You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 11 Atomic Structure
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Atomic Structure Textbook Exercises
I. Choice the correct answer.
9th Science Atomic Structure Question 1.
Among the following the odd pair is ………………
(a) \(_{8}^{18} \mathrm{O},^{37}_{7} \mathrm{Cl}\)
(b) \(_{18}^{40} \mathrm{Ar}, \stackrel{14}{7} \mathrm{N}\)
(c) \(\frac{30}{14} \mathrm{Si}, \frac{31}{15} \mathrm{P}\)
(d) \(_{24}^{54} \mathrm{Cr},_{19}^{39} \mathrm{K}\)
Answer:
(b) \(_{18}^{40} \mathrm{Ar}, \stackrel{14}{7} \mathrm{N}\)
Atomic Structure Class 9 Samacheer Kalvi Question 2.
Change in the number of neutrons in an atom changes it to
(a) an ion
(b) an isotope
(c) an isobar
(d) another element
Answer:
(b) an isotope
Chapter 11 Atomic Structure Question 3.
The term nucleons refer to
(a) Protons and electrons
(b) Only Neutrons
(c) Electrons and neutrons
(d) Protons and neutrons
Answer:
(d) Protons and neutrons
9th Science Atomic Structure Answers Question 4.
The number of protons, neutrons and electrons present respectively in 35Br
(a) 80, 80, 35
(b) 35, 55, 80
(c) 35, 35, 80
(d) 35, 45, 35
Answer:
(d) 35, 45, 35
Atomic Structure Book Back Answers Question 5.
The correct electronic configuration of potassium is
(a) 2,8,9
(b) 2,8,1
(c) 2,8,8,1
(d) 2,8,8,3
Answer:
(c) 2,8,8,1
II. True or false / if false give the correct answer.
- In an atom, electrons revolve around the nucleus in fixed orbits – True
- Isotopes of an element have the different atomic numbers – False.
Correct Statement: Isotopes are atoms of the same element, which have same atomic number but different mass numbers. - Electrons have negligible mass and charge – False.
Correct Statement: Electrons have negligible mass and have negative charge. - Smaller the size of the orbit, lower is the energy of the orbit – True
- The maximum number of electrons in L shell is 10 – False.
Correct Statement: The maximum number of electron in L shell is 8
III. Fill in the Blanks.
- Calcium and Argon are examples of a pair of ………………
- Total Number of electrons that can be accommodated in an orbit is given by ………………..
- …………… isotope is used in the nuclear reactors.
- The number of neutrons present in \(_{3}^{7} \mathrm{Li}\) is ……………….
- The valency of Argon is
Answer:
- Isobars
- 2n2
- Radio
- 4
- 0
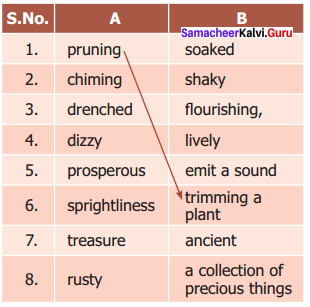
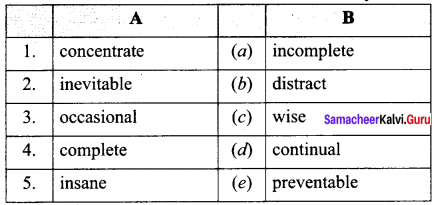
IV. Match the following.
| 1. | Dalton | (a) | Hydrogen atom model |
| 2. | Thomson | (b) | Planetary model |
| 3. | Rutherford | (c) | First atomic theory |
| 4. | Neils Bohr | (d) | Plum pudding model |
| (e) | Discovery of neutrons |
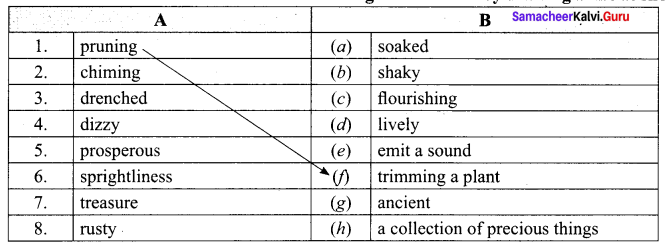
Answer:
- (c)
- (d)
- (b)
- (a)
V. Complete the following table.
9th Atomic Structure Book Back Answers Question 1.
|
Atomic |
Mass number |
Numbers of Neutrons | Numbers of Protons | Number of Electrons | Name of the Element |
| 9 | – | 10 | – | – | – |
| 16 | – | 16 | – | – | – |
| – | 24 | – | – | 12 | Magnesium |
| – | 2 | – | 1 | – | – |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | – |
Answer:
|
Atomic |
Mass number |
Numbers of Neutrons | Numbers of Protons | Number of Electrons | Name of the Element |
| 9 | 19 | 10 | 9 | 9 | Potassium |
| 16 | 32 | 16 | 16 | 16 | Sulphur |
| 12 | 24 | 12 | 12 | 12 | Magnesium |
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Deuterium |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Hydrogen |
VI. Answer very briefly.
9th Science Atomic Structure Book Back Answers Question 1.
Name an element which has the same number of electrons in its first and second shell.
Answer:
Beryllium
9th Science Guide Atomic Structure Question 2.
Write the electronic configuration of K and Cl
Answer:
Electronic configuration of
K+ – 2, 8, 8
Cl– – 2, 8, 8
Atomic Structure Answers Question 3.
Compare the charge and mass of protons and electrons.
Answer:
| Mass | Charge | |
| Proton | 1.672 × 10<sup>- 24</sup>g | Positive |
| Electron | 9.108 × 10<sup>- 28</sup>g | Negative |
Atomic Structure In Tamil Question 4.
For an atom ‘X’, K, L and M shells are completely filled. How many electrons will be present in it?
Answer:
K – 2, L – 8, M – 18, 28 electrons – Nickel
Structure Of Atom Exercise Solution Class 9 Question 5.
Ca2+ has completely filled outer shell. Justify your answer.
Answer:
Ca2+ – K – 2, L – 8, M – 8, N – 2
Calcium loses two electrons and they become Ca2+ ions. Electronic configuration: 2, 8, 8
VII. Answer briefly.
Atomic Structure 9th Class Question 1.
State the law of multiple proportion.
Answer:
When two elements combine together to form more than one compound, the mass of two elements combines with a fixed mass in simple ratio.
Question 2.
List the uses of isotopes.
Answer:
The uses of radioactive isotopes are as follows.
| Radioactive isotopes | Uses |
| Uranium 235 | fuel in, nuclear reactors |
| Cobalt 60 | Treatment of cancer |
| Iodine 131 | Treatment of goiter |
| Carbon 14 | Find the age of plants and animals |
Question 3.
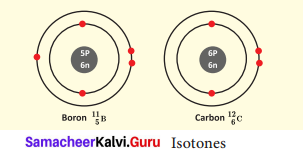
What is Isotone? Give an example.
Answer:
Atoms of different elements with different atomic number and different mass number, but with the same number of neutrons are called isotones.
Eg. Boron and carbon.
Question 4.
Draw the structure of oxygen and sulphur atoms.
Answer:
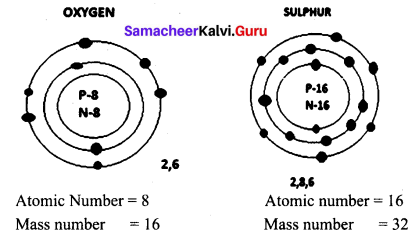
Question 5.
Calculate the number of neutrons, protons and electrons
- atomic number 3 and mass number 7
- atomic number 92 and mass number 238
Answer:
- Number of neutrons – 4
Number of protons – 3
Number of electrons – 3 - Number of neutrons – 146
Number of protons – 92
Number of electrons – 92
VIII. Long answer.
Question 1.
What conclusions were made from the observations of Gold foil experiment?
Answer:
In Rutherford’s Alpha ray scattering experiment, the following conclusions were made from the observations.
- Atom has a very small nucleus at the centre.
- There is a large empty space around the nucleus.
- The entire mass of an atom is concentrated in a very small positively charged region, which is called Nucleus.
- The electrons are distributed in the vacant space around the nucleus.
- The electrons move in circular paths around the nucleus.
Question 2.
Explain the postulates of Bohr’s atomic model.
Answer:
The main postulates of Neil’s Bohr are as follows.
- In atoms, electrons revolve around the nucleus in special orbits called discrete orbits or shells or energy levels.
- While the electrons revolve, they do not radiate energy.
- The circular orbits are numbered as 1,2,3,4 or designated as K, L, M, N shells. These numbers are referred as principal quantum numbers (n).
- K shell (n = 1) is closer to the nucleus and is associated with lowest energy. L, M, N are the next higher energy levels. As the distance from the nucleus increases, the energy of the shells also increase.
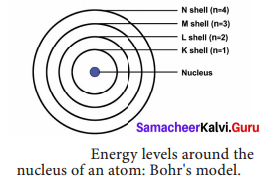
- The energy of each orbit or shell is a fixed quantity.
- As the distance from the nucleus increases, the size of the orbits also increases.
- The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in an energy level is 2n2 (n = quantum number of its orbit).
- When an electron absorbs energy, it jumps from lower energy level to higher energy level.
- When an electron returns from higher energy level to lower energy level, it gives off energy.
Question 3.
State the Gay Lussac’s law of combining volumes, explain with an illustration.
Answer:
Whenever gases react together, the volumes of the reacting gases and the products bear a simple whole number ratio, provided all the volumes are measured under similar conditions of temperature and pressure.
Steps:
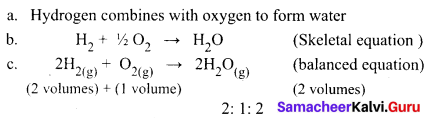
Two volumes of hydrogen react with one volume of oxygen to form two volumes of water vapour that is the ratio by volume, which gases bears is
2:1:2, which is a simple whole number ratio.
Activity
Question 1.
Symbolically represent the following atoms using atomic number and mass number,
- Carbon
- Oxygen
- Silicon
- Beryllium
Answer:
- Carbon = \(_{6}^{12} \mathrm{C}\)
- Oxygen = \(\begin{array}{c}{16} \\ {8}\end{array}\)
- silicon = \(_{14}^{28} \mathrm{S}\)
- Beryllium = \(_{4}^{9} \mathrm{Be}\)
Test Yourself
Question 2.
Calculate the number of neutrons in the following atoms:
- \(\begin{array}{l}{27} \\ {13}\end{array} \mathbf{A} \mathbf{I}\)
- \(\begin{array}{l}{31} \\ {15}\end{array}\)
- \(\begin{array}{l}{190} \\ {76}\end{array}\)
- \(_{24}^{54} C_{1}\)
Answer:
Number of neutrons (n) = Mass number (A) – Atomic number (z)
- \(\begin{array}{l}{27} \\ {13}\end{array} \mathbf{A} \mathbf{I}\) Number of neutrons (n) = 27 (A) – 13 (Z) = 14
- \(\begin{array}{l}{31} \\ {15}\end{array}\) Number of neutrons (n) = 31 (A) – 15 (Z) =16
- \(\begin{array}{l}{190} \\ {76}\end{array}\) Number of neutrons (n) = 190 (A) – 76 (Z) = 114
- \(_{24}^{54} C_{1}\) Number of neutrons (n) = 54 (A) – 24 (Z) = 30
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Atomic Structure In Text Problems
Question 1.
Calculate the atomic number of an element whose mass number is 39 and number of neutrons is 20. Also find the name of the element.
Solution:
Mass Number = Atomic number + Number of neutrons
Atomic Number = Mass number – Number of neutrons
= 39 – 20
Atomic Number = 19
Element having atomic number 19 is Potassium (K)
Question 2.
What is the Electronic configuration of Aluminium?
Electronic configuration of Aluminium atom: (Z = 13) K shell = 2 , L shell = 8 and M shell = 3 electron. So its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 3
Question 3.
Find the valency of Magnesium and Sulphur.
Answer:
Electronic configuration of magnesium is 2, 8, 2. So valency is 2.
Electronic configuration of sulphur is 2, 8, 6. So valency is 2 i.e.(8 – 6)