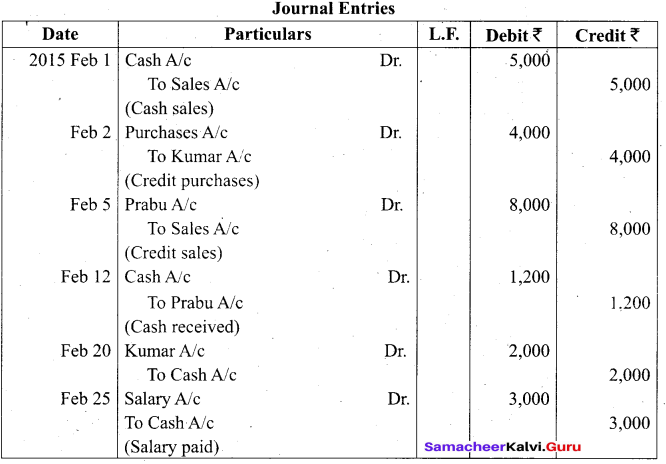
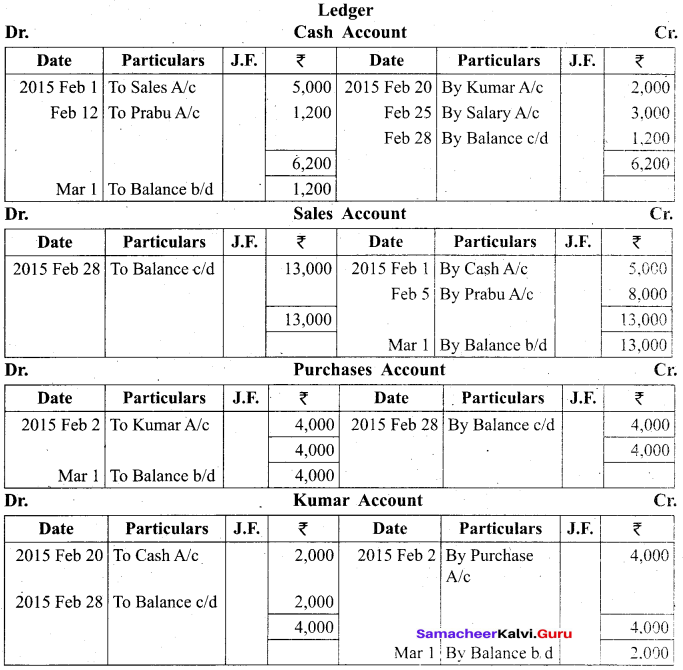
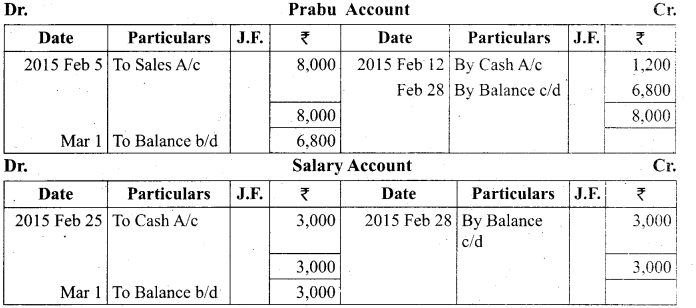
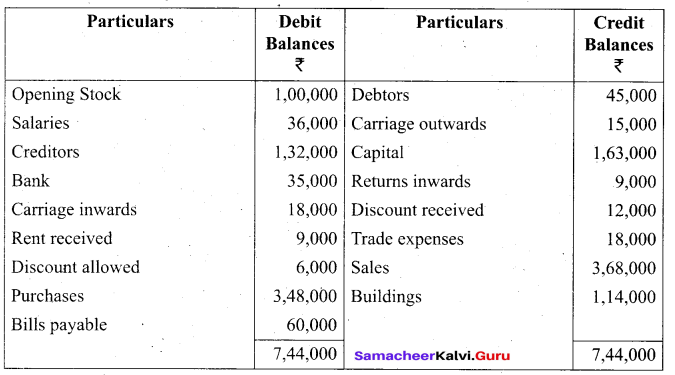
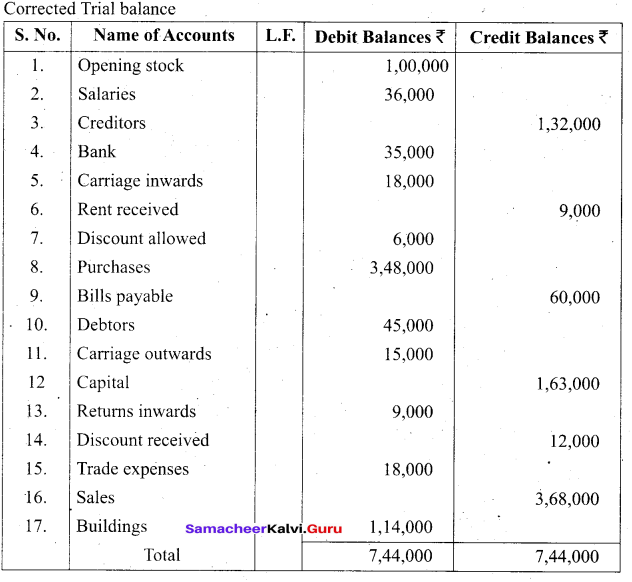
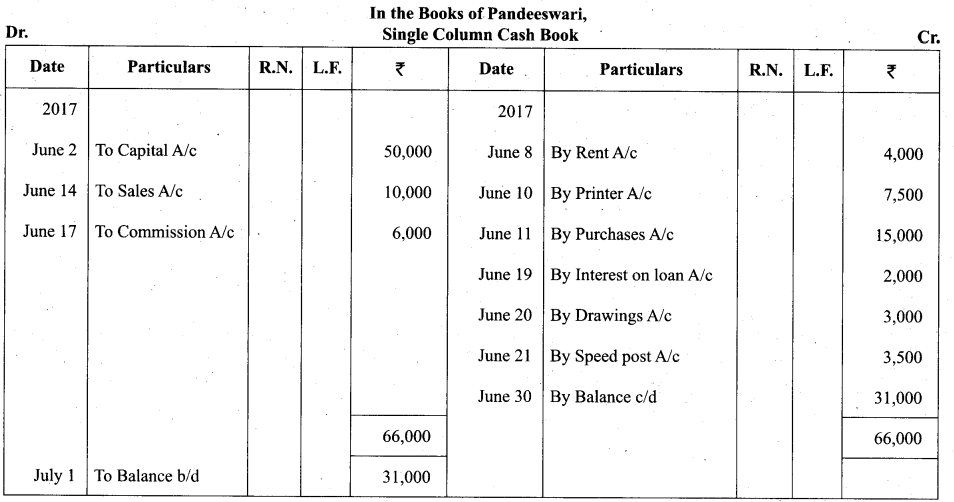
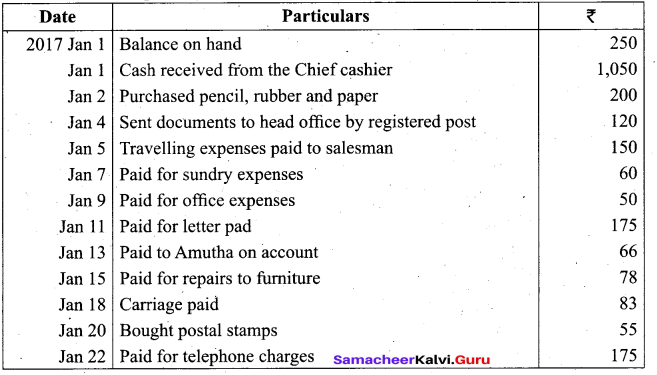
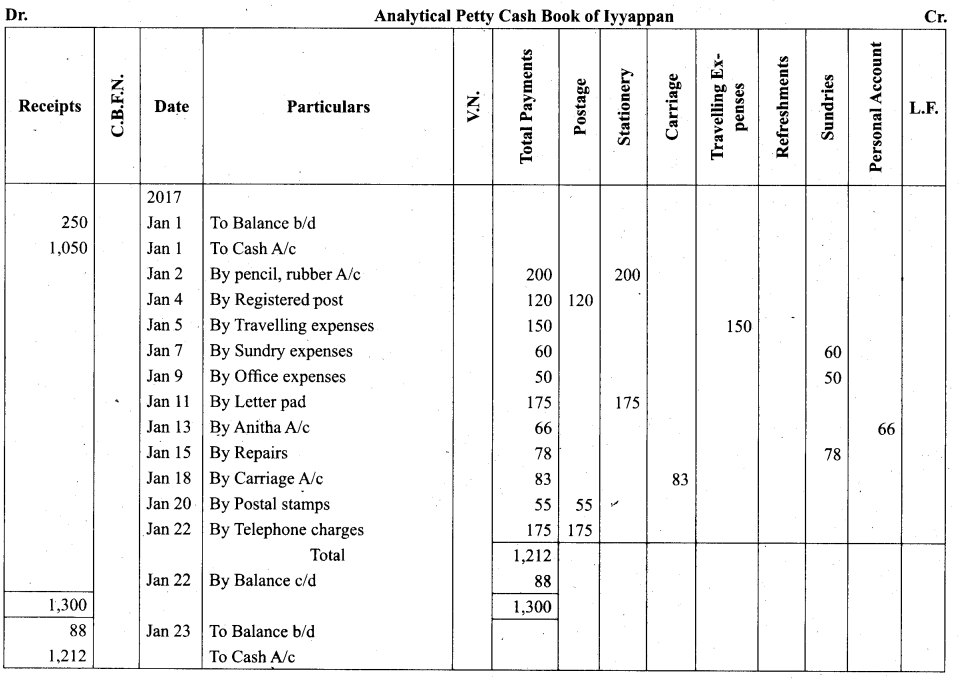
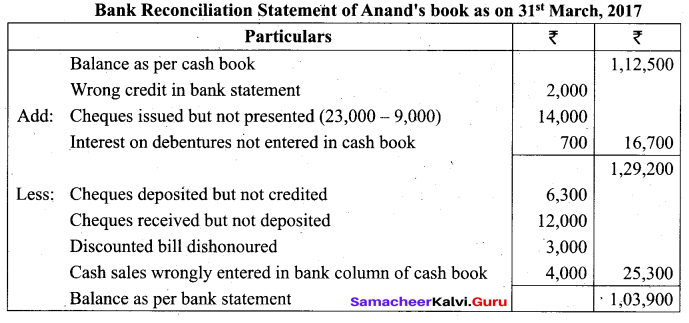
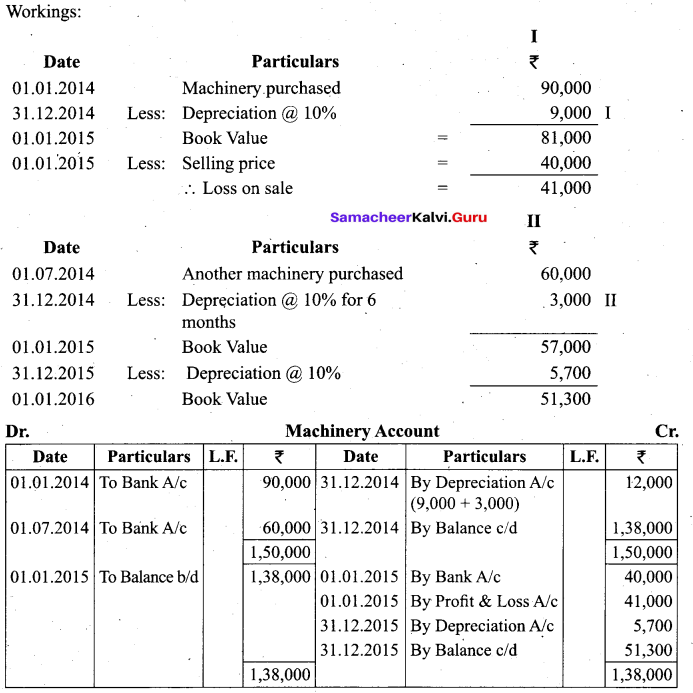
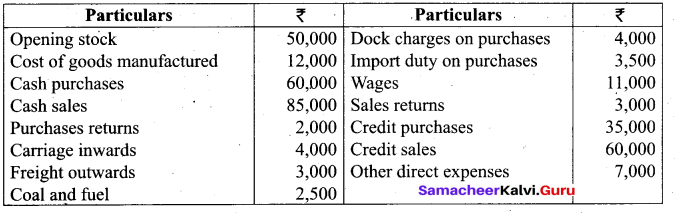
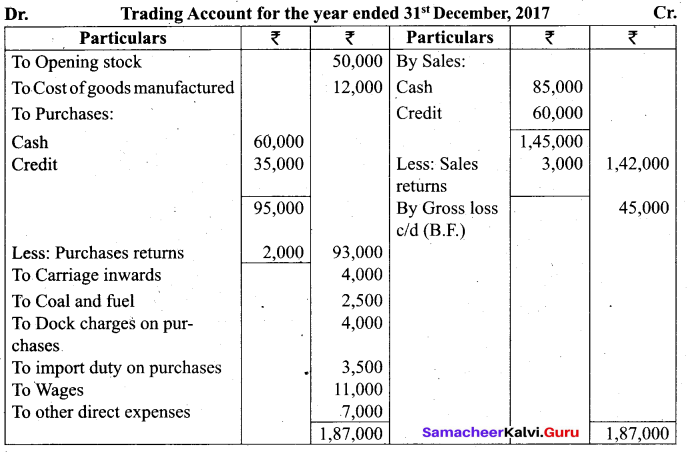
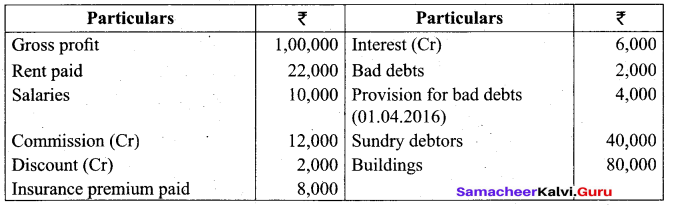
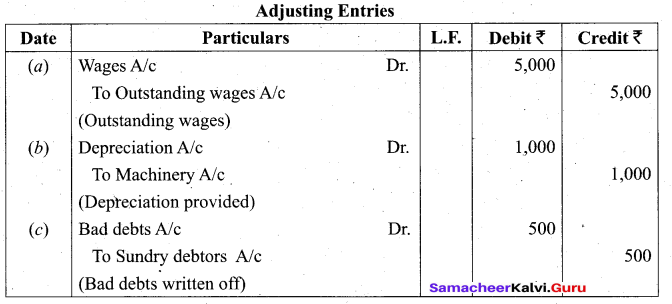
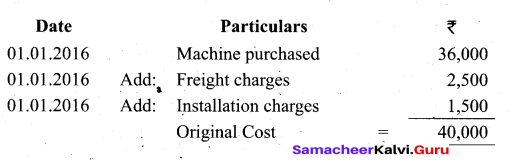
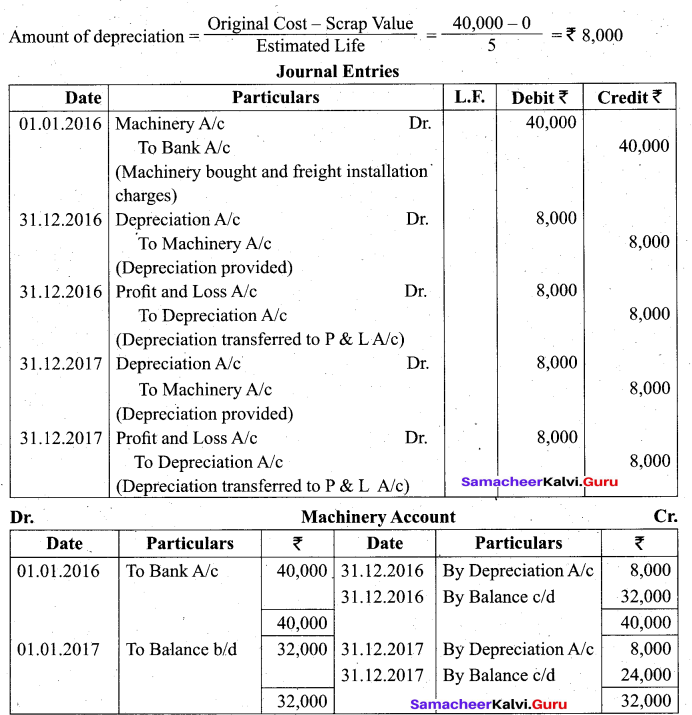
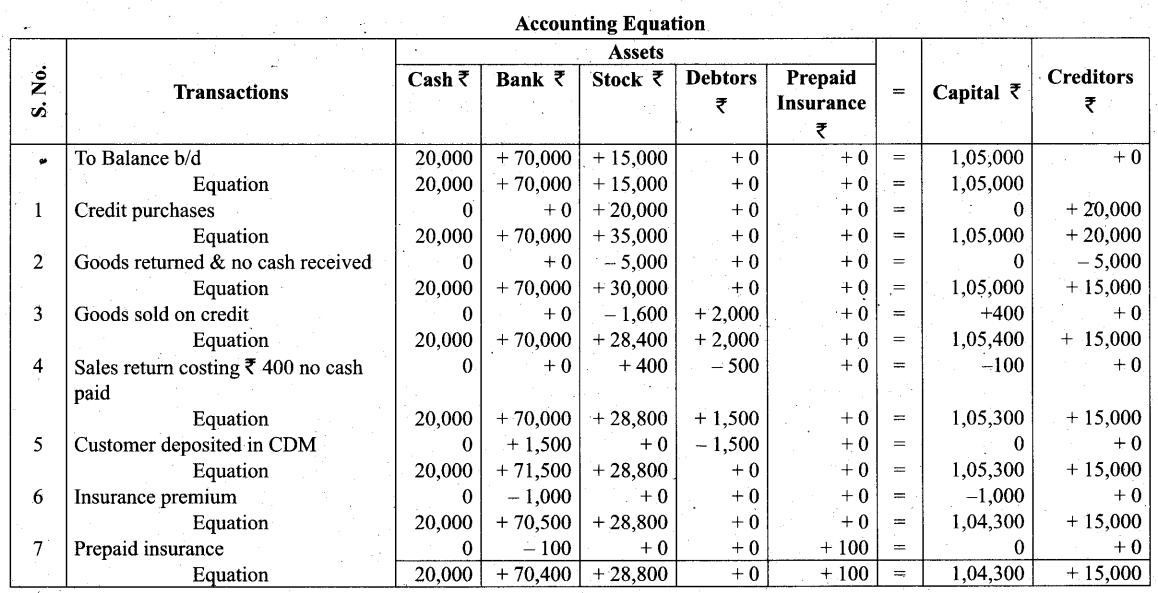
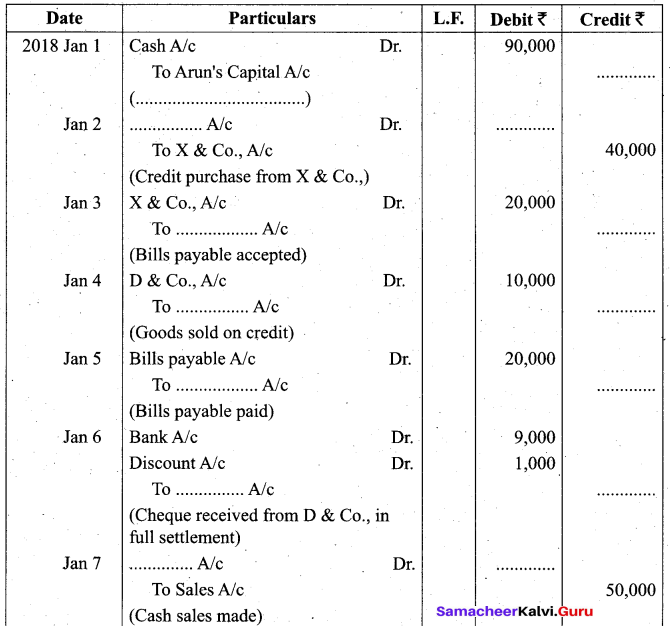
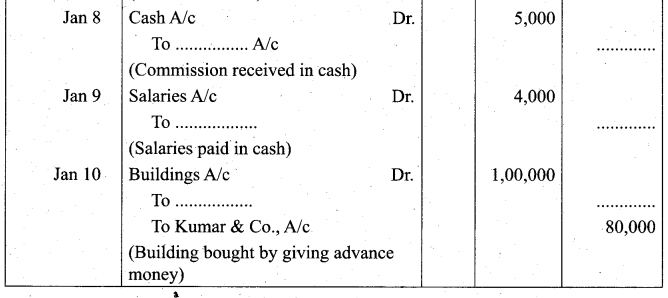
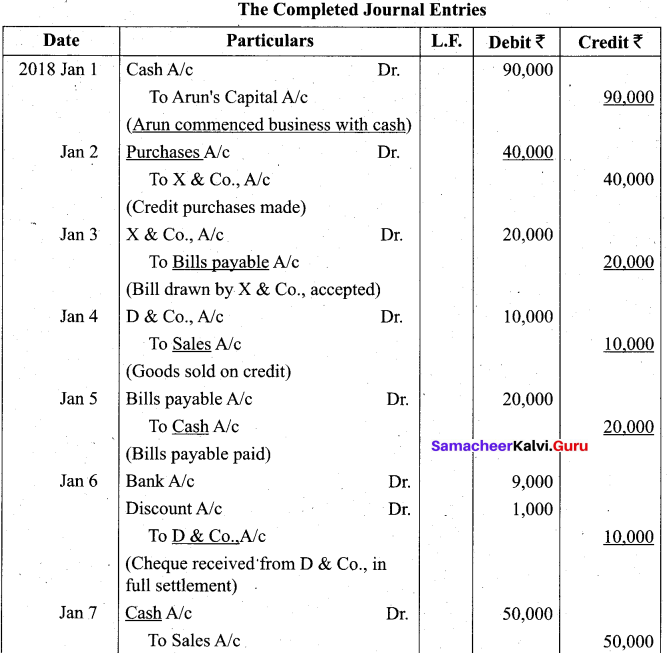
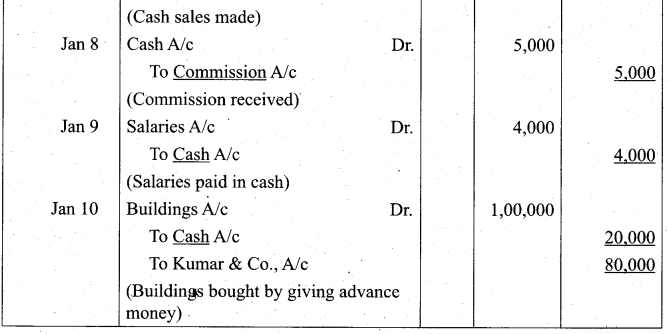
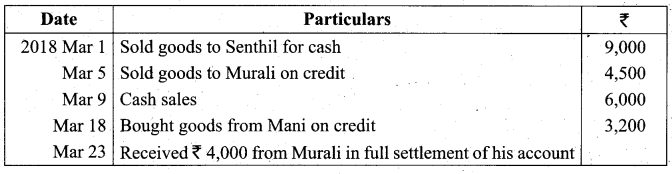
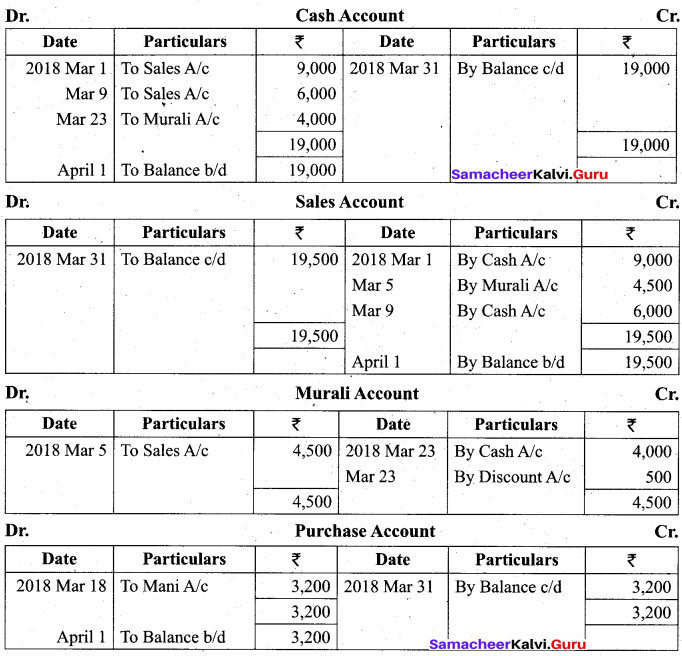
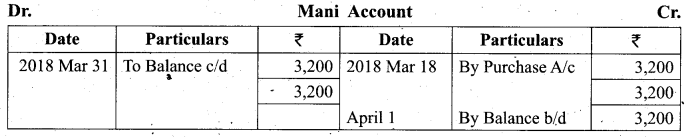
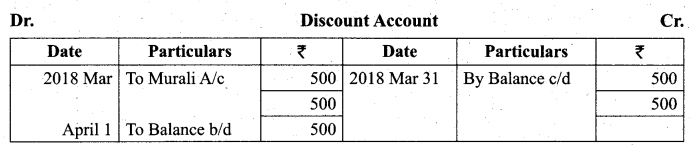
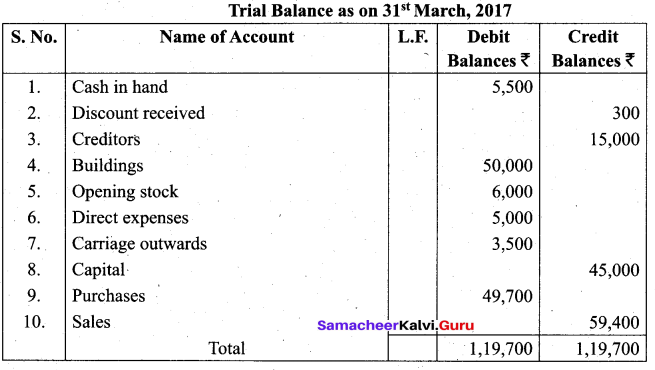
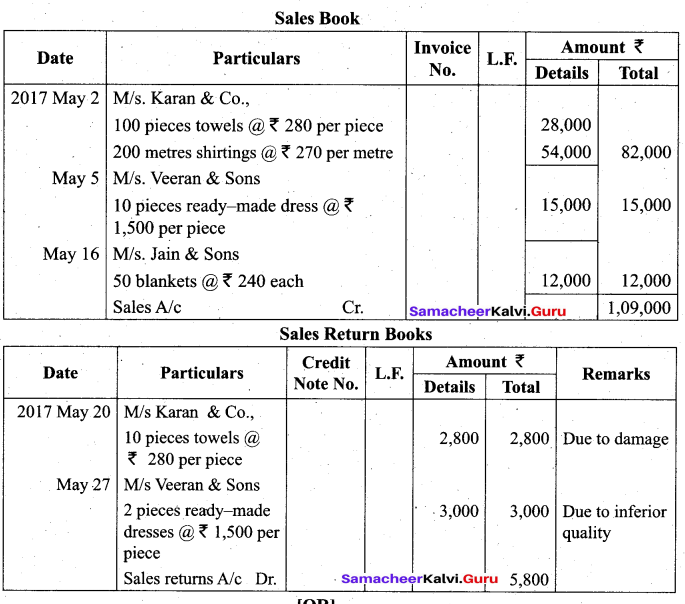
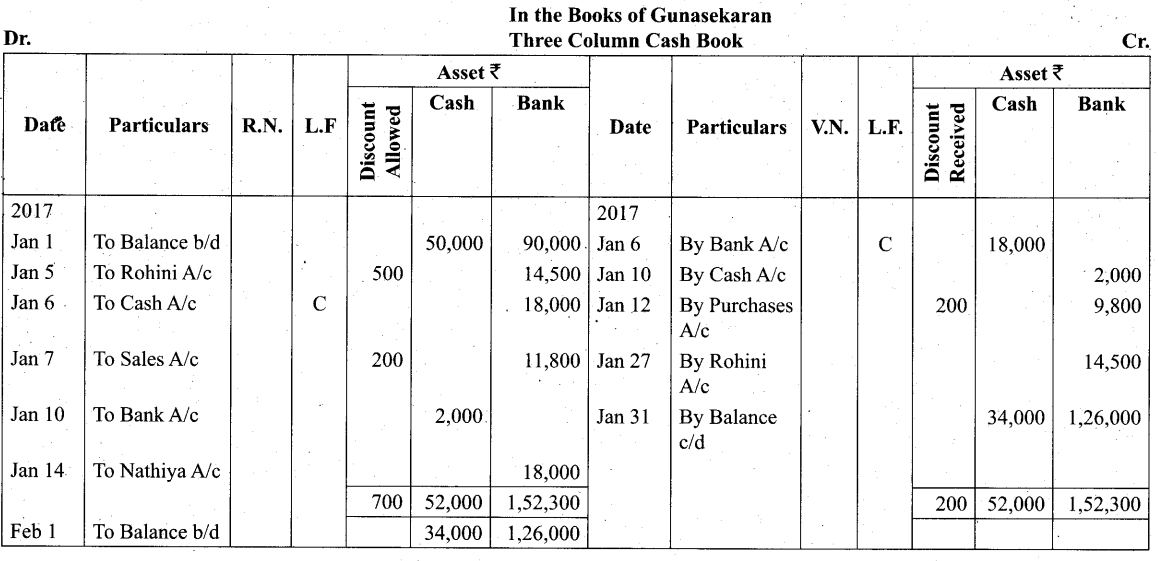
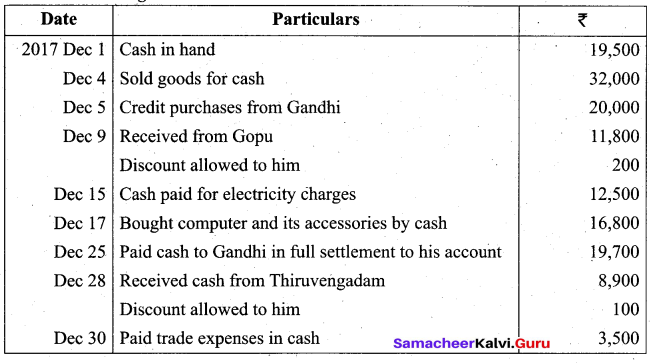
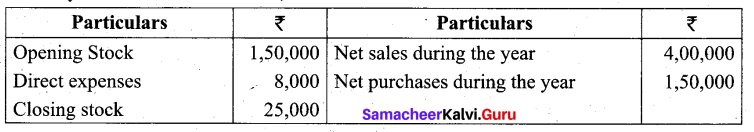
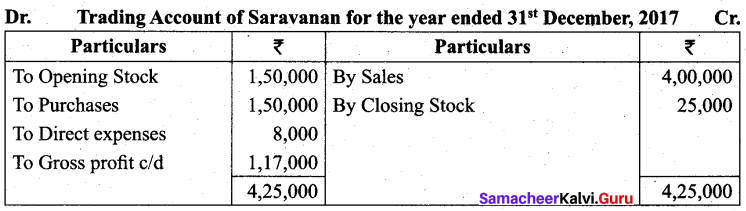
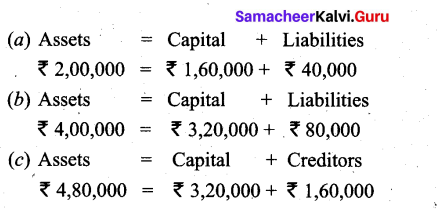
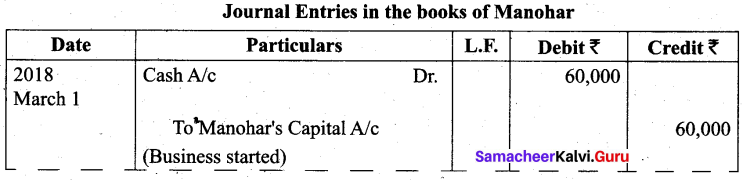
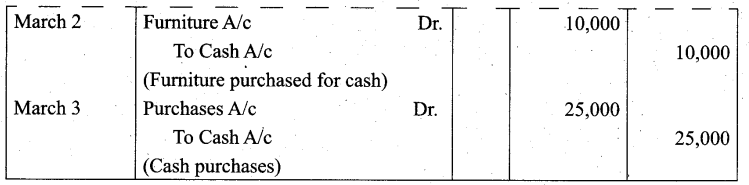
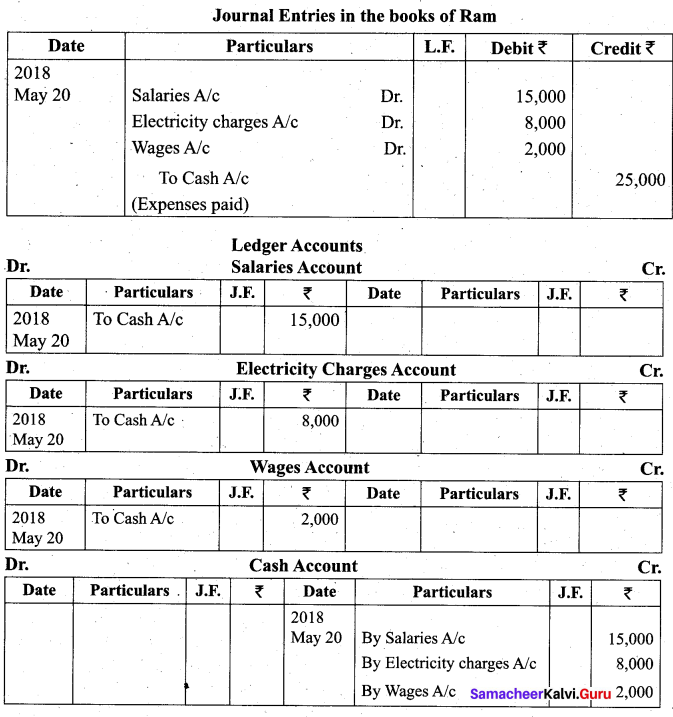
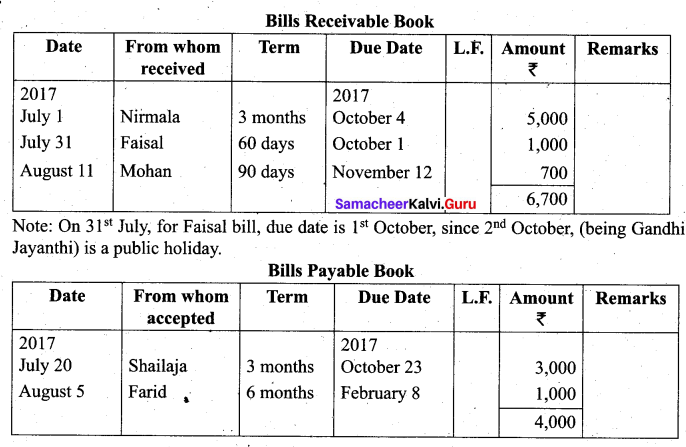
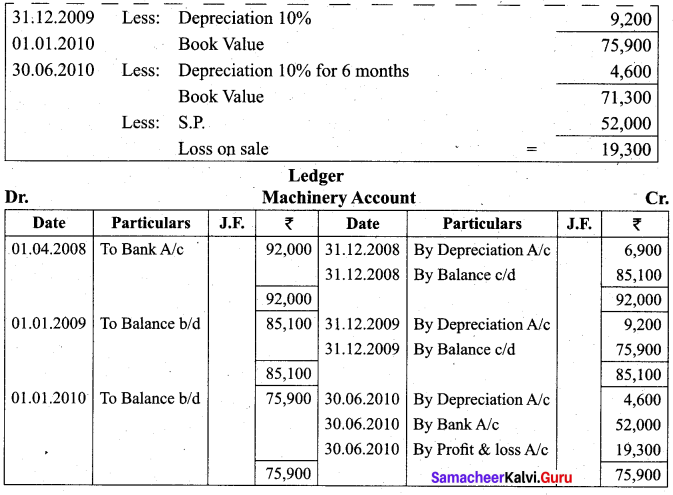
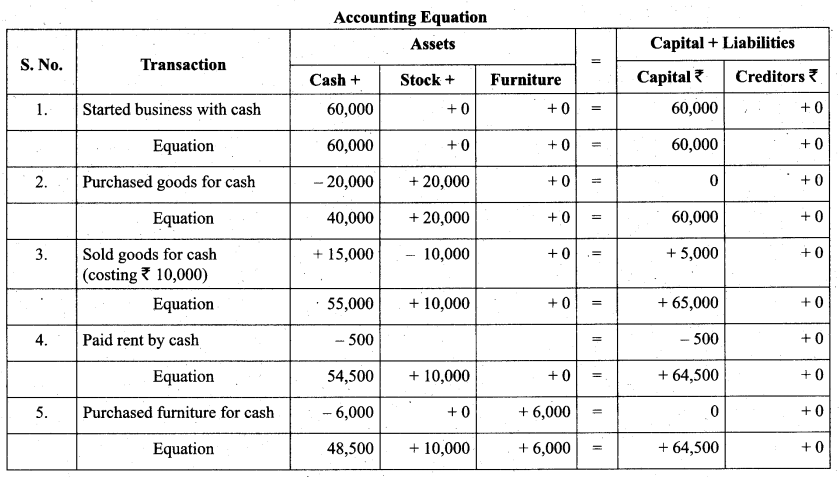
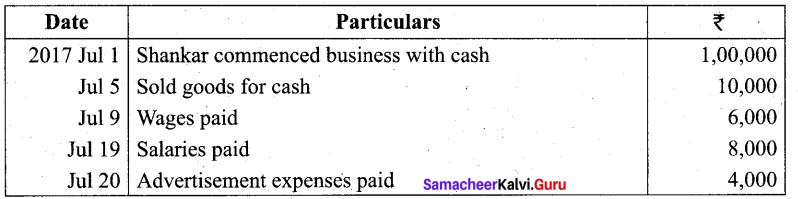
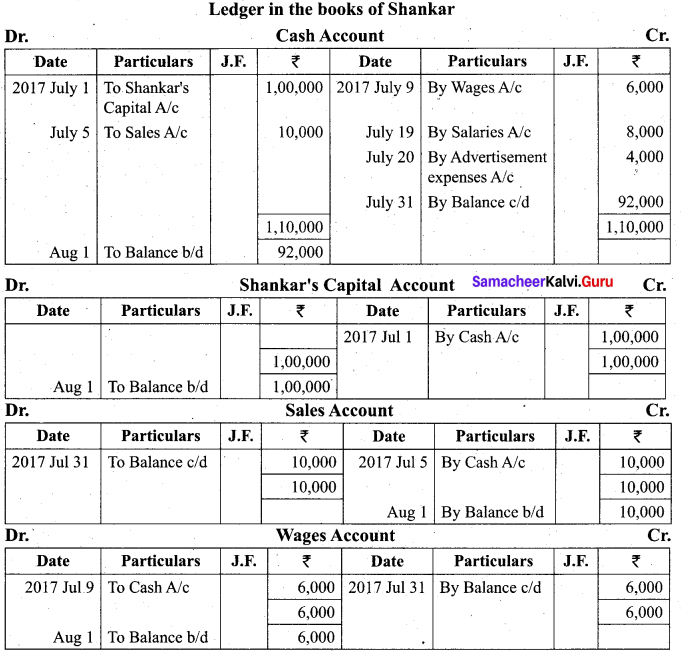
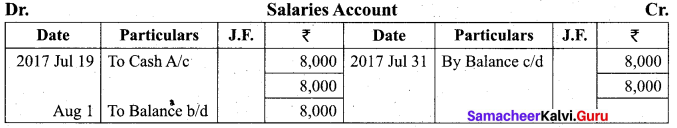
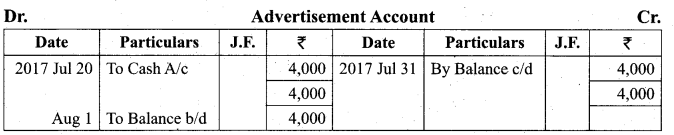
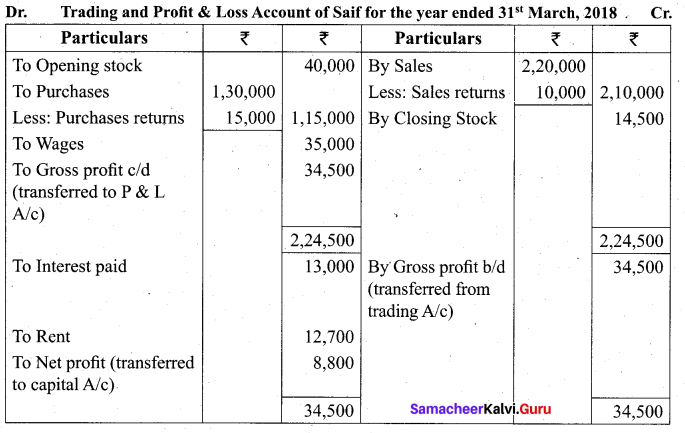
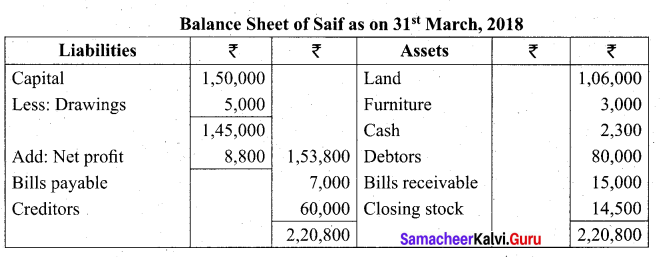
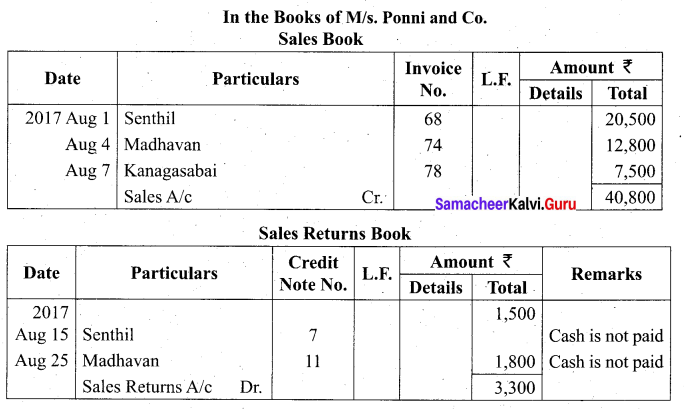
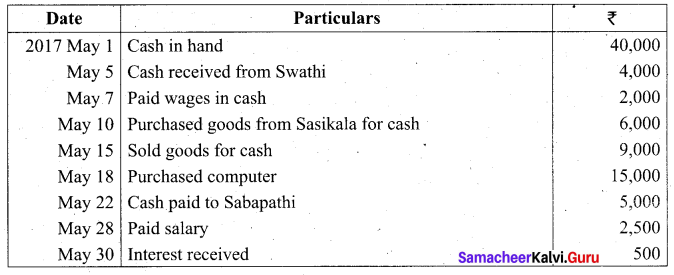
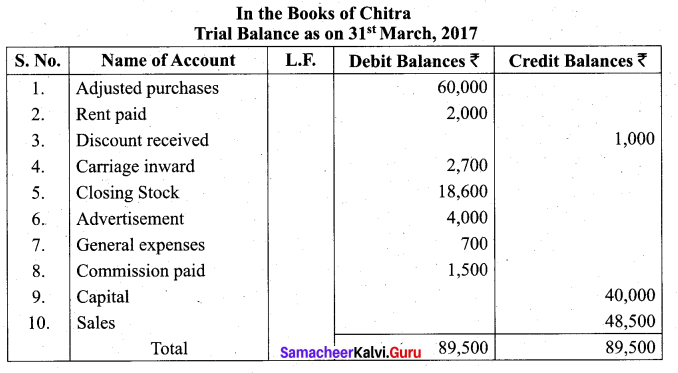
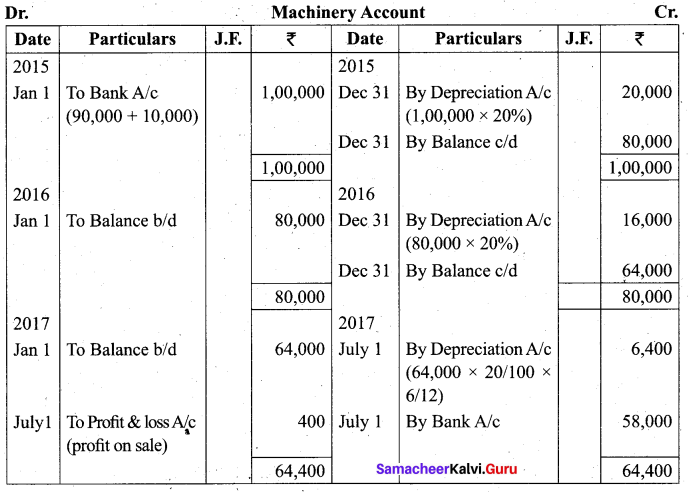
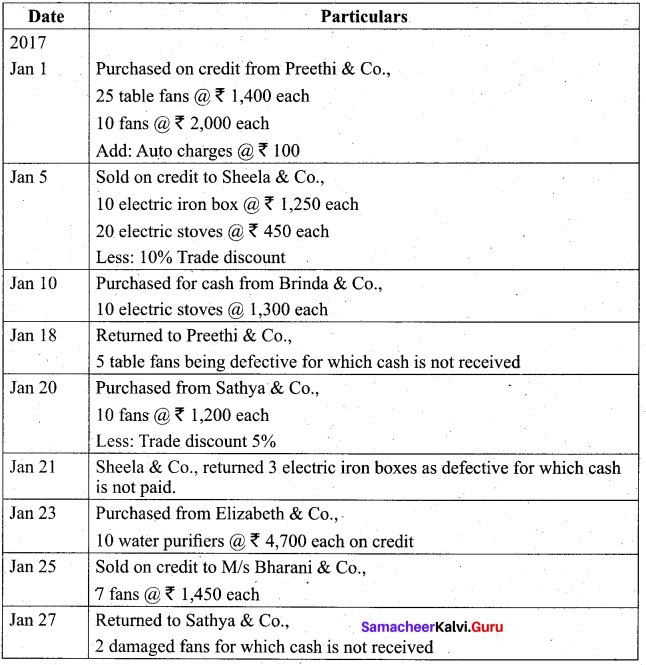
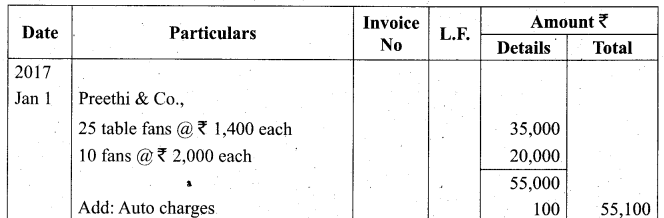
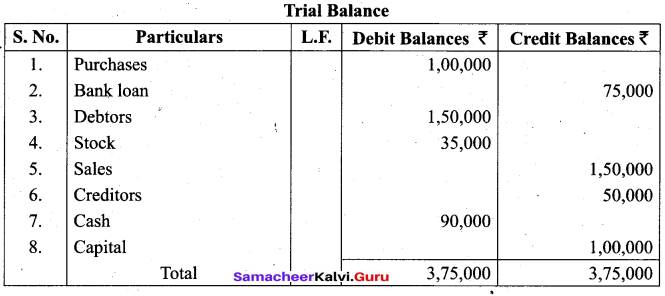
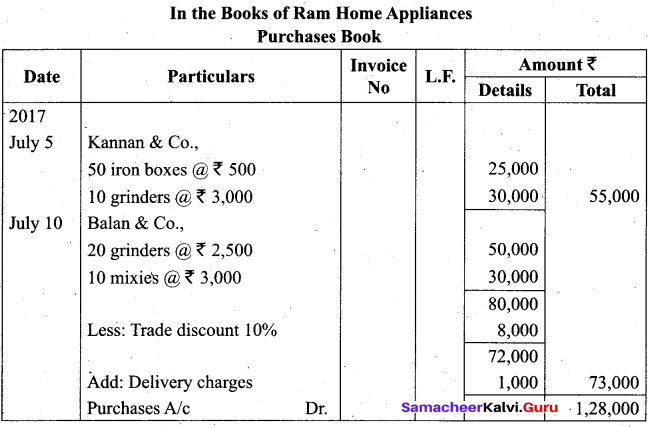
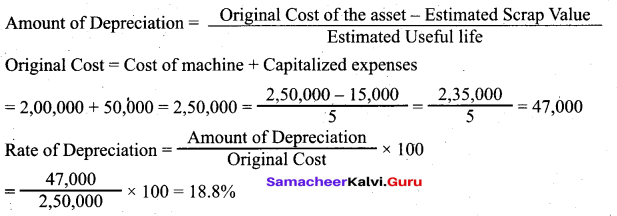
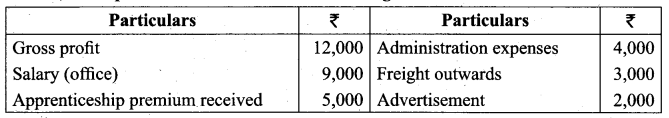
Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Biology Model Question Paper 2 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Biology Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 11th Biology Model Question Paper 2 English Medium
Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts Questions for Botany and Zoology are asked separately.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III, and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 8 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and Writing the option code and the Corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 9 to 4 in Part II are two-marks questions. This also is answered in about one or list sentences.
- Question numbers 15 to 19 in Part III are three-marks questions These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 20 and 21 in Part IV are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
Bio-Botany [Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Which one of the following statement about virus is correct?
(a) Possess their own metabolic system
(b) They are facultative parasites
(c) They contain DNA or RNA
(d) Enzymes are present
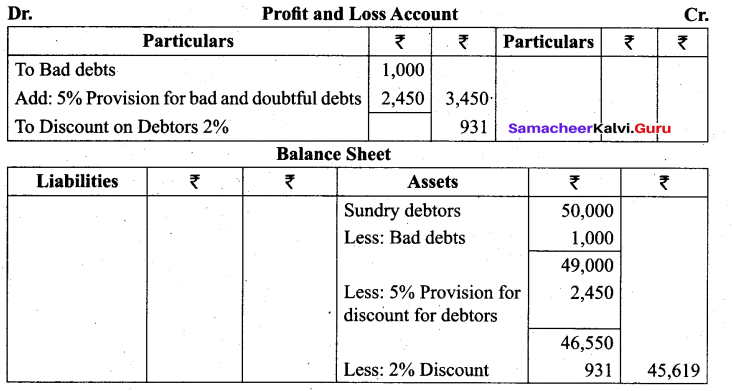
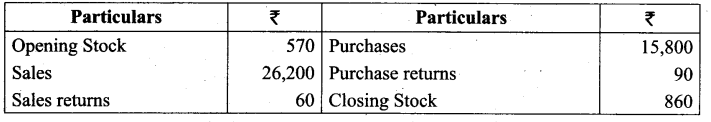
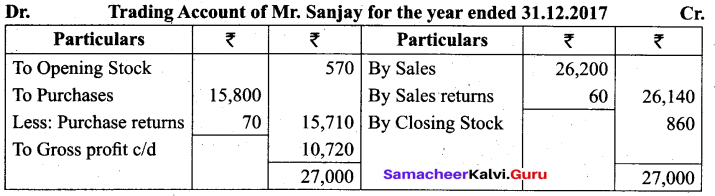
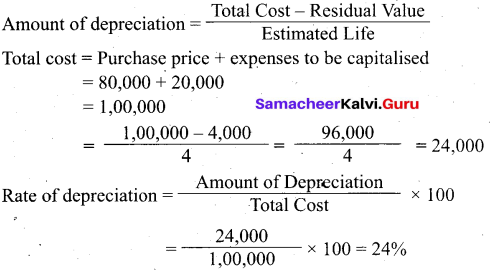
Answer:
(c) They contain DNA or RNA
![]()
Question 2.
An example of colonial algae is…………………….
(a) Chlorella
(b) Volvox
(c) Ulothrix
(d) Spirogyra
Answer:
(b) Volvox
Question 3.
In Artabotrys, ……………………….is modified into hook.
(a) leaflets
(b) inflorescence axis
(c) petiole
(d) axillary buds
Answer:
(b) inflorescence axis
Question 4.
In china rose the flower are……………………….
(a) Actinomorphic. Epigynous with valvate aestivation
(b) Zygomorphic, hypogynous with imbricate aestivation
(c) Zygomorphic, epigynous with twisted aestivation
(d) Actinomorphic, hypogynous with twisted aestivation
Answer:
(d) Actinomorphic, hypogynous with twisted aestivation
Question 5.
Terminalisation of chiasmata occurs at ……………..
(a) Zygotene
(b) Leptotene
(c) Diakinesis
(d) Pachytene
Answer:
(c) Diakinesis
![]()
Question 6.
The study of tissues is called as………………..
(a) Anatomy
(b) Cytology
(c) Histology
(d) Embryology
Answer:
(c) Histology
Question 7.
Identify the wrong statement(s).
(i) Molybdenum is a micronutrient.
(ii) Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen are skeletal elements.
(iii) Manganese is the activator for RUBP carboxylase.
(iv) Potassium maintains osmotic potential of the cell.
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) Only (if)
(d) Only (iv)
Answer:
(b) (ii) and (iii)
![]()
Question 8.
Foolish seedling disease affects ………………….
(a) Maize
(b) Rice
(c) Sorghum
(d) Wheat
Answer:
(b) Rice
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
Deuteromycetes are imperfect fungi – Justify.
Answer:
The fungi belonging to Deuteromycetes lack sexual reproduction and are called imperfect fungi.
Question 10.
Why bryophytes are called as Non-vascular cryptogam?
Answer:
Vascular tissue like xylem and phloem are completely absent in bryophytes, hence called as ‘Non-vascular cryptogams’.
![]()
Question 11.
What are root stocks? What are its function?
Answer:
Perennial and some biennial herbs have underground stems, which are generally known as root stocks. Root stock functions as a storage and protective organ.
Question 12.
Define Cladogram.
Answer:
The outcome of a cladistic analysis is a cladogram, a tree-shaped diagram that represent the best hypothesis of phylogenetic relationships.
![]()
Question 13.
Mention the drawbacks of diffusion.
Answer:
In diffusion, there is a lack of control over the transport of selective molecules. There is a possibility of harmful substances entering the cell by a concentration gradient.
Question 14.
What is Phytol tail? Mention its role.
Answer:
a. Phytol tail is the lipophilic tail of chlorophyll molecule.
b. It helps in anchoring the chlorophyll to lamellae.
Part – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
State the 3 types of viral symmetry.
Answer:
- Cuboid symmetry – Example: Adenovirus and Herpes virus.
- Helical symmetry – Example: Influenza virus and TMV.
- Complex or Atypical – Example: Bacteriophage and Vaccinia virus.
Question 16.
What is the importance of inflorescence.
Answer:
Function of inflorescence is to display the flowers for effective pollination and facilitate seed dispersal. The grouping of flowers in one place gives a better attraction to the visiting pollinators and maximize the energy of the plant.
![]()
Question 17.
Write a brief note on Manganese toxicity.
Answer:
Increased Concentration of Manganese will prevent the uptake of Fe and Mg, prevent translocation of Ca to the shoot apex and cause their deficiency. The symptoms of manganese toxicity are appearance of brown spots surrounded by chlorotic veins.
Question 18.
Draw the ultra structure of Plant Cell.
Answer:
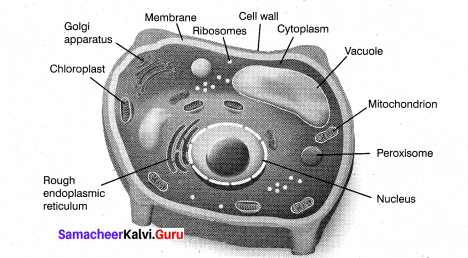
Question 19.
Mention the role of ethylene in agriculture field.
Answer:
- Ethylene normally reduces flowering in plants except in Pine apple and Mango.
- It increases the number of female flowers and decreases the number of male flowers.
- Ethylene spray in cucumber crop produces female flowers and increases the yield.
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
Explain the various phases in Cell Cycle.
Answer:
The different phases of cell cycle are as follows:
Interphase: Longest part of the cell cycle, but it is of extremely variable length. At first glance the nucleus appears to be resting but this is not the case at all. The chromosomes previously visible as thread like structure, have dispersed. Now they are actively involved in protein synthesis, at least for most of the interphase.
C-Value is the amount in picograms of DNA contained within a haploid nucleus.
G1 Phase: The first gap phase – 2C amount of DNA in cells of G1 The cells become metabolically active and grows by producing proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and cell organelles including mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. Many checkpoints control the cell cycle. The checkpoint called the restriction point at the end of G1 it determines a cells fate whether it will continue in the cell cycle and divide or enter a stage called G0 as a quiescent stage and probably as specified cell or die. Cells are arrested in G1 due to:
Nutrient deprivation: Lack of growth factors or density dependant inhibition.
Undergo metabolic changes and enter into G0 state.
Biochemicals inside cells activates the cell division. The proteins called kinases and cyclins activate genes and their proteins to perform cell division. Cyclins act as major checkpoint which operates in G0 to determine whether or not a cell divides.
G0 Phase: Some cells exit G1 and enters a quiescent stage called G0 , where the cells remain metabolically active without proliferation. Cells can exist for long periods in G0 phase. In G0 cells cease growth with reduced rate of RNA and protein synthesis. The G0 phase is not permanent. Mature neuron and skeletal muscle cell remain permanently in G0. Many cells in animals remains in G0 unless called on to proliferate by appropriate growth factors or other extracellular signals. G0 cells are not dormant.
S phase – Synthesis phase – cells with intermediate amounts of DNA.
Growth of the cell continues as replication of DNA occur, protein molecules called histones are synthesised and attached to the DNA. The centrioles duplicate in the cytoplasm. DNA content increases from 2C to 4C.
G2 – The second Gap phase – 4C amount of DNA in cells of G2 and mitosis Cell growth continues by protein and cell organelle synthesis, mitochondria and chloroplasts divide. DNA content remains as 4C. Tubulin is synthesised and microtubules are formed. Microtubles organise to form spindle fibre. The spindle begins to form and nuclear division follows.
One of the proteins synthesized only in the G2 period is known as Maturation Promoting Factor (MPF). It brings about condensation of interphase chromosomes into the mitotic form.
DNA damage checkpoints operates in G1 S and G2 phases of the cell cycle.
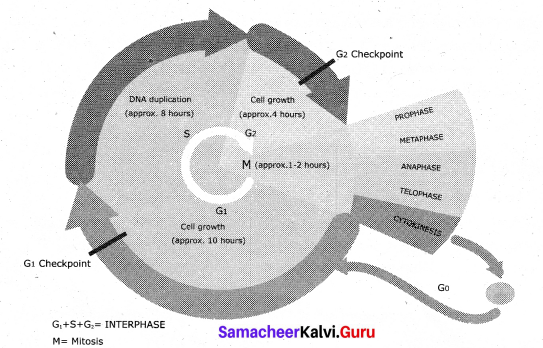
![]()
[OR]
Explain in detail about the various life cycle patterns in plants.
Answer:
Life cycle patterns in plants
Alternation of Generation: Alternation of generation is common in all plants. Alternation of the haploid gametophytic phase (n) with diploid sporophytic phase (2n) during the life cycle is called alternation of generation. Following type of life cycles are found in plants.
a. Haplontic life cycle:
Gametophytic phase is dominant, photosynthetic and independent, whereas sporophytic phase is represented by the zygote. Zygote undergoes meiosis to restore haploid condition. Example: Volvox and Spirogyra.
b. Diplontic life cycle:
Sporophytic phase (2n) is dominant, photosynthetic and independent. The gametophytic phase is represented by the single to few celled gametophyte. The gametes fuse to form zygote which develops into sporophyte. e.g., Fucus, gymnosperms and angiosperms.
c. Haplodiplontic life cycle:
This type of life cycle is found in Bryophytes and pteridophytes which is intermediate between haplontic and diplontic type. Both the phases are multicellular, but they differ in their dominant phase. In Bryophytes dominant independent phase is gametophyte and it alternates with short-lived multicellular sporophyte totally or partially dependent on the gametophyte.
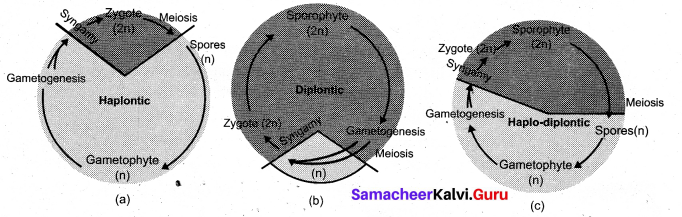
Life cycle patterns in plants (a) Haplontic, (b) Diplontic, (c) Haplo-diplontic
In Pteridophytes sporophyte is the independent phase. It alternates with multicellular saprophytic or autotrophic, independent, short lived gametophyte (n).
![]()
Question 21.
Describe Lundegardh’s Cytochrome Pump Theory.
Answer:
Lundegardh’s Cytochrome Pump Theory:
Lundegardh and Burstrom (1933) observed a correlation between respiration and anion absorption. When a plant is transferred from water to a salt solution the rate of respiration increases which is called as anion respiration or salt respiration. Based on this observation Lundegardh (1950 and 1954) proposed cytochrome pump theory which is based on the following assumptions:
- The mechanism of anion and cation absorption are different.
- Anions are absorbed through cytochrome chain by an active process, cations are absorbed passively.
- An oxygen gradient responsible for oxidation at the outer surface of the membrane and reduction at the inner surface.
According to this theory, the enzyme dehydrogenase on inner surface is responsible for the fonnation of protons (H+) and electrons (e– ). As electrons pass outward through electron transport chain there is a corresponding inward passage of anions. Anions are picked up by oxidized cytochrome oxidase and are transferred to other members of chain as they transfer the electron to the next component.
The theory assumes that cations (C+) move passively along the electrical gradient created by the accumulation of anions (A–) at the inner surface of the membrane.
Main defects of the above theory are:
- Cations also induce respiration.
- Fails to explain the selective uptake of ions.
- It explains absorption of anions only.
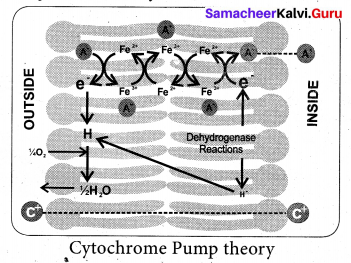
[OR]
State the differences between photorespiration and dark respiration.
Answer:
Photorespiration
- It takes place in photosynthetic green cells.
- It takes place only in the presence of light.
- It involves chloroplast, peroxisome and mitochondria.
- It does not involve Glycolysis, Kreb’s Cycle, and ETS.
- Substrate is glycolic acid.
- It is not essential for survival.
- No phosphorylation and yield of ATP.
- NADH2 is oxidised to NAD+.
- Hydrogen peroxide is produced.
- End products are CO2 and PGA.
Dark respiration :
- It takes place in all living cells.
- It takes place all the time.
- It involves only mitochondria.
- It involves glycolysis, Kreb’s Cycle and ETS.
- Substrate is carbohydrates, protein or fats.
- Essential for survival.
- Phosphorylation produces ATP energy.
- NAD+ is reduced to NADH2.
- Hydrogen peroxide is not produced.
- End products are CO2 and water.
Bio-Zoology[Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [Answers are in bold] [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Turbellarians are free living……………
(a) Flatworms
(b) Trematodes
(c) Nematodes
(d) cesrtodes
Answer:
(a) Flatworms
![]()
Question 2.
Renal portal system is absent in …………..
(a) Reptiles
(b) Amphibians
(c) Reptiles and amphibians
(d) Birds
Answer:
(d) Birds
Question 3.
Match the List I and List II:

(a) 1 – (in), 2 – (iv), 3 – (ii), 4 – (i)
(b) 1 – (ii), 2 – (i), 3 (iv), 4 – (iii)
(c) 1 – (iii), 2 – (/), 3 – (iv), 4 – (ii)
(d) 1 – (ii), 2 – (iv), 3 – (in), 4 – (i)
Answer:
(a) 1 – (in), 2 – (iv), 3 – (ii), 4 – (i)
Question 4.
PNS stands for …………………..
(a) Peripheral neural system
(b) Primary neural system
(c) Pitutiary nephron system
(d) Peripheral nephron system
Answer:
(a) Peripheral neural system
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following is an correct statement?
(a) Large intestine completes digestion and absorbs nutrients.
(b) Anus expels wastes.
(c) Rectum is the openifig for waste elimination.
(d) Esophagus helps in the conduction of the food to stomach.
Answer:
(d) Esophagus helps in the conduction of the food to stomach.
Question 6.
Which of the following is an incorrect statement?
(a) Hind brain comprises of cerebellum, pons varolii and medulla oblongata.
(ft) The mid brain is located between the diencephalon and the pons.
(c) Hypothalamus forms the floor of the diencephalon.
(d) The superficial region of the cerebrum is called gyri.
Answer:
(d) The superficial region of the cerebrum is called gyri.
Question 7.
There is no DNA in ………………….
(a) Mature RBC’s
(b) Mature spermatozoa
(c) Hair root
(d) Ovum
Answer:
(a) Mature RBC’s
Question 8.
Centres for sense of smell are located in ……………………. .
(a) Cerebellum
(b) Mid brain
(c) Olfactory lobes
(d) Cerebrum
Answer:
(c) Olfactory lobes
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
What is radial symmetry?
Answer:
When any plane passing through the central axis of the body divides an organism into two identical parts, it is called radial symmetry, e.g., Cnidarian.
Question 10.
Why do you call cockroach a pest?
Answer:
Cockroach destroy food and contaminates it with their offensive odour. They are carriers of a number of bacterial diseases. The cockroach allergen can cause asthma to sensitive people.
Question 11.
Why do plants not require a digestive system?
Answer:
Plants are autotrophs. They prepare their own food using C02, H20 in the pressure of sunlight trapped by the chlorophyll pigment present in the leaves. There is no need of digestive system for plants as they use the starch as such.
![]()
Question 12.
Draw the the structure of Blood Vessel – Large Vein.
Answer:
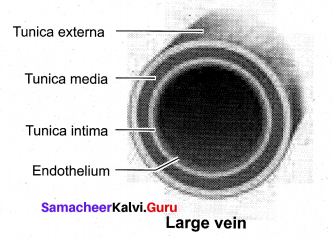
Question 13.
What are Nodes of Rannier?
Answer:
The Schwann cells covering the axen are not Continuous. There are gaps in the myelin sheath
between adjacent schwann cells. These gaps are called Nodes of Ranvier.
Question 14.
Define outbreeding.
Answer:
The breeding between unrelated animals is called outbreeding.
Part – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
What is Vermicompost?
Answer:
Vermicompost is the compost produced by the action of earthworms in association with all other organisms in the compost unit.
Question 16.
What is the difference between a zoo and wild life sanctuary?
Answer:
Zoo :
- Zoo is a place where animals and birds are in captivity of artificially created habitat.
- Public can have easy access to the zoo.
- Zoo is based on commercial aspects.
- Animals are caged and hence they are not free to roam about.
Wild Life Sanctuary :
- Wild life sanctuary is the natural habitat of wild animals and birds.
- Public does not have easy access to the wild life sanctuaries.
- Sanctuaries are non-commercial.
- In a sanctuary, animals can roam about freely.
Question 17.
What is lymph? Write its function.
Answer:
About 90% of fluid that leaks from capillaries eventually seeps back into the capillaries and the remaining 10% is collected and returned to blood system by means of a series of tubules known as lymph vessels or lymphatics. The fluid inside the lymphatics is called lymph.
The lymph nodes successfully prevent the invading microorganisms from reaching the blood stream. Cells found in the lymphatics are the lymphocytes. Lymphocytes collected in the lymphatic fluid are carried via the arterial blood and are recycled back to the lymph. Fats are absorbed through lymph in the lacteals present in the villi of the intestinal wall.
![]()
Question 18.
Draw the diagram of LS of the human eye and label the parts.
Answer:
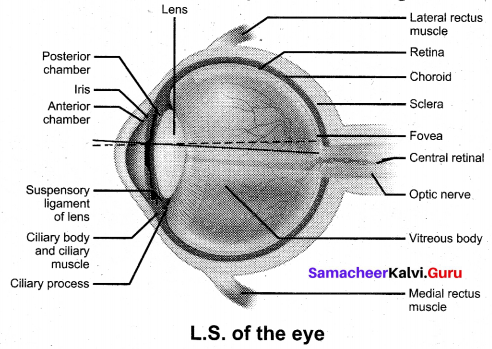
Question 19.
What are the main duties of a worker bee?
Each worker has to perform different types of work in her life time. During the first half of her life, she becomes a nurse bee attending to indoor duties such as secretion of royal jelly, prepares beebread to feed the larvae, feeds the queen, takes care of the queen and drones, secretes bees wax, builds combs, cleans and fans the bee hive. Then she becomes a soldier and guards the bee hive. In the second half her life lasting for three weeks, she searches and gathers the pollen, nectar, propolis and water. –
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
Draw the flowchart of classification of phylum chordata.
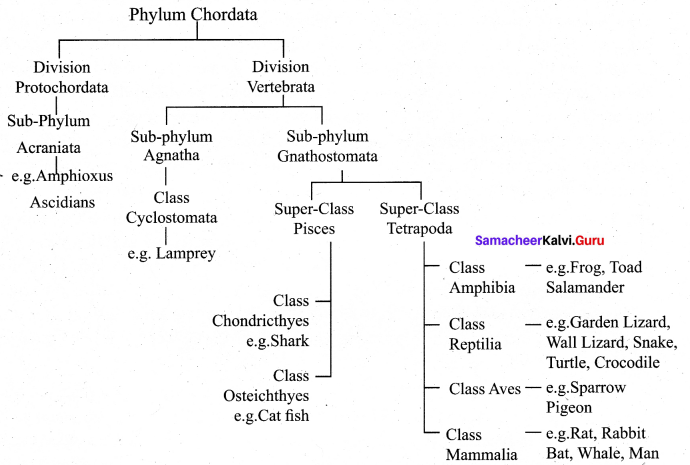
![]()
[OR]
Describe the life cycle of Lampito mauritii.
Answer:
Lampito mauritii begins its life cycle, from the fertilized eggs. The eggs are held in a protective cocoon. These cocoons have an incubation period of about 14-18 days after which they hatch to release juveniles The juveniles undergo changes into non-clitellate forms in Phase -1 after about 15 days, which then cocoon develops a clitellum, called the clitellate at the end of the growth phase – II taking 15¬17 days to complete. During the reproductive stage, earthworms copulate, and later shed their cocoons in the soil after about 10 days.
The life cycle of Lampito mauritii takes about 60 days to complete.
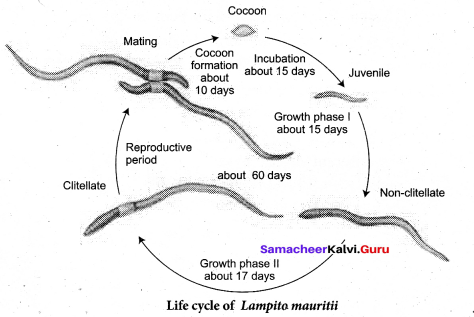
![]()
Question 21.
Explain the structure of Nephron.
Answer:
Each kidney has nearly one million complex tubular structures called nephron. Each nephron consists of a filtering corpuscle called renal corpuscle (malpighian body) and a renal tubule. The renal tubule opens into a longer tubule called the collecting duct. The renal tubule begins with a double walled cup shaped structure called the Bowman’s capsule, which encloses a ball of capillaries that delivers fluid to the tubules, called the glomerulus. The Bowman’s capsule and the glomerulus together constitute the renal corpuscle.
The endothelium of glomerulus has many pores (fenestrae). The external parietal layer of the Bowman’s capsule is made up of simple squamous epithelium and the visceral layer is made of epithelial cells called podocytes. The podocytes end in foot processes which cling to the basement membrane of the glomerulus. The openings between the foot processes are called filtration slits.
The renal tubule continues further to form the proximal convoluted tubule [PCT] followed by a U-shaped loop of Henle (Henle’s loop) that has a thin descending and a thick ascending limb. The ascending limb continues as a highly coiled tubular region called the distal convoluted tubule [DCT], The DCT of many nephrons open into a straight tube called collecting duct.
The collecting duct runs through the medullary pyramids in the region of the pelvis. Several collecting ducts fuse to form papillary duct that delivers urine into the calyces, which opens into the renal pelvis.
In the renal tubules, PCT and DCT of the nephron are situated in the cortical region of the kidney whereas the loop of Henle is in the medullary region. In majority of nephrons, the loop of Henle is too short and extends only very little into the medulla and are called cortical nephrons. Some nephrons have very long loop of Henle that run deep into the medulla and are called juxta medullary nephrons (JMN).
The capillary bed of the nephrons- First capillary bed of the nephron is the glomerulus and the other is the peritubular capillaries. The glomerular capillary bed is different from other capillary beds in that it is supplied by the afferent and drained by the efferent arteriole. The efferent arteriole that comes out of the glomerulus forms a fine capillary network around the renal tubule called the peritubular capillaries.
The efferent arteriole serving the juxta medullary nephron forms bundles of long straight vessel called vasa recta and runs parallel to the loop of Henle. Vasa recta is absent or reduced in cortical nephrons.
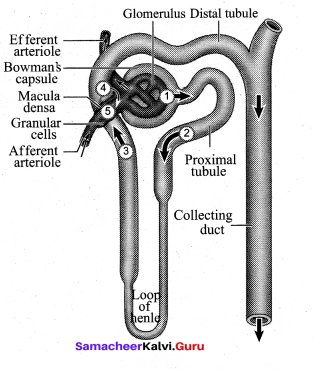
![]()
[OR]
Explain the endoerenal function of gonads.
Answer:
Testis: A pair of testis is present in the scrotal sac of males. The testis functions as a sex organ and also as an endocrine gland. The testis is composed of seminiferous tubules and interstitial cells or Leydig cells. The Leydig cells secrete several male sex hormones, collectively called androgens, mainly testosterone.
Functions of testosterone: Under the influence of FSH and LH, testosterone initiates maturation of male reproductive organs, and the appearance of secondary sexual characters, muscular growth, growth of facial and axillary hair, masculine voice and male sexual behaviour. It enhances the total bone matrix and plays a stimulating role in the process of . spermatogenesis.
Ovary: Females have a pair of ovaries located in the pelvic region of the abdomen. The ovary is composed of ovarian follicles and stromal tissues.lt produces the eggs or ova. The ovaries secrete the steroid hormones oestrogen and progesterone. Oestrogen is responsible for the maturation of reproductive organs and the development of secondary sexual characters at puberty. Along with progesterone, oestrogens promotes breast development and initiate the cyclic changes during menstrual cycle.
Progesterone prepares the uterus for implantation of the fertilized ovum.lt decreases the uterine contraction during pregnancy and stimulates the development of mammary glands and milk secretion. It is responsible for premenstrual changes in the uteris and is essential for the formation of placenta.








 Output
Output







 `
`