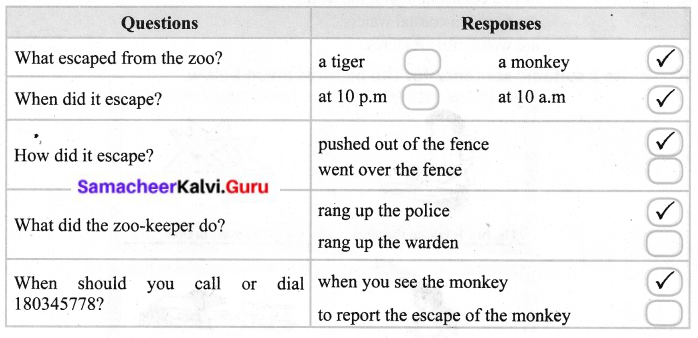
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Solutions Term 2 Chapter 1 Heat
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Heat Text Book Exercises
I. Choose the best answer
Heat Lesson For Class 8 Question 1.
Heat is a form of ………….
(a) electrical energy
(b) gravitational energy
(c) thermal energy
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) thermal energy
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Term 2 Question 2.
If you apply some heat energy to a substance, which of the following can take place in it?
(a) Expansion
(b) Increase in temperature
(c) Change of state
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
8th Standard Science Heat Question 3.
Which of the following substances will absorb more heat energy?
(a) Solid
(b) Liquid
(c) Gas
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Science Term 2 Question 4.
If you apply equal amount of heat to a solid, liquid and gas individually, which of the following will have more expansion?
(a) Solid
(b) Liquid
(c) Gas
(d) All of them
Answer:
(c) Gas
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 8th Science Question 5.
The process of converting a liquid into a solid is called ……………
(a) sublimation
(b) condensation
(c) freezing
(d) deposition
Answer:
(c) freezing
8th Science Heat Lesson Question 6.
Conduction is the heat transfer which takes place in a …………….
(a) solid
(b) liquid
(c) gas
(d) All of them
II. Fill in the blanks
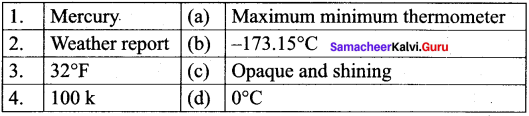
- A calorimeter is a device used to measure the …………….
- …………… is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1°C.
- A thermostat is a device which maintains ……………
- The process of converting a substance from gas to solid is called ……………
- If you apply heat energy, the temperature of a system will …………….
- If the temperature of a liquid in a container is decreased, then the inter atomic distance will ……………
Answer:
- heat capacity of water
- Specific heat capacity
- temperature of an object constant
- deposition
- increase
- decrease
III. State True or False. If false, correct the statement
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Guide Term 2 Question 1.
The applied heat energy can be realized as an increase in the average kinetic energy of the molecules.
Answer:
True
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Question 2.
The dimensions of a substance are increased if the temperature of the substance is decreased.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
The dimensions of a substance are increased if the temperature of the substance is increased.
Thermal Expansion Is Always A Nuisance Question 3.
The process of converting a substance from solid to gas is called condensation.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
The process of converting a substance from solid to gas is called sublimation.
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Solution Question 4.
Convection is the process by which the thermal energy flows in solids.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
Convection is the process by which the thermal energy flows in liquids and gases.
8th Science Samacheer Kalvi Question 5.
The amount of heat gained by a substance is equal to the product of its mass and latent heat.
Answer:
True
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Guide Question 6.
In a thermos flask, the silvered walls reflect and radiate the heat to the outside.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
In a thermos flask, the silvered walls reflect radiated heat back to the liquid in the bottle.
III. Match the following
8th Science Term 2 Question 1.
| 1. Conduction | (a) Liquid |
| 2.Convection | (b) Gas to liquid |
| 3. Radiation | (c) Solid to gas |
| 4. Sublimation | (d) Gas |
| 5. Condensation | (e) Solid |
Answer:
- e
- a
- d
- c
- b
V. Read the directions given below and answer the questions.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If the assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) If the assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Heat Class 8 Question 1.
Assertion : Radiation is a form of heat transfer which takes place even in vacuum.
Reason : The thermal energy is transferred from one part of a substance to another part without the actual movement of the atoms or molecules.
Answer:
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Book Solutions Question 2.
Assertion : A system can be converted from one state to another state.
Reason : It takes place when the temperature of the system is constant.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
VI. Answer briefly
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Book Back Answers Question 1.
What are the applications of conduction in our daily life?
Answer:
- We cook food in vessels made up of metals. When the vessel is heated, heat is transferred from the metal to the food.
- When we iron dresses heat is transferred from the iron to the cloth.
- Handles of cooking utensils are made up of plastic or wood because they are poor conductors of heat.
- The temperature inside igloo (snow house) is warm because snow is a poor conductor of heat.
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 8 Science Question 2.
What are the effects of heat?
Answer:
- Expansion
- Increase in temperature
- Change in state
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Answers Question 3.
Name three types of heat transfer.
Answer:
Three types of heat transfer are:
Answer:
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
8th Standard Science Term 2 Question 4.
What is conduction?
Answer:
The process of heat transfer in solids from the region of higher temperature to the region of lower temperature without the actual movement of atoms or molecules is called as conduction.
Kalvi Guru 8th Science Question 5.
Write a note on convection.
Answer:
The form of heat transfer from places of high temperature to places of low temperature by the actual movement of molecules is called convection. Convection takes place in liquids and gases.
Heat Samacheer Kalvi Question 6.
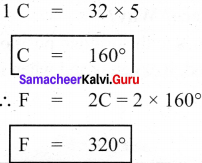
Define specific heat capacity.
Answer:
Specific heat capacity of a substance is defined as the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kilogram of a substance by 1°C or 1 K. It is denoted by the symbol C.
Question 7.
Define one calorie.
Answer:
One calorie is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water through 1°C.
VII. Answer in detail
Question 1.
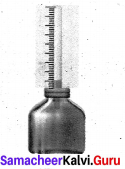
With the help of a neat diagram explain the working of a calorimeter.
Answer:
1. A calorimeter is a device used to measure the amount of heat gained or lost by a substance.
2. It consists of a vessel made up of metals like copper or aluminium which are good conductors of heat and electricity.
3. The metallic vessel is kept in an insulating jacket to prevent heat loss to the environment.
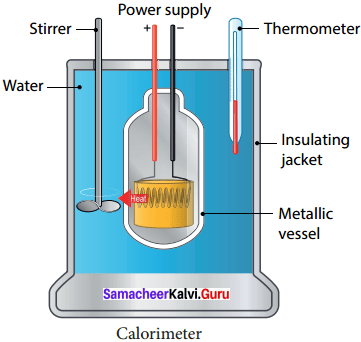
4. There are two holes in it. Through one hole a thermometer is inserted to measure the temperature Of the Contents.
5. A stirrer is inserted through another hole for stirring the content in the vessel.
6. The vessel is filled with liquid which is heated by passing current through the hating element.
7. Using this device we can measure the heat capacity of the liquid in the container.
Question 2.
Write a note on thermostat.
Answer:
1. A thermostat is a device which maintains the temperature of a place or an object constant.
2. The word thermostat is derived from two Greek words, ‘thermo’ meaning heat and ‘static’ meaning staying the same.
3. Thermostats are used in any device or system that gets heated or cools down – to a pre – set temperature. It turns an appliance or a circuit on or off when a particular temperature is reached.
4. Devices which use thermostat include building heater, central heater in a room, air conditioner, water heater, as well as kitchen equipment including oven and refrigerators.
5. Sometimes, a thermostat functions both as the sensor and the controller of a thermal 6 system.
Question 3.
Explain the working of thermos flask.
Answer:
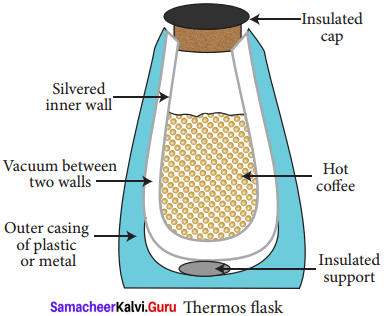
- A thermos flask has double walls, which are evacuated.
- It is silvered on the inside.
- The vacuum between the two walls prevents heat being transferred from the inside to the outside by conduction and convection.
- With very little air between the walls, there is almost no transfer of heat from the inner wall to the outer wall or vice versa.
- Conduction can only occur at the points where the two walls meet, at the top of the bottle and through an insulated support at the bottom.
- The silvered walls reflect radiated heat back to the liquid in the bottle.
VIII. Higher Order Thinking Questions
Question 1.
Why does the bottom of a lake not freeze in severe winter even when the surface is all frozen?
Answer:
Lakes don’t completely freeze because the ice (and eventually snow) on the surface acts to insulate die water below. To freeze water into ice, a large quantity of heat is to be withdrawn. This heat cannot be
Question 2.
Which one of the following statements about thermal conductivity is correct? Give reason.
(a) Steel > Wood > Water
(b) Steel > Water > Wood
(c) Water > Steel > Wood
(d) Water > Wood > Steel
Answer:
(b) Steel > Water > Wood
Reason:
Thermal conductivity is defined as the heat flow per unit time.
Steel has a higher thermal conductivity than water and wood.
[Thermal conductivity of steel = 50.2 w/mk
Thermal conductivity of water = 0.6 w/mk Thermal conductivity of wood = 0.12 w/mk]
IX. Problems
Question 1.
An iron ball requires 1000 J of heat to raise its temperature by 20°C. Calculate theheat capacity of the ball.
Solution:
Heat capacity C’ = \(\frac{Q}{∆T}\)
Here, A = 1000 J
T = 20°C – 0°C = 20°C = 20 k
C = \(\frac{1000}{20}\) = 50 JK-1
The heat capacity of the ball = 50 JK-1
Question 2.
The heat capacity of the vessel of mass 100 kg is 8000 J/°C. Find its specific heat capacity.
Solution:
Specific heat capacity, C = \(\frac{Q}{mx∆T}\)
Here, m = 100 kg
Heat capacity = \(\frac{Q}{∆T}\) = 8000 J/°C = 8000 J/K
C = \(\frac{Q}{mx∆T}\) = 100 x 8000 J = 8,00,000 JKg-1 K-1
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Heat Intext Activities
Activity – 2
Question 1.
Take a cup of water and note its temperature. Heat the water for few minutes and note the temperature again. What caused the temperature change?
Question (i)
Do you find any increase in the temperature?
Answer:
When the water is heated, water molecules receives heat energy, increases the kinetic energy of the molecules.
Question (ii)
What caused the temperature change?
Answer:
- When the molecules receive more energy, the temperature of the water increases.
- Heat energy causes increase in temperature.
Activity – 3
Question 1.
Take few ice cubes in a container and heat them for some time. What happens? The ice cubes melt and become water. Now heat the water for some time. What do you observe? The volume of water in the vessel decreases. What do you understand from this Activity?
Answer:
- In ice cubes, the force of attraction between the water molecules is more. So they are close together.
- When we heat them the force of attraction decreases and the ice cubes become water.
- when we heat the water, the force of attraction between the molecules decreases further.
- Hence they move away from one another and become vapor.
- Since water vapor escape to the surrounding,water level decreases.
- From this Activity we understand that heat energy causes change in the state of the substances.
Activity – 4
Question 1.
Take hot water in a cup and put a silver spoon in it. Leave the spoon inside the water for some time. Now touch the end of the spoon. Do you feel the heat?
Answer:
- Yes, we feel hot.
- It is because heat in the hot water is transferred from one end to other end of the spoon.
- In solid substances such as silver spoon, atoms are arranged very closely.
- So heat transfer takes place from the higher temperature region to lower temperature region.
- This is due to conduction.
Activity – 5
Question 1.
Take some water in a vessel and heat it on a stove. Touch the surface of the water. It will be cold. Touch it after some time. It will be hot now. How did the heat which was supplied at the bottom reach the top?
Answer:
- When water in the vessel is heated, water molecules at the bottom receive heat energy and move upward.
- Then the molecules at the top comes down and get heated.
- This kind of heat transfer is known as convection.
Activity – 6
Question 1.
Take some amount of water and cooking oil in two separate vessels. Heat them till they reach a particular temperature (Caution: Heat the oil under the supervision of your teacher). Which one is heated first? Water will take more time to get heated. Why?
Answer:
- Heat transfer depends on the nature of the substance.
- Water has high specific heat capacity than that of cooking oil.
- A substance with high specific heat capacity absorbs a large quantity of heat.
- Thus, it takes long time to heat up.
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Heat Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
1 calorie equals ……………….
(a) 0.42 J
(b) 4.2 J
(c) 420 J
(d) 4200 J
Answer:
(b) 4.2 J
Question 2.
The SI unit of heat energy is ………………
(a) joule
(b) calorie
(c) kilo calorie
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) joule
Question 3.
Which of the following is not a scale of temperature?
(a) Kelvin scale
(b) Celsius scale
(c) Richter scale
(d) Fahrenheit scale
Answer:
(c) Richter scale
Question 4.
Convection of heat takes place in ……………
(a) liquids only
(b) gases only
(c) metals only
(d) liquids and gases
Answer:
(d) liquids and gases
Question 5.
In solid substances, heat is transferred by –
(a) conduction
(b) radiation
(c) convection
(d) only a and b
Answer:
(b) radiation
Question 6.
In conduction, heat flows from ………………
(a) hotter to hotter region
(b) colder to hotter region
(c) hotter to colder region
(d) colder to colder region
Answer:
(c) hotter to colder region
Question 7.
Mud houses are cooler in summer and warmer in winter because –
(a) mud is a bad conductor of heat
(b) mud is a good conductor of heat
(c) mud is a super conductor of heat
(d) none
Answer:
(c) mud is a super conductor of heat
Question 8.
Process of change of state from gaseous state to liquid state is called …………….
(a) freezing
(b) condensation
(c) sublimation
(d) boiling
Answer:
(b) condensation
Question 9.
Substances which allow heat to pass through them are called …………….
(a) conductors
(b) insulators
(c) moderators
(d) none
Answer:
(a) conductors
Question 10.
When two objects are in thermal contact, the heat is transferred by ………………
(a) convection
(b) radiation
(c) conduction
(d) none
Answer:
(c) conduction
II. Fill in the Blanks
- In vacuum, heat energy can travel by the process of ……………….
- In ice cubes the force of attraction between the water molecules is ……………….
- When we heat water, the force of attraction decreases and the ice cubes becomes ……………….
- ………………. is the only matter on the Earth that can be found naturally in all three states.
- Radiation is defined as the heat transfer from one place to another in the form of ………………..
- Heat capacity C’= ……………….
- 1 Calorie = …………….. J.
- Specific heat capacity C = ………………..
- The device which is used to measure the heat capacity of the liquid is …………………
- ……………….. is a device which maintains the temperature of a place or an object constant.
- The vacuum flask was invented by …………………
- Vacuum flask is also called as …………………
- The water in the black can becomes ……………….. than that in white can after exposing to the sun.
- The handles of cooking utensils are made of …………………
- Black color is a ……………….. absorber of heat.
Answer:
- radiation
- morel
- water
- Water
- electro magnetic waves
- \(\frac{Q}{∆T}\)
- 4.186 J
- \(\frac{Q}{mx∆T}\)
- Calorimeter
- Thermostat
- Sir James Dewar
- Dewar flask
- hotter
- insulators
- good
III. True or False – if false give the correct statement
Question 1.
Heat is the transfer of energy between two objects with different temperature.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
When ice changes into a liquid, it absorbs energy.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Heat energy flows from a body at low temperature to a body at higher temperature.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
Heat energy flows from a body at high temperature to a body at lower temperature.
Question 4.
J/Kg °C is the unit of specific heat capacity.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Conductors have generally high specific heat capacities and insulators have low specific heat capacities.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
Conductors have generally low specific heat capacities and insulators have high specific heat capacities.
Question 6.
Temperature is a measure of average kinetic energy of molecules.
Answer:
True
Question 7.
When a liquid evaporates, it gives off energy.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
When a liquid evaporates, it absorbs energy.
Question 8.
When a liquid boils, energy is absorbed.
Answer:
True
Question 9.
Water has the lowest specific heat capacity.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
Water has the very high specific heat capacity.
Question 10.
While a substance is undergoing a change of state, the temperature of the body remains the same.
Answer:
True
Question 11.
In summer, we prefer light – colored clothes and in winter we usually wear dark – colored clothes.
Answer:
True
Question 12.
The transfer of heat by radiation does not require any medium.
Answer:
True
Question 13.
Metals like copper, aluminium are good conductors of heat and electricity.
Answer:
True
Question 14.
In thermos flask, the vacuum between the two walls prevents heat from the inside to the outside by radiation.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
In thermos flask, the vacuum between the two walls prevents heat from the inside to the outside by conduction and convection.
Question 15.
Thermostat is a device can measure the heat capacity of the liquid in the container.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
Calorimeter is a device can measure the heat capacity of the liquid in the container.
IV. Match the following
Question 1.
| 1. | Heat | (a) | Good absorber |
| 2. | Temperature | (b) | Form of energy |
| 3. | Black surface | (c) | Insulators |
| 4. | Rubber, cork | (d) | Measure of hotness or coldness |
Answer:
- b
- d
- a
- c
Question 2.
| 1. | Specific heat capacity | (a) | Dewar bottle |
| 2. | Calorimeter | (b) | Lavoisier and simon |
| 3. | Vacuum flask | (c) | J Kg-1 K-1 |
| 4. | Ice – calorimeter | (d) | Heat capacity |
Answer:
- c
- d
- a
- b
Question 3.
| 1. | Conduction | (a) | liquids and gases |
| 2. | Convection | (b) | Poor conductor |
| 3. | Radiation | (c) | Solids |
| 4. | Snow | (d) | Vacuum |
Answer:
- c
- a
- d
- b
Question 4.
| 1. | Solid to liquid | (a) | Condensation |
| 2. | Liquid to gas | (b) | Deposition |
| 3. | Gas to solid | (c) | Melting |
| 4. | Gas to liquid | (d) | Vaporization |
Answer:
- c
- d
- b
- a
V. Assertion and Reason.
Question 1.
Mark the correct choice as:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If the assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) If the assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Question 1.
Assertion : When a very hot liquid is poured into a thick glass tumbler it cracks.
Reason : Unequal expansion of the inner and outer glass walls causes the glass to crack.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 2.
Assertion : Radiation is a process of transfer of heat in which a material medium is not necessary.
Reason : The heat from the sun reaches us through millions of miles of empty space by convection.
Answer:
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
Question 3.
Assertion : Temperature is the measure of the heat energy.
Reason : Energy is the capacity to do work.
Answer:
Assertion is false, but the reason is true
Question 4.
Assertion : Small gaps left between railway lines.
Reason : It allows for contraction of rails during summer.
Answer:
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
VI. Answer briefly
Question 1.
Write the relation between joule and calorie.
Answer:
1 Calorie = 4.186 J.
1 K cal = 4186 J = 4.186 KJ.
Question 2.
Mention the factors affecting the flow of heat.
Answer:
- Mass and materials of the bodies in contact.
- Difference in their temperatures.
Question 3.
What is the principle of calorimetry?
Answer:
Heat lost by the hot body is equal to the heat gained by the cold body.
Question 4.
What are the various modes of transfer of heat?
Answer:
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
Question 5.
Which color absorb heat radiation and which color reflects heat radiation?
Answer:
Black surfaces absorb heat radiation. White color reflects heat radiation.
Question 6.
What is the SI unit of heat capacity?
Answer:
The SI unit of heat capacity is JK-1
Question 7.
Mention the SI unit of specific heat capacity?
Answer:
The SI unit of specific heat capacity is J Kg-1 K-1.
Question 8.
What is the function of a thermostat in a device?
Answer:
Thermostat functions both as the sensor and the controller of a thermal system.
Question 9.
Name some appliances which uses thermostat.
Answer:
Central heater in a room, air conditioner, water heater, oven and refrigerators.
Question 10.
What is the function of silvered wall in a thermos flask?
Answer:
The silvered walls reflect radiated heat back to the liquid in the flask.
Question 11.
You would have noticed some space being left in railway tracks. Why?
Answer:
- It is because railway tracks which are made up of iron (metal) expand during summer.
- When there is a gap, there will not be any damage in the track due to expansion of the metal rod.
Question 12.
What is transfer of heat?
Answer:
If heat energy is supplied to any substance, it will be transferred from one part of the substance to another part.
Question 13.
Mention the applications of convection in daily life.
Answer:
- Formation of land breeze and sea breeze is due to convection of air.
- Wind flows from one region to another region by convection.
- In hot air balloons heat is transferred by convection and so the balloon raises.
- In refrigerators, cool air moves downward and replaces the hot air because of convection.
Question 14.
Define radiation.
Answer:
Radiation is defined as the way of heat transfer from one place to another in the form of electromagnetic waves.
Question 15.
Mention the applications of radiation in daily life.
Answer:
- Heat energy from the Sun reaches the Earth by radiation.
- While standing near fire we feel the heat which is transferred as radiation.
- Black surfaces absorb heat radiation. So that the bottom of the cooking vessels are painted black.
- White color reflects heat radiation. That’s why we are advised to wear white cloth during summer.
Question 16.
Why do we wear woolen clothes in winter?
Answer:
- The fibers of wool have the property of trapping air in between them.
- In trapping the air, woolen clothes do not allow the heat to flow away from the body, which would then become cold.
- Besides, wool is poor conductor of heat. So this property further prevents heat from leaving the body.
Question 17.
Can convection take place in solids? Why?
Answer:
- No. The molecules in a solid are only free to vibrate about their fixed positions.
- For convection to take place, the molecules need to move carrying the heat with them.
- Hence convection cannot take place in solids.
Question 18.
Distinguish between heat capacity and specific heat capacity.
Answer:
| Heat capacity |
Specific heat capacity |
| 1. It is the heat required to raise the temperature of a given mass of a substance through 1°C. | 1. It is the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance through 1°C. |
| 2. It depends on the mass of the body | 2. It does not depend on the mass of the body. |
| 3. Its unit is J°C-1 | 3. Its unit is J Kg-1°C-1 |
Question 19.
Arrange the following in order of decreasing expansion of heating : Steel, milk, air.
Answer:
Air, milk, steel.
Question 20.
Distinguish between evaporation and vaporization.
Answer:
|
Evaporation |
Vaporization |
| 1. Evaporation takes place at all temperature. | 1. Vaporization takes place at fixed temperature. |
| 2. Slow and gradual process | 2. Violent and rapid process. |
| 3. Takes place at the surface of the liquid | 3. Takes place through the entire liquid. |
VII. Answer in detail
Question 1.
Describe an experiment to prove that solids expands on heating and contract on cooling.
Answer:
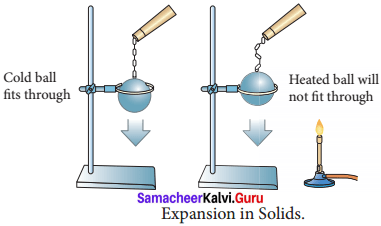
- Take a metal ball and a metal ring of suitable diameter.
- Pass the metal ball through the ring.
- You can observe that the metal ball can easily go through it.
- Now heat the metal ball and then try to pass it fits through through the ring.
- It will not pass through the ring.
- Keep the metal ball on the ring for some time.
- In few minutes, it will fall through the ring. Expansion in Solids
- When the ball is heated the atoms in the ball gain heat energy.
- They start vibrating and force each other apart.
- As a result an expansion takes place. That’s why the ball did not go through the ring.
- After some time, as the ball lost the heat energy to the surrounding it came back to its original size and it went through the ring.
- This shows that heat energy causes expansion in solids.
Question 2.
Write a note on radiation.
Answer:
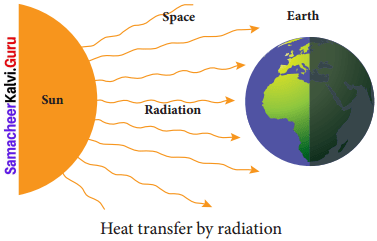
- Radiation is the third form of heat transfer.
- By conduction, heat is transferred through solids, by convection heat is transferred through liquids and gases, but by radiation heat can be transferred through empty space even through vacuum.
- Heat energy from the Sun reaches the Earth by this form of heat transfer.
- Radiation is defined as the way of heat transfer from one place to another in the form of electromagnetic waves.
Question 3.
Write the difference between conduction, convection, and radiation.
Answer:
|
Conduction |
Convection |
Radiation |
| Heat is transferred without the actual movement of the molecules | Heat transfer takes place due to the movement of the molecules themselves. | Heat is transferred without a medium. |
| Conduction is possible only in solids with the exception of mercury which is a liquid | Convection takes place in liquids and gases only. | Radiation requires no medium. It takes place even in vacuum. |
| Transfer is slow | Transfer is faster | Transfer is the fastest |
| Heat transfer can be in any direction. | Heat transfer is mainly upwards. | Heat transfer takes place in all direction. |
Question 4.
Distinguish between heat and temperature.
Answer:
|
Heat |
Temperature |
| 1. It is a form of energy. | 1. It is a thermal condition of body. |
| 2. It flows from one object to other object when there is a difference in temperature | 2. It is a quantity that indicates whether or not and in which direction heat will flow. |
| 3. It is the total amount of internal energy of a body | 3. It is proportional to average kinetic energy of the molecules of a body. |
| 4. In the transmission of heat, total amount of heat remains unchanged. | 4. In the transmission of heat, temperature does not remain same. |
| 5. Its SI unit is joule (J) | 5. Its SI unit is kelvin (K). |
VIII. Problems for practice
Question 1.
What is the rise in temperature of 5 kg of water if it is given 84,000 J heat energy? Specific heat capacity of water 4200 J Kg-1 °C-1.
Solution:
Given, m = 5 kg
Q = 84,000 J
C = 4200 J Kg-1 °C-1
Let rise in the temperature be ∆T.
Heat energy (Q) = mC∆T
84,000 = 5 x 4200 x ∆T
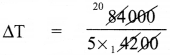
= 4°C
Question 2.
A body of mass 750 g requires 13,500 J of heat energy in order to raise its temperature from 25 °C to 55 °C. Calculate its specific heat capacity.
Solution:
Given
m = 750 g = 0.750 kg
∆T (55 – 25)°C = 30°C
Q = 13,500 J
Q = mC∆T
or
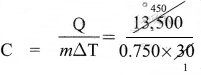
= 600 JKg-1
Question 3.
An iron ball requires 9000 J heat energy to raise its temperature by 10°C. Calculate the heat capacity of the iron bail.
Solution:
Given, Q = 9000 J
∆T = 10°C
Heat capacity, C = \(\frac{Q}{∆T}\) = \(\frac{9000}{10}\) = 900 J°C-1
IX. Picture based Questions
Question 1.
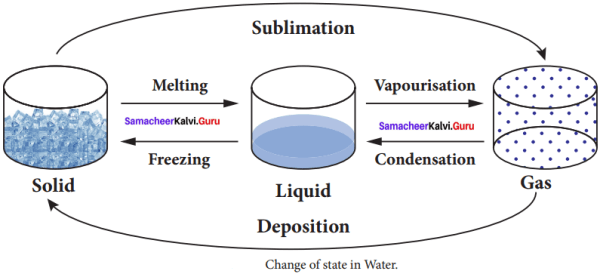
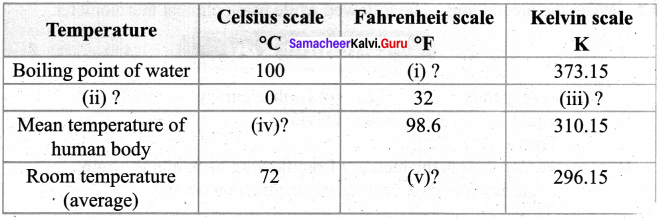
Answer:
- Freezing
- Vaporization
- Condensation
- Deposition