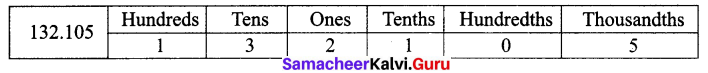
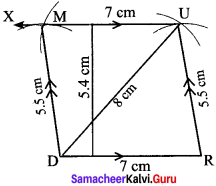
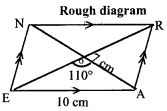
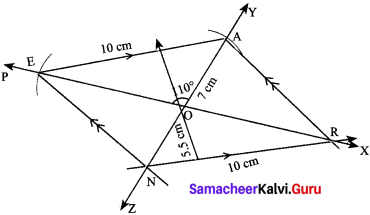
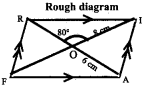
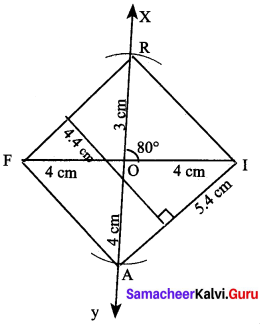
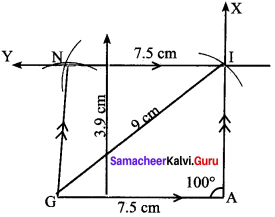
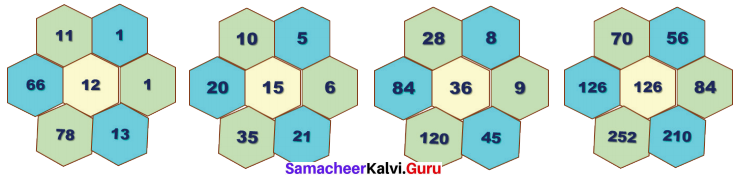
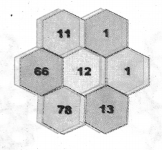
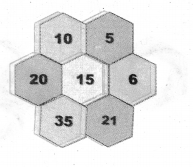
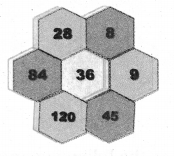
Students can Download Maths Chapter 4 Information Processing Intext Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Solutions Term 2 Chapter 4 Information Processing Intext Questions
Exercise 4.1
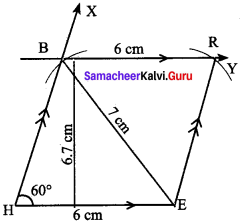
Activity 1. (Text book Page no. 83)
Question 1.
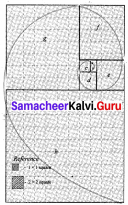
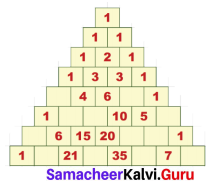
Draw a Golden Spiral using Fibonacci squares.
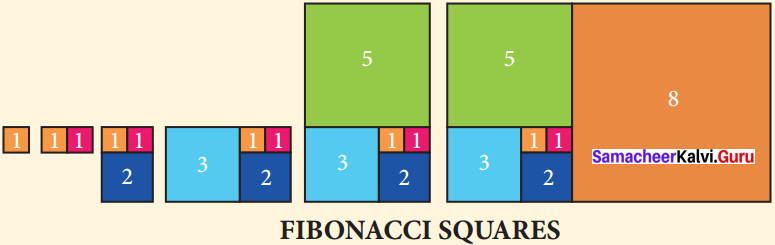
Answer:
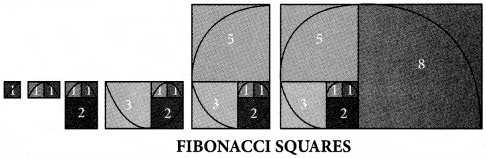
Activity – 2 (Text book Page no. 85)
![]()
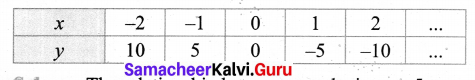
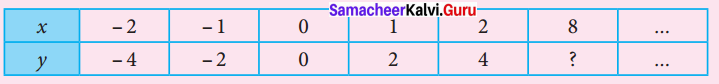
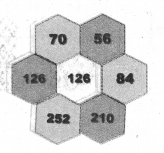
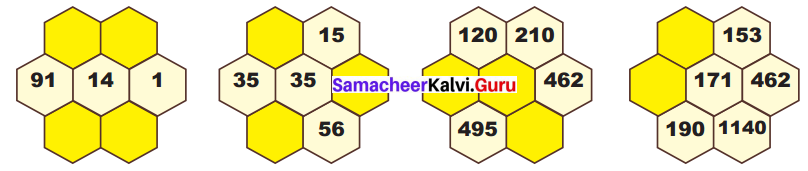
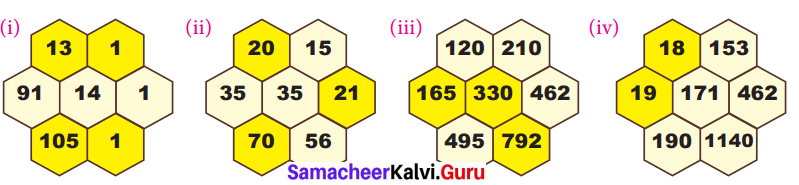
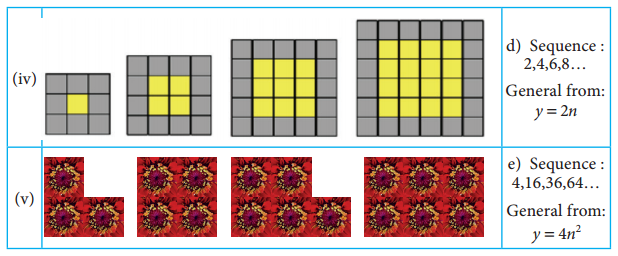
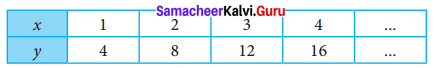
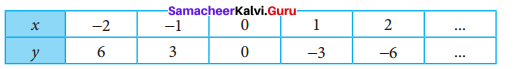
Question 1.
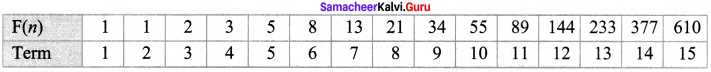
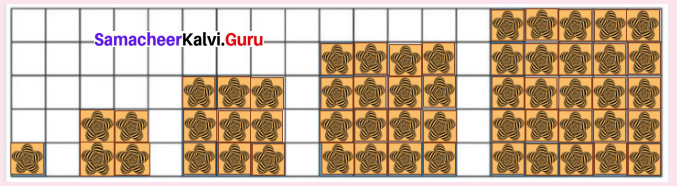
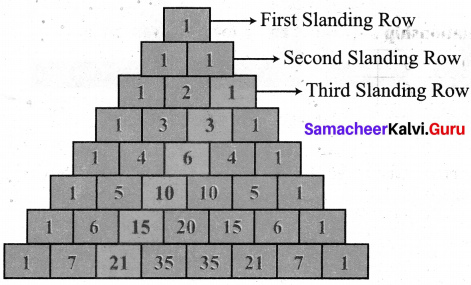
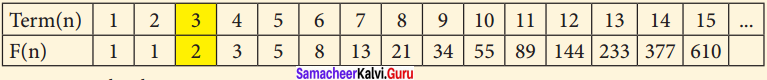
Using the given Table I, find the pattern, Answer the following questions and colour the values in the given Table II. One is done for you.
Table I

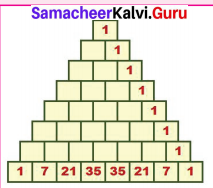
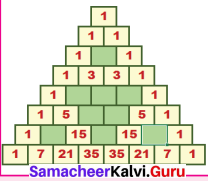
1. Where are the even Fibonacci Numbers?
Colour both the term n and where F(n) is even in
Do you find any pattern?
Every Third Fibonacci number is a multiple of 2(even).
i.e. a multiple of F(3) or 2 = F(3).
2. Where there are Fibonacci numbers which are multiple of 3?
Colour both the term n and where F(n) is multiple of 3 in red.
Write down the pattern you find
Every 4th Fibonacci number is a multiple of 3.
i.e. a multiple of F(4) or 3 = F(4).
3. What about the multiple of 5?
Colour both the term n and where F(n) is multiple of 5 in 1
Write down the pattern you find.
Every 5th Fibonacci number is a multiple of F(5) or 5 = F(5)
i.e. a multiple of F(4) or 3 = F(4)
4. What about the multiple of 8?
Colour both the term n where F(n) is multiple of 8 in green.
Write down the pattern you find.
Every 6th Fibonacci number i.e. a multiple of F(6) or 8 = F(6)
Table II
Solution:
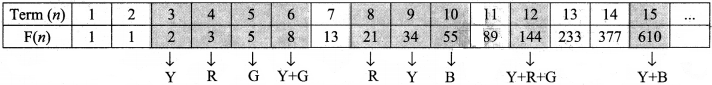
R – Red
Y – Yellow
B – Blue
G – Green
Exercise 4.3
Try This (Text book Page no. 94)
Question 1.
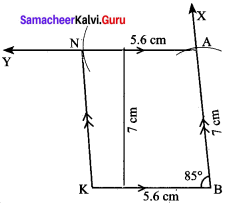
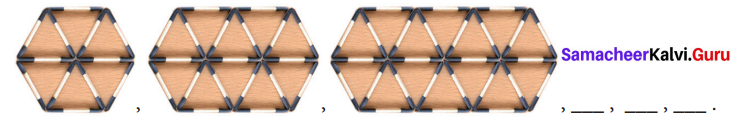
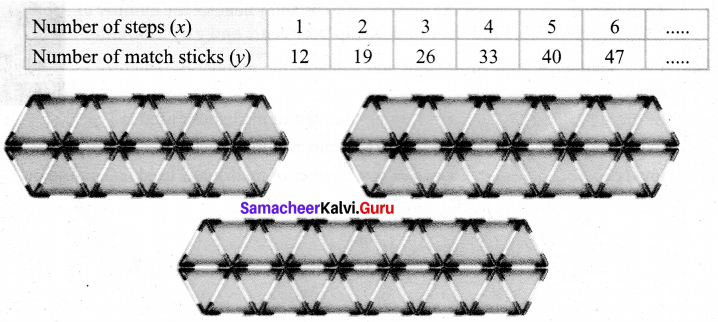
Convert cipher code written in the school panel board as given in figure below.

Solution:
Cipher code given.
EAPLKEAPUSG UG NWP AJWYP NYEJKXG KOYAPUWNG, SWEFYPAPUWNG WX AVCWXUPLEG; UP UG AJWYP YNBKXGPANBUNC – QUVVAE FAYV PLYXGPWN
Mathematics is not about numbers, equations, computations or algorithms, it is about understanding. – William Paul Thurston
Activity 3. (Text book Page No. 95)
Code 1: Pigpen
Question 1.
Fill in the blank boxes and decode
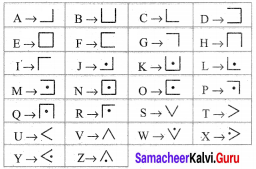
The Pigpen code looks like meaningless writing, but it is quite easy to catch on to. Each letter is represented by the part of the “Pigpen” that surrounds it.
The first code uses the following key. To complete the code, you need to work out how to use the key to decode the message.
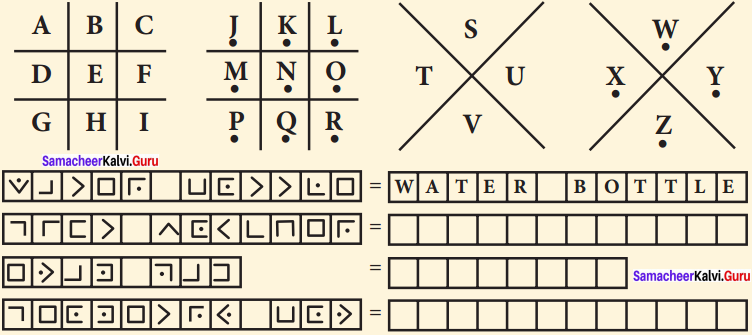
Solution:
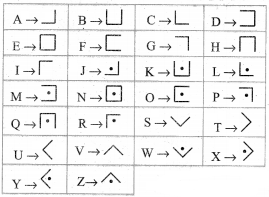
To decode
Try These (Text book Page no. 97)
![]()
Question 1.
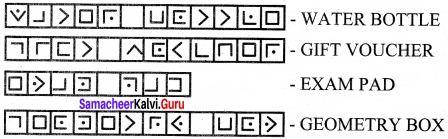
Use Pigpen Cipher code and write the code for your name ………. chapter names
(i) LIFE MATHEMATICS
(ii) ALGEBRA
(iii) GEOMETRY
(iv) INFORMATION PROCESSING
Solution:
For Pigpen, we should first construct the Criss Cross pattern & then fill with alphabets.
Step 1:
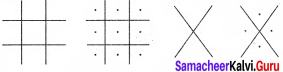
Step 2:
Fill the above with all the alphabets from A to Z.
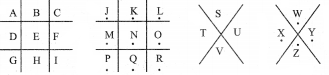
Step 3:
So, the secret code is got by the outline of each letter in the above patterns. So for
![]()
Similarly for all the others. Therefore Pigpen code is
Hence if your name is RAM, the corresponding pattern is
![]()
Let us now write the given words with Pigpen code.

Question 2.
Decode the following Shifting and Substituting secret codes given below. Which one is a easier for you?

Solution:
Decode using shifting method. Let us shift & see by trial & error method.
Let us substitute ‘b’ for ‘a’, V for ‘b’ & so on.
![]()
Message: M N S G H M F H R H L O N R R H A K D
Decoded text: NOTHING IS IMPOSSIBLE
Decode using substituting method:
![]()
We find that Pigpen code has been used, by substituting for the symbols from the table that we constructed earlier, we go the message.
NOTHING IS IMPOSSIBLE