Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Maths Previous Year Question Paper June 2019 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Maths Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 11th Maths Previous Year Question Paper June 2019 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer - Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in above three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 2.30 Hours
Maximum Marks: 90
PART – I
I. Choose the correct answer. Answer all the questions. [20 × 1 = 20]
Question 1.
The range of the function \(\frac{1}{1-2sin x}\) is………….
(a) (-∞, -1) ∪(\(\frac{1}{3}\), ∞)
(b) (-1, \(\frac{1}{3}\))
(c) [-1, \(\frac{1}{3}\)]
(d) (-∞, -1] ∪(\(\frac{1}{3}\), ∞)
Answer:
(d) (-∞, -1] ∪(\(\frac{1}{3}\), ∞)
Question 2.
If the function f : [-3, 3] → S defined by f(x) = x² is onto, then S is…………
(a) [-9, 9]
(b) R
(c) [-3, 3]
(d) [0, 9]
Answer:
(d) [0, 9]
Question 3.
The number of solutions of x² + |x – 1| = 1 is ………..
(a) 1
(b) 0
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer:
(c) 2
![]()
Question 4.
cos 1° + cos 2° + cos 3° + …. + cos 179° =……………..
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) -1
(d) 89
Answer:
(a) 0
Question 5.
If tan α and tan β are the roots of x² + ax + b = 0, then \(\frac{sin(α+β)}{sin α sin β}\) is equal to…………
(a) \(\frac{b}{a}\)
(b) \(\frac{a}{b}\)
(c) –\(\frac{a}{b}\)
(d) –\(\frac{b}{a}\)
Answer:
(b) \(\frac{a}{b}\)
Question 6.
The number of sides of a polygon having 44 diagonals is…………
(a) 4
(b) 4
(c) 11
(d) 22
Answer:
(d) 22
Question 7.
The H.M. of two positive numbers whose A.M. and G.M. are 16, 8 respectively is………….
(a) 10
(b) 6
(c) 5
(d) 4
Answer:
(d) 4
Question 8.
The nth term of the sequence \(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{3}{4}\), \(\frac{7}{8}\), \(\frac{15}{16}\) is……………
(a) 2n – n – 1
(b) 1 – 2-n
(c) 2-n+ n – 1
(d) 2n-1
Answer:
(b) 1 – 2-n
Question 9.
The intercepts of the perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining (1,2) and (3,4) with coordinate axes are
(a) 5, -5
(b) 5, 5
(c) 5, 3
(d) 5, -4
Answer:
(b) 5, 5
Question 10.
The image of the point (2, 3) in the line y = -x is
(a) (-3, -2)
(b) (-3, 2)
(c) (-2, -3)
(d) (3, 2)
Answer:
(a) (-3, -2)
![]()
Question 11.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc} \lambda & 1 \\ -1 & -\lambda \end{array}\right]\), then for what value of λ, A² = 0?………
(a) 0
(b) ± 1
(c) -1
(d) 1
Answer:
(b) ± 1
Question 12.
If \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\) are having same magnitute and angle between them is 60° and their scalar product is \(\frac{1}{2}\), then |\(\vec {a}\)| is
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 7
(d) 1
Answer:
(d) 1
Question 13.
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow \infty} \frac{a^{x}-b^{x}}{x}\) = …………..
(a) log ab
(b) log (\(\frac{a}{b}\))
(c) log (\(\frac{b}{a}\))
(d) \(\frac{a}{b}\)
Answer:
(b) log (\(\frac{a}{b}\))
Question 14.
If f(x) = \(\left\{\begin{array}{ccc}x, & x \text { is irrational } \\ 1-x, & x \text { is rational }\end{array}\right.\) then f is………..
(a) discontinuous at x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
(b) continuous at x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
(c) continuous everywhere
(d) discontinuous everywhere
Answer:
(b) continuous at x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 15.
The derivative of f(x) = x |x| at x = -3 is…………..
(a) 6
(b) -6
(c) does not exist
(d) 0
Answer:
(a) 6
Question 16.
If f(x) = x² – 3x, then the points at which f(x) = f'(x) are…………..
(a) both positive integers
(b) both negative integers
(c) both irrational
(d) one rational and another irrational
Answer:
(c) both irrational
![]()
Question 17.
\(\int \tan ^{-1}(\sqrt{\frac{1-\cos 2 x}{1+\cos 2 x}})\) dx ………….
(a) x² + c
(b) 2x² + c
(c) \(\frac{x²}{2}\) + c
(d) –\(\frac{x²}{2}\) + c
Answer:
(c) \(\frac{x^2}{2}\) + c
Question 18.
e-7x sin 5x dx is…………
(a) \(\frac{e^{-7x}}{74}\) [-7 sin 5x – 5 cos 5x] + c
(b) \(\frac{e^{-7x}}{74}\) [7 sin 5x + 5 cos 5x] + c
(c) \(\frac{e^{-7x}}{74}\) [7 sin 5x – 5 cos 5x] + c
(d) \(\frac{e^{-7x}}{74}\) [-7 sin 5x + 5 cos 5x] + c
Answer:
(a) \(\frac{e^{-7x}}{74}\) [-7 sin 5x – 5 cos 5x] + c
Question 19.
If A and B are any two events then the probability that exactly one of them occur is
(a) P(A ∪\(\bar { B }\)) + P(\(\bar { A }\) ∪B)
(b) P(A ∩\(\bar { B }\)) + P(\(\bar { A }\) ∩B)
(c) P(A) + P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
(d) P(A) + P(B) + 2P(A ∩ B)
Answer:
(a) P(A ∪\(\bar { B }\)) + P(\(\bar { A }\) ∪B)
Question 20.
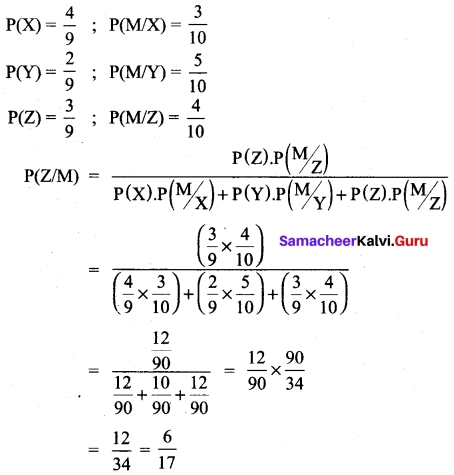
In a certain college 4% of the boys and 1 % of the girls are taller than 1.8 meter. Further 60% of the students are girls. If a student is selected at random and is taller than 1.8 meters, then the probability that the student is a girl is ………….
(a) \(\frac{2}{11}\)
(b) \(\frac{3}{11}\)
(c) \(\frac{5}{11}\)
(d) \(\frac{7}{11}\)
Answer:
(b) \(\frac{3}{11}\)
PART- II
II. Answer any seven questions. Question No: 30 is compulsory. [7 × 2 = 14]
Question 21.
Resolve \(\frac{3x+1}{(x-2)(x+1)}\) into partial fractions.
Answer:

Equating numerator parts
3x + 1 = A (x + 1) + B (x – 2)
This equation is true for any value of x.
To find A and B
Put x = -1
-3 + 1 = A (0) + B (-1 -2)
-3 B = -2 ⇒ B = 2/3
Put x = 2
3(2) + 1 = A(2 + 1) + B (0)
3A = 7 ⇒ A = 7/3
Hence \(\frac{3x+1}{(x-2)(x+1)}\) = \(\frac{7}{3(x-2)}\) + \(\frac{2}{3(x+1)}\)
![]()
Question 22.
Prove that
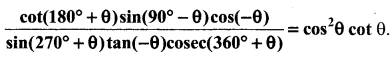
Answer:
cot (180° + θ) = cot θ
sin (90° – θ) = cos θ
cos (- θ) = cos θ
sin (270 + θ) = – cos θ
tan (-θ) = – tan θ
cosec (360° + θ) = cosec θ
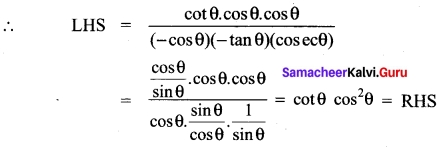
Question 23.
If cos θ = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (a + \(\frac{1}{a}\)), show that cos 3θ = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (a³ + \(\frac{1}{a³}\))
Answer:
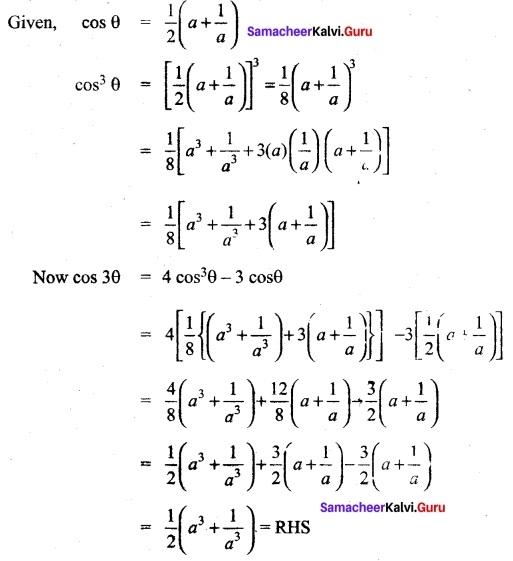
Question 24.
If the letters of the word IITJEE are permuted in all possible ways and the strings thus formed are arranged in the lexicographic order, find the rank of the word IITJEE.
Answer:
The lexicographic order of the letters of given word is E, E, I, I, J, T. In the lexicographic order, the strings which begin with E come first. If we fill the first place with E, remaining 5 letters (E, I, I, J, T) can be arranged in \(\frac{5!}{2!}\) ways. On proceeding like this we get,
E – – – – = \(\frac{5!}{2!}\) = 60 ways
IIE – – – = 3! = 6 ways
IIJ – – – = \(\frac{3!}{1!}\) = 3 ways
IITE – – =2! = 2 ways
IITJEE = 1 way
The rank of the word IITJEE = 60 + 6 + 3 + 2 +1 = 72.
Question 25.
Prove that \(\frac{(2n)!}{n!}\) = 2n (1, 3, 5 ……..(2n – 1)).
Answer:
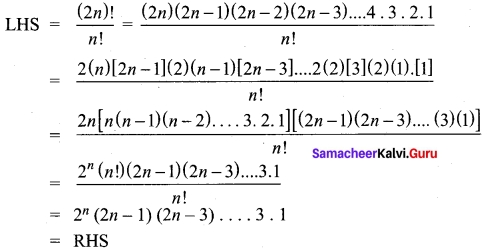
Question 26.
Write the equation of the line passing through the point (1, -1) and parallel to the line x + 3y – 4 = 0
Answer:
Equation of a line parallel to x + 3y – 4 = 0 will be of the form x + 3y + k = 0
It passes through (1,-1)
⇒ (1) + 3(-1) + k = 0
-2 + k = 0 ⇒ k = 2
So the required equation is x + 3y + 2 = 0
Question 27.
If (k, 2), (2, 4) and (3, 2) are vertices of the triangle of area 4 square units then determine the value of k.
Answer:
Area of Δ with vertices (k, 2) (2, 4) and (3, 2) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\left|\begin{array}{lll} k & 2 & 1 \\ 2 & 4 & 1 \\ 3 & 2 & 1 \end{array}\right|\) = 4 (given)
⇒ \(\left|\begin{array}{lll} k & 2 & 1 \\ 2 & 4 & 1 \\ 3 & 2 & 1 \end{array}\right|\) = 2(4) = 8
(i.e.,) k (4 – 2) -2(2 – 3) + 1 (4 – 12) = ±8
(i.e.,) 2k – 2(-1) + 1(-8) = ± 8
(i.e.,) 2k + 2 – 8 = 8
(i.e.,) 2k = 8 + 8 – 2 = 14
k = 14/2 = 7
∴ k = 7
or
2k + 2 – 8 = -8
⇒ 2k = -8 + 8 – 2
2k = -2
k = -1
So k = 7 (or) k = -1
![]()
Question 28.
Find λ, when the projection of \(\vec {a}\) = λ\(\hat{j}\) + \(\hat{j}\) + 4\(\hat{k}\) on \(\vec {b}\) = 2\(\hat{i}\) + 6\(\hat{j}\) + 2\(\hat{k}\) is 4 units.
Answer:
\(\vec {a}\) = λ\(\hat{j}\) + \(\hat{j}\) + 4\(\hat{k}\) and \(\vec {b}\) = 2\(\hat{i}\) + 6\(\hat{j}\) + 2\(\hat{k}\)
Now \(\vec {a}\) – \(\vec {b}\) = (λ) (2) + (1) (6) + (4) (3)
= 2λ + 6 + 12 = 2λ +18
|\(\vec {a}\)| = \(\sqrt{4+36+9}\) = \(\sqrt{49}\) = 7
Here \(\frac{2λ+18}{7}\) = 4
⇒ 2λ+ 18 = 4 × 7 = 28
2λ = 28 – 18 = 10
λ = 10/2 = 5
Question 29.
Find \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) if y = ex sin x
Answer:
y = ex sin x
⇒ y’ = uv’ + vu’
Now u = ex ⇒ u’ = \(\frac{du}{dx}\) = ex
v = sin x ⇒ v’ = \(\frac{dv}{dx}\) = cos x
y’ = ex (cos x) + sin x (ex)
= ex [sin x + cos x]
Question 30.
Find \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) if x² + y² = 1
Answer:
We differentiate both sides of the equation.
\(\frac{d}{dx}\) (x)² + \(\frac{d}{dx}\) (y)² = \(\frac{d}{dx}\) (1)
2x + 2y \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = 0
Solving for the derivative yields
\(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = –\(\frac{x}{y}\)
PART – III
III. Answer any seven questions. Question No. 40 is compulsory. [7 × 3 = 21]
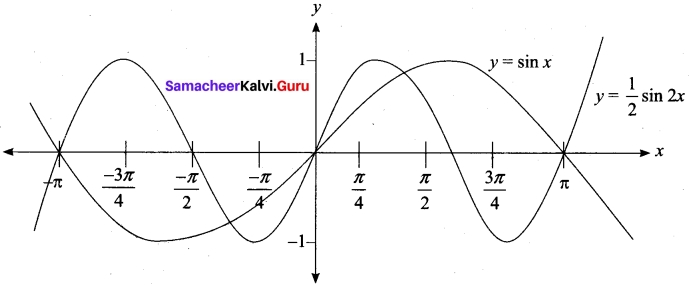
Question 31.
From the curve y = sin x, draw y = sin |x|
Answer:
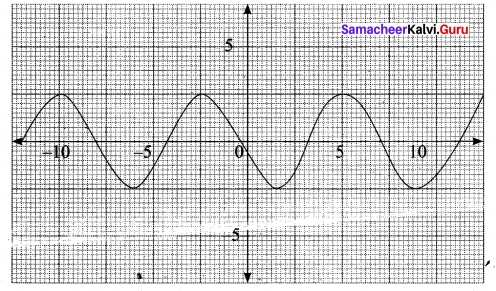
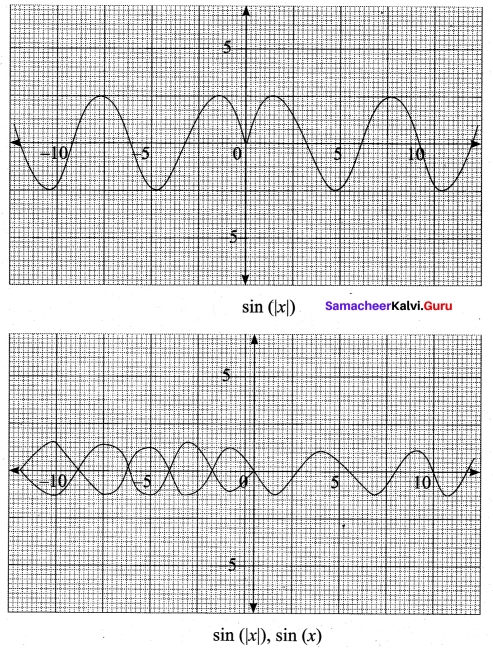
Question 32.
If one root of k (x – 1)² = 5x – 7 is double the other root, show that k = 2 or -25
Answer:
k(x – 1)² = 5x – 7
(i.e.,) k (x² – 2x + 1) – 5x + 7 = 0
x² (k) + x(-2k – 5) + k + 7 = 0
kx² – x(2k + 5) + (k + 7) = 0
Here it is given that one root is double the other.
So let the roots to α and 2α
Sum of the roots = α + 2α = 3α = \(\frac{2k+5}{k}\) α \(\frac{2k+5}{3k}\) ……..(1)
Product of the roots = α(2α) = 2α² = \(\frac{k+7}{k}\)
⇒ α² = \(\frac{k+7}{2k}\) = ……..(2)
Substituting a value from (1) in (2)
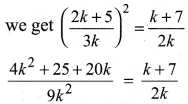
2(4k² + 25 + 20k) = 9k (k + 7)
2(4k² + 25 + 20k) = 9k² + 63k
8k² + 50 + 40k – 9k² – 65k = 0
-k² – 25k + 50 = 0
k² + 23k – 50 = 0
(k + 25) (k – 2) = 0
k = -25 or 2
![]()
Question 33.
If θ + ∅ = α and tan θ = k tan ∅, then prove that sin(θ – ∅) =\(\frac{k-1}{k+1}\)
Answer:
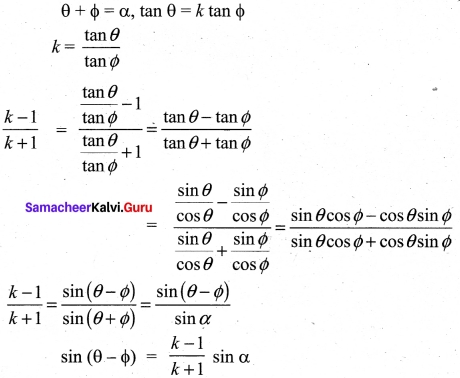
Question 34.
If a, b, c are in geometric progression, and if a\(\frac{1}{x}\) = b\(\frac{1}{y}\) = c\(\frac{1}{z}\) then prove that x, y, z are in arithmetic progression.
Answer:
Given a, b, c are in G.P.
⇒ b² = ac
⇒ log b² = log ac
(i.e.) 2 log b = log a + log c …(1)
We are given a\(\frac{1}{x}\) = b\(\frac{1}{y}\) = c\(\frac{1}{z}\) = k (say)
⇒ log ak = \(\frac{1}{x}\) = bk \(\frac{1}{y}\) = ck \(\frac{1}{z}\)
⇒ ak = \(\frac{1}{x}\) ⇒ x = log ka
Similarly y = log kb
z = log kc
Substituting these values in equation (1) we get 2y = x + z ⇒ x, y, z are in A.P.
Question 35.
Show that the points (1,3), (2,1) and (\(\frac{1}{2}\), 4) are collinear.
Answer:
Let the given points be A (1, 3), B (2, 1), and C (\(\frac{1}{2}\), 4)
Slope of AB = \(\frac{1-3}{2-1}\) = \(\frac{-2}{1}\) = -2 = m1
Slope of BC = \(\frac{4-1}{1/2-1}\) = \(\frac{3}{-3/2}\) = -2 = m2
Slope of AB = Slope of BC ⇒ AB parallel to BC but B is a common point.
⇒ The points A, B, C are collinear.
Question 36.
If A and B are symmetric matrices of same order, prove that AB + BA is a symmetric matrix.
Answer:
Given A and B are symmetric matrices
⇒ AT = A and BT = B
To prove AB + BA is a symmetric matrix.
Proof: Now(AB + BA)T = (AB)T + (BA)T = BTAT + ATBT
= BA + AB = AB + BA
i.e. (AB + BA)T = AB + BA
⇒ (AB + BA) is a symmetric matrix.
Question 37.
Let \(\vec {a}\), \(\vec {b}\), \(\vec {c}\) be three vectors such that |\(\vec {a}\)| = 3, |\(\vec {b}\)| = 4, |\(\vec {c}\)| = 5 and each one of them being perpendicular to the sum of the other two, find |\(\vec {a}\) + \(\vec {b}\) + \(\vec {c}\)|.
Answer:
Given |\(\vec {a}\)| = 3; |\(\vec {b}\)| = 4; |\(\vec {c}\)| = 5
Now, (\(\vec {a}\) + \(\vec {b}\) + \(\vec {c}\))² = a-2 +b -2+c-2 + 2(\(\vec {a}\).\(\vec {b}\) + \(\vec {b}\).\(\vec {c}\) + \(\vec {a}\).\(\vec {c}\))
= 3² + 4² + 5² + 2 \(\vec {a}\).\(\vec {b}\) + 2\(\vec {b}\).\(\vec {c}\) + 2\(\vec {a}\).\(\vec {c}\)
= 9 + 16 + 25 + \(\vec {a}\).\(\vec {b}\) + \(\vec {a}\).\(\vec {b}\) + \(\vec {b}\).\(\vec {c}\) + \(\vec {b}\).\(\vec {c}\) + \(\vec {a}\).\(\vec {c}\) + \(\vec {a}\).\(\vec {c}\)
= 50 + \(\vec {a}\).(\(\vec {b}\) + \(\vec {c}\)) + \(\vec {b}\).(\(\vec {c}\) + \(\vec {a}\)) + \(\vec {c}\).(\(\vec {a}\) + \(\vec {b}\))
= 50 + 0 + 0 + 0 = 50
(one vector is ⊥r to the sum of other two vectors)
|\(\vec {a}\) + \(\vec {b}\) + \(\vec {c}\)| = \(\sqrt {50}\) = \(\sqrt {25×2}\) = 5√2
![]()
Question 38.
Evaluate \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{\sqrt{1+x^{2}}-1}{x}\)
Answer:
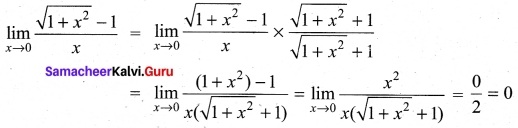
Question 39.
Find the derivatives of the following functions y = xcos x
Answer:
y = xcos x
Taking log on both sides, we get
log y = log xcos x = cos x log x
Differentiating w.r.to x we get
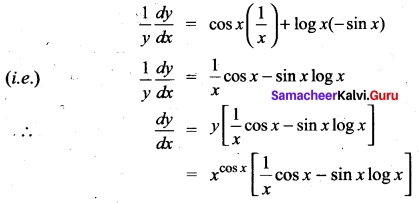
Question 40.
Evaluate
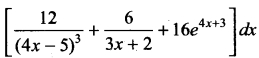
Answer:
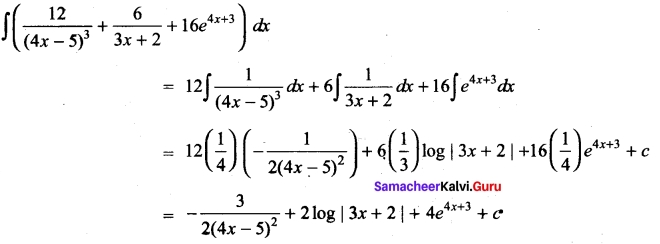
PART – IV
IV. Answer all the questions. [7 x 5 = 35]
Question 41 (a).
Let f, g: R → R be defined as f(x) = 2x – |x| and g(x) = 2x + |x|. Find fog.
Answer:

fog (x) = f(g(x))
= f(x) = 3x
For x > 0
fog (x) = f(g(x))
= f(3x) = 3x
[OR]
(b) Prove that \(\lim _{\theta \rightarrow 0} \frac{\sin \theta}{\theta}\) = 1
Answer:
Let θ → 0, thought positive values
∴ Let 0 < θ < \(\frac{π}{2}\)
Draw a circule center O and radius unity and let
∠AOB = θ radiAnswer:
Let the tagent at A meet OB product in the piont P.
Jion AB. From the figure it is clear that
Area of ΔAOB < Area of sector AOB < Area of ΔOAP
i.e., \(\frac{1}{2}\) OA. OB sin θ < 1 (radius)² θ < \(\frac{1}{2}\) OA. AP
or sin θ < θ < tan θ
[ ∵ \(\frac{AP}{OA}\) = tan θ or AP = tan θ as OA = 1
Dividing by sin θ, which is positive

Question 42 (a).
(i) If A × A has 16 elements, S = {(a, b) ∈ A × A: a < b} ; (-1, 2) and (0,1) are two elements of S, then find the remaining elements of S.
(ii) Find the range of the function \(\frac{1}{2 cos x – 1}\)
Answer:
(i) n(A × A) = 16
⇒ n(A) = 4
S = {(-1, 0), (-1, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2)}
(ii) The range of cos x is – 1 to 1
-1 ≤ cos x ≤ 1
(× by 2) -2 ≤ 2 cos x ≤ 2
adding -1 throughout
-2 -1 ≤ 2 cos x – 1 ≤ 2 – 1
(i.e.,) -3 ≤ 2 cos x – 1 ≤ 1
so 1 ≤ \(\frac{1}{2 cos x – 1}\) ≤ \(\frac{-1}{3}\)
The range is outside \(\frac{-1}{3}\) and 1
i.e., range is (-∞,\(\frac{-1}{3}\)] ∪ [1, ∞)
![]()
[OR]
(b) Evaluate: \(\int \frac{3 x+5}{x^{2}+4 x+7}\) dx
Answer:
Let I = \(\int \frac{3 x+5}{x^{2}+4 x+7}\) dx
3x + 5 = A \(\frac{d}{dx}\) (x² + 4x + 7) + B
3x + 5 = A(2x + 4) + B
Comparing the coefficients of like terms we got
2A = 3 ⇒ A = \(\frac{3}{2}\); 4A + B = 5 ⇒ B = -1
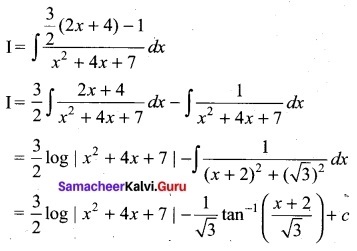
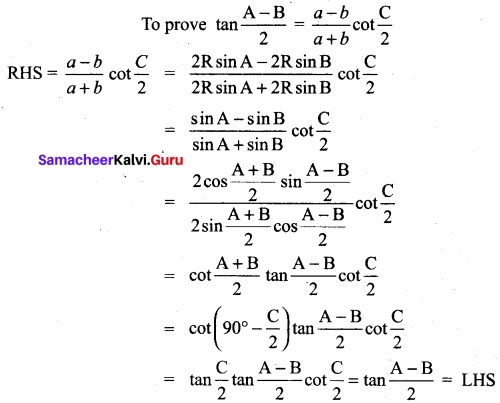
Question 43 (a).
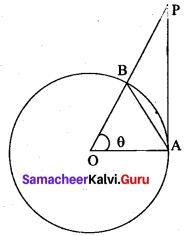
Derive cosine formula using the law of sines in a ΔABC.
Answer:
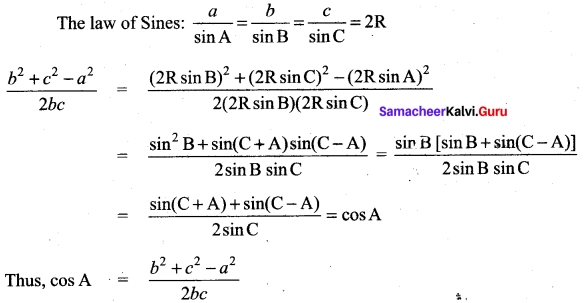
[OR]
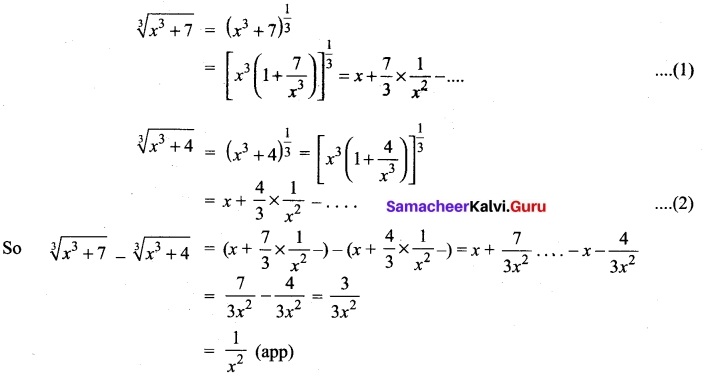
(b) Find \(\sqrt[3]{65}\) using binomial expansion upto two decimal places.
Answer:
We know that for |x| < 1,
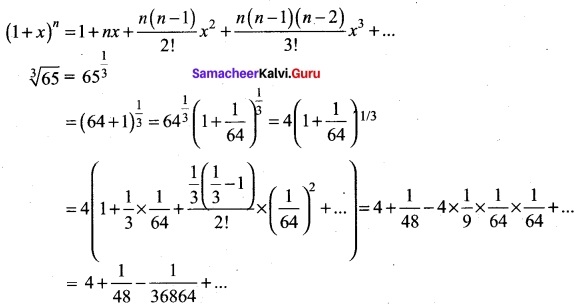
≈ 4 + 0.02 ( Since \(\frac{1}{36864}\) + …….. is very small)
\(\sqrt[3]{65}\) = 4.02 (approximately)
![]()
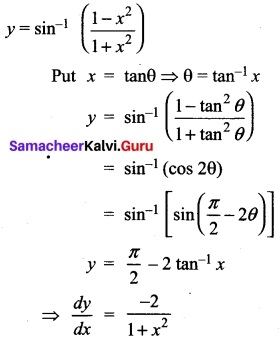
Question 44 (a).
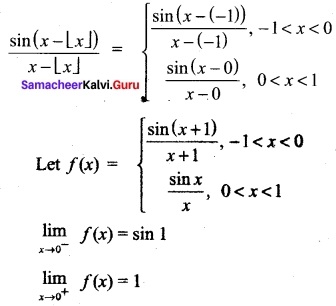
(i) Do the limit of the function \(\frac{sin |x|}{x}\) Li exist as x → 0? State reason for the answer.
Answer:
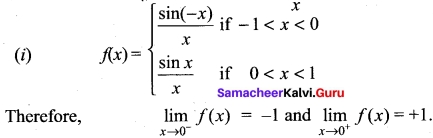
Hence the limit does ndt exist. Since that f(0–) ≠ f(0+)
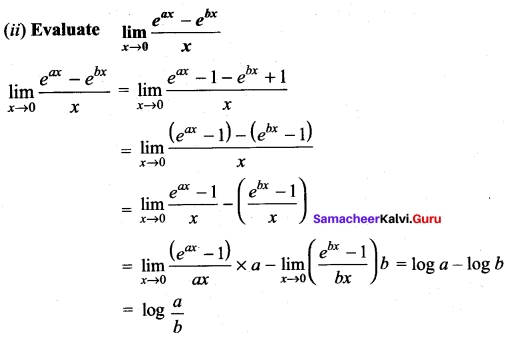
[OR]
(b) 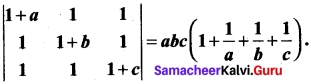
Answer:
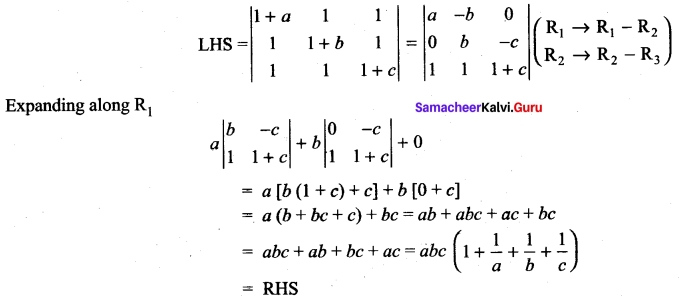
Question 45.
(i) Evaluate \(\int \frac{x \sin ^{-1} x}{\sqrt{1-x^{2}}}\) dx
Answer:
Let sin-1 x = t
⇒ \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^{2}}}\) dx = dt
Now sin-1 x = t ⇒ x = sin t
So I = ∫(sin t) (t) dt = ∫ t sin t dt
Now ∫t sin t dt = ∫ t d (-cos t)
= t(- cos t) – ∫(-cos t) dt
= -t cos t + ∫cos t dt
= – t cos t + sin t
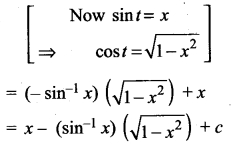
[OR]
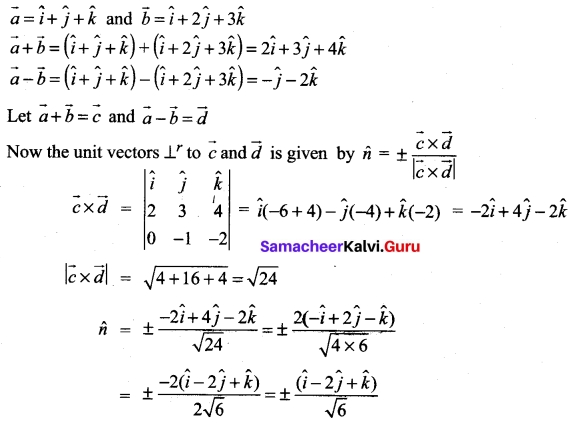
(b) Show that the points whose position vectors 4\(\hat{i}\) + 5\(\hat{j}\) + \(\hat{k}\),- \(\hat{j}\) – \(\hat{k}\), 3\(\hat{i}\) +9\(\hat{j}\) + 4\(\hat{k}\) and -4\(\hat{i}\) + 4\(\hat{j}\) + 4\(\hat{k}\) are coplanar.
Answer:
Let the given points be A, B, C and D. To prove that the point A, B, C, D are coplanar, we have to prove that the vectors \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}\), \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AC}}\) and \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AD}}\) are coplanar.
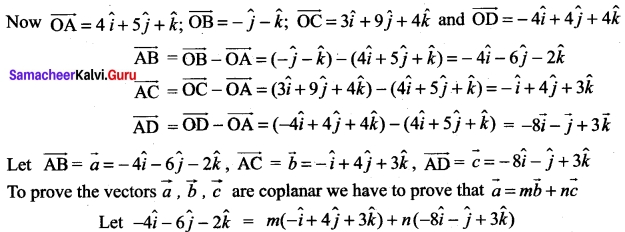
Equating \(\hat{i}\), \(\hat{j}\) and \(\hat{k}\) components we get
-4 = -m – 8n
⇒ m + 8n = 4 ….(i)
-6 = 4m – n
⇒ 4m – n = -6 ……. (ii)
-2 = 3m + 3n
⇒ 3m + 3n = -2 …….. (iii)
Solving (i) and (ii)

Substituting m = –\(\frac{4}{3}\) in (i) we get,
–\(\frac{4}{3}\) + 8n = 4
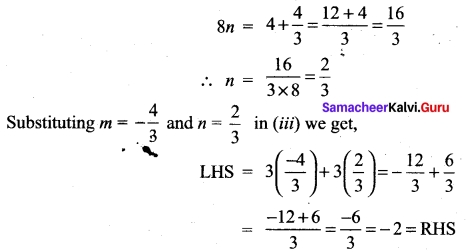
we are able to write one vector as a linear combination of the other two vectors ⇒ the given vectors \(\vec{a}\), \(\vec{b}\), \(\vec{c}\) are coplanar.
(i.e.,) The given points A, B, C, D are coplanar.
![]()
Question 46 (a).
If Q is a point on the locus of x² + y² + 4x – 3x + 7 = 0, then find the equation of locus of P which divides segment OQ externally in the ratio 3 : 4, where O is the origin.
Answer:
Let (h, k) be the moving-point O = (0, 0), Let PQ = (a, b) on x² + y² + 4x – 3y + 7 = 0
P divides OQ externally in the ratio 3 : 4
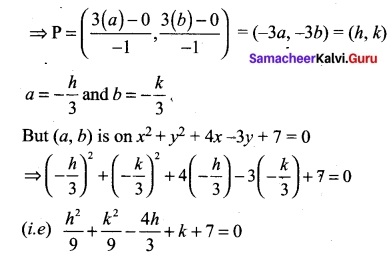
h² + k² – 12h + 9k + 63 = 0, Locus of (h, k) is x² + y² – 12x + 9y + 63 = 0
[OR]
(b) A consulting firm rents car from three agencies such that 50% from agency L, 30% from agency M and 20% from agency N. If 90% of the cars from L, 70% of cars from M and 60% of cars from N are in good conditions (i) what is the probability that the firm will get a car in good condition? (ii) if a car is in good condition, what is probability that it has come from agency N?
Answer:
Let A1, A2 and A3 be the events that the cars are rented from the agencies X, Y and Z respectively.
Let G be the event of getting a car in good condition.
We have to find
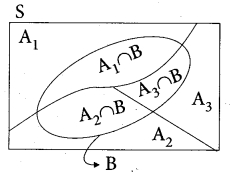
(i) The total probability of event G that is, P(G).
(ii) Find the conditional probability A3, given G that is, P(A3/G) We have
P(A1) = 0.50, P(G/A1) = 0.90
P(A2) = 0.30, P(G/A2) = 0.70
P(A3) = 0.20, P(G/A3) = 0.60.
(i) Since A1, A2 and A3 are mutually exclusive and exhaustive events and G is an event in S, then the total probability of event G is P(G).
P(G) = P(A1) P(G/A1) + P(A2) P(G/A2) + P(A3) P(G/A3)
P(G) = (0.50) (0.90) + (0.30) (0.70) + (0.20) (0.60)
P(G) = 0.78.
(ii) The conditional probability A3 given G is P(A3/G)
By Bayes’ theorem,

![]()
Question 47 (a).
Using the Mathematical induction, show that for any natural number n,
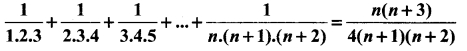
Answer:
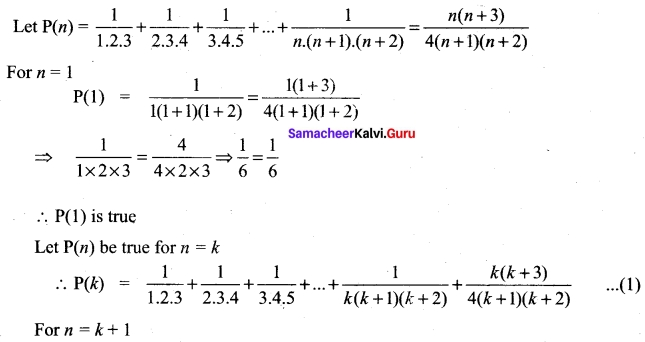
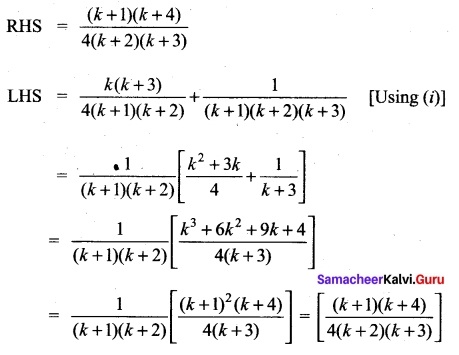
∴ P(k + 1) is true
Thus P(k) is true ⇒ P(k + 1) is true.
Hence by principle of mathematical induction,
P(n) is true for all n ∈ Z.
(b) If 7 = (cos-1 x)², prove that (1 – x²) \(\frac{d²y}{dx²}\) -x\(\frac{dx}{dy}\) -2 = 0. Hence find y2, when x = 0.
Answer:
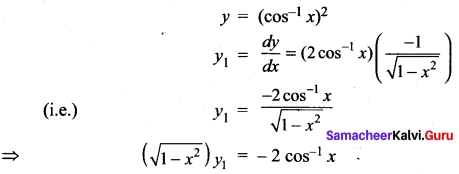
Squaring on both sides (1 – x²) (\(y_{1}^{2}\)) = 4(cos-1 x)² = 4y
⇒ (1 – x²)(\(y_{1}^{2}\)) = 4y
Differentiating again w.r.to x we get
(1 – x²) (2y1, y2) + (\(y_{1}^{2}\)) (-2x) = 4y1
⇒ (1 – x²) (2y1, y2) = 4y1 + 2xy\(y_{1}^{2}\)
(i.e.,) (1 – x²) (2y1, y2) = 2y1 (2 +xy1)
(÷ by 2y1)(1 – x²)y² = 2 + xy1
So (1 – x²)y2 – xy1 – 2 = 0
When x = 0
(1 – 0) y2 – 0y1 – 2 = 0
y2 – 2 = 0
y2 = 2
![]()

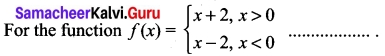
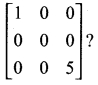


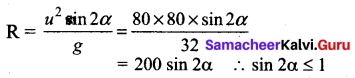
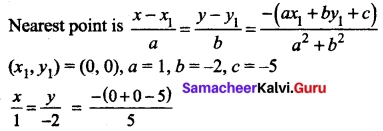
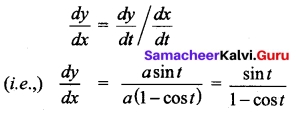
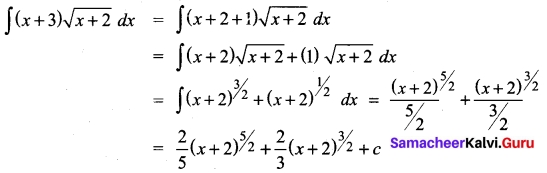
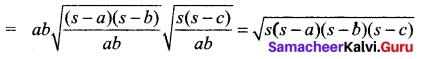
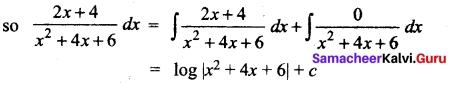

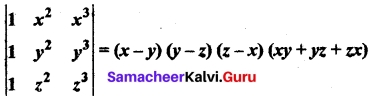
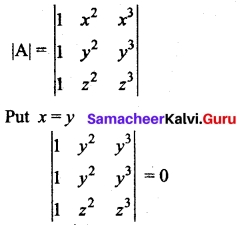
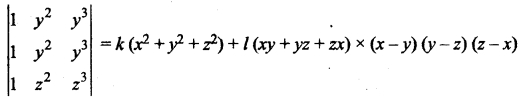

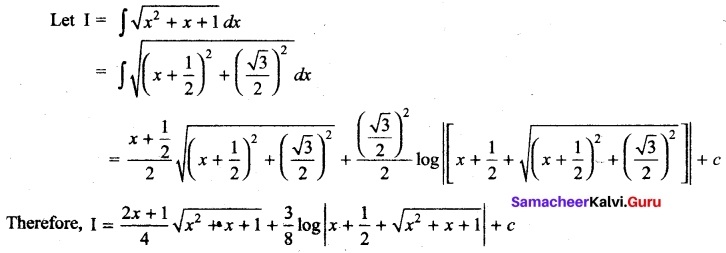



 Output:
Output: