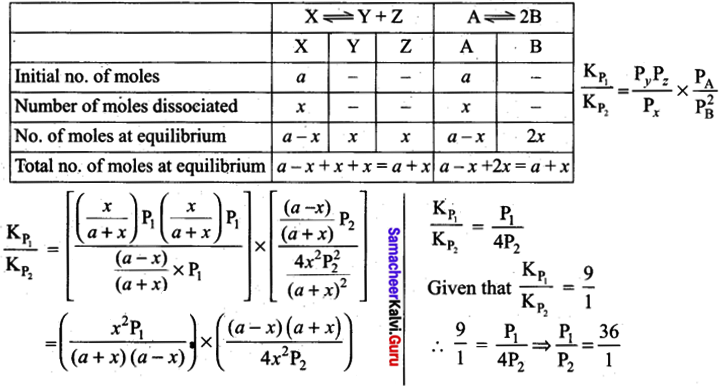
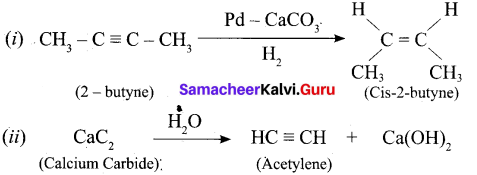
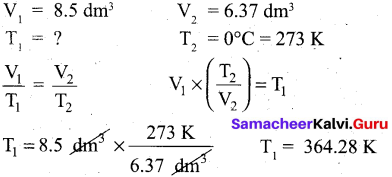
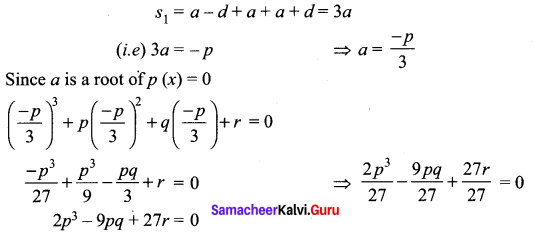
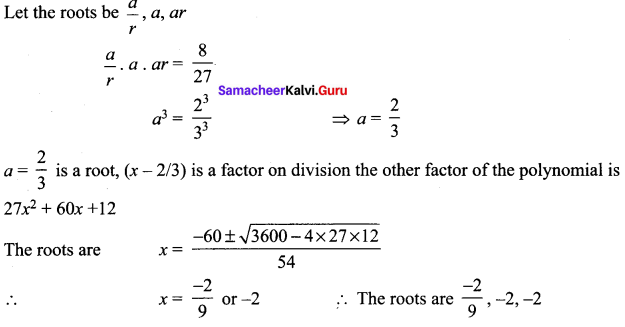
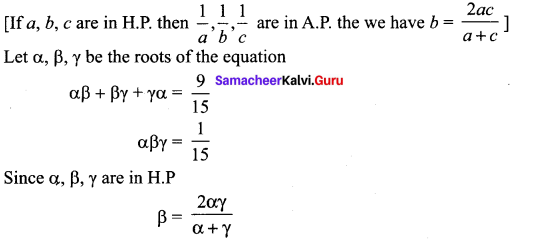
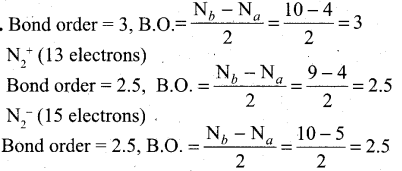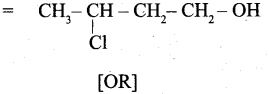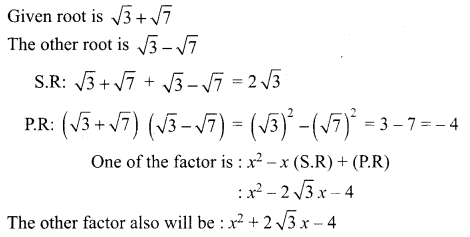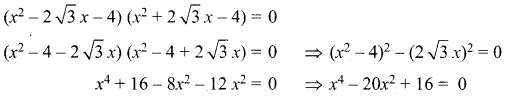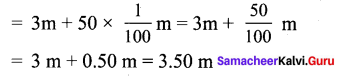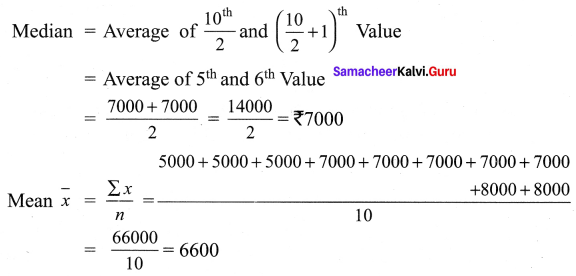Students can Download Tamil Chapter 1.4 ஆழ்கடலின் அடியில் Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Tamil Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
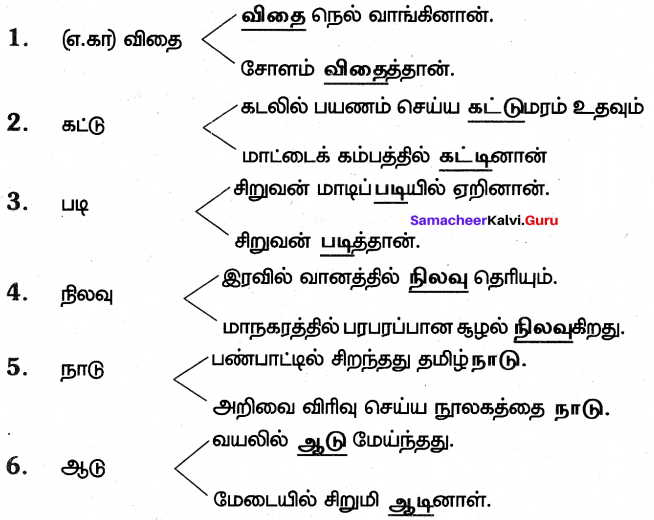
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Tamil Solutions Term 2 Chapter 1.4 ஆழ்கடலின் அடியில்
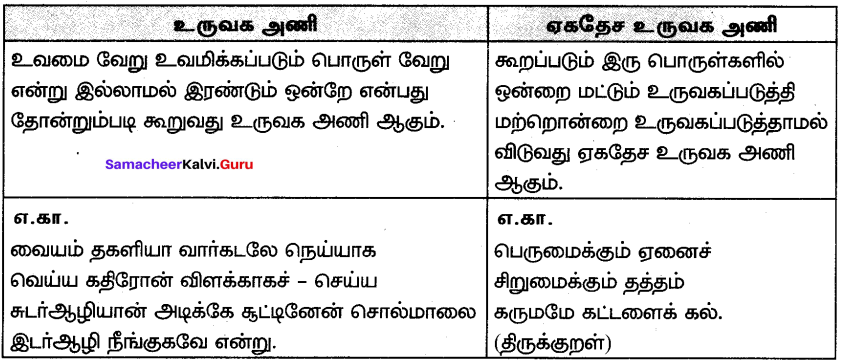
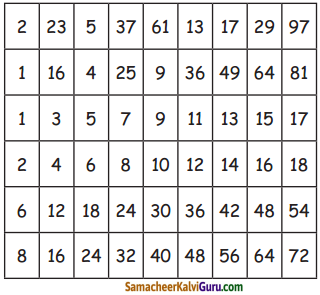
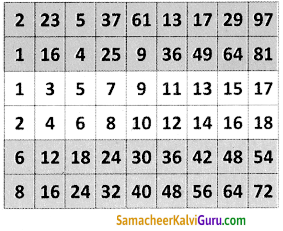
மதிப்பீடு
Question 1.
ஆழ்கடலில் அடியில்’ கதையைச் சுருக்கி எழுதுக.
Answer:
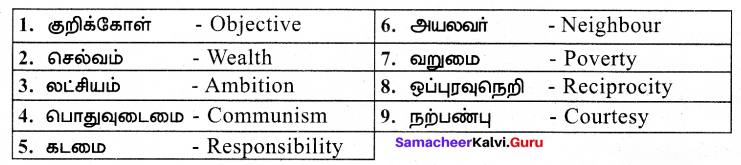
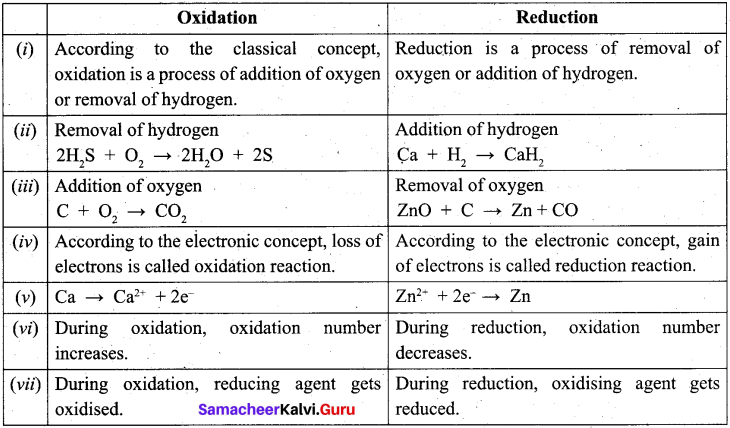
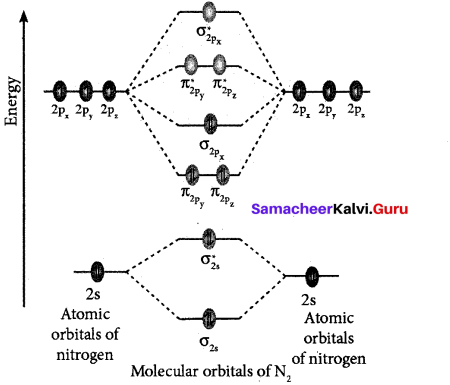
1886 ஆம் ஆண்டு கடலில் செல்லும் பெரிய கப்பல்களை, உலோகத்தால் ஆன உடலைக் கொண்ட ஒரு விந்தையான விலங்கு தாக்குவதாகச் செய்தி வெளியானது. அதனைக் கண்டறிய நியூயார்க் நகரிலிருந்து போர்க்கப்பல் ஒன்று புறப்பட்டது. அதில் விலங்கியல் பேராசிரியரான பியரி , அக்கப்பலின் தலைவர் ஃபராகட், திமிங்கலங்களை வேட்டையாடும் நெட் என்ற வீரர் மற்றும் பியரியின் உதவியாளர் கான்சீல் ஆகியோர் சென்றனர்.
![]()
மூன்று மாதங்கள் அவர்கள், அமெரிக்காவுக்கும், ஜப்பானுக்கும் உள்ள பெருங்கடல் பரப்பில் தேடினார்கள். அவ்விலங்கு கண்ணில் படவில்லை. அதனால் அவர்கள் தங்கள் நகரத்திற்குத் திரும்ப எண்ணினர். அப்போது பளபளப்பான உடலைக் கொண்ட விலங்கு கப்பலை நோக்கி வந்தது. நெட் வலிமை வாய்ந்த ஈட்டிகளை எய்தார். அவ்விலங்கு வேகமாக மோதியதில் அவர்கள் கப்பலில் இருந்து தூக்கி வீசப்பட்டனர். மயக்கமடைந்த பியரி கண் விழித்த போது, பியரி, நெட், கான்சீல் ஆகியோர் அவ்விலங்கின் மீது அமர்ந்திருந்தனர். நெட், “இது விலங்கு இல்லை ; ஒரு நீர்மூழ்கிக்கப்பல்” என்று கூறினார்.
மூவரும் அக்கப்பலின் உள்ளிருப்பவர்களை உதவிக்கு அழைத்தனர். கதவு திறக்கப்பட்டது. கப்பலின் உள்ளிருந்து வந்தவர்கள் மூவரையும் சிறைப்பிடித்தனர். நெமோ என்று ஒருவர் இம்மூவரிடம் பேசினார். “நாட்டிலஸ் என்னும் இந்த நீர்மூழ்கிக் கப்பலை ஒரு விந்தையான விலங்கு என்று நம்ப வைத்திருக்கிறோம். இவ்வுண்மை தெரிந்த உங்களை விடமாட்டேன்” என்று கூறினார்.
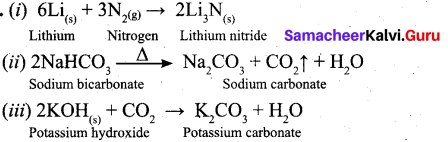
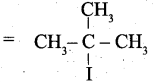
கப்பலினுள் எல்லா இடங்களுக்கும் சென்றனர். அதில் நூலகம் மற்றும் அருங்காட்சியகம் ஆகிய அரிய அறிவுக் கருவூலங்கள் யாருக்கும் பயன்படாமல் இருந்தன. கப்பலின் இயங்குமுறைகளைப் பற்றி நெமோவிடம் கேட்டறிந்தனர். கப்பலில் உள்ளோர் மூச்சு விடுவதற்கான காற்று எவ்வாறு கிடைக்கிறது என்பது பற்றியெல்லாம் கூறினார் நெமோ. ஒருநாள் கப்பல் கடலுக்குள் இருக்கும் மணல் திட்டில் சிக்கிக் கொண்டது.
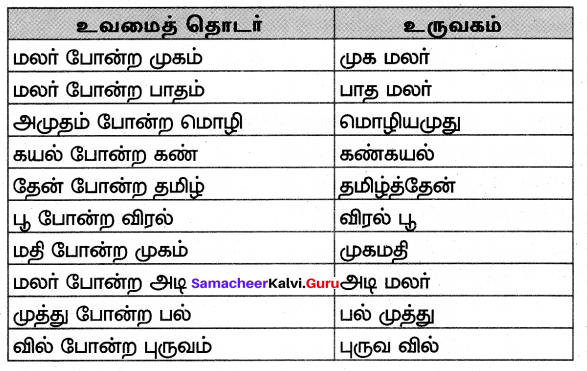
![]()
நாட்டிலஸின் மேல்தளத்தில் நின்றபோது பக்கத்தில் ஒரு தீவு தெரிந்தது. இம்மூவரும் நெமோவிடம் அனுமதி பெற்று படகில் சென்று அத்தீவில் காய்கறிகளை வாங்கிக் கொண்டு படகில் ஏற்றினர். அத்தீவைச் சார்ந்த, மனிதர்களைக் கொன்று தின்னும் வழக்கமுடையவர்கள் துரத்தினார்கள். மூவரும் தப்பித்துக் கப்பலுக்குள் வந்துவிட்டனர். ஆனால் அம்மனிதர்கள் பல படகுகளில் வந்து கப்பலைச் சூழ்ந்து கொண்டனர். ஏழு நாட்களுக்குப் பிறகு மேல் மூடியைத் திறந்தார். அந்த மனிதர்கள் ஏணியில் ஏற முயன்றனர். நெமோ அதில் மின்சாரத்தைப் பாய்ச்சி இருந்ததால் ஓடிவிட்டனர்.
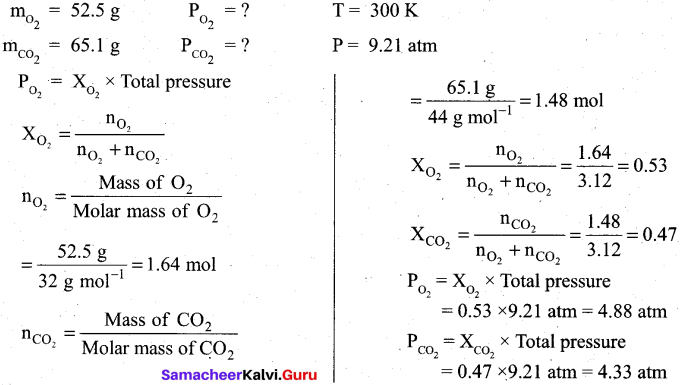
பல நாட்களுக்குப் பிறகு இந்தியாவுக்கும் இலங்கைக்கும் அருகில் நாட்டிலஸ் சென்று கொண்டிருந்தது. முத்துச் சிப்பிகளைச் சேகரிக்க நெமோவும் பியரியும் கடலுக்குள் சென்றனர். அப்போது முத்துக் குளிப்பதற்காக ஓர் இந்தியர் கடலுக்குள் இறங்கியதைப் பார்த்தனர். அவரைச் சுறாமீனிடமிருந்து காப்பாற்றினர்.
வழியில் போரின்போது கடலில் மூழ்கடிக்கப்பட்ட கப்பலைப் பார்த்தனர். அதில் 5 இருந்த தங்கம், வெள்ளி, வைரம் போன்றவற்றை எடுத்துக் கொண்டனர். கடலினுள் உள்ள எரிமலை, கடலுக்குள் மூழ்கிய அட்லாண்டிஸ் நகர இடிபாடுகளைக் கண்டனர். பூமியின் தென் துருவத்தில் பென்குவின், கடல் சிங்கம் போன்ற அரிய பறவைகளையும் விலங்குகளையும் கண்டனர். ஆக்டோபஸ் ஒன்றைக் கொன்றனர்.
![]()
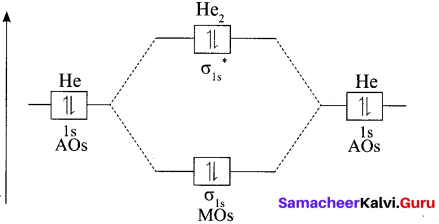
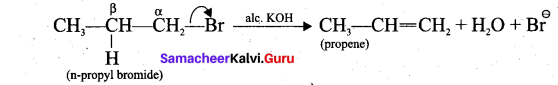
மூவரும் தப்பிக்க முயன்றனர். அதனால் கப்பலுடன் இணைக்கப்பட்ட படகில் ஏறினர். அப்போது நாட்டிலஸ் கடல் சுழலுக்குள் சிக்கிக் கொண்டது. இம்மூவரும் கடலுக்குள் வீசப்பட்டனர். மயக்கம் தெளிந்த போது நார்வே நாட்டில் ஒரு மீனவரின் குடிசையில் இருந்தனர். நெமோ பற்றியும் நாட்டிலஸ் பற்றியும் யாருக்கும் எந்தச் செய்தியும் கிடைக்கவில்லை
கற்பவை கற்றபின்
Question 1.
ஆழ்கடல் காட்சியொன்றைக் கற்பனையாகப் படம் வரைந்து வண்ணம் தீட்டுக.
Answer:
மாணவர்கள் தாங்களாகவே செய்ய வேண்டியவை.
![]()
Question 2.
நீர்மூழ்கிக் கப்பல் இயங்கும் முறை பற்றிய செய்திகளைத் திரட்டித் தொகுத்து எழுதுக.
Answer:
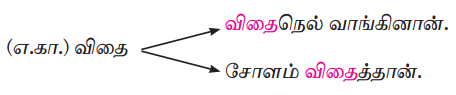
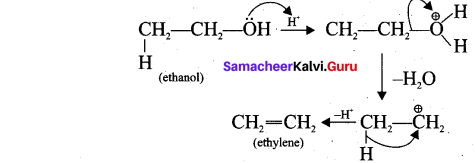
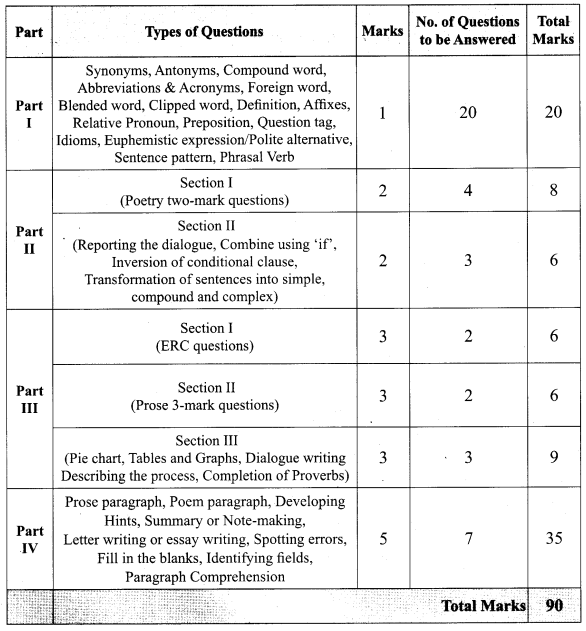
கடலுக்குள்ளே செல்லும் நீர்மூழ்கிக் கப்பலைப் பற்றிக் கேள்விப்பட்டிருப்போம். உள்ளே சென்று பார்ப்பதற்கு வாய்ப்பில்லை. இந்த நீர்மூழ்கிக் கப்பலின் பயன் என்ன? அது எப்படிச் செயல்படுகிறது? கடலில் நடைபெறும் போர்களில் ஒற்றர்களைப் போல செயல்படுபவையே நீர்மூழ்கிக் கப்பல்கள். கடலின் உள்ளே நீண்ட தூரம் வரை செல்லக்கூடியவை. புஷ்வெல் என்பவர் நீர்மூழ்கிக் கப்பலைக் கண்டுபிடித்தார். சில வருடங்களுக்கு முன்னால் சிறிய அளவில் செய்யப்பட்டன. தற்போது 400 அடி நீளம் வரை உள்ளன. நீர்மூழ்கிக் கப்பலில் இரண்டு என்ஜின்கள் உள்ளன. நீர்மட்டத்திற்கு மேலே ஒரு என்ஜின் உள்ளது.
![]()
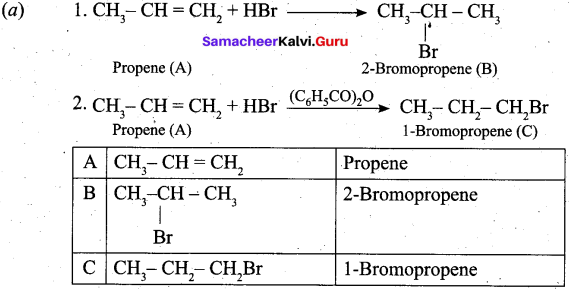
இது கப்பல் செல்லும் போது நீராவியால் இயக்கப்படும். இன்னொன்று கப்பல் நீரில் மூழ்கிச் செல்லும்போது மின்சாரத்தால் இயக்கப்படும். தற்போதுள்ள புதிய கப்பல்கள் 12,000 மைல் தூரம் வரை நிற்காமல் செல்லக்கூடியவை. 60 மணிநேரம் மின்சார ஆற்றலும் செயல்படுத்தக்கூடிய வகையில் அமைக்கப்பட்டுள்ளன. காற்று வாங்க மேடை ஒன்று இருக்கும். மேலே பீரங்கி இருக்கும். கடலின் உள்ளே செல்லும்போது பீரங்கியை உள்ளே இழுத்துக் கொள்ளும் வசதி உள்ளது.
மேடையின் மீது ஒரு சிறிய கோபுரம் அமைந்திருக்கும். கோபுர உச்சியில் பெரிஸ்கோப் இரட்டைக் கண்ணாடி 2 அல்லது 3 பொருத்தப்பட்டிருக்கும். ஒன்று சரியாகத் தெரியாவிட்டாலும் திருப்பிப் பார்க்கும் வசதியும் உள்ளது. எனவே, நீரினுள் இருக்கும் போது கண்ணாடியின் உதவியால் மாலுமி மேலே நடைபெறும் செயல்களைப் பார்த்துத் தெரிந்து கொள்ளலாம். பெரிஸ்கோப் செயல்படவில்லையெனில் கப்பலுக்கு வழி தெரியாது. எனவே, நீர்மூழ்கிக் கப்பலின் கண்கள் என்றே இதனை அழைக்கலாம்.’
கப்பலின் ஓரங்களில் வெடிகுண்டு வைக்கும் அறை இருக்கும். நீரினுள் மூழ்கும் முன்பு அனைத்துக் கதவுகளும் அடைக்கப்பட்டு கோபுர வாசலும் மூடப்படும். பின்னர் நீர்த்தொட்டி திறக்கப்படும். கடல் நீர் தொட்டிகளுக்குள் வந்து நிறைந்ததும் கப்பலின் எடை மிகுந்து கீழே செல்லும். இதற்குச் சிறகுகளும் உறுதுணையாகச் செயல்படும். கப்பல் கடலுக்குள் மூழ்கும் போது, முன்புறம் தாழ்ந்தும் பின்புறம் உயர்ந்தும் மீன் போல நீந்திச் செல்வதுபோல் இருக்கும்.
![]()
எவ்வளவு ஆழம் செல்ல வேண்டுமோ அதற்கேற்ப தொட்டிகளில் தண்ணீர் நிரப்பப்பட வேண்டும். கப்பல் மேலே வரும்போது, காற்றுக் குழாய்கள் திறக்கப்படும். காற்றானது நீர்த்தொட்டிகளுக்குள் சென்று அங்கிருக்கும் நீரை வெளியேற்றும். இதனால் கப்பலின் எடை குறைந்து மேலே நீர்மட்டத்திற்கு வரும். கப்பலின் உள்ளே எடை ஒரே அளவில் இருக்க வேண்டும். கொஞ்சம் கவனிக்கத் தவறினாலும் ஆபத்து ஏற்பட வாய்ப்புள்ளது. கப்பலின் எடை குறையும் போதெல்லாம் அந்த அளவுக்குச் சரியான நீரைத் தொட்டிகளில் நிரப்ப வேண்டும். கப்பலின் இருமுனைகளிலும் உள்ள எடை தராசுத் தட்டுகள் போல் சமமாக இருக்க வேண்டும்.
![]()
நீராவிக் கருவிகள் கப்பலை நீர்மட்டத்திற்கு இழுத்துச் செல்வதுடன், வேண்டும் போது காற்றுக்குழாய்களை நிரப்பவும் மின்னாற்றலைப் புதுப்பிக்கவும் உதவுகின்றன. திடீரென ஏற்படும் ஆபத்திலிருந்து தப்பிக்க காற்று உடைகள் இருக்கும். இவை மூச்சுவிடவும், கரைசேரவும் உறுதுணை செய்யும்.