Students can find the most related topics which helps them to analyse the concepts if they practice according to the chapter-wise page. It is necessary for the students to practice more Questions and Answers for Tamilnadu State Board Solutions of 11th Commerce are given in the pdf format in chapter 20 International Finance Questions and Answers so that students can prepare in both online and offline modes. So, Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Book Solutions Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, to score good marks.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Solutions Chapter 20 International Finance
Get the Questions and Answers, in Tamilnadu State Board 11th Commerce Solutions for Chapter 20 International Finance. Learn the concepts of 11th Commerce Chapter-Wise by referring to the Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Chapter 20 International Finance Questions and Answers. Hence we suggest the students to Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Book Solutions Questions and Answers pdf to enhance your knowledge.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce International Finance Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
An instrument representing ownership interest in securities of a foreign issuer is called …………….
(a) an ownership certificate
(b) a depositary receipt
(c) an ownership receipt
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) a depositary receipt
Question 2.
Issuance of DRs is based on the increase of demand in the ……………
(a) International market
(b) Local market
(c) Existing shareholders
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) International market
Question 3.
ADRs are issued in …………….
(a) Canada
(b) China
(c) India
(d) The USA
Answer:
(d) The USA
Question 4.
Depositary receipts that are traded in an international market other than the United States are called …………….
(a) Global Depositary Receipts
(b) International Depositary Receipts
(c) Open Market Depositary Receipts
(d) Special Drawing Rights
Answer:
(a) Global Depositary Receipts
Question 5.
……………. bond is a special type of bond issued in the currency other than the home currency.
(a) Government Bonds
(b) Foreign Currency Convertible Bond
(c) Corporate Bonds
(d) Investment Bonds
Answer:
(b) Foreign Currency Convertible Bond
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Who are Foreign Institutional Investors?
Answer:
The Foreign Institutional Investors (FI1) can be defined as an investment made by a Non – resident in equity of domestic company without intention of acquiring management control.
Question 2.
What is a Depository Receipt?
Answer:
A depository receipt is a negotiable financial instrument issued by a bank to represent a foreign company’s equity shares or securities. They are issued to attract a greater amount of investment from other countries.
Question 3.
What is a GDR (Global Depository Receipt)?
Answer:
GDR is an instrument issued abroad by a company to raise funds in some foreign currencies and is listed and traded on a foreign stock exchange.
Question 4.
What is an American Depositary Receipt (ADR)?
Answer:
ADR is a dollar denominated negotiable certificate representing a non-US company in US market which allows the US citizens to invest in overseas securities.
Question 5.
What is a Foreign Currency Convertible Bond?
Answer:
Foreign currency convertible bond is a special type of bond issued in the currency other than the home currency. In other words, companies issue foreign currency convertible bonds to raise money in foreign currency
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the importance of international finance.
Answer:
- International finance helps in calculating exchange rates of various currencies of nations and the relative worth of each and every nation in terms thereof.
- It helps in comparing the inflation rates and getting an idea about investing in international debt securities.
- It helps in ascertaining the.economic status of the various countries and in judging the foreign market.
Question 2.
What are Foreign Currency Convertible Bonds?
Answer:
Foreign currency convertible bond is a special type of bond issued in the currency other than the home currency. In other words, companies issue foreign currency convertible bonds to raise money in foreign currency.
Question 3.
Explain any three disadvantages of FDI.
Answer:
1. Exploiting Natural Resources : The FDI Companies deplete natural resources like water, forest, mines etc. As a result such resources are not available for the usage of common man in the host country.
2. Heavy Outflow of capital : Foreign companies are said to take away huge tunes in the form of dividend, royalty fees etc. This causes a huge outflow of capital from the host country.
3. Not Transferring Technology : Some foreign enterprises do not transfer the technology to developing countries. They mostly transfer second hand technology to the host country.
Question 4.
State any three features of ADR.
Answer:
- ADRs are denominated only in US dollars.
- They are issued only to investors who are American residents.
- The depository bank should be located in US.
Question 5.
State any three features of GDR.
Answer:
- It is a negotiable instrument and can be traded freely like any other security.
- GDRs are issued to investors across the country. It is denominated in any acceptable freely convertible currency.
- GDR is denominated in any foreign currency but the underlying shares would be denominated in local currency of the issuer.
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Describe the importance of international finance?
Answer:
- International finance helps in calculating exchange rates of various currencies of nations and the relative worth of each and every nation in terms thereof
- It helps in comparing the inflation rates and getting an idea about investing in international debt securities.
- It helps in ascertaining the economic status of the various countries and in judging the foreign market.
- International Financial Reporting System (IFRS) facilitates comparison of financial statements made by various countries.
- It helps in understanding the basics of international organisations and maintaining the balance among them.
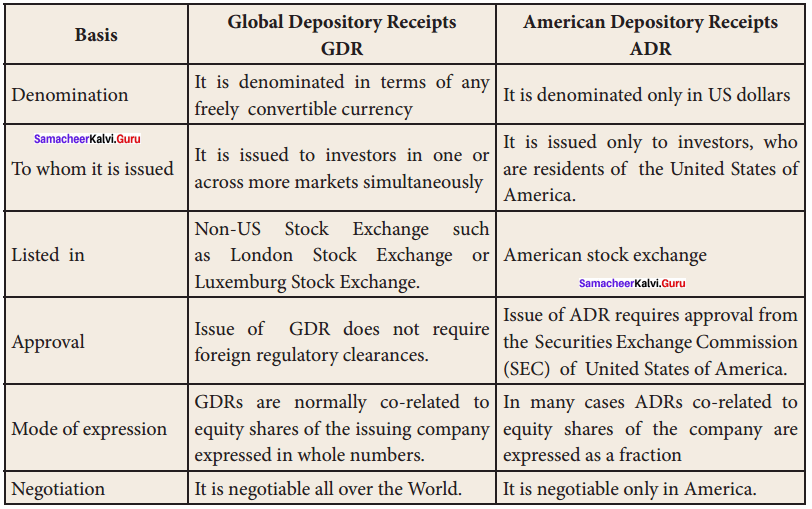
Question 2.
Distinguish between GDR and ADR.
Answer:
Question 3.
State any five features of FCCB.
Answer:
- FCCB is issued by an Indian company in foreign currency.
- These are listed and traded in foreign stock exchange and similar to the debenture.
- It is a convertible debt instrument. It carries interest coupon. It is unsecured.
- It gives its holders the right to convert for a fixed numbers of shares at a pre – determined price.
- It can be converted into equity or depository receipt after a certain period.
Question 4.
Explain any five advantages of FDI.
Answer:
1. Achieving Higher Growth in National Income Developing countries get much needed capital through FDI to achieve higher rate of growth in national income.
International Finance
2. Help in Addressing BOP Crisis FDI provides inflow of foreign exchange resources into a country. This helps the country to solve adverse balance of payment position.
3. Faster Economic Development FDI brings technology, management and marketing skills along with it. These are crucial for achieving faster economic development of developing countries.
4. Generating Employment Opportunities: FDI generates a lot of employment opportunities in developing countries, especially in high skill areas.
5. Encouraging Competition in Host Countries Entry of FDI into developing country promotes healthy competition therein. This leads to enterprise in developing countries operating efficiently and effectively in the market. Consumers get a variety of products of good quality at market determined price which usually benefits the customers.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce International Finance Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
…………….. is a section of financial economics that deals with the monetary interactions that occur between two or more countries.
(a) International finance
(b) Business finance
(c) DR
(d) GDR
Answer:
(a) International finance
Question 2.
From …………….., Foreign International Investors have been allowed to invest in all securities traded on the primary and secondary markets.
(a) 1992
(b) 1991
(c) 1995
(d) 1996
Answer:
(a) 1992
Question 3.
………………. is an instrument issued abroad by a company to raise funds in some foreign currencies and is listed and traded on a foreign stock exchange.
(a) GDR
(b) DR
(c) FDI
(d) FII
Answer:
(a) GDR
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
Answer:
Foreign direct investment (FDI) is an investment made by a company or an individual in one country with business interests in another country, in the form of either establishing business operations or acquiring business assets in the other country, such as ownership or controlling interest in a foreign company.
Question 2.
What are Commercial Banks?
Answer:
Most of the commercial banks extend foreign currency loans for promoting business opportunities. The loans and services of various types, provided by banks differ from country to country.
Question 3.
What is International capital markets?
Answer:
Modem organisations including multinational companies depend upon sizeable borrowings in rupees as well as in foreign currencies. Prominent financial instruments used for this purpose are Depository Receipts.
Share this Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for 11th Commerce Chapter 20 International Finance Questions and Answers with your friends to help them to overcome the issues in exams. Keep visiting this site Tamilnadu State Board Solutions frequently to get the latest information on different subjects. Clarify your doubts by posting the comments and get the answers in an easy manner.