Students can Download English lesson 2 Crossing The River Questions and Answers, Summary, Activity, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 8th English Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th English Solutions Term 2 Supplementary Chapter 2 Crossing The River
Read And Understand
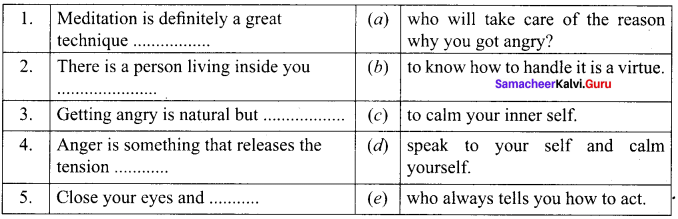
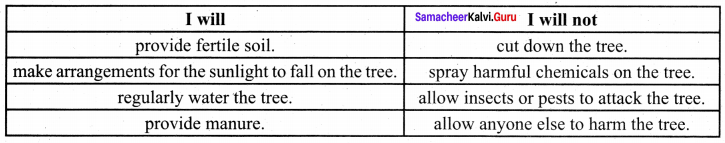
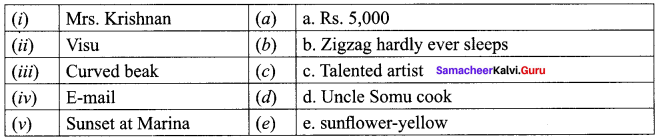
A. Match the following

Answer:
- e
- c
- d
- f
- a
- b
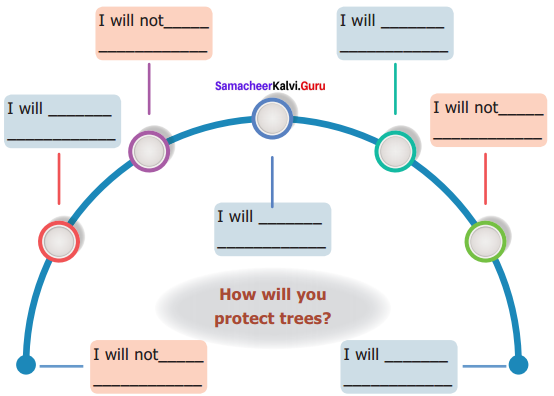
B. Fill in the blanks.
- Pundit have many _______ and _______
- Moti is a poor
- The milkmaid discharged her duties _______
- Moti feels it as a _______to serve the great pundit
- The pundit was an _______speaker
- Moti assured to give the milk at the dawn _______
Answer:
- disciples, admirers
- milkmaid
- faithfully
- great privilege
- eloquent
- enthusiastically
C. Answer the following:
Crossing The River 8th Std Question 1.
What was the pundit’s discourse about?
Answer:
The pundits discourse was about God and Truth and similar tough and complex matters.
Crossing The River Questions And Answers Question 2.
Why did Moti, the milkmaid, feel happy?
Answer:
She left happy that she made a humble contribution towards the pundits physical well being by regularly supplying him with pure milk.
Crossing The River Summary 8th Standard Question 3.
What was the resolution of Moti?
Answer:
Moti’s resolution was that even if the landlord failed to pay her for the milk and her labour, she would not fail in her duty.
Crossing The River Book Back Answers Question 4.
Give reason for the pundit to ask for the milk at dawn.
Answer:
The pundit was under a vow for performing a certain ritual for which he needed the milk at down
8th English Crossing The River Question 5.
Why did Moti come late on the first day of-the ritual?
Answer:
She came late on the first day of the ritual because the boatman did not turn up that early even though Moti informed him of the need for her to cross the river.
Crossing The River 8th Standard Supplementary Question 6.
Mention an incident that shows the naivety of Moti.
Answer:
When Moti came late to pundits house, she explained that she couldn’t cross the river without the of the boatman. When the pundit commented jocularly that one could cross even the ocean of life by uttering the name of Vishnu, she told him that she did not know about it. She thanked him for passing the secret on to her. The pandit laughed at her naivety.
Crossing The River Summary Question 7.
How did the milkmaid cross the river?
Answer:
She just uttered the name of Vishnu and walked across the river.
Crossing The River 8th Std Book Back Answers Question 8.
What was the secret shared by pundit to milkmaid?
Answer:
The secret was that one could cross even the ocean of life by buttering the name of Vishnu. This was shared by the pundit to the milkmaid.
8th Crossing The River Question 9.
How did the pundit appreciate the milk maid? Who else did he convey his thanks for?
Answer:
He appreciated the pain she had taken in getting up early, milking the cow and delivering the milk to him at dawn. He also asked the milkmaid to convey his thanks to the boatman.
Crossing The River Summary Class 8 Question 10.
Why did the pundit faint at the end of the story?
Answer:
When the pundit saw the mlilk maid crossing the river with ease, he was dumbstruck and almost fainted.
D. Identify the speaker:
- “But I apply the secret?”
- “Tell the boatman how pleased I am with him.”
Answer:
- Moti, the milkmaid
- The pundit
Step To Success
A. Select correct options to fill in the blanks.
1. As I _______in the rain for the bus to arrive, it appeared as ______ it would not arrive, ______ it took all my patience.
(a) weighted, though, so
(b) wetted, if, so
(c) waited, though, till
Answer:
(c) waited, though, till
B. Select option that correctly forms the 2nd pair similar to the 1st.
Question 1.
Bread : Yeast:: Curd : ?
(a) Germs
(b) Bacteria
(c) Fungi
(d) Virus
Answer:
(b) Bacteria
Question 2.
Fungi: Fungus :: Species : ?
(a) Specey
(b) Specy
(c) Specie
(d) Species
Answer:
(d) Species
[Clue : The singular form of ‘Fungi’ is ‘Fungus’. And for ‘Species’, it is the same in singular, in plural.]
Question 3.
Throw : Worth :: Tide : ?
(a) Water
(b) Ocean
(c) Edit
(d) Sea
Answer:
(c) Edit
Question 4.
Lion: Forest :: Otter : ?
(a) Cage
(b) Water
(c) The Alps
(d) Burrow
Answer:
(b) Water
Connecting To Self
Question 1.
Answer:

Crossing The River Additional Questions
I Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
The _____ was one only admirers of the Pundit.
(a) boatman
(b) landlord
(c) farmer
(d) helper
Answer:
(b) landlord
Question 2.
Moti _____ before the Pundit.
(a) sang
(b) wrote the secret
(c) prostrated
(d) shouted
Answer:
(c) prostrated
Question 3.
The Pundit was speaking about _____ and Truth.
(a) doctrine
(b) Life
(c) philosophy
(d) God
Answer:
(d) God
Question 4.
“One could cross the _____ of life by uttering the name of Vishnu”.
(a) river
(b) bay
(c) ocean
(d) sea
Answer:
(c) ocean
Question 5.
The story draws a _____ between scholarship and innocence.
(a) similarity
(b) analogy
(c) equivalent
(d) contrast
Answer:
(d) contrast
II. Fill in the blanks:
- The landlord had _______ a poor milkmaid,Moti,to the Pundit
- She crossed the river by the help of a _______
- Often the _______ himself received the milk.
- What a great privilege it is to ______ a great Pundit?’
Answer:
- Commissioned
- ferry boat
- pundith
- serve
III. dentify the character and speaker:
- “Well, sir, nobody had told me that!”
- “That is secret!”
- “Thank you sir, passing it on to me”
- “Who then plied the boat for you?”
- “You forgot the secret you passed on to me”
- “What do you mean?”
- “But I apply the secret!”
Answer:
- Moti, the milkmaid
- The Pundit
- Moti, the milkmaid
- The Pundit
- Moti, the milkmaid
- The Pundit
- Moti, the milkmaid
IV. Write True or False against each statement:
- The milkmaid did not do her duty sincerely.
- The boatman did not turn up early morning.
- The poor woman would hardly understand the importance of the wise observation of the Pundit.
- The water remained knee deep for Moti.
- The Pundit almost fainted.
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
V. Match the following:

Answer:
- (c)
- (d)
- (a)
- (e)
- (b)
VI. Give Very Short Answers :
Question 1.
Who was the landlord?
Answer:
He was one of the admirers of the Pundit.
Question 2.
What was the name of the milkmaid?
Answer:
The milkmaids name was Moti.
Question 3.
Who helped here to cross the river?
Answer:
The boatman helped her to cross the river.
Question 4.
Did Moti fail in her duty?
Answer:
No, Moti did not fail in her duty.
Question 5.
What did Moti do, when she reached the river-bank?
Answer:
She paid reverence to the river.
VII. Write Short Answers :
Question 1.
How did the milkmaid discharge her duty?
Answer:
The milkmaid discharged her duty faithfully, by delivering milk every morning.
Question 2.
What did the boatman tell to Moti?
Answer:
The boatman told her that it would not be possible for him to fly the boat in darkness as the river was in spate.
Question 3.
How does the story draw a contrast between scholarship and innocence?
Answer:
The story draws a contrast between the scholarship and innocence by demonstrating the miracle of faith.
VIII Answer in Detail:
Question 1.
“The Pundit was an eloquent speaker”.Elucidate.
Answer:
The celebrated Pundit had many disciples and admirers as he was an eloquent speaker. Whenever he gave a discourse, hundreds of people gathered to listen to him. The milkmaid also made it a point to listen to him as she was sure that the Pundit was speaking about God and Truth. The only one who was very near to God and Truth could command such wisdom’, she thought. She was happy that she made a humble contribution to supplying milk to the Pundit.
IX. Rearrange the jumbled sentences :
1. Among them was the landlord of the area who lived on the other side of the river.
2. The milkmaid discharged her duty faithfully day after day.
3. The celebrated Pundit had many disciples and admirers.
4. She crossed the river by the help of a ferry boat.
5. The landlord had commissioned a poor milkmaid Moti to supply milk to the Pundit.
Answer:
3,1,5,2,4
3.The celebrated Pundit had many disciples and admirers.
1. Among them was the landlord of the area who lived on the other side of the river.
5. The landlord had commissioned a poor milkmaid Moti to supply milk to the Pundit.
2. The milkmaid discharged her duty faithfully day after day.
4. She crossed the river by the help of a ferry boat.
X. Read the passage and answer the questions :
Question 1.
One day, while receiving the milk, the Pundit told Moti. “Woman! Can you bring the milk at the least an hour before the sunrise for only a month? I am under a vow for performing a certain ritual for which I need the milk that early.”
(a) Who was Moti?
Answer:
Moti was a milkmaid.
(b) What did the Pundit tell Moti?
Answer:
The Pundit told her to bring milk, an hour before the sunrise for only a month.
(c) Why did he say so?
Answer:
He said so because he was under a vow for performing a certain ritual.
Question 2.
Moti stepped out onto the road. It was a foggy dawn. No doubt the woman was kidding him – concluded the Pundit and he followed her tiptoe. Upon reaching the river-bank, Moti put her empty pot down and folded hands, paid obeisance to the river. Then, picking up the pot, she stepped into The water.
(a) How was the dawn?
Answer:
It was a foggy dawn.
(b) What did the Pundit conclude?
Answer:
The Pundit concluded that the milkmaid was kidding him.
(c) What did she do on reaching the river-bank?
Answer:
She folded her hands and paid reverence to the river.
Crossing The River Summary
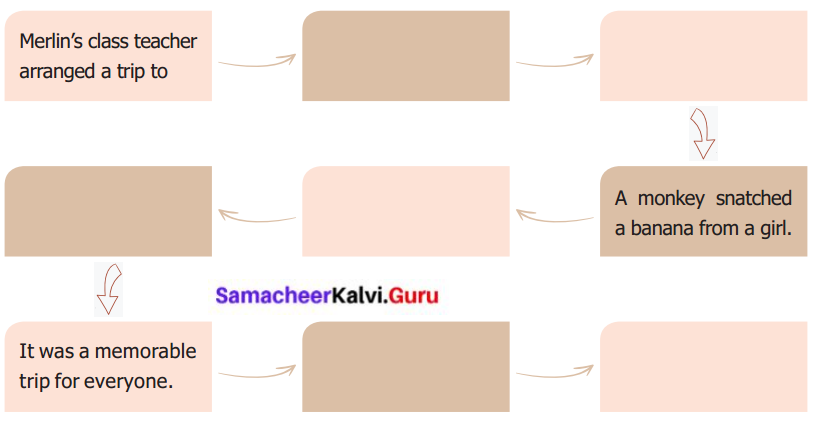
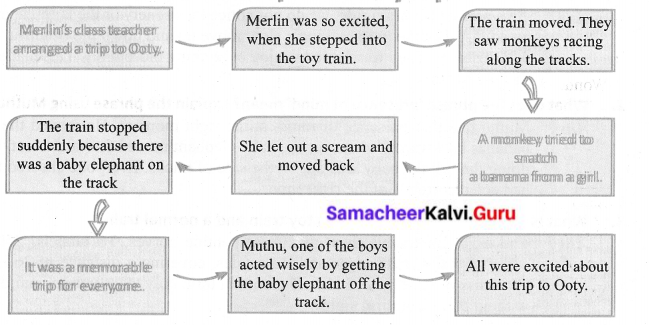
The milkmaid, Moti, supplied milk to a celebrated Pundit who had many disciples and admirers. The milkmaid thought that it was a great privilege to serve a great Pundit and discharged her duties sincerely. One day, the Pundit asked her to deliver the milk at least an hour before sunrise, as he was under a vow for performing a certain ritual. The milkmaid agreed but came to deliver the milk long after sunrise. When questioned by the Pundit, she said that she couldn’t cross the river without the boatman. The Pundit commented jocularly that one could cross even the ocean of life by uttering the name of Lord Vishnu. She thanked the Pundit for passing on the secret to her.
Days passed and the period of Pundit’s vow came to an end. The Pundit thanked her and asked her to tell the boatman that he was pleased with him for his task. The milkmaid told him that she crossed the river without the boatman’s help. She just uttered the name of Vishnu and crossed the river. The Pundit was surprised to hear this. He followed her to know the truth. When he saw the milkmaid paying respect to the river and then crossing it with ease, he almost fainted.
While demonstrating the miracle of faith, the story also draws a contrast between scholarship and innocence. It shows the difference between a knowledge of there theory and the knowledge that works through one’s faith in God.