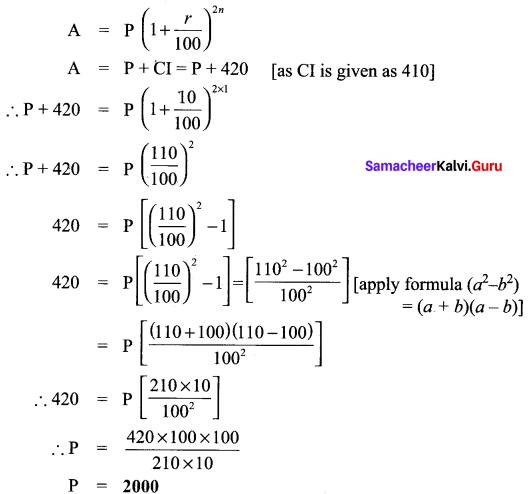
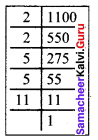
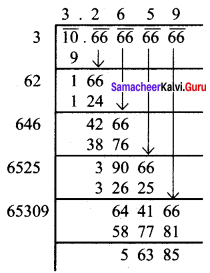
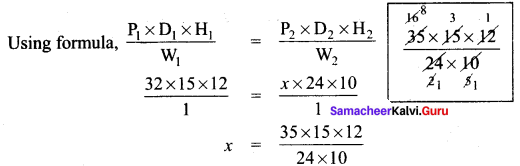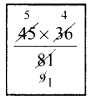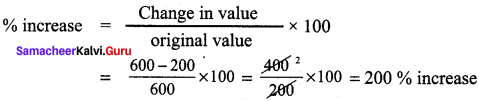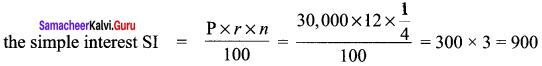Students can Download Maths Chapter 3 Geometry Ex 3.1 Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Solutions Term 3 Chapter 3 Geometry Ex 3.1
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
- The altitudes of a triangle intersect at………..
- The medians of a triangle cross each other at………..
- The meeting point of the angle bisectors of a triangle is………..
- The perpendicular bisectors of the sides a triangle meet at………..
- The centroid of a triangle divides each medians in the ratio………..
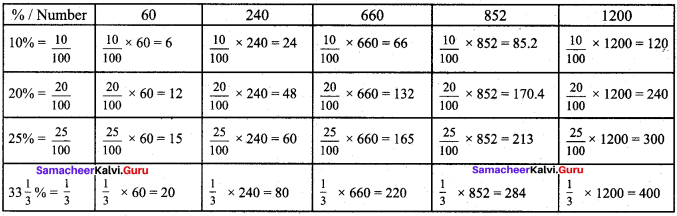
Solution:
- Orthocentre
- Centroid
- Incentre
- Circumcentre
- 2 : 1
![]()
Question 2.
Say True or False:
(i) In any triangle the Centroid and the Incentre are located inside the triangle.
(ii) The centroid, orthocentre, and incentre of a triangle are collinear.
(iii) The incentre is equidistant from all the vertices of a triangle.
Solution:
(i) True
(ii) True
(iii) False
Question 3.
(a) Where does the circumcentre lie in the case of
(i) An acute angled triangle.
Solution:
Inside the triangle.
(ii) An obtuse-angled triangle.
Solution:
Exterior of the triangle.
(iii) A right angled triangle.
Solution:
On the hypotenuse.
(b) Where does the orthocentre lie in the case of
(i) An acute-angled triangle.
Solution:
Interior of the triangle.
(ii) An obtuse-angled triangle.
Solution:
Exterior of the triangle.
(iii) A right angled triangle.
Solution:
On the vertex containing 90°.
Question 4.
Fill in the blanks:
In the triangle ABC,
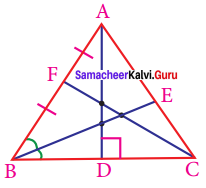
(i) The angle bisector is……….
(ii) The altitude is………..
(iii) The median is…………
Solution:
(i) BE
(ii) AD
(iii) CF
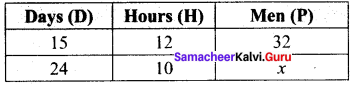
Question 5.
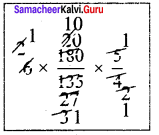
In right triangle ABC, what is the length of altitude drawn from the vertex A to BC?
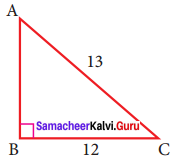
Solution:
In this right angled triangle ΔABC, length of the altitude drawn from vertex A is the leg AB itself. By Pythagoras theorem.
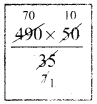
AC² = AB² + BC²
13² = AB² + 12²
169 = AB² + 144
AB² = 169 – 144 = 25
AB² = 52
AB = 5cm
![]()
Question 6.
In triangle XYZ, YM is the angle bisector of ∠Y and ∠Y is 100°. Find ∠XYM and ∠ZYM.
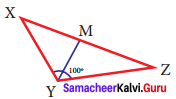
Solution:
Given YM is the angle bisector of ∠Y.
also ∠Y = 100°
Angle -bisector divides the angle into two congruent angles.
∠XYM = ∠ZYM
∠Y = ∠XYM + ∠ZYM
100° = ∠XYM + ∠ZYM [∴ ∠XYM = ∠ZYM]
2 ∠XYM = 100°
∠XYM = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (100°)
∠XYM = 50°
∴ ∠ZYM = 50°
Question 7.
In triangle PQR, PS is a median and QS = 3.5 cm, then find QR?
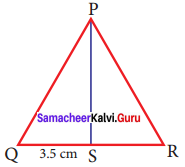
Solution:
Given PS is the median and QS = 3.5 cm
Median is the line drawn from a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side.
∴ QS = RS
so QS = RS = 3.5 cm
∴ QR = QS +SR = 3.5 + 3.5 = 7 cm
QR = 7 cm
Question 8.
In triangle ABC, line is a perpendicular bisector of BC. If BC = 12 cm, SM = 8 cm, find CS.
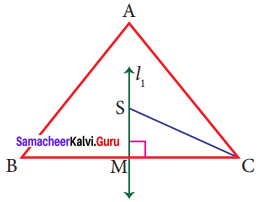
Solution:
Given l1 is the perpendicular bisector of BC.
∴ ∠SMC = 90° and BM = MC
BC = 12 cm
⇒ BM + MC = 12 cm
MC + MC = 12 cm [∴ BM = MC]
2MC = 12
MC = \(\frac{12}{2}\)
MC = 6 cm
Given SM = 8 cm
By Pythagoras theorem SC² = SM² + MC²
SC² = 8² + 6²
SC² = 64 + 36
CS² = 100
CS² = 10²
CS = 10 cm
![]()