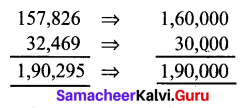You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Solutions Term 1 Chapter 1 Numbers Ex 1.5
![]()
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks.
(i) The difference between the smallest natural number and the smallest whole number is _____
(ii) 17 × ___ = 34 × 17
(iii) When _____ is added to a number, it remains the same.
(iv) Division by ____ is not defined.
(v) Multiplication by ____ leaves a number unchanged.
Solution:
(i) 1
Hint: 1 – 0 = 1
(ii) 34
(iii) 0
(iv) 0
(v) 1
Question 2.
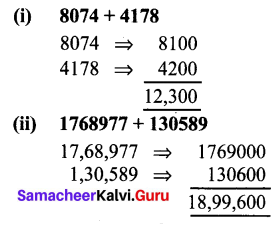
![]()
Say True or False.
- 0 is the identity for multiplication of whole numbers.
- Sum of two whole numbers is always less than their product.
- Both addition and multiplication are associative for whole numbers.
- Both addition and multiplication are commutative for whole numbers.
- Multiplication is distributive over addition for whole numbers.
Solution:
- False
- False
- True
- True
- True
Question 3.
Name the property being illustrated in each of the cases given below:
- 75 + 34 = 34 + 75
- (12 × 4) × 8 = 12 × (4 × 8)
- 50 + 0 = 50
- 50 × 1 = 50
- 50 × 42 = 50 × 40 + 50 × 2
Solution:
- Addition is commutative
- Multiplication is associative
- 0 is the additive identity
- 1 is the multiplicative identity.
- Distributivity of multiplication over addition
Question 4.
Use the properties of whole numbers and simplify.
(i) 50 × 102
(ii) 500 × 689 – 500 × 89
(iii) 4 × 132 × 25
(iv) 196 + 34 + 104
Solution:
(i) 50 × 102
= 50 × (100 + 2)
= (50 × 100) + (50 × 2)
= 5000 + 100 = 5100
(ii) 500 × 689 – 500 × 89
= 500 × (689 – 89)
= 344500 – 44500
= 300000
= 500 × (689 – 89)
= 500 × 600
= 3,00000
(iii) (4 × 132) × 25
= 4 × (132 × 25)
= (4 × 132) × 25
= 528 × 25
= 13200
= 4 × (132 × 25)
= 4 × 3300
= 13200
(iv) (196 + 34) + 104 = 196 + (34 + 104)
(196 + 34) + 104 = 230 + 104 = 334
196 + (34 + 104) = 196 + 138 = 334
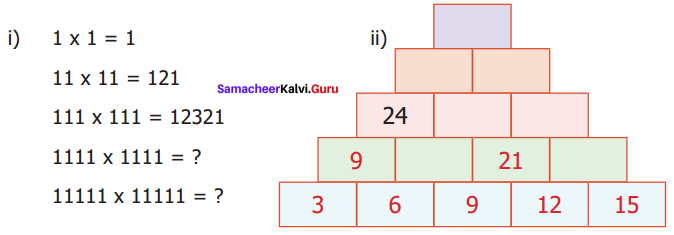
![]()
Objective Type Questions
Question 5.
(53 + 49) × 0 is
(a) 102
(b) 0
(c) 1
(d) 53 + 49 + 0
Solution:
(b) 0
53 × 0 + 49 × 0 = 0 + 0 = 0
Question 6.
\(\frac{59}{1}\) is
(a) 1
(b) 0
(c) \(\frac{1}{59}\)
(d) 59
Solution:
(d) 59
Question 7.
The product of a non-zero whole number and its successor is always
(a) an even number
(b) an odd number
(c) zero
(d) none of these
Solution:
(a) an even number
Question 8.
The whole number that does not have a predecessor is
(a) 10
(b) 0
(c) 1
(d) none of these
Solution:
(b) 0
0 is the smallest whole number
Question 9.
Which of the following expressions is not zero?
(a) 0 × 0
(b) 0 + 0
(c) 2/0
(d) 0/2
Solution:
(c) 2/0
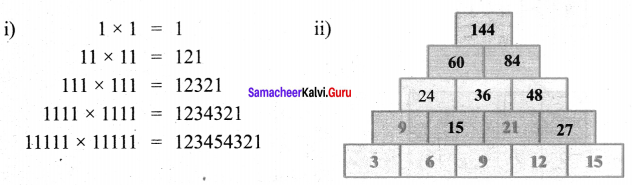
![]()
Question 10.
Which of the following is not true?
(a) (4237 + 5498) + 3439 = 4237 + (5498 + 3439)
(b) (4237 × 5498) × 3439 = 4237 × (5498 × 3439)
(c) 4237 + 5498 × 3439 = (4237 + 5498) × 3439
(d) 4237 × (5498 + 3439) = (4237 × 5498) + (4237 × 3439)
Solution:
(c) 4237 + 5498 × 3439 = (4237 + 5498) × 3439